Mineral Nutrition In Plants Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1. Iron is mainly absorbed in :
- Ferrous form
- Ferric form
- Combined form
- All the above.
Answer: 4. Ferrous form
Question 2. Micronutrients are those elements :
- Not important for plant growth
- Required in large quantity
- Required in small quantities and are important as macro-nutrients
- Not present in the soil.
Answer: 3. Required in small quantities and are important as macro-nutrients
Question 3. Which of the following micronutrients can be absorbed by foliage?
- Hydrogen
- Potassium
- Sodium
- Zinc.
Answer: 2. Potassium
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question and Answers
Question 4. Which of the following elements are not absorbed from the soil?
- Nitrogen
- Iron
- Boron
- Carbon.
Answer: 4. Carbon.
Question 5. Which of the following is a component of chlorophyll?
- Calcium
- Sodium
- Zinc
- Magnesium.
Answer: 4. Magnesium.
Question 6. Bidirectional translocation of minerals takes place through :
- Xylem
- Phloem
- Parenchyma
- Cambium.
Answer: 1. Xylem
Mineral Nutrition Mcqs For Neet
Question 7. The most abundant element in plants is :
- Oxygen
- Nitrogen
- Carbon
- Hydrogen.
Answer : 3. Carbon
Question 8. Minerals of soil are derived from :
- Rocks
- Clay
- Carbon
- Organisms.
Answer: 1. Rocks
Question 9. Trace elements are :
- Required in very minute quantity
- Radioactive
- Those which draw other elements
- First discovered in protoplasm.
Answer: 1. Required in very minute quantity
Question 10. Pre-mature leaf-fall is caused by to deficiency of :
- Zinc
- Cobalt
- Nitrogen
- Potassium.
Answer : 3. Nitrogen
Question 11. The chlorophyll is not formed without :
- Potassium
- Magnesium
- Calcium
- Phosphorus.
Answer: 2. Magnesium
Mineral Nutrition Mcqs For Neet
Question 12. The movement of mineral ions into plant root cells as a result of diffusion is called :
- Endocytosis
- Osmosis
- Passive absorption
- Active absorption.
Answer: 3. Passive absorption
Question 13. Woodward (1669) observed that plants grow better in muddy water than in rainwater because :
- Muddy water had macronutrients dissolved in it
- Muddy water had micronutrients dissolved in it
- Muddy water had most of the essential elements dissolved in it
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Muddy water had most of the essential elements dissolved in it
Question 14. Who gave the criteria of essentiality?
- R. Hill
- F.F. Blackman
- M.P. Kaushik
- D.L. Arnon.
Answer: 4. D.L. Arnon.
Question 15. Which one of the following elements is essential for the photolysis of water?
- Chlorine
- Calcium
- Sodium
- Sulphur.
Answer: 1. Chlorine
Mineral Nutrition Mcqs For Neet
Question 16. Which one of the following plants cannot fix atmospheric nitrogen directly?
- Bean
- Castor
- Gram
- Pea.
Answer: 2. Castor
Question 17. In the nitrogen cycle, nitrite is converted to nitrate by :
- Azotobacter
- Rhizobium
- Nitrosowonas
- Nitrobacter.
Answer: 4. Nitrobacter.
Question 18. Plants absorb mineral salts from the soil solution through:
- A semipermeable membrane into the cytoplasm by selective absorption
- Perforations at the apex of root hair cells
- The cell wall which is permeable
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. A semipermeable membrane into the cytoplasm by selective absorption
Mineral Nutrition In Plants Mcqs Neet
Question 19. Deficiency of iron causes :
- Bending of leaf tip
- Interveinal chlorosis first in young leaves
- Decrease in protein synthesis
- Reduced leaves and stunted growth.
Answer: 2. Interveinal chlorosis first in young leaves
Question 20. The function of Mg and Fe is:
- Synthesis of chlorophyll
- Synthesis of proteins
- Synthesis of fat
- Synthesis of organic acids.
Answer: 1. Synthesis of chlorophyll
Question 21. Which of the following elements is involved in nitrogen metabolism in the reduction of nitrates?
