NEET Biology Homeostasis and Osmoregulation Excretion
- Elimination: Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste products from the organism.
- The metabolism of carbs and lipids generates CO2 and H2O, which are readily excreted. Excretion occurs via the lungs (expired air), skin (sweat), or kidneys (urine).
- Protein metabolism generates nitrogenous waste products, including ammonia, which is the primary nitrogenous catabolic byproduct of protein resulting from amino acid degradation.
- Nephrology: Examination of the anatomy, function, and pathologies of the kidneys (G. nephros = kidney, logos = discourse).
- Urology: Examination of the female urinary tract and the male urogenital tract (G our = urine, logos = discourse)
- Urography: The X-ray assessment of the urinary system following the administration of contrast agents.
NEET Biology Homeostasis and Osmoregulation Excretory Products
- They are mainly excess of amino acid, ammonia, urea, uric acid, trimethyl amine oxide (in teleost fishes), guanine (in spiders), allantoin, hippuric acid, ornithinic acid, creatine, and creatinine.
- In addition, CO2, ammonia, sweat, and bile pigments are all excretory products.
- Nature of Excretory products. Based on the nature of the nitrogenous excretory end-products, animals are classified into the following main categories.
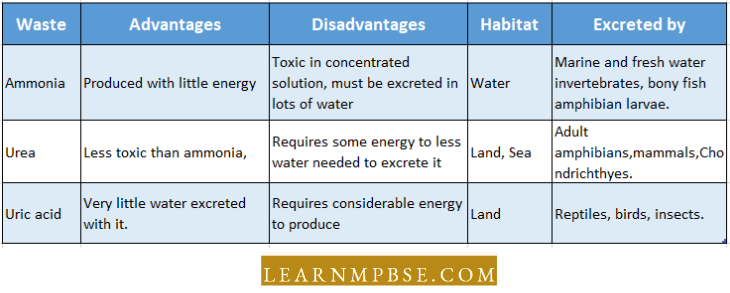
- Ammonotelic animals. These animals excrete their nitrogenous wastes as ammonia. Excretion of ammonia is suited to an aquatic habitat.
- Ammonia is found as the chief excretory product in the majority of primitive aquatic animals, certain Protozoa, Polychaetes, Crustaceans, some mollusks, and teleost fishes.
- It is also excreted by secondarily aquatic animals such as larvae of insects, aquatic tortoises, and turtles. Amphibian tadpoles excrete mainly ammonia whereas adults produce urea.
- Uricotelic animals. The nitrogenous excretory end product is uric acid. Most terrestrial animals, including insects, terrestrial gastropods, terrestrial reptiles, and birds excrete mainly uric acid.
- Ureotelic animals. Urea is the major excretory product For Example Earthworms, some gastropods, adult amphibians, Elasmobranch fishes, and mammals.
- Aminotelic animals eliminate amino acids. They are mollusks (Unio, Pila, etc) and echinoderms (Starfish, Sea cucumber, etc.)
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
NEET Biology Homeostasis and Osmoregulation List Of Excretory Products
- Ammonia
- Urea
- Uric acid
- Creatine. Normally in the urine of children, pregnant and lactating mothers, creatine excretion increases during catabolism of tissue proteins.
- Creatinine. Formed during the metabolism of creatine derived from catabolism of muscular proteins.
- Trimethylamine Oxide (TMAO). Marino telcos fishes excrete a large proportion of their nitrogen as trimethylamine oxide (a soluble non-toxic substance). It resembles urea.
- Guanine. Spiders exclusively excrete guanine which resembles uric acid.
- Ornithinic Acid. It is excreted in small amounts by birds and is formed by a combination of benzoic acid,
- Hippuric acid. The benzoic acid present in the diet of mammals combines with glycine to form less toxic hippuric acid.
- Pterydlnes. Pigments are present in the insects. Excreted in fecal matter or deposited in wings or fat bodies.
- Mineral ions.
- Allantoin. Formed by oxidation of uric acid.
- Amino acids. Excess is eliminated as such in Unio and echinoderms.
Homeostasis and Osmoregulation NEET Notes
NEET Biology Homeostasis and Osmoregulation Excretory Organs Of Invertebrates
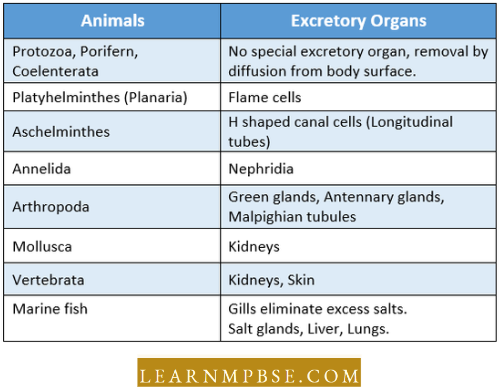
- There are no special excretory organs in protozoans, porifers, and coelenterates.
- Ammonia is the main excretory product and diffuses directly out of the body through the general surface.
- Plantyhelminthes. (Planaria, Liver fluke, etc.) Carry out excretion by flame cells and main excretory products arc nitrogenous wastes.
- Annelids have nephridin for excretion and osmoregulation.
