NEET Biology Blood Circulatory System in Animals Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. The main difference in the circulation of blood and lymph is :
- Lymphatics possess valves
- movement of lymph is due to lymph heart
- Lymph always moves towards the heart
- Lymph moves unidirectionally in lymphatics.
Answer: 3. Lymph always moves towards the heart
Question 2. If you were asked to dissect an animal so as to reveal a valve, which of the following places would be good to try:
- At the opening between the right atrium and the right ventricle
- the fork where the pulmonary artery splits and one branch goes to each lung
- the base of the aorta where it leaves the left ventricle
- a vein in the arm.
Answer: 2. the fork where the pulmonary artery splits and one branch goes to each lung
Question 3. The introduction of a bacterial antigen into the body triggers a response specifically against the antigen by :
- causing antibody molecules to assume a shape that permits them to bind and agglutinate the antibody
- causing mutations in cells so that they produce antibodies to the antigen that caused the mutation
- causing cells with the proper antibody to disintegrate and release the antibody
- stimulating the reproduction of cells that make the antibody to that antigen.
Answer: 4. stimulating reproduction of cells that make the antibody to that antigen
Question 4. If most of its lymphocytes were drained out of an animal via the thoracic duct, the animal would not:
- lose its ability to combat cancer and produce new lymphocytes
- lose its ability to reject skin grafts
- lose its ability to mount a secondary immune response
- produce an increased number of red blood cells.
Answer: 4. produce an increased number of red blood cells.
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question and Answers
Question 5. Haemoglobin transports oxygen to the extent of:
- 97% to 98%
- 90 to 92%
- 60 to 70%
- 70 to 80%.
Answer: 1. 97% to 98%
Blood Circulatory System MCQs For NEET
Question 6. Which one of the following blood vessels has a thick muscular coat?
- Veins
- Capillaries
- Arteries
- Lymphatics.
Answer: 3. Arteries
Question 7. Which chamber of the human heart has the thickest muscular wall?
- Right atrium
- Left atrium
- Right ventricle
- Left ventricle.
Answer: 4. Left ventricle
Question 8. The blood flow is fast and with jerks in :
- arteries
- veins
- veins and capillaries
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. arteries
Question 9. Haemoglobin is found dissolved in the plasma of:
- man
- frog
- birds
- earthworm.
Answer: 4. earthworm.
Question 10. The correct sequence followed by the blood flowing through the heart of the frog is:
- sinus venosus, right auricle, left auricle, truncus arteriosus
- truncus arteriosus, ventricle, right auricle, left auricle
- sinus venosus, left auricle, truncus arteriosus, right auricle
- sinus venosus, right auricle, ventricle, truncus arteriosus.
Answer: 4. sinus venosus, right auricle, ventricle, truneus arteriosus.
Question 11. Which of the following is not a difference between the circulatory system of mammals and those of insects?
- Substances must cross a vessel wall to reach the cells of mammals, but the blood of insects is in direct contact with their cells
- Blood moves randomly in an insect but in a definite path in a mammal
- Insects do not transport oxygen in their transport system, whereas mammals do
- Mammals have much higher blood pressure than that of insects.
Answer: 2. Blood moves randomly in an insect, but in a definite path in a mammal
Question 12. A type of blood bank from which reserves of erythrocytes may be quickly mobilized when needed by the body is the :
- liver
- bone marrow
- intestinal mesentery
- spleen.
Answer: 4. spleen.
Blood Circulatory System MCQs For NEET
Question 13. The posterior pair of lymph hearts in frogs pump lymph into :
- brachial vein
- femoral vein
- sciatic vein
- external jugular vein.
Answer: 2. femoral vein
Question 14. Blood enters the heart because muscles of the :
- atria contract
- atria relax
- ventricles contract
- ventricles relax.
Answer: 2. atria relax
Question 15. The breakdown product of haemoglobin is :
- biliverdin and bilirubin
- globulin
- biliverdin
- calcium.
Answer: 1. biliverdin and bilirubin
Question 16. Blood from the kidneys of humans is returned by :
- renal arterioles
- renal vein and renal portal vein
- renal veins
- Bidder’s canal.
Answer: 3. Renal veins
Question 17. How many renal veins emerge out of frog and mammalian kidneys respectively?
- 2,4
- 4,1
- 4,4
- 1,1.