- Zinc
- Molybdenum
- Boron
- Manganese.
Answer: 2. Molybdenum
Question 22. The mineral constituent of the cell wall is :
- Iron
- Sulphur
- Potassium
- Calcium.
Answer: 4. Calcium.
Question 23. Active uptake of minerals by roots mainly depends on the :
- Availability of oxygen Light
- Temperature
- Availability of carbon dioxide.
Answer: 1. Availability of oxygen Light
Mineral Nutrition In Plants Mcqs Neet
Question 24. Which of the following is a macronutrient?
- Ca
- Mn
- Zn
- Cu.
Answer: 1. Ca
Question 25. Which of the following is a trace element?
- Zn
- Ca
- P
- Mg.
Answer: 1. Zn
Question 26. Synthesis of IAA requires:
- Iron
- Zinc
- Calcium
- Nitrogen.
Answer: 2. Zinc
Question 27. Which of the following is common to ferredoxin and cytochrome? ,
- Na
- K
- Fe
- Mg.
Answer : 3. Fe
Question 28. The brown colour of the leaves of cabbage is due to the deficiency of:
- Boron
- Nitrogen
- Sulphur
- Calcium.
Answer: 1. Boron
Neet Mcqs On Essential Minerals In Plants
Question 29. Most of the minerals in inorganic form are transported through :
- xylem
- Phloem
- Cortex
- Cambium.
Answer: 1. xylem
Mineral Nutrition MCQ Question 30. The mass flow hypothesis explains the transport of:
- Water
- Food materials
- Salts
- Auxins.
Answer: 2. Food materials
Question 31. Which of the following does not require carrier molecules during transport through cell membranes?
- Na+ and K+ transport
- Active transport of sugars and amino acids
- Simple diffusion
- Facilitated diffusion.
Answer: 3. Simple diffusion
Question 32. In a citrus plantation, all the plants were found to be suffering from the die-back disease and spraying of fungicides was of no help. This problem was due to the deficiency of:
- Auxins
- Zinc
- Gibberellic acid
- Copper.
Answer: 4. Copper.
Question 33. In fruit trees a disease exanthema is caused by the deficiency of:
- Na
- Ca
- Cu
- P
Answer: 3. Cu
Neet Mcqs On Essential Minerals In Plants
Question 34. Active transport of molecules from outside to inside across a membrane requires:
- Cyclic AMP
- Acetylcholine
- ATP (energy)
- Choline.
Answer: 3. ATP (energy)
Question 35. If chlorophyll is burnt, what will be left?
- Fe
- Na
- Mg
- Mn.
Answer: 3. Mg
Mineral Nutrition MCQ Question 36. Deficiency of molybdenum causes:
- Poor development of vasculature
- Bending of leaves
- Chlorosis of leaves
- Mottling or necrosis of leaves.
Answer: 4. Mottling or necrosis of leaves
Question 37. Which one of the following elements plays an important role in biological nitrogen fixation?
- Molybdenum
- Manganese
- Copper
- Zinc.
Answer: 1. Molybdenum
Question 38. Photolysis of water is increased by :
- Manganese
- Zinc
- Boron
- Copper.
Answer: 1. Manganese
Neet Mcqs On Essential Minerals In Plants
Question 39. The role of inorganic nutrients in plant growth was at first indicated by :
- Wood ward
- Knop ‘
- Stewart
- De Saussure.
Answer: 2. Knop ‘
Question 40. Which of the following essential mineral elements is not a constituent of any enzyme, but stimulates the reactions of many enzymes?
- Potassium
- Zinc
- Manganese
- Magnesium.
Answer: 1. Potassium
Question 41. The essential nutrient element required by plants in the least quantity is :
- Chlorine
- Zinc
- Molybdenum
- Manganese.
Answer: 3. Molybdenum
Question 42. Ammonium sulfate is a :
- Enzyme
- Fertilizer
- Weed killer
- Pesticide.
Answer: 2. Fertilizer
Question 43. For normal growth of plants one of the following is not required :
- Magnesium
- Lead
- Potassium
- Iron.