- Arthropods – Crustaceans carry out excretion through green (antennary) glands and the excretory product called urine contains ammonia, some urea, and amino acid.
- Insects, centipedes, and millipedes eliminate uric acids as solid precipitate extracted by blind malpighian tubules.
- Scorpions and spiders (Arachnids) have malpighian tubules or coxal glands or both for excretion.
- Molluscs have one or two pairs of kidneys, Keber’s organs, and organs of Bojanus for excretion.
- Echinoderms lack special structure but excretion is carried out by diffusion through gills and tube feet.
NEET Biology Homeostasis and Osmoregulation Excretory Organs Of Vertebrates
- Integument. Substances such as salts, water, CO2, and fat derivatives are removed Guanosine → guanine from the body through the integument.
- Gills. In marine fishes, in addition to removing CO2 gills remove excess salts.
- Alimentary Canal. It helps in removing certain salts such as calcium phosphate from the body.
- Salt glands. In some marine fishes, reptiles, and birds, salt-excreting glands are found.
- Liver. The liver produces urea during the ornithine cycle. It also excretes bile pigments.
- Lungs. Lungs remove CO2 along with certain volatile substances like alcohol, ketone bodies, aromatic oils, water vapors, etc.
- The neural gland is an excretory gland in the urochordates which opens into the pharynx
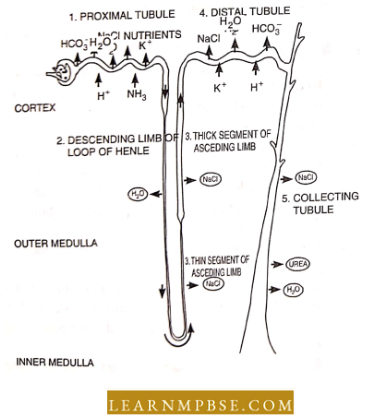
- Kidney. This is a major excretory organ which develops from the mesoderm. The kidney is divided into two main parts
- outer cortex which contains all the pails of the nephron except Henlc’s loop and
- the inner medulla which contains Kettle’s loops.
- The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney.
- Each nephron is composed of a body (Bowman’s capsule and glomerulus), secretory tubule, proximal convoluted tubule (PCF), Henlc’s loop, and distal convoluted tubule CT).
- A stir of ureters carries urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
- A urinary bladder is a sac-like structure with a clastic wall that stores urine.
- The urethra is a small narrow tube that connects the urinary bladder to the exterior. It is very narrow and small for women.
Archinephrie. It is also called the ancestral kidney. It is believed that the primitive vertebrate ancestor had this type of kidney.
- Such a kidney is found today in the larvae of certain cyclostomes {example, Mexico) but do not occur in any adult vertebrate. Glomeruli are only present in some of the posterior tubules.
Pronephric Kidney. It appears as an embryonic functional kidney in cyclostomes, fishes, and amphibians. It is non-functional in the embryonic life of reptiles, birds, and mammals.
- It is retained throughout life in adult cyclostomes and a few bony fishes. It is also called the anterior kidney due to its anterior position. Each tubule has a glomerulus.
Homeostasis And Osmoregulation NEET Study
Mesonephric Kidney. It is also called the middle kidney. In lamprey, most adult fishes, and amphibians, the mesonephric kidney is functional both in the embryo as well as in adults.
- In reptiles, birds, and mammals it is functional in embryos and is replaced by a metanephric kidney in the adults. It consists of a large number of tubules that develop internal glomeruli enclosed in capsules forming Malpighian bodies.
- In sharks, ami caecilians (limbless amphibians) mimics extend posteriorly throughout the length of the coelom. Mich a kidney is called an opisthonephric kidney.
Metanephric kidney. It is also called the posterior kidney. Tubules (nephrons) are very large in number. Ilie glomeruli arc is very well developed. Mctancphric kidneys are found in adult amniotes (reptiles, birds, and mammals).
Opisthonephros. Temporary structure develops behind pronephros
NEET Biology Homeostasis and Osmoregulation Valuable Information
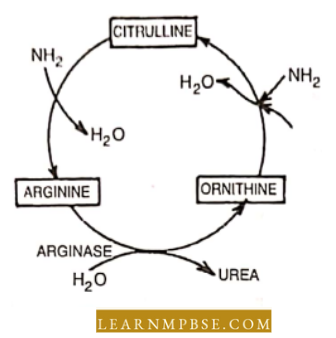
Ornithine cycle occurs in the liver.
- Waste products of adenine and guanine metabolism are excreted by man as uric acid.
- Glucose is completely reabsorbed by blood in the tubules in a normal human kidney.
- About 1500 ml of water is lost by plasma through the kidney in 24 hours.
- Branchiostoma is the chordate that possesses nephridia with flame cells (Solenocytes).
- The neural gland is an excretory organ of urochordates.
- The kidney is dark red in the cortex and pale red in the medulla.
- The main excretory organ of prawns are paired green glands.
- Malpighian tubules show peristaltic movement i.e. 5-15 per minute at 20-25°C in cockroaches.
- Earthworm excretes ammonia when sufficient water is available but eliminates urea during a shortage of water.
