NEET Biology Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Animal Sources
Animal Husbandry. It is a branch of science that deals with the improvement of domesticated animals, with regard to race, reproduction, and feeding.
Livestock. The animals like cattle, sheep, goats, camels, horses, pigs, and poultry form the livestock.
Apiculture. Rearing and management of honey bees for obtaining honey and wax is called apiculture.
Poultry Fanning deals with the rearing of game birds such as domestic fowls, ducks, turkeys, and pheasants which yield eggs and meat, rich in protein and other nutrients.
Aquaculture is the production of aquatic plants along with animals like prawns, fishes, oysters, etc.
Piscicultural Practices (production of fishes) differ depending on whether the fishes belong to freshwater or marine water.
Marine Fishery practices include trapping and collecting by using trawlers, nets, baits, electronic locators, etc. The most important edible freshwater fish in India is the rohu. catla and Singhara: marine ones arc Bombay duck, hilsa, and pomphret.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production NEET Notes
Animal Husbandry
Animal husbandry is the agricultural practice of breeding and rearing livestock. Consequently, it is an essential skill for farmers, embodying both scientific and artistic elements.
- Animal husbandry pertains to the management and breeding of livestock such as buffaloes, cows, pigs, horses, cattle, sheep, camels, and goats that are beneficial to people.
It encompasses poultry farming and aquaculture. - Fisheries encompass the cultivation, capture, and sale of fish, mollusks, and crustaceans.
- Since ancient times, humans have utilized creatures such as bees, silkworms, prawns, crabs, fish, birds, pigs, cattle, sheep, and camels for products like milk, eggs, meat, wool, silk, and honey.
- It is believed that over 70 percent of the global livestock population resides in India and China.
- It is noteworthy that the contribution to global agricultural output is about 25 percent, indicating a low productivity per unit.
- Therefore, with traditional methods of animal breeding and care, it is essential to implement advanced technology to enhance quality and output.
NEET Biology Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Dairy Farm Management
Dairying is the management of animals for milk and its products for human consumption.
- In dairy farm management, we deal with processes and systems that increase yield, and improve the quality of milk,
- Milk yield is primarily dependent on the quality of breeds on the farm. Selection of good breeds having high yielding potential (under the climatic conditions of the area), combined with resistance to diseases is very important.
- For the yield potential to be realized the cattle have to be well looked after – they have to be housed well, should have adequate water, and be maintained disease-free.
- The feeding of cattle should be carried out in a scientific manner – with special emphasis on the quality and quantity of fodder.
- Besides, stringent cleanliness and hygiene (both of the cattle and the handlers; are of paramount importance while milking, storing, and transporting the milk and its products.
- Nowadays, of course, many of these processes have become mechanized, which reduces the chance of direct contact of the product with the handler.
- Ensuring this stringent measurement would, of course, require regular inspections, with proper record keeping. It could also help to identify and rectify the problems as early as possible. Regular visits by a veterinary doctor should be mandatory.
Animal Husbandry And Plant Breeding NEET
Improvement Of Livestock:
- Four Essential Methods For Livestock Improvement: breeding, weeding, feeding, and heeding.
- Both the male and female animals selected for breeding should be of superior quality.
- Weeding aims that uneconomic animals must be prevented from reproducing.
- Feeding is also very important for animals. Each animal should be fed on a balanced ration.
- Heeding implies good animal management and general supervision including housing care and maintenance of proper cleanliness and hygiene.
- Proper health care.
- Suitable environmental conditions for housing accommodation.
- Resistance to disease.
- Regular inspections by veterinary doctors. Three Principle Factors For Productive Potentialities Of Livestock;
- Genetic make up
- Nutrition and
- Environment including the climatic conditions.
Breeds Of Cattle – 26 Indian breeds. The cattle breeds are classified into three groups:
- Milch Breeds: The cows are good milk-producing bullocks and are of poor quality.
- Drought Breeds: Bullocks are good for working, and cows are poor milk producers.