Answer: 2. 4,1
Question 18. Select advantage of a double circulation ova u single circulation
- In the double circulation, all the blood going to the tissue is oxygenated. whereas in single circulation it is not
- In the double circulation. the blood can transport more types of substances
- In double circulation, the blood is at higher pressure when it enters the body tissues and the blood travels around the body faster
- In a double circulation, there are twice as many blood vessels servicing the body tissues.
Answer: 3. In double circulation, the blood is at higher pressure when it enters the body tissues and the blood travels around the body faster
Question 19. In the amphibian heart, the cavity present at the base of truncus arteriosus is called :
- cavum pulmocutaneum
- synagium
- pylangium
- cavum aorticum.
Answer: 3. pylangium
Blood Circulatory System MCQs For NEET
Question 20. The shoulder and forelimb are connected to the heart by :
- subclavian artery
- oesophageal artery
- occipitovertebral
- dorsal aorta.
Answer: 1. subclavian artery
Question 21. What will happen to the body of an adult man if the spleen is removed?
- RBC production will be lowered
- Antibody production will be less
- Filtration of dead RBC will not be there
- WBC production will be lowered.
Answer: 3. Filtration of dead RBC will not be there
Question 22. In persons suffering from sickle cell anaemia, erythrocytes become sickle-shaped when :
- CO2, concentration in the blood rises
- 02 concentration in blood rises
- 02concentration in the blood falls considerably
- diet provides an insufficient amount of vitamin B12
Answer: 3. 02concentration in the blood falls considerably
Question 23. The greatest amount of oxygen will be lost from the blood while it is travelling through :
- the capillaries around the alveoli
- the left atrium of the heart
- the arteries
- the capillaries in the body.
Answer: 4. the capillaries in the body.
Question 24. The blood pressure is high in :
- veins of the portal system
- veins bringing the blood from the head
- arteries
- capillaries.
Answer: 3. arteries
Question 25. The exchange of materials between blood and interstitial fluid only at the :
- capillaries
- veins
- arteries
- arterioles.
Answer: 1. capillaries
Important Questions On Circulatory System NEET
Question 26. The rate of heartbeat per minute is highest in the case of:
- elephant
- whale
- man
- mouse.
Answer: 4. mouse
Question 27. Pick up the cells of bone marrow which give rise to all types of corpuscles of blood :
- Plasmocytes
- Megablasts
- Osteoblasts
- Reticular cells and haemocytoblasts.
Answer: 4. Reticular cells and haemocytoblasts.
Question 28. The proximal veins collect blood from :
- head and hind limbs
- lore limbs and hind limbs
- head and forelimbs
- trunk and forelimbs.
Answer: 3. head and forelimbs
Question 29. Thrombosis in which coronary artery is met most frequently in Ml (Myocardial infarction):
- Right coronary artery
- Left anterior descending artery
- Left green flex coronary artery
- Right circumflex coronary artery.
Answer: 1. Right coronary artery
Question 30. The portal system present in all the vertebrates is :
- hepatic
- renal
- pulmonary
- Both 1 and 3
Answer: 1. hepatic
Question 31. S.A. node is a small flattened ellipsoid strip of muscle fibre measuring about:
- 0.3 mm
- 3 mm
- 0.6 mm
- 6 mm.
Answer: 1. 0.3 mm
Question 32. Haemolysis can occur in one of the following cases:
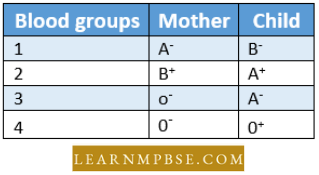
Answer: 4.
Question 33. The first heart sound created by the closure of the AV valve is loud. It lasts for:
- 0.10 sec
- 0.16 to 90
- 0.5 sec
- 0.5 to 20 sec.
Answer: 2. 0.16 to 90
Important Questions On Circulatory System NEET
Question 34. Patients in which atrial impulse suddenly falls to be transmitted to ventricles. Such a case is called :
- Ventricular escape
- Stokes
- Adams syndrome
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 35. The free edges of the auriculo-ventricular valves are joined to the wall of the heart of fine collagen fibres called :
- papillary
- columnar camera
- chordate tendineae
- connecting fibres.