- Amphibian larvae are ammonotelic and turn ureotelic during metamorphosis.
- Desert snakes are mostly uricotelic.
- The toad Xenopus and lung fishes are normally ammonotelic when living in water but they turn ureotelic and retain urea when lying immobile or dormant during summer.
- Urine yields an aromatic smell due to the presence of crinoids.
- Urine on standing gives a pungent smell because of the conversion of urea into ammonia due to microbial action.
- Sharks retain so much urea in their blood that their osmotic blood pressure approaches that of seawater. It minimizes the loss of water from the body to the concentrated saline water of the sea.
- Chloragogen (Yellow) Cells. These are found in the visceral peritoneum of the gut and in the coelomic fluid in the earthworm. They function like the vertebrate liver. They store and distribute food, synthesize hemoglobin, and produce urea by deamination for excretion.
- A remarkable fall in blood pressure affects the normal functions of the kidney because of reduced renal filtration.
- A large amount of NaCI is excreted along with sweat.
- Muscular cramps may occur due to salt deficiency.
NEET Biology Homeostasis and Osmoregulation Physiology Of Excretion
Ammonia, a metabolic waste, quickly diffuses and reacts with water to produce a very hazardous substance.
Ammonia is transformed into urea in the liver via the ornithine cycle as follows:
Renal Physiology:
The kidneys filter urea and other waste products from the blood and excrete them through urine.
It occurs through three processes:
- Glomerular filtration.
- Reabsorption
- Tubular secretion.
NEET Biology Homeostasis and Osmoregulation Functions Of Kidney
The kidney performs excretion, and osmoregulation; regulates pH, salt contents, blood pressure, the expulsion of medicines, poisons, etc. homeostasis and secretes renin.
- Regulatory Functions of Kidneys
- Regulation of osmotic pressure of ECF. (extracellular fluid)
- Regulation of pH.
- Regulation of electrolyte pattern of ECF.
- Regulation of erythrocytes (RBCs) count in blood.
- Regulation of Renal Blood Flow. These are the homeostatic functions of kidneys.
- Erythropoiesis. Macula-dense juxtaglomerular cells near the glomerulus are believed to produce renal Erythropoietic factor which increases the production of RBC in bone marrow.
Homeostasis and Osmoregulation NEET Notes
NEET Biology Homeostasis and Osmoregulation Disorders Of Excretory System
- Dysuria-painful urination.
- Polyuria-unusually large amounts of urine.
- Oligouria-scanty urine.
- Gout-Deposition of uric acid at joints.
- Azotemia-Presence of urea and other nitrogenous wastes in blood.
- Haematuria-Presence of blood in the urine.
- Bacteriuria-Bacteria in urine.
- IVP-Intra venous pyelogram-X-ray film of kidneys after injection of the contrasting medium.
- Uremia In this condition there are high concentrations of non-protein nitrogens which include urea, uric acid, creatinine, and a few less important compounds. Urea accumulation in the blood is comparatively high in uremia.
- Bright’s disease (Nephritis). Inflammation of the kidney.
- Urethritis Inflammation of the lining of the urethra due to bacterial infection (commonly
Gambino. causing painful urination. - Nocturnal Enuresis. Bed-wetting during sleep.
- Renal colic is an excruciating pain on account of kidney stones. The incidence of annex stones is slightly higher in males than females.
- Polycystic disease or kidney. Inherited kidney disorder characterized by multiple bilateral cysts that cause enlargement of the kidney.
- Nocturia is a renal disease in which the volume of urine rises so much at night that the person is compelled to wake up to ease out.
- The urine of a man suffering from diabetes inspires is tasteless and watery.
- Glycosuria (diabetes colitis). It is a disorder in which the concentration of glucose becomes very high and the excess is removed along with urine. It is caused by to deficiency of hormone insulin.
- Nephrolithiasis. Presence of stone in kidney.
- Pyelolithotomy. Removal of a stone from the renal pelvis.
NEET Biology Homeostasis and Osmoregulation Artificial Kidney
- An artificial kidney is used to filter the blood of a person with kidney failure. It functions on the principle of dialysis i.e. the separation of smaller molecules from larger ones in a solution through a semipermeable membrane between the solution and the water.
- The smaller molecules pass through the membrane into the water on the other side, the larger ones do not. In the case of man blood is the fluid which is sent for filtration, it is called hemodialysis.
- The kidney machine sends blood into a cellophane tube suspended in a saline solution of the same composition as that of blood plasma except that no urea is present.
- As the blood flows through the cellophane tube excess nitrogenous waste products like ammonia and urea, and an excess of H+ ions diffuse out into the surrounding saline solution because the cellophane tube has pores large enough to allow the free passage of those small molecules.
- The blood, after its purification, is pumped back into the body through a vein. The artificial kidney is so efficient that the filtration of urea from the blood is more rapid than the normal kidney.
- The use of artificial kidneys, however, is of great discomfort to the patient and there is a risk of blood clotting. And then the patient needs to get his blood dialysed every second or third day which is an expensive and troublesome affair
- Maintenance of homeostasis or a steady state is very important for normal life processes.
- The specialized transport epithelia of animals are engaged in osmoregulation.
- Osmoregulation is the maintenance of water and salt levels in the body.