- General Utility Breeds (Dual-Purpose Breeds): Crows are good milk producers, and bullocks are good draught animals.
Some Breeds Of Indian Cattle:
- Milch Breeds: Gir, Sahiwal, Red Sindhi, Deoni.
- Drought Breeds: Malvi, Nageri, Hallikar, Kangayam
- General Utility Breeds: Haryana, Ongole, Kankrej, Tharparkar
New Breeds
- Karan Swiss: Evolved at the.NDRI, Kamal
- Breeding between Sahiwal cows with the semen of Brown Swiss bulls imported from the U.S.A.
- Sunandini: Originated in NDRL Kerala.
- Cross between the local non-descript cattle with Jersy, Brown Swiss, and Holestein-Friesian breeds.
- Karan Fries: Evolved at the NDRI, Kamal.
- Cross between Tharparkar and Holstein Friesian.
Some Exotic Breeds Of Cattle Are Jersy, Holstein-Friesian, Ayrshire, and Brown Swiss
Feeding Cattle: The feed consists of two main components roughage and concentrates.
- Roughages: Contain high fiber content and include fodder, hay, straw, and silage.
- Concentrates: Include broken grams, cereals and millets, rice polish, cotton seeds, forage crops, oil cake, oil seeds, and animal by-products.
Green Revolution And Its Impact NEET
Indian Buffaloes; Bubalns Bubalis.
- Breeds Of Indian Buffaloes: 7 breeds of buffaloes in India.
- Good, well-defined milk breeds – Punjab, Rajasthan and Gujrat.
- Drought breeds – Central and – South India.
- Some Breeds Of Indian Buffaloes: are Murrah, Bhadawari, Jaffrabadi, Surti, Mehsana, Nagpuri, or Ellichpuri, Nili Ravi.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production NEET Important Questions
Difference Between Cow And Buffaloes
- Heat period is weaker in buffalo than cows (silent heat).
- Sexual maturity in buffalo bull is later than an ox.
- High calf mortality in buffaloes.
- More annual milk yield.
- Mineral content (Ca, P) is higher in buffaloes.
- Better adaptability, disease resistance, and life span than cows.
- Milk is free from carotenoids.
Uses Of Cows And Buffaloes: Milk, agricultural operations, manure and fuel, leather, meat, hair (for making brushes), bone meal, glue, and gelatin, horns, and hybridization.
Food Production And Biotechnology NEET
Cow And Buffaloes Memory Points
Cow:
- Domesticated animals are used for
- Agricultural operations
- Milk
- Transport
- Manure and Fuel
- Leather
- Glue and Gelatin
- Meat.
- The most important breeds of milk cows in the United States are Holstein, Friesian, Jersey, Guernsey, Ayrshire, Brown Swiss, etc.
- There Are 26 Breeds Of Cattle, Classified Into:
- A balanced diet for a cow is rich in carbohydrates, fats, proteins, minerals, vitamins, and water.
- Feeds are divided into roughages and concentrates.
- Roughages contain fibre including hay, fodder, and silage.
- The concentrate mixture is made up of grains and seed by-products.
- The most Common And Nutritious Feed For cats is grasses.
- The Two Breeds – The Karanswiss and Sunandini are developed through cross-breeding at the National Dairy Research Institute, Kamal (Haryana), and in Kerala respectively.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production NEET Mcqs With Answers
Buffaloes
- Number of breeds of buffalo in India.
- Indian buffaloes – Bubalis bubalis.
- The average yield of buffalo is 495 kgs. with 6.5 – 7.5 percent fat.
- The average yield of Zebu Cow is 186 kgs. with 4.5 – 5.0 percent fat.
- Sex Vigour in buffalo increases in the colder season.
- The uterine and ovarian cycle of buffalo is 21 days (subject to great variations)
- The duration of heat is 1 to 1 1/2 days.
- On average, the length of gestation is 307 days or 10 months for a buffalo.