Answer: 3. chordate tendineae
Question 36. The right auricle of the heart of a human is :
- equal to the left
- smaller than the left
- larger than the left
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. larger than the left
Important Questions On Circulatory System NEET
Question 37. The heart of fish is :
- two chambered
- single chambered
- four chambered
- three-chambered.
Answer: 1. two chambered
Question 38. Opening of pulmonary vein to left auricle is guarded by :
- three semilunar valves
- bicuspid valve
- tricuspid valve
- No valve.
Answer: 4. No valve.
Question 39. In a closed circulatory system, blood is completely closed within :
- vessels
- skeleton
- sinuses
- heart.
Answer: 1. vessels
Question 40. The heart is enclosed in a double-walled thin bag called :
- peritoneal
- pericardial
- pericardium
- visceral peritoneum.
Answer: 3. pericardium
Question 41. The main function of pericardial fluid is :
- lubrication
- protective
- protective and lubrication
- antiseptic.
Answer: 3. protective and lubrication
Question 42. The heart is made of:
- cardiac muscles
- longitudinal muscles
- horizontal muscles
- connective muscles and horizontal muscles.
Answer: 1. cardiac muscles
Question 43. The absolute refractory period of the heart is :
- during contraction when the heart is in a non-responding period
- during expansion
- during negative charge
- during positive charge.
Answer: 1. during a contraction when the heart is in a non-responding period
Important Questions On Circulatory System NEET
Question 44. The heart muscles work rhythmically always by :
- external stimuli
- their own property
- action of liver
- action of hormones.
Answer: 2. their own property
Question 45. In the mammalian heart, there is very swift conduction of stimulation all over the heart because of:
- bundle of His and Purkinje fibres
- pericardial fluid
- peritoneum
- proteins in the heart.
Answer: 1. bundle of His and Purkinje fibres
Types Of Circulatory System MCQs
Question 46. Heartbeats are affected by :
- vagus nerve which increases the heartbeats
- vagus nerve which reduces the heartbeats
- central nervous system
- digestive system.
Answer: 2. vagus nerve which reduces the heartbeats
Question 47. Heartbeats are accelerated by the :
- cranial nerve
- stomach peristalsis
- number of red blood cells
- sympathetic nerves.
Answer: 4. sympathetic nerves.
Question 48. Ringer’s solution contains :
- Iodine and salt
- Acetic acid and wax
- Sodium and potassium ions
- Water and acid fuschin.
Answer: 3. Sodium and potassium ions
Types Of Circulatory System MCQs
Question 49. The heartbeat is initiated by a special heart tissue embodied in the wall of the right wall of the right auricle. This is called :
- sinu-auricular node
- sinu-ventricular node
- auriculo-vcntricular node
- Rt. ventricle and Lt. ventricle nodes.
Answer: 1. sinu-auricular node
Question 50. The common name of the sinus-auricular node is:
- Pacesetter
- Pacemaker
- Blood regulator
- Blood colloid.
Answer: 2. Pacemaker
Question 51. As in other cells, heart muscle fibres also carry an electric charge. This is:
- positive on the outer surface and negative on the inner
- negative on the outer surface and positive on the inner
- positive on both inner and outer surfaces
- negative on both inner and outer surfaces.
Answer: 1. positive on the outer surface and negative on the inner
Types Of Circulatory System MCQs
Question 52. The opening of auricles into the ventricle in frogs is guarded by :
- a single semilunar valve
- three semilunar valves
- auriculo-ventricular valve
- a sphincter.
Answer: 3. auriculo-ventricular valve
Question 53. During the coagulation of blood, vitamin K helps in the :
- conversion of prothrombin to thrombin
- formation of prothrombin
- conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin
- formation of thromboplastin.
Answer: 2. formation of prothrombin
Question 54. Oxygenated blood enters the heart in the :
- right ventricle
- right auricle
- left ventricle
- left auricle.
Answer: 4. left auricle.
Question 55. The sciatic vein collects blood and pours it in :
- pelvic vein
- renal portal vein
- renal vein
- anterior abdominal vein.
Answer: 2. renal portal vein
Human vs Animal Circulatory System NEET MCQs
Question 56. Blood from the lungs of humans is carried by :
- azygos vein
- anterior abdominal
- pulmonary vein
- cutaneous vein.