Answer: 2. Lead
Macro And Micronutrients In Plants Mcqs For Neet
Question 44. The essential element for the synthesis of auxin is :
- Zn
- Phosphorus
- Sulphur
- Potassium.
Answer: 1. Zn
Question 45. Pre-mature leaf-fail is caused due to the deficiency of :
- Molybdenum
- Sodium
- Phosphorus
- Sulphur.
Answer: 3. Phosphorus
Question 46. Which one of the following can fix atmospheric nitrogen directly?
- Pea
- Brassica
- Castor
- Petunia.
Answer: 1. Pea
Biology MCQ Mineral Nutrition Question 47. Mg and Fe are required by the plants for the :
- Energy transfer is concerned with photosynthesis
- Synthesis of chlorophyll pigments in leaves
- Mechanism of stomatal opening and closing
- Translocation of carbohydrates from the leaf to the stem.
Answer: 2. Synthesis of chlorophyll pigments in leaves
Question 48. The non-essential elements in the plant are:
- Calcium
- Barium
- Iron
- Magnesium.
Answer: 2. Barium
Macro And Micronutrients In Plants Mcqs For Neet
Question 49. An example of an anaerobic nitrogen-fixing saprophytic bacterium is :
- Azotobacter
- Rhizobium
- Clostridium
- Pseudomonas.
Answer: 3. Clostridium
Question 50. Organisms which fix free nitrogen in the soil are :
- Green algae
- Ferns
- Blue-green algae
- Mosses.
Answer: 3. Blue-green algae
Question 51. Nodules with nitrogen-fixing bacteria are present in the roots of:
- Cotton
- Gram
- Wheat
- Maize.
Answer: 2. Gram
Question 52. Members of the bean family are particularly important for the rotation of crops:
- Because they add green manure
- They add nitrates to the soil
- They make the soil porous
- They add calcium to the soil.
Answer: 2. They add nitrates to the soil
Question 53. Nitrogen is an essential component of :
- Fats
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Hormones.
Answer: 3. Proteins
Question 54. The most important element associated with proto-plasm and proteinaceous materials of plants is :
- Oxygen
- Nitrogen
- Potassium
- Sulphur.
Answer: 2. Nitrogen
Question 55. Which is a micronutrient?
- Calcium
- Zinc
- Magnesium
- Phosphorus.
Answer: 2. Zinc
Macro And Micronutrients In Plants Mcqs For Neet
Question 56. Minerals are absorbed by roots mainly by :
- Active absorption
- Diffusion
- Donnan equilibrium
- Transfusion.
Answer: 1. Active absorption
NEET Biology Mineral Nutrition In Plants Question 57. Which of the following elements can plants take directly from air?
- Phosphorus
- Nitrogen
- Carbon
- Calcium.
Answer: 3. Carbon
Question 58. Chlorosis in plants occurs due to :
- High sunlight intensity
- Low light intensity
- Yellow pigment
- Deficiency of magnesium and iron in the soil.
Answer: 4. Deficiency of magnesium and iron in the soil.
Question 59. Hydroponics is ;
- The study of soil conservators
- Culture of plants in water
- The study of plant ecology
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Culture of plants in water
Question 60. Non-essential elements for the proper growth of the plant are:
- Potassium
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Culture of plants in water
Answer: 1. Potassium
Question 61. Nitrogen is usually absorbed by the plant in the form of:
- Nitrogen peroxide
- Free nitrogen
- Nitrate
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Nitrate
Mineral Nutrition Mcqs For Neet
Question 62. Insectivorous plants can grow well in a soil deficient in: _
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Nitrogen
- Iron.
Answer: 3. Nitrogen
Question 63. Without essential mineral nutrients leaves of many plants turn yellow because of:
- Plasmolysis
- Etiolation
- chlorosis
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. chlorosis
NEET Biology Mineral Nutrition In Plants Question 64. Which element is essential as an electron carrier?
- Iron
- Zinc
- Potassium
- Calcium.