- The length of gestation of a cow is 284 days or 9 months.
- Breeding season for buffaloes: September to February.
- Calving season – July to November.
- In buffaloes, the period of lactation is 281 days, the dry period is 139 days, calving interval is 420 days.
- Gastroenteritis is the second highest cause of buffalo calf mortality.
- India possesses the largest number of buffaloes.
- Some important disease-resistant varieties are Zebu Cattle or Bos indicus. They are resistant to Rinderpest, Foot and mouth disease, Anthrax, Black quarter, and Haemorrhagic septicemia.
NEET Biology Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Animal Breeding
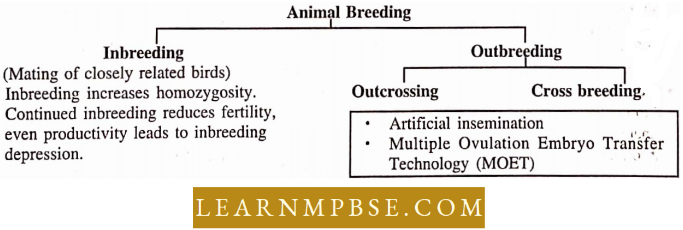
Animal Breeding Aims At:
- Increasing the quantity of yield.
- Improving the quality of the produce.
Breeding is of two types Natural breeding and artificial breeding
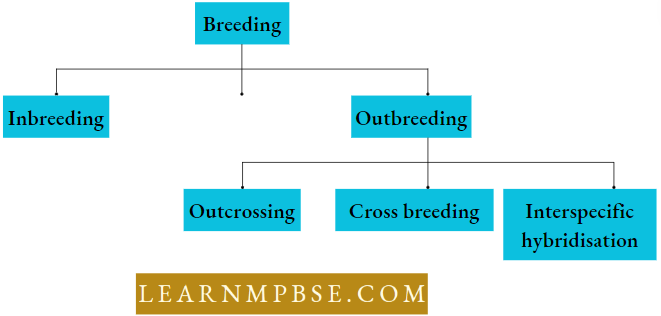
Inbreeding
- The breeding strategy includes the identification of superior males and females of the same breed and mating them in pairs.
- The progeny of such matings are evaluated and superior males and females are identified for further mating.
- Inbreeding increases homozygosity and thus inbreeding is necessary for evolving a pure line in any animal.
- Inbreeding exposes the harmful recessive alleles, which become eliminated by selection.
- Inbreeding also helps in the accumulation of superior genes and the elimination of less desirable genes.
- However continued inbreeding causes inbreeding depression, which reduces fertility and even productivity.
- Under such a situation the selected animals of the breeding population are mated with unrelated superior animals of the same breed to restore fertility and yield.
Outbreeding: Outbreeding refers to the breeding of unrelated animals either of the same breed or of different breeds or even different species.
Outbreeding is of the following types
- Outcrossing
- Outcrossing is the practice of mating animals of the same breed, but that have no common ancestors on either side of their pedigree up to 4-6 generations.
- A single outcross helps to overcome inbreeding depression.
- It is the best breeding method for animals that are below average in productivity and growth rate.
- Growth rate.
- Cross-breeding
- It is a method of outbreeding in which superior males of one breed are mated with the superior females of another breed of the same species.
- This helps in combining the desirable qualities of the two different breeds into the progeny.
- The hybrid progeny may be directly used for commercial production or they may be subjected to some form of inbreeding and selection, to develop new stable breeds.
- One example of cross-breeding is discardable, a new breed of sheep developed by crossing Bikaneri ewes Marino rams.
- Interspecific Hybridisation: It is a method of outbreeding in which male and female animals of two different species are crossed to combine the desirable features of both parents into one. for example, the male is produced by a cross between a male donkey and a female horse.
Artificial Insenunalion: It is the process in which the semen collected from a superior male is inserted into the reproductive tract of the selected female by the breeder.