Answer: 3. Pulmonary vein
Question 57. When a normal frog is injected with the physiological concentration of adrenaline, the heartbeat shows :
- Initiation of heartbeat
- Conduction of heartbeat
- Increased rate of heartbeat
- Release of acetylcholine.
Answer: 3. Increased rate of heartbeat
Question 58. The circulation of blood was first discovered by :
- Lamarck
- William Harvey
- Darwin
- Hugo de Vries.
Answer: 2. William Harvey
Question 59. The opening of the upper chamber of the heart into the lower chamber is known as :
- sinu-auricular aperture
- auriculo-ventricular aperture
- atrioventricular septum
- atrioventricular node.
Answer: 2. auriculo-ventricular aperture
Question 60. The blood leaving the lungs is richer than the blood entering the lungs in :
- the number of RBC per ml. of blood
- the amount of oxygen per ml. of blood
- the amount of haemoglobin per ml. of blood
- the amount of nutrients per ml. of blood.
Answer: 2. the amount of oxygen per ml. of blood
Question 61. The artery which carries deoxygenated blood is known as :
- pulmonary artery
- aorta
- coronary artery
- pulmocutaneous.
Answer: 1. pulmonary artery
Question 62. When the valves prevent the backflow of the blood, the circulation stent is called as
- bilateral
- lateral
- closed
- Open
Answer: 2. lateral
Question 63. The intravenous injection of blood plasma or serum with the object of restoring the blood volume is known its:
- transplantation
- Trasfusion
- transcription
- vaccination.
Answer: 2. Transfusion
Human vs Animal Circulatory System NEET MCQs
Question 64. Which of the following statements is true for arteries?
- Arteries are thin-walled and blood in them is under low pressure
- Arteries are thin-walled and blood in them is under high pressure
- Arteries are thick-walled and blood in them is under low pressure
- Arteries are thick-walled and blood in them is under high pressure.
Answer: 4. Arteries are thick-walled and blood in them is under high pressure.
Question 65. Perfusion of the heart of a frog with acetylcholine will cause :
- decreased heartbeat
- systolic arrest
- diastolic arrest
- extra systole.
Answer: 1. decreased heartbeat
Question 66. The connection between arteries and veins is through :
- Arteriole
- venule
- capillaries
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. capillaries
Human vs Animal Circulatory System NEET MCQs
Question 67. The blood which after circulation comes from the liver to the heart has :
- increased CO2, content
- increased bile content
- increased blood content
- increased 02 content.
Answer: 1. increased CO2 content
Question 68. The innermost coat of the wall of the artery is called :
- tunica extrema
- tunica media
- arnica adventitia
- endothelium.
Answer: 4. endothelium
Question 69. The wall of the vein is :
- thin
- thick
- equal to that of the artery
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. thin
Question 70. Tunica media of blood vessels is formed of:
- endothelium
- connective tissue
- unstriped muscle fibres
- Both 1 and 3.
Answer: 3. Unstriped muscle fibres
Question 71. An adult human with average health has systolic and diastolic pressures as :
- 80 mm Hg and 80 mm Hg
- 70 mm Hg and 120 mm Hg
- 120 mm Hg and 80 mm Hg
- 50 mm Hg and 80 mm Hg.
Answer: 3. 120 mm Hg and 80 mm Hg
Question 72. With respect to the ABO group, there are found major blood types because this blood group is determined by :
- three alleles, all of which are co-dominant
- three alleles, all of which are recessive
- three alleles, of which two are recessive and the third is dominant
- three alleles, of which two are codominant and the third is recessive.
Answer: 4. three alleles, of which two are codominant and the third is recessive
Human vs Animal Circulatory System NEET MCQs
Question 73. Heartbeats are affected by.
- Carbon dioxide
- Oxygen
- Vagus nerve
- All of these.
Answer: 3. Vagus nerve
Question 74. Which of the following Is the cancerous state of blood?
- Chloremia
- leukaemia
- Uremia
- Proteinemia
Answer: 2. leukaemia
Question 75. Oxygenated blood Is found lit :
- Pulmonary veins
- Pulmonary arteries
- Right atrium
- Right ventricle,
Answer: 1. Pulmonniy veins
Question 76. Heartbeat originates from :
- Pacemaker
- Cardiac muscles
- Left atrium
- Right ventricle.
Answer: 1. Pacemaker
Question 77. In vertebrate blood the carrier of oxygen to the tissues or respiratory pigment is.