- Osmoconformers show’ an excellent ability to tolerate a wide range of cellular osmotic environments. c& osmoregulators maintain an internal osmolarity.
- Water and solute regulation in terrestrial environment
- Terrestrial animals adapt as follows to regulate water and solute.
- Minimizing water loss by forming a waxy coating of the exoskeleton of insects and shells in land snails.
- Formation of a stratified keratinized layer of skin.
- Drinking and eating moist food.
- Kangaroo rats can recover 90 % of water loss by using metabolic water.
- Nasal counter current mechanism.
- Most desert animals are nocturnal to avoid the heat of the day.
- formation of dry feces and concentrated urine.
- Osmoregulation by kidneys in mammals. Kidneys play an important role in maintaining the concentration and osmotic pressure of the blood when the water intake of an animal is very high. The urine, excreted has to be hypotonic in order to remove the excess of water.
- Contrarily, when there is a threat of excessive water loss from the body, the urine needs to be hypertonic to reduce the loss of water with urine. Thus the osmotic concentration of the blood is maintained.
- Almost all vertebrates including mammals can produce hypotonic urine, diluted and lower in osmotic pressure than their blood. Many freshwater vertebrates like fishes secrete very dilute urine.
- In mammals, osmoregulation is carried by :
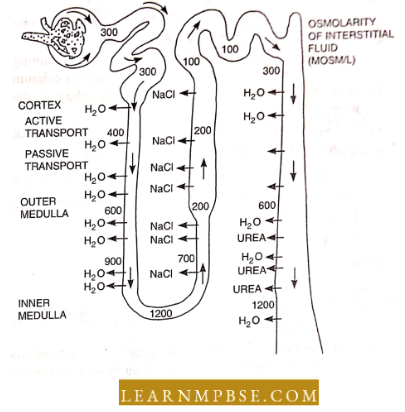
- Counter-current mechanism (flow of fluids in two opposite directions in two loops and vasa recta and osmolarity sea water is 1000 most.
- ADH – HAAS control system. ADH hormone af- feels permeability of DCT and CT.
Osmoregulation NEET Notes
Juxtaglomerular apparatus. (JGA). It is a specialized structure, located where the distal convoluted tubule passes close to Bowman’s capsule between the afferent and efferent arterioles.
- The cells of this apparatus secrete substances like renin which modulates blood pressure and thus renal blood flow and GFR are regulated.
- Myogenic and juxtaglomerular mechanisms work together to autoregulate the GFR over a wide range of blood pressure. In addition to these extrinsic neural control also regulates the filtration rate.
- Hormonal Control. The hormones taking part in the regulatory mechanism of urine formation are as follows:
- Control by juxtaglomerular apparatus which operates multi-hormonal Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone system. (RAAS).
- Aldosterone. Mineral corticoids are secreted. by the adrenal cortex under the impact of ACTH on the pituitary, osmotic concentration of blood plasma, and renin-angiotensin mechanism. Aldosterone increases Na+ absorption of tubules along with Cl“ but it also brings about excessive potassium ions.
- An antidiuretic hormone secreted by the posterior lobe of the pituitary regulates the amount of water excreted in the urine.
- It increases the reabsorption of water in the distal convoluted tubules and collecting tubules as well and deficiency of this hormone lowers the permeability of cells of the distal convoluted tubule, collecting tubule, and collecting duct, by decreasing the reabsorption of water.
- Its release is triggered by osmoreceptors of the hypothalamus when these receptors detect an increase in osmolarity in the blood above a set point of 300 most L ‘l. Then these cells promote thirst.
Atrial natriuratic Factor. (ANF) a peptide hormone opposes the regulation by UAAS.
Parathormone. This hot mono helps in maintaining calcium-phosphorus balance, evinces hiss of calcium
in mine ami increases the elimination of phosphate in the mine.
- Thyroxine is secreted by the thyroid controls the working of the kidney and its deficiency reduces urine output.
- Kidneys conserve as much water as possible, urine can roach an osmolarity of about 1200 most considerably hypertonic to blood (about 300 tons).
Conservation of water is an adaptive feature.
- Micturition is an act of voiding the urine.
- Proteinuria, Albuminuria, Glycoairia
- Hematuria, Haemoglobinuria, and Uremia are the common disorders of the kidney.
- An artificial kidney is used to remove the excess urea from the blood of a patient by a process called hemodialysis.
- Lungs eliminate around 18 L of CO2 per hour and about 100 ml. of water per day in normal resting conditions.
- The skin eliminates wastes such as sweat and sebum.
The liver is the main site for the elimination of cholesterol, bile pigments, and inactivated products of steroid hormones, some vitamins, and drugs.
NEET Biology Homeostasis and Osmoregulation Quanta To Memory
- Cyclostomes (Hagfish) Embryo–archinephros Adult pronephros and opisthonephos.
- Lamprey– Adults–opisthonephros
- Fishes–Elasmobranch (Scoliodon)
- Two regions–anterior non-renal and posterior wide– renal
- Trimethylamine excretory products of teleost fishes Bony fishes–Aglomerular kidneys, ammonotelic
- Urodaeum–Middle chamber of the cloaca in which the ureter opens.