- The advantages of this practice are:
- Semen can. be used immediately or stored/frozen and used at a later date when the female is in the right reproductive phase.
- Semen can be transported in the frozen form to a distant place where the selected female animals are present.
- Semen from one selected male animal can be used on a number of female animals.
- The disadvantage is that the success rate is fairly low.
Apiculture And Sericulture NEET Notes
Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer (MOET): It is a method to improve the herds.
- The steps in the method are as follows:
- A cow is administered hormones (like FSH) to induce follicular maturation and superovulation, i.e., the production of 6-8 ova in one cycle.
- The cow is mated with the selected bull or artificially inseminated.
- The fertilized eggs at 8-32-celled stages are recovered and transferred to surrogate mothers.
- This technology has been used for cattle, rabbits, mares, etc.
- High milk-yielding breeds of females and high-quality meat-yielding bulls have been bred successfully to increase the herd size in a short time.
Sheep
- Breeds of Indian Sheep which do not give any wool – Deccani and Nellore.
- Exotic breeds of sheep are – Dorset, Horn, Suffolk coereidale, or Merino.
- Sheep are most suitable as a class of livestock for utilizing waste lands or weeds from the fields.
Shearing
- Shearing means cutting wool in sheep with shears.
- Shearing is done after the winter or after the rainy season.
- Shearing is done mechanically either with clippers, a pair of scissors, or by a power-operated machine.
Camel-Camelus: There Are Two Types Of Camels
- One humped – Arabian – Camelus dromidarius
- Two humped – Bactrian – Camelus bactrianus
Camel found in India – Arabian Adaptations so as to be called the ship of the desert:
- A thick skin to prevent water loss.
- Thick foot pads to move on loose, hot sands.
- Long eyelashes to protect the eye from sand.
- Hard lips to prevent injury from thorny bushes they browse.
- Hump – the storehouse of fat.
Indicator of good nutrition in camels – the size of the hump.
- Camels breed in winter (November to March).
- Camels suffer from diseases like – anthrax, pneumonia, camel pox, and surra, e Camels, Llamas, and alpacas are included in one family – camelidae.
- The wt. of camel at maturity is 500-700 kgs. The gestation period of the camels – is 300 days
- Lactation period – 18 months.
- Females produce a calf twice in three years.
- The camels are monooestrous under desert conditions.
- Females mate at the age of 4 years.
Apiculture And Sericulture NEET Notes
Elephants – Elephas maximum. (Loxodonta Africans)
- Elephants are found in forests with tall trees where bamboos grow in profusion.
- Mean intake varies from 4.2 to 5.6% of the animal’s body weight.
- The daily water consumption of an elephant is 140 – 230 liters.
- Puberty occurs at the age of 8 -12 years.
- The gestation period is 21-22 months.
- The calving interval is 4 years
Pig – Sits Scrofa
- Pig droppings are a good source of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
- The dominant coat color in pigs is white.
- To feed a pig, maize can be replaced by millet to an extent of 50 percent, similarly, maize can also be replaced by wheat bran and tapioca meal to an extent of 50 percent.
- The marketable body wt. of pigs is 90-95 kgs.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production NEET Revision Notes
Domestic horse – Equus caballm
- No. of important Indian breeds is 6.
- Mineral specially added to the diet ofliorscs is a common salt. Donkeys – Eqitus asinu
- Two kinds of donkeys found in India are small grey and large white.
- A large white donkey is found in the Rann of Kutch.
NEET Biology Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Poultry
It deals with the rearing of fowls, ducks, turkeys, and pheasants for their eggs and meat,
- The average production of an Indian breed is about 60 eggs per annum.
- High-yielding varieties can yield up to 240 eggs per annum.
- The best table bird with plenty of flavored flesh-Aseel.
- Exotic breeds – White leghorn, Rhode Island red, Plymouth rock. New Hampshire, Orpington, Anstrnlorp, Sussex. Minorca.