- Plasma
- Lymphocytes
- Leucocytes
- Haemoglobin.
Answer: 4. Haemoglobin
Question 78. Who discovered the Rh factor?
- Huxley
- Landsteincr
- Landsteiner and Weiner
- Weiner.
Answer: 3. Landsteiner and Weiner
NEET Biology Chapter-wise MCQs
Question 79. The gene for the main factor for the clotting of blood is present.
- X chromosome
- Y chromosome
- Both the X and Y chromosome
- Autosomes.
Answer: 1. X chromosome
Question 80. Which of the following is not a granulocyte?
- Lymphocyte
- Eosinophil
- Basophil
- Neutrophil.
Answer: 1. Lymphocyte
Question 81. The life span of human W.B.C. is approximately :
- 48 hours
- 24 hours
- 120 days
- 100 hours.
Answer: 1. 48 hours
Question 82. Megakaryocytes give rise to :
- Erythrocytes
- Granulocytes
- Agranulocytes
- Thrombocytes.
Answer: 4. Thrombocytes
Question 83. Which of the following statements is not correct for sickle cell anaemia?
- The sixth amino acid (from the NH2 terminus) of the beta chain is glutamic acid
- Erythrocytes elongate and form sickle-shaped cells
- Individuals homozygous for the haemoglobin S allele are Hb B /Hb B
- The beta chain of haemoglobin S contains valine.
Answer: 1. Sixth amino acid (from the NH2 terminus) of the beta chain is glutamic acid
Question 84. The mitral valve is present between :
- Left auricle and left ventricle
- Right auricle and right ventricle
- The right ventricle and aortic arch
- Left ventricle and pulmonary arch.
Answer: 1. Left auricle and left ventricle
Question 85. Which of the following factors is known as the ‘Christmas factor’ :
- Factor VIII
- Factor XII
- Factor IV
- Factor IX.
Answer: 4. Factor IX
Question 86. Nucleated RBCs found in :
- Man
- Rat
- Frog
- Rabbit
Answer: 3. Frog
Question 87. In rabbits cardiac sphincter is found in :
- Heart, on left dorsal aorta.
- Heart, on right auricle and ventricle
- Between the oesophagus and stomach
- Between stomach and duodenum.
Answer: 3. Between the oesophagus and stomach
NEET Biology Chapter-wise MCQs
Question 88. The tendons connecting papillary muscles and heart valves are called :
- Muscle column
- Heart tendon
- Chordae tendineae
- Pedirate muscles.
Answer: 3. Chordae tendineae
Body Fluids And Circulation MCQ Question 89. QRS is related to:
- Ventricular contraction
- Ventricular relaxation
- Auricular contraction
- Depolarisation.
Answer: 1. Ventricular contraction
Question 90. Sinus venous is absent in :
- Mammals
- Frog
- Reptiles
- Amphibians.
Answer: 1. Mammals
Question 91. The pacemaker of the heart is made up of :
- Smooth muscles
- Cardiac muscles
- Nerve tissue
- Triage
Answer: 2. Cardiac muscles
Question 92. The pacemaker of the heart is introduced for :
- Regulation of heartbeat
- Conduction of heartbeat
- To stop the heartbeat
- Pacemaker is absent.
Answer: 1. Regulation of heartbeat
NEET Biology Chapter-wise MCQs
Question 93. Vertebrate’s heart originates from :
- A splanchnic layer of mesoderm facing the anterior intestinal part
- Ectoderm lying over the forebrain
- The inner lining of the neural tube
- Primitive streak
Answer: 1. Splanchnic layer of mesoderm facing the anterior intestinal part
Question 94. The rate of heartbeat is controlled by :
- Vagus only
- Sympathetic nervous system
- Both the vagus and sympathetic nervous system
- Hormones only.
Answer: 3. Both the vagus and sympathetic nervous system
Question 95. O2 carrying capacity of blood is :
- 1200ml./100 ml of blood
- 1200ml./100 ml of blood
- l20 ml 7100 ml of blood
- 500ml./100 ml of blood.
Answer: 3. l20 ml 7100 ml of blood
Question 96. At high altitudes, some changes take place in blood. This change is :
- Increase in leucocyte count
- Increase in red blood corpuscles count
- Decrease in red blood cell count
- Increase in blood platelets.