- Adult Birds–Metanephric
- Embryo–Mesonephric
- A long loop of Henle for reabsorption of water, No urinary bladder except Ostrich Malpighian body = Renal corpuscle A frog can lose water through its skin and nephron. Salts are also lost through the skin.
- Reptiles conserve water in two ways.
- impermeable coat of homy scales.
- Small glomeruli in the kidney and reabsorption of water in the urinary tubules and cloaca.
- Desert mammals have exceptionally long Henle loops for greater reabsorption of water.
- Kangaroo rats of deserts survive on metabolic water alone as they take dry food. One gm of carbohydrates, protein or fat yield ( 0.6 gm 0.4 gm 1.1 gm of water respectively) on complete oxidation.
- Marine turtles, Sea snakes, and Sea birds have special Salt secreting glands, that excrete salts of seawater as they drink seawater.
- Hormones–ADH, Aldosterone, and Thyroxine are involved in urine formation.
- Botryoidal tissue is found in leeches and excretory in function.
- Filtration fraction Ratio between GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate) and RPF (Renal plasma flow)
- Uriod–a bad-smelling substance formed by a breakdown by bacteria.
- Renal threshold. Maximum limit up to which a substance can be reabsorbed from nephric filtration into blood capillaries.
- Homoeostasis includes water balance, salt balance, acid-base balance, and balance of harmful substances.
- The loop of Henle is located in the medulla of the kidney.
- Cells of an earthworm analogous to the vertebrate liver are known as chloragogen cells.
- The largest number of sweat glands in man are found on the palms.
- Urine is light yellow, repulsive odor, is slightly acidic, having a specific gravity between 1.003 and 1.04.
- The urea reabsorbing segment is found in the renal tubule of sharks.
- The right human kidney is slightly lower than the left kidney because the liver pushes the kidney of its side down.
- The sweat glands in rabbits are mostly concentrated on the lips.
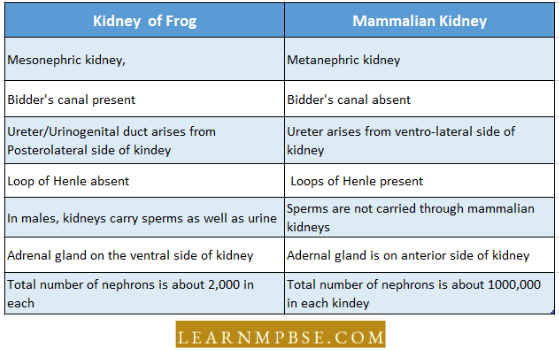
- Bidder’s Canal. Present in the male frog’s kidney, transfers sperm from the vasa efferentia to the ureter.
- Nephrectomy. Surgical removal of a kidney.
Urinary Bladder. Absent in cyclostomes, cartilaginous fishes, snakes, crocodilians, and birds.
- The first kidney transplant in India was performed on December 1. 1971, at the Christian Medical College, Vellore, Tamil Nadu on a 35-year-old patient named Shanmughan.
- Each kidney has about sixteen renal pyramids.
- The terminal and non-convoluted part of the PCT of the nephron is called the pars recta.
- Columns of Bertini. Conical projections of the renal cortex into the renal medulla between the renal pyramids.
- The hepatic vein has with maximum amount of urea, while the renal vein has with minimum amount of urea.
- Both afferent and efferent arterioles in Bowman’s capsule are arterial.
NEET Biology Notes PDF
NEET Biology Homeostasis and Osmoregulation Questions From Competitive Examinations
Question 1. The figure shows a human urinary system with structures labeled 1 to 4. Select an option that correctly identifies them and gives their characteristics and functions.
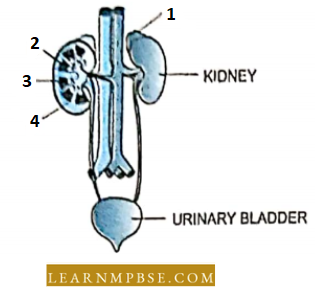
- B – pelvis – broad funnel-shaped space inner to the hilum, directly connected to loops of Henle.
- C – medulla – inner zone of kidney and contains complex nephrons.
- D – cortex – the outer part of the kidney and does not contain any part of nephrons.
- A – adrenal gland – located at the anterior part of the kidney. Secrete catecholamines which stimulate glycogen breakdown.
Answer: 4. A – adrenal gland – located at the anterior part of the kidney. Secrete catecholamines which stimulate glycogen breakdown.
Question 2. The formation of concentrated (hyperosmotic) urine in vertebrates generally depends on :
- Length of the proximal convoluted tubule
- Length of Henle’s loop
- Area of bowman’s capsule epithelium
- Capillary network forming glomerulus.
Answer: 2. Length of Henle’s loop
Question 3. Ciliated funnels found on the ventral side of the kidney in frogs are:
- Ostia
- Corpora adipose
- Nephrostome
- Bidder’s organs.
Answer: 3. Nephrostome
Question 4. Urine is always fluid except in :
- Reptiles and amphibians
- Reptiles and mammals
- Reptiles and frogs
- Reptiles and birds.
Answer: 4. Reptiles and birds.