Poultry: Poultry farming deals with the rearing of fowls (chicken), ducks, turkeys, and pheasants for their eggs and meat. India and the neighboring countries are recognized as the original home of the red jungle fowl (Callus gallus).
- There is evidence that Aseel or Malay fowl were carried to Europe through the Middle East about 2,000 years ago and have given rise to the present-day European breeds.
- Poultry and poultry products are a rich source of animal protein and other nutrients such as fats vitamins and minerals, Consumption of eggs would pave the way for overcoming the protein malnutrition prevalent, especially among children in India.
- Poultry farming has definite advantages over livestock-rearing. Poultry birds are easy to raise, can be acclimatized to a wide range of climatic conditions, have short life spans, and are prolific breeders.
- Hens have an average yield of 60 eggs per year (up to 240 eggs in high-yielding varieties). Poultry farming requires less space is easier to manage and maintain and brings fast returns within a span of six months.
- In a poultry farm, comfortable, well-ventilated, and illuminated, dry houses are built. Birds of different ages the kept in separate houses. In regions with moderate climates, they are kept in cages (coops). The floor is littered with chopped straw, paddy husk, dry leaves, or groundnut hulls.
- It is made rat-proof and provided with water channels with proper drainage. Minerals that are important for poultry diets are calcium, phosphorous, sodium, copper, lo-zinc, iron manganese, and zinc. Vitamins required are vitamin A, D3,E, and pyridoxine. riboflavin, pantothenic acid, niacin, folic acid B12, and choline.
- The male breeder’s diet should contain extra calcium, manganese, and vitamin H to ensure proper fertility. Thus a balanced diet is required so that the utilization for building of tissues and egg production is maximised. Clean and fresh water is very much essential for birds.
Light Management:
Illumination is crucial for optimal egg yield. Optimal manufacturing necessitates 14 to 16 hours of light, including natural sunshine.
- When the pullets (young hens, particularly at the onset of egg production) commence laying, provide supplemental lighting if daylight is less than 12 hours.
- Incrementally augment the light duration by 20 minutes each week until a total of 10 hours is achieved.
- A single 40-watt tube light adequately illuminates a 30 sq.m area, whereas a 40-watt bulb is suitable for an 18 sq.m floor area. The illumination must distribute evenly. The illumination should not be sustained during the entire night.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production NEET Study Material
Methods For Improvement Of Poultry Farming
- Selection of disease-free suitable breeds.
- The most common egg type variety is single comb while leghorn.
- Meat type variety – Plymouth Rock, Cornish, New Hampshire.
Breeds Of Fowls
- Indigenous Breeds: Aseel, Karaknath, Basara, Briihma, and Cochin.
- Exotic Breeds: White Leghorn, Rhode Island Red, Plymouth Rock, New Hampshire.
Advantage Of Poultry
- Food: Eggs and meat are rich in proteins, minerals fats, and vitamins.
- Economic uplift and employment.
- Birds fecal matter as manure.
- Feathers
- Recreation.
- For food widely distributed as domestic animals, the most common species of jungle fowls are Gulins, gallus, G. Lafayette, and G.sonneratti.
- Poultry feed includes all the nutrients and is made of cereals and millets, oil cake, protein concentrates, fish and meat meal, minerals, and green vegetables.
The domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus) population of our country can be roughly classified into two types:
- Indigenous (desi type),
- Exotic (improved type)
Some of the indigenous breeds like Aseel, Karaknath, Ghagus, Brahma, and Busra are the best table birds, The Aseel fowls are used in cock-flighting. The exotic breeds are classified, according to their source of origin, into American class, English class, Mediterranean class, and Asiatic class.
- Some examples are White Leghorn, Rhode Island Red, Plymouth Rock, and New Hampshire. They are now completely acclimatized to Indian conditions. Some of them are excellent egg-layers, whereas others give good meat.
- The indigenous breeds are crossed with exotic breeds to improve egg production. Heterosis has been utilized for producing better egg layers and broilers (birds grown for meat) with high nutritive value.