Answer: 1. Iron
Question 65. Enzyme-catalyzed reactions can be inhibited by :
- Mg2++
- Zn2++
- Cu2++
- Hg2++.
Answer: 4. Hg2++.
Question 66. If a dried leaf is taken in a crucible and heated to 600°C, a grey-coloured powder is left behind. It is referred to as:
- Dry weight
- Plant ash
- Wilting percentage
- Protein content of the plant.
Answer: 2. Plant ash
Question 67. In the nodules of roots in leguminous plants, we find :
- N2 producing bacteria
- Denitrifying bacteria
- Fixing bacteria
- Ammonifying bacteria.
Answer: 3. Fixing bacteria
Question 68. Which of the following is an obligate stem parasite?
- Cuscuta
- Orobanche
- Dalbergia sissoo
- Monotropa.
Answer: 1. Cuscuta
Mineral Nutrition Mcqs For Neet
Question 69. Which of the following is a partial root parasite?
- Sanlalum album
- Rafflesia
- Monotropa
- Mango,
Answer: 1. Sanlalum album
Question 70. Pick up the saprophytic angiosperm :
- Neottia
- Agaricus
- Eucalyptus
- Cuscuta.
Answer: 1. Neottia
Question 71. Helotism is master and slave relationship found in :
- Lichens
- Mysmicophytes
- Nepenthes
- Cuscuta.
Answer: 1. Lichens
Question 72. The insectivorous plant, Nepenthes is also known as:
- Sundew plant
- Ficus
- Pitcher plant
- Dischidia.
Answer: 3. Pitcher plant
Question 73. The traps of carnivorous plants contain :
- Polysaccharides
- Digestive enzymes
- Phospholipids
- Weedicidcs.
Answer: 2. Digestive enzyme
Question 74. Which of the following formulae describes nitrogen fixation?
- N2 +3H2→ 2NH3
- 2NH+4 +202 + 8e→ N2 + 4H20
- 2NH3 →N2+ 3H2 ‘
- 2N2+ glucose —> 2 Amino acids.
Answer: 1. N2 +3H2→ 2NH3
Neet Mcqs On Essential Minerals In Plants
Question 75. Mineral uptake by a terrestrial plant is limited by insufficient:
- Blue light
- Soil water
- Apoplast
- Phellogen.
Answer: 2. Soil water
Question 76. Plants that have mutualistic relations with nitrogen¬fixing bacteria provide the bacteria with :
- N2
- Enzymes
- Sugars
- Nitrite.
Answer: 3. Sugars
Question 77. The nodule in a plant root where nitrogen-fixing bacteria live forms from cells of the :
- Epidermis.
- Cortex.
- Endodermis
- Vascular cylinder.
Answer: 2. Cortex.
Mineral Nutrition MCQ Question 78. Plants, such as clover and beans, that have nitrogen-fixing bacteria in their roots are in which of the following families?
- Orchidaceae
- Asteraceae
- Solanaceae
- Leguminosae.
Answer: 2. Asteraceae
Question 79. Contact exchange of ions occurs:
- Between root and soil particles
- Root and soil solution
- Cell and external solution
- All the above.
Answer: 1. Between root and soil particles
Question 80. Bacteria that fix nitrogen for such plants as clover and beans are in which of the following genera?
- Denitrovibrio
- Rhizobium
- Pseudomonas
- Nitrobacter.
Answer: 2. Rhizobium
Neet Mcqs On Essential Minerals In Plants
Question 81. Salt respiration is :
- Excretion of salt through respiratory channels
- Decrease in respiration during salt absorption
- Additional respiration involved in salt absorption
- Linking of ion movement with respiratory chain.
Answer: 3. Additional respiration involved in salt absorption
Question 82. Which of the following plants will enrich the soil with nitrogen?
- Corn
- Alfalfa
- Wheatgrass
- Beets.
Answer: 2. Alfalfa
Question 83. Organisms that fix nitrogen in aquatic habitats are :
- Green algae
- Cyanobacteria
- Crown algae
Protozoa.
Answer: 2. Cyanobacteria
Question 84. ‘Grey-Speck’ disease is caused by the deficiency of:
- Molybdenum
- Zinc
- Manganese
- Boron.