Homeostasis And Osmoregulation Neet Mcqs
Question 5. Urine is transported through :
- Wbcs
- Erythrocytes
- Blood plasma
- All of the above.
Answer: 3. Blood plasma
Question 6. In hydra, wastes of food digestion and nitrogenous wastes are removed from :
- Mouth & mouth
- Mouth & tentacles
- Body wall and body wall
- Mouth and body wall,
Answer: 4. Mouth and body wall
Question 7. Blood vessels leading into the bowman’s capsule are called :
- Renal vein
- Renal artery
- Efferent arteriole
- Afferent arteriole.
Answer: 4. Afferent arteriole.
Question 8. In peritoneal dialysis, dialysate is passed into :
- Urinary bladder
- Abdominal cavity
- Thoracic cavity
- Stomach.
Answer: 2. Abdominal cavity
Question 9. Separation of amino acid and carboxylic groups is called :
- Deamination
- Transamination
- Egestion,
- Excretion.
Answer: 1. Deamination
Homeostasis And Osmoregulation Neet Mcqs
Question 10. The presence of urea in the blood is referred to as:
- Uraemia
- Hacmaturia
- Diarrhea
- Anuria,
Answer: 1. Uraemia
Question 11. Reabsorption of water in the distal part of kidney tubules is controlled by :
- Vasopressin
- Oxytocin
- Calcitonin
- Relaxin.
Answer: 1. Vasopressin
Question 12. Cockroaches are :
- Ureotelic
- Uricotelic
- Ammonotelic
- Aminotelic.
Answer: 2. Uricotelic
Question 13. In the nephron, Na+ is reabsorbed in :
- Glomerulus
- Pct
- Dct
- Loop of Henle.
Answer: 4. Loop of Henle
Question 14. The volume of urine is regulated by :
- Aldosterone
- Aldosterone, ADH and testosterone
- Aldosterone and ADH
- Ads alone.
Answer: 3. Aldosterone and ADH
Question 15. Absorption of Na+ and K+ ions occur in :
- Bowman’s capsule
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Loop of Henle.
Answer: 3. Distal convoluted tubule
Question 16. The liquid which collects in the cavity of the bowman’s capsule is :
- Blood plasma minus blood proteins
- Glycogen and water
- Urea, glycogen, and water
- Urea.
Answer: 1. Blood plasma minus blood proteins
Osmoregulation In Animals NEET
Question 17. Renin is secreted from :
- Juxtaglomerular cells
- Podocytes
- Nephridia
- Stomach.
Answer: 1. Juxtaglomerular cells
Question 18. Ornithine cycle removes :
- CO2 and ammonia from blood in the liver
- Ammonia and urea from blood in the liver
- CO2 and urea from blood in the liver
- Ammonia and uric acid from blood in the liver.
Answer: 1. CO2 and ammonia from blood in the liver
Question 19. Match the excretory organs listed under column 1 with the animals given under column 2. Choose the answer which gives the correct combination of alphabets of two columns :
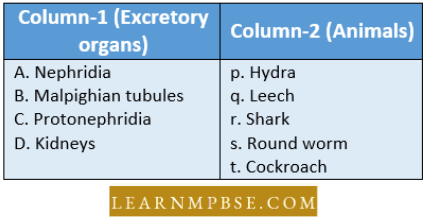
- A = t; b = q; c = s; d = r
- A = q; b = t; c = s; d = r
- A = q; b =s; c = t; d = p
- A = s; b = q; c = p; d = t.
Answer: 1. A = t; b = q; c = s; d = r
Homeostasis And Osmoregulation Neet Mcqs
Question 20. Animals which excrete urea produced during the metabolism of amino acids are:
- Ureotclisni
- Uricotelism
- Ammonolelism
- Aminotelism.
Answer: 1. Ureotclisni
Question 21. Which of the following nephritis is not found in earthworms?
- Septal nephridia
- Maeronephric
- Integumentary
- Pharyngeal.
Answer: 2. Maeronephric
Question 22. Excretory waste of birds and reptiles are :
- Urea
- Urea and uric acid
- Uric acid
- Ammonia and uric acid.
Answer: 4. Ammonia and uric acid.
Question 23. When a freshwater protozoan possessing a contractile vacuole, is placed in a glass containing marine water, the vacuole will :
- Increase in size
- Decrease in size
- Increase in number
- Disappear.
Answer: 2. Decrease in size
Question 24. Which one of the following is not correct for a normal human?
- The pH of urine is around 8.
- On average, 25-30 mg of urea is excreted via urine.
- The presence of ketone bodies in urine is an indicator of diabetes mellitus.
- Glycosuria can be treated with hemodialysis.
- Relaxation of smooth muscles of the bladder and simultaneous contraction of the urethral sphincter causes the release of urine.
Answer: 3. Glycosuria can be treated with hemodialysis.
Question 25. Osmoregulation in paramecium is a function of contractile vacuole trichocysts
- Contractile vacuole
- Trichoyts
- Cytopyge
- Cytostome.
Answer: 1. Contractile vacuole
Question 26. Blood leaving the liver and moving to the heart will have more concentration of:
- Bile
- Urea
- Glycogen
- Amino acid.