- Some of the diseases like fowl pox ranikhet, coryza, fowl cholera, and aspergillosis take a heavy toll on poultry. But with better management, proper housing and nutrition, and timely vaccination of the chicks, these diseases can be controlled.
- Ducks comprise 6 percent of the total poultry population in India. They are abundant in the southern and eastern parts of India. There are 20 breeds of duck of which Muscorl, Pekin, Aylesbury, and Campbell are popular exotic breeds. Indigenous breeds include Indian Runner.
- Syhelt meta, etc. Brown and white geese are common in India. Turkeys which are in demand during Christmas time, belong to the breeds Narfold, British White, Broad Breasted Bronze, and Beltsville Small White.
Poultry Diseases
- Encephalomalacla: The deficiency of vitamin E causes the softening of brain tissue in young poultry.
- Coccidiosis: The protozoan Eimeria causes coccidiosis in fowls. It causes bloody diarrhea.
Bacterial Diseases
- Pasteurella – Fowl cholera
- Salmonella pullorum – Pullorum
- Mycoplasma gallisepticum – Mycoplasmosis
- Spirochaete – Spirochaetosis
Aquare: It involves the production of useful aquatic plants and animals such as fishes, prawns, shrimps, lobsters, crabs, and mollusks (edible and pearl oysters) by proper utilization of small and large bodies of water.
- Fisheries: Industry devoted to catching, processing, or selling fish.
- Fisheries have an important place in the Indian economy. It provides income and employment to millions of fishermen and farmers, particularly in the coastal states. For many, it is the only source of their livelihood.
- In order to meet the increasing demands on fisheries, different techniques have been employed to increase production. For example, through aquaculture and pisciculture, we have been able to increase the production of aquatic plants and animals, both fresh-water and marine.
- This has led to the development and flourishing of the fishery industry, and it has brought a lot of income to the farmers in particular and the country in general.
- Aquaculture: Production of useful aquatic plants and animals such as fishes, prawns, shrimps lobster, crabs mollusks, etc.
- Pisciculture: Production of fishes. Fishes are reared in small rivers, ponds, lakes, and canals.
Fish Farming/Fisheries: There are 2 types of fisheries-Inland and Marine fisheries.
Inland Fisheries: Freshwater: Cultivation in rivers, canals, reservoirs lakes, ponds, and tanks.
Brackish Water: Estuaries, Lagoons, reservoirs.
Types Of Ponds: 3 types of ponds are required for Indian major carp.
Genetically Modified Crops NEET
Nursery Ponds
- Receive tender hatching and spawn.
- Small and seasonal nurseries are preferred.
- Production of zooplankton to serve as food for the spawn.
Rearing Ponds: Fries (young fish) are collected from nursery ponds and released into rearing ponds to develop in fingerlings
Stocking Ponds: Fingerlings are transferred from rearing to stocking ponds, where they develop into adult fish and are kept for stocking.
Types Of Breeding
- Natural Breeding/Bundh Breeding: Breading is done in natural bundhs, a special type of ponds formed by the accumulation of large quantities of rainwater in a low-lying area, and natural conditions are provided with exits also.
- Artificial Breeding: Sperm from males and ova from females are collected and fertilization is done in in-vitro conditions.
- Hormone gonadotrophins are also used. FSH and LH secreted by the pituitary, influence the maturation of gonads and spawning in fish.
Composite Farming: Selected species of fish are stocked together in proper proportion to increase fish production many times.
Compatible species do not harm each other, example, Catla catla (surface feeder), Labeo-rohita (Column feeder), and Cirrhinus mrigtila (bottom feeder) are used for composite farming. Some edible freshwater fishes.
- Rohu – Labeo-rohita
- Calbasu – L. Calbasu
- Catla – Catla catla
- Mirgal – Cirrhinus mrigala
- Magur – Clarius
- Common carp
Marine Fisheries: Fishery aspect of seawater of the ocean. A recent survey revealed abundant resources of sardines and mackerel on the southwest coast. Fishing trawlers fitted with sophisticated electronic fish-locating equipment have also been introduced to give a fillip to deep-sea fishing.