Answer: 2. Increase in red blood corpuscles count
Question 97. The chambered heart are found in :
- Squamata
- Lacertilian
- Crocodilia
- DiOphidia.
Answer: 3. Crocodilia
Question 98. Normal WBC count is 5000 to 10,000 cub/mm of blood. When the number of WBCs falls below normal level this is called leucopenia. It occurs due to :
- Tuberculosis
- Typhoid fever
- Allergies
- Blood cancer.
Answer: 1. Tuberculosis
Question 99. The pulse rate is the result of:
- Atrial systole
- Atrial diastole
- Ventricular systole
- Ventricular diastole.
Answer: 3. Ventricular systole
Question 100. The venous system of a frog differs from rabbit in having :
- Hepatic portal system
- Renal portal system
- Both hepatic and renal portal systems
- Veins
Answer: 2. Renal portal system
Blood Circulatory System MCQs For NEET
Question 101. The heart is innervated by :
- Vagus
- Facial
- Trigeminal
- Glossopharyngeal
Answer: 1. Vagus
Question 102. The right atrium of a man’s heart receives blood from
- Sinus venous
- Pulmonary veins
- Inferior vena cava
- Superior and Inferior vena cava
Answer: 4. Superior and Inferior vena cava
Question 103. During diastole
- Blood leaves the heart
- Blood enters the heart
- Blood leaves the ventricle
- Blood enters the lungs.
Answer: 2. Blood enters the heart
Question 104. The bicuspid valve allows blood from :
- Right auricle lo left ventricle
- Right auricle lo right ventricle
- Left auricle lo left ventricle
- Postcaval to heart.
Answer: 3. Left auricle lo left ventricle
Question 105. Blood pressure is defined as :
- The force with which blood pushes against the wall of the blood vessels
- The force with which blood is pushed to the legs
- The force with which blood comes out of the atrium.
- The force with which blood comes out of the ventricle.
Answer: 1. The force with which blood pushes against the wall of the blood vessels
Blood Circulatory System MCQs For NEET
Question 106. Blood supply to the kidney is :
- 25%
- 20%
- 90%
- 50%.
Answer: 1. 25%
Question 107. Match the column :
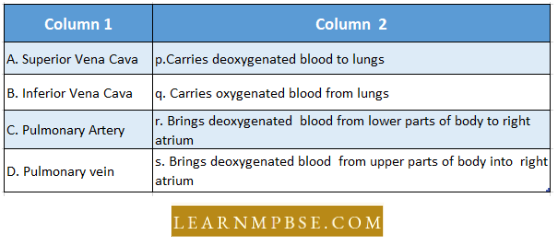
- A — q, B — t, C— r, D — p
- A — t, B — p, C — q, D — r
- A — t, B — r, C — p, D — q
- A — t, B — p, C — r, D — q.
Answer: 3. A — t, B — r, C — p, D — q
Question 108. During high blood pressure, regulation of heartbeat and circulation is controlled by :
- Vasodilator and vasoconstrictor centres.
- Cardio-stimulatory and vasoconstrictor centres
- Cardio-inhibitory and vasoconstrictor centres
- Cardio-inhibitory and vasodilator centres.
Answer: 2. Cardio-stimulatory and vasoconstrictor centres
Question 109. What is true about veins?
- All veins carry deoxygenated blood
- All veins carry oxygenated blood
- They carry blood from organs towards the heart
- They carry blood from the heart towards the organs.
Answer: 3. They carry blood from organs towards the heart
Question 110. Blood pressure is measured by :
- Sphygmomanometer
- Phonocardiogrant
- Electrocardiogram
- Stethoscope.
Answer: 1. Sphygmomanometer
Question 111. In which of the capillary system is present
- Arthropods
- Cephalopods
- Tunicates
- Hemicordates
Answer: 2. Cephalopods
Blood Circulatory System MCQs For NEET
Question 112. The respiratory pigment is dissolved in the plasma of blood in the case of:
- Crustaceans
- Cyclostomes
- cnidarians
- chondricthythes.
Answer: 1. Crustaceans
Question 113. The heart of the cockroach is 13-chambered, Each chamber bears a pair of aperture guarded by valves. The apertures are :
- Sinn-auricular aperture
- Aurieuloventrieular aperture
- Ostia
- Osculum.