Answer: 2. Urea
Question 27. Which one of the following statements is correct concerning saltwater balance inside the body of living organisms?
- When water is not available camels do not produce urine but store urea in tissues
- Salmon fish excrete a lot of stored salt through the gill membrane when in fresh water.
- Paramecium discharges concentrated salt solution by contractile vacuoles
- The body fluids of freshwater animals are generally hypotonic to surrounding water.
Answer: 1. When water is not available camels do not produce urine but store urea in tissues
Question 28. Which one of the following groups of structure/organs have similar functions?
- Typhlosole in earthworms, intestinal villi in rats, and contractile vacuole in amoeba.
- Nephridia in earthworms, malpighian tubules in cockroaches, and urinary tubules in rats.
- Antennae of cockroach, tympanum of frog, and clitellum of earthworm.
- Incisors of rats, the gizzard of cockroaches, and tube feet of starfish.
Answer: 2. Nephridia in the earthworm, malpighian tubules in cockroaches, and urinary tubules in rat
Question 29. Based on excretion, people are:
- Ammonotclic
- Ureotelic
- Uricotelic
- None of these.
Answer: 1. Ammonotclic
Osmoregulation In Animals NEET
Question 30. Which has the minimum concentration of urea in blood?
- Renal arteries
- Renal vein
- Aortic arteries
- Vena cava.
Answer: 2. Renal vein
Homeostasis And Osmoregulation NEET Notes
Question 31. The net pressure gradient that causes the fluid to filter out of the glomeruli into the capsule is :
- 20 Mm hg
- 75 Mm hg
- 30 Mm hg
- 50 mm hg.
Answer: 1. 20 Mm hg
Question 32. A person is undergoing prolonged fasting. His urine will be found to contain abnormal quantities of :
- Fats
- Ketones
- Amino acids
- Glucose.
Answer: 2. Ketones
Question 33. Seagulls excrete an excess of NaCl from :
- Liver
- Lungs
- Nasal cavity
- Kidney.
Answer: 3. Nasal cavity
Question 34. Juxtaglomerular cells of the renal cortex synthesize an enzyme called :
- ADH
- Oxytocin
- Renin
- Urochrome.
Answer: 3. Renin
Question 35. Which of the following statements is true?
A. Urine is hypertonic in distal convoluted tubule
B. When the urine passes into the collecting tubule, it becomes hypotonic.
C. Urine is isotonic in the proximal convoluted tubule
D. Urine becomes more and more hypotonic as it passes through the Henle’s loop.
Choose The Correct Answer
- A And D only
- A, B, And C only
- B And C only
- C Only.
Answer: 4. C Only.
Question 36. Match the excretory functions of section 1 with the parts of the excretory system in section 2. Choose the correct combination from among the answers given.
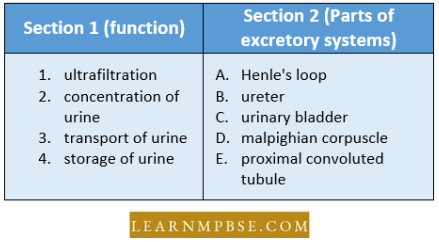
- 1 – D, 2 – a, 3 – b, 4 – c
- 1 – D, 2 – c, 3 – b, 4 – a
- 1 – E, 2 – d, 3 – a, 4 – c
- 1 – E, 2 – d, 3 – a, 4 – b
Answer: 1. 1 – D, 2 – a, 3 – b, 4 – c
Question 37. The voluntary response to the distension of the urinary bladder is :
- Polyurea
- Micturition
- Mellitus
- Menstruation
Answer: 2. Micturition
Question 38. Glucose is mainly reabsorbed in,
- Pct
- Dct
- Henle’s loop
- Nephron.
Answer: 1. Pct
Homeostasis In Human Body NEET
Question 39. Marine teleost fishes secrete :
- Uric acid
- Urea
- Ammonia
- All of these.
Answer: 2. Urea
Question 40. Antennary glands of crustaceans are for :
- Respiration
- Neurosecretion
- Excretion
- Olfaction.
Answer: 3. Excretion
Homeostasis And Osmoregulation NEET Notes
Question 41. Part of the nephron impermeable to salt is :
- Descending limb of the loop of Henle
- Ascending limb of the loop of Henle
- Collecting ducts
- Distal convoluted tubule
Answer: 1. Descending limb of the loop of Henle
Question 42. Refer to the following mg diagram and identify the parts of a kidney indicated.
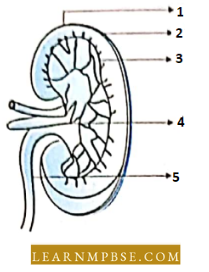
- 1 = Cortex, 2 = neplmm. 3 = Pelvis. 4 = Medulla, 5 = ureter
- 1 = Cortex. 2 = Medulla, 3 = nephron, 4 = pelvis. 5 = Ureter
- 1 = Nephron, 2 = cortex, 3 = medulla, 4 = ureter, 5 = pelvis
- 1 = Nephron, 2 = cortex, 3 = medulla, 4 = pelvis, 5 = ureter
- 1 = Nephron, 2 = ureter, 3 = pelvis, 4 = medulla, 5 = cortex
Answer: 4. 1 = Nephron, 2 = cortex, 3 = medulla, 4 = pelvis, 5 = ureter
Question 43. Match the entries in column 1 with those in column 2 and choose die correct answer from the following.