Integrated Fisheries project located at Cochin engaged in the exploration and utilization of marine resources in S.W. India.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production NEET Study Material
Edible Marine Fishes
- Eel – Anguilla
- Hilsha – Hilsa
- Pomphret – Stromateus
- Salmon – Aluitheronema
- Bombay duct – Harpodon
- Sardine – Sardinella
- Mackeral
Marine Fishes Use/Importance
- Fish as food
- Fish for controlling disease: Larvivorous (gambusia).
- Scientific value: Lung fishes of importance.
- Aesthetic value: Aquarium fishes, Macropodus, Carassius (goldfish), pterophyllum (angel fish), and Betta (fighting fish).
- Fish product: Fish oil
- Fish glue: Sticky product obtained from the skin of cod.
- Isinglass: Gelatinous substance from the air bladder of perches, Indian salmon used in the preparation of special cement and in clarification of wine and beer.
- Shagreen: Skin of sharks and rays used in polishing wood and other materials as well as for covering jewelry boxes and swords.
- Leather and artificial pearls (from silver bony scales of cyprinids
- Employment.
Pisciculture production of fishes.
- Seed fish are produced by aquaculture techniques of induced breeding by administration of pituitary hormones.
- Fish is a valuable food source of proteins.
- India is among the six foremost seafood-producing nations in the world.
- Fresh water includes the country’s great river systems, an extensive network of irrigation canals, reservoirs, lakes, tanks, ponds, etc.
- Brackish water includes estuaries, lagoons, and mangrove swamps.
- An Integrated fishery project located at Cochin is engaged in the exploration and utilization of marine resources and is the biggest of its kind in Southeast Asia.
- Inland fisheries provide 40% of total fish production.
NEET Biology Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Apiculture or Beekeeping
Beekeeping or apiculture is the maintenance of hives of honeybees for the production of honey. It has been an age-old cottage industry.
Common Species Of Honey Bee: Apis mellifera, Apis indica, Apis dorsata, Apis florea. Social Organisation: Good and well-developed honeycomb. 40-50 thousand individuals.
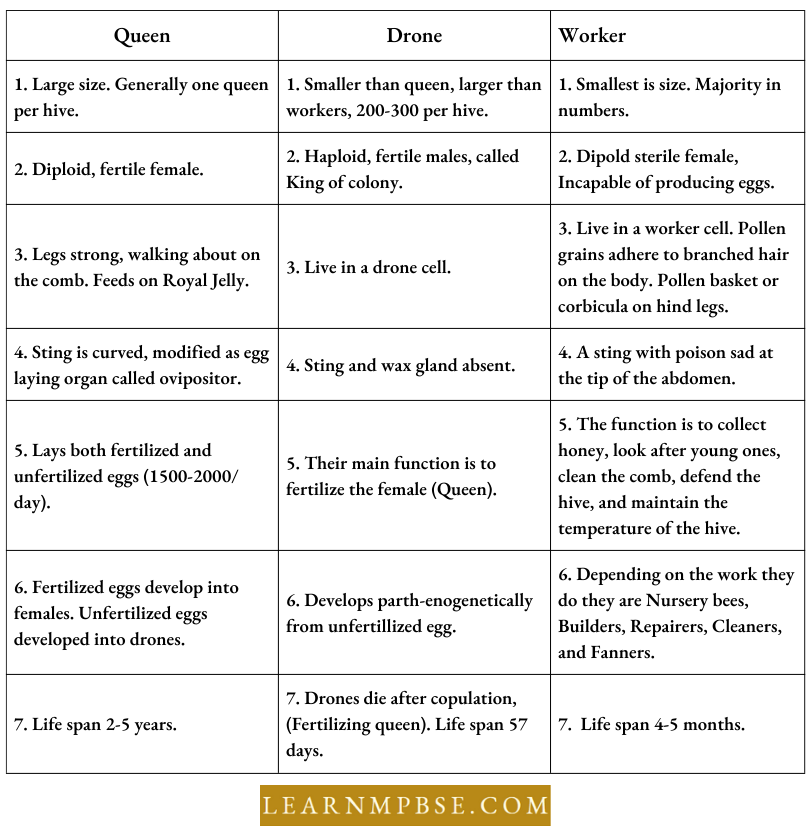
Social Organization (Castes) Of Honey Bee: The nest of the honey bee is known as the bee hive. The hive consists of 32 to 60 thousand individuals, showing a highly organized division of labor in the colony. Bees are polymorphic, consisting of three types of individuals (Castes) viz, QUEEN, DRONE, and WORKER. The characters are given in the following table.