Answer: 3. Manganese
Mineral Nutrition MCQ Question 85. The need of individual plants for any particular element is normally defined in terms of:
- Critical period
- Critical condition
- Critical concentration
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Critical concentration
Question 86. Permeability of protoplasm is accelerated by :
- Na
- K
- Ca
- P.
Answer: 2. K
Question 87. Black necrosis of the stem and root tip is caused by the deficiency of:
- Magnesium
- Chlorine
- Copper
- Boron.
Answer: 4. Boron.
Mineral Nutrition In Plants Mcqs Neet
Question 88. Which of the following is not caused by a deficiency of mineral nutrition?
- Necrosis
- Etiolation
- Chlorosis
- Shortening of internodes.
Answer: Etiolation
Mineral Nutrition MCQ Question 89. Which of the following is not essential for plant growth?
- Zn
- I,
- K
- Fe.
Answer: 2. I
Question 90. Which of the following nutrient elements is most important for protein synthesis?
- N,
- K
- Mg
- Fe.
Answer: 1. N
Question 91. Which of die following is not a major element?
- Zn
- Ca
- Mg
- P.
Answer: 1. Zn
Question 92. Nitrogen fixation by bacteria requires the enzyme :
- Decarboxylase
- Nitrogenase
- Nitrogen deaminase
- Nitrodioxidase.
Answer: 2. Nitrogenase
Question 93. Zinc is essential for:
- Biosynthesis of chlorophylls
- Biosynthesis of 3—IA A
- Stomatal closing
- Oxidation of carbohydrates.
Answer: 2. Biosynthesis of 3—IA A
Question 94. Plants that have naturalistic relations with nitrogen¬fixing bacteria receive from the bacteria :
- Ammonium
- Amino acids
- Nitrate
- Nitrite.
Answer: 1. Ammonium
Mineral Nutrition In Plants Mcqs Neet
Mineral Nutrition MCQ Question 95. An association between a fungus and a root of a higher plant is termed mycorrhiza which is an example of:
- Parasitism
- Helotism
- Symbiosis
- Myrmecophily.
Answer: 3. Symbiosis
Question 96. Which of the following groups of plants can grow in nitrogen-deficient soils?
- Lichens
- Gymnosperms
- Bryophytes
- Insectivorous plants.
Answer: 4. Insectivorous plants.
Question 97. The theory which suggests that C02 produced in respiration plays an important role in mineral absorption is:
- Contact exchange theory
- Carbonic acid exchange theory
- Active absorption dietary
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Carbonic acid exchange theory
Question 98. Nodulation of legumes is reduced in deficiency of:
- Sulphur and potassium
- Sulphur and boron
- Manganese and copper
- Zinc and iron.
Answer: 2. Sulphur and boron
Question 99. Presence of phosphorus:
- Brings about healthy root growth
- Promotes fruit ripening
- Retards protein formation
None.
Answer: 3. Retards protein formation
Biology MCQ Mineral Nutrition Question 100. A balancing element is :
- Ca
- Mg
- K
- All the above.
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 101. Match List I ( nutrient) with List II (deficiency symp¬tom in leaf) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:

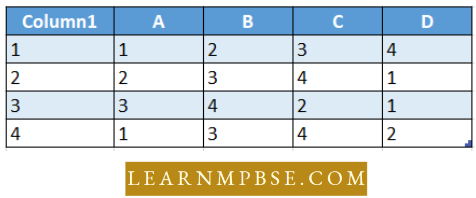
Answer: 2.
Question 102. The soluble resources of phosphorus and nitrogen in soil generally get depleted because they are usually found as:
- A disproportionate mixture of negatively and positively charged ions
- Negatively charged ions
- Only positively charged ions
- A balanced mixture of negatively and positively charged ions.
Answer: 2. Negatively charged ions
Question 103. At times of heavy rain, minerals in the upper layers of the soil are moved downward by a process known as:
- Smearing
- Leaching
- Weathering
- Gravitation.
Answer: 2. Leaching