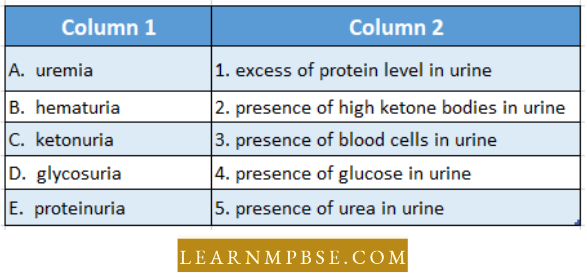
- A-5, b-3, c-2, d-4, e-1
- A-4, b-5, c-3, d-2, e-1
- A-5, b-3, c-4, d-2, e-1
- A-3, b-5, c-2, d-1, e-4
- A-2, b-1, c-3, d-4, e-5.
Answer: 1. A-5, b-3, c-2, d-4, e-1
Question 44. Which of the following is the first formed nitrogenous waste of vertebrates?
- NH2
- Urea
- NH3
- NH4.
Answer: 3. NH3
Question 45. Which of the following is added as an artificial kidney in hemodialysis?
- Dialysing liquid
- Dialyzer
- Bubble trap
- Blood pump.
Answer: 2. Dialyzer
Question 46. Earthworms are :
- Uricotelic when plenty of water is available
- Uricotelic under conditions of water scarcity
- Ammonotelic when plenty of water is available
- Ureotelic when plenty of water is available.
Answer: 3. Ammonotelic when plenty of water is available
Question 47. Angiotensinogen is a protein produced and secreted by
- Endothelial cells (cells lining the blood vessels)
- Liver cells
- Juxtaglomerular (jg) cells
- Macula densa cells
Answer: 2. Liver cells
Question 48. A person who is on a long hunger strike and is surviving only on the water will have :
- Less amino acids in his urine
- More glucose in his blood
- Less urea in his urine
- More sodium in his urine.
Answer: 3. Less urea in his urine
Question 49. The shifting of ammonotelism to ureotelism is seen in :
- Frog
- Fishes
- Snake
- Protopier
Answer: 1. Frog
Homeostasis And Osmoregulation Neet Biology Notes
Question 50. The proximal convoluted tubule (pct) is lined with
- Cuboidal epithelium
- Simple brush border epithelium
- Simple cuboidal brush border epithelium
- Columnar epithelium.
Answer: 3. Simple cuboidal brush border epithelium
Question 51. Jg cells, under low glomerular blood flow. Release
- Angiotensin I
- Angiotensin ii
- ADH
- Aldosterone.
Answer: 3. ADH
Question 52. Consider the following four statements (1-4) about certain desert animals such as kangaroo rats:
- They have a dark colour high rate of reproduction and excrete solid urine.
- They do not drink water, breathe it at a slow rate to conserve water, and have their hotly covered with thick hairs.
- They feed on dry seeds and do not require drinking water.
- They excrete very concentrated urine and do not use water to regulate body temperature.
Which two of the above statements for such animals are true?
- 1 And 2
- 3 And 4
- 2 And 3
- 3 And 1
Answer: 3. 2 And 3
Question 53. Which one of the following correctly explains the function of a specific part of a human nephron?
- Podocytes: create minute spaces (slit pores) for the filtration of blood into the bowman’s capsule
- Henle’s loop: most reabsorption of the major substances from the glomerular filtrate
- Distal convoluted tubule: reabsorption of k+ ions into the surrounding blood capillaries
- Afferent arteriole: carries the blood away from die glomerulus towards the renal vein.
Answer: 1. Podocytes: create minute spaces (slit pores) for the filtration of blood into the bowman’s capsule
Question 54. Which one of the following statements is correct concerning kidney function regulation?
- When someone drinks a lot of water, ADH release is suppressed
- Exposure to cold temperatures stimulates ADH release
- An increase in glomerular blood flow stimulates the formation of angiotensin
- During summer when the body loses a lot of water by evaporation, the release of ADH is suppressed.
Answer: 1. When someone drinks a lot of water, ADH release is suppressed
Question 55. Which one of the following is not a part of a renal pyramid?
- Peritubular capillaries
- Convoluted tubules
- Collecting ducts
- Loops of Henle.
Answer: 2. Convoluted tubules
Question 56. The maximum amount of electrolytes and water (70-80 percent) from the glomerular filtrate are reabsorbed in which part of the nephron?
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Descending limb of the loop of Henle
- Ascending limb of the loop of Henle.
Answer: 2. Proximal convoluted tubule
Question 57. Juxtaglomerular apparatus is made up of :
- Juxtaglomerular cell, macula densa, and lacis cell
- Juxtaglomerular cell, Purkinje cell, and chief cell
- Juxtaglomerular cell, lacis cell, and myoepithelial cell
- Juxtaglomerular cell, macula densa, and argentaffin cell
Answer: 1. Juxtaglomerular cell, macula densa, and lacis cell