Answer: 3. Ostia
Question 114. Which of the following is involved in maintaining the pH of the blood by buffering action?
- Na+, K+ and Cl+2
- Ca4. Mg44 and HC03
- HP04-2 and P04-3
- All of the above.
Answer: 3. HP04-2 and P04-3
Question 115. Erythrocytes do not contain :
- Haemoglobin
- Carbonic anhydrase
- Cl-
- None of the above.
Answer: 4. None of the above
Question 116. Neutrophils are responsible for protection against infection. They constitute how much % age of total leucocyte count:
- 3 %
- 0.5 % to 1
- 62 %
- 30 %.
Answer: 3. 62 %
Question 117. Monocytes have kidney-shaped nuclei and constitute 5-6 per cent of total WBC. The diameter of a monocyte is about:
- 10 -18 mm
- 10 – 10 mm
- 2 – 4 mm
- 12 – 15 mm.
Answer: 1. 10 -18 mm
Question 118. If there is a complete mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in the heart, then :
- blood to the lungs would be low in oxygen and the tissues would receive blood rich in oxygen
- blood to the lungs would be rich in oxygen and the tissues would receive blood which is low in oxygen
- lungs and tissues would receive blood with the same amounts of oxygen
- tissues would receive completely oxygenated blood and lungs would receive complete
deoxygenated blood.
Answer: 3. lungs and tissues would receive blood with the same amounts of oxygen
Body Fluids And Circulation NEET Biology Question 119. QRS in ECG is related to :
- Atrial contraction
- Ventricular contraction
- Ventricular relaxation
- Atrial relaxation.
Answer: 2. Ventricular contraction
Question 120. The most important centre for the formation of lymph is:
- bone marrow
- liver
- pancreas
- gastric glands.
Answer: 2. liver
Question 121. Which one of the following statements is correct?
- The greater the 02 affinity of haemoglobin, the lower the extraction rate of oxygen
- Terrestrial amphibians require much lower environmental oxygen pressure than aquatic forms
- Aquatic reptile lorry require twice the environmental oxygen pressure than the terrestrial forms
- The oxygen extraction power of haemoglobin is inversely proportional to the atmospheric pressure.
Answer: 4. The oxygen extraction power of haemoglobin is inversely proportional to the atmospheric pressure.
Question 122. Mammals native to high altitudes have haemoglobins of greater oxygen affinity than low-altitude forms because :
- they need more oxygen than their, low altitude counterparts
- the haemoglobin allows the extraction of oxygen from environments poor in oxygen (high altitudes) relative to low altitudes
- they have less number of erythrocytes than their counterparts on low altitudes and increased oxygen affinity balances the reduced percentage of erythrocytes
- the statement is not correct.
Answer: 2. the haemoglobin allows extraction of oxygen from environments poor in oxygen (high altitudes) relative to low altitudes
Question 123. The innermost layer of blood capillaries is made up of:
- endothelial cells
- haemocytes
- elastic membrane
- 1 and 3.
Answer: 4. 1 and 3
Body Fluids And Circulation NEET Biology Question 124. The cords of Billorth are blood spaces which are found in :
- liver
- tonsils
- kidneys
- spleen.
Answer: 4. spleen.
Question 125. Match the different leucocytes given under Column1 with their functions given under Column 2; choose the answer that gives the correct combination of alphabets of two columns
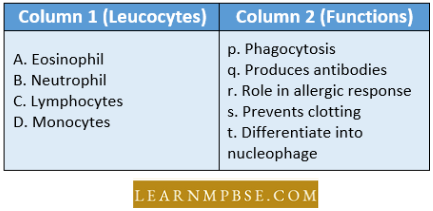
- A = t, B = p, C = q, D = t
- A = r, B = p, C = q, D = t
- A = q, B = r, C = s, D = t
- A = p, B = q, C = r, D = s.
Answer: 2. A = r, B = p, C = q, D = t
Question 126. Which vitamin helps in blood coagulation?
- Vitamin K
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin D
Answer: 1. Vitamin K
Question 127. Which one of the following is mainly responsible for the second heart sound?
- Closure of atrioventricular valves.
- Opening of atrioventricular valves.
- Closure of semilunar valves.
- Thrust of blood on ventricular wall during atria contraction.
Answer: 3. Closure of semilunar valves