Honey is a food of high nutritive value and also finds use in the indigenous system of medicine.
- It is composed of levulose, dextrose, maltose and other sugars, enzymes and pigments, ash, water, vitamins and minerals.
- Honey produced by the honey bee Apis species is probably the oldest sweetening agent in our civilization. Honey contains two sugars – dextrose and levulose – and a mixture of several other substances. It is tasty, health-giving, and also medicinally useful.
Honeybees also yield wax, which has multiple uses. A large quantity of honey is still collected from wild sources. However, bee-keeping (apiculture) using domesticated bees has been practiced in many parts of the world, including India (using A. dorsata, A. florea, and A. indica).
- From its mandibular gland, the developing queen secretes a queen substance. It inhibits the worker bees from building brood chambers for future queens. Honeybee also produces beeswax, which finds many uses in industry, such as in the preparation of cosmetics and polishes of various kinds.
- The increased demand for honey has led to large-scale beekeeping practices; it has become an established income-generating industry, whether practiced on a small or on a large scale.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production NEET Question Bank
Bee Diseases
- Pebrine – N.apis,
- Paralysis dysentery
- Acarine disease – Acarapis wood
Bee-keeping: It can be practiced in any area where there are sufficient bee pastures of some wild shrubs, fruit orchards, and cultivated crops. There are several species of honeybees that can be reared. Of these, the most common species is Apis indica. Beehives can be kept in one’s courtyard, on the verandah of the house of even on the roof. Beekeeping is not labor-intensive.
For Successful Bee-keeping
- Knowledge of nature and habits of honey bees.
- Selection of suitable locations for keeping bee hives.
- Catching and hiving of swarms.
- Management beehives during summers
- Handling and collection of honey and bee wax.
Bee Communication: Karl van Frisch (1946-69: Awarded Nobel prize for decoding the language of honey bees. Bee performs two types of dance
Round Dance: Food source is within 75 m.
Genetically Modified Crops NEET
Tail Wagging Dance/Waggle Dance: Food is more than 75 m away.
Bees are the pollinators of many of our crop species (see concerned chapter) such as sunflower, Brassica, apple, and pear. Keeping beehives in crop fields during the flowering period.
Apiculture: Science of rearing bees for economic value,
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production NEET Question Bank
- Types Of Honey Bees;
- Apis indica (Indian bee)
- Apis mellifera (Italian bee)
- Apis dorsata (Rock bee)
- Apis florea (Little bee)
- Most Important And Useful Bee – Apis Mellifera
- Worker bees are immature, sterile females.
- The compartments of honeycomb are called cells and are divided by thin plates of wax.
- The foundation to build honeycombs is provided by a comb foundation – a wax sheet.
- Honeybees are reared in apiaries
- Apis dorsata is the main source of bee wax.
- Sugars in honey are glucose, fructose, and levulose.
Silkworms Sericulture: The science of rearing silkworms for producing silk.
Main cottage industry of silk – China, Japan, India, and some European countries.
Silkworms Life Cycle: Egg Larva → Pupa → Adult
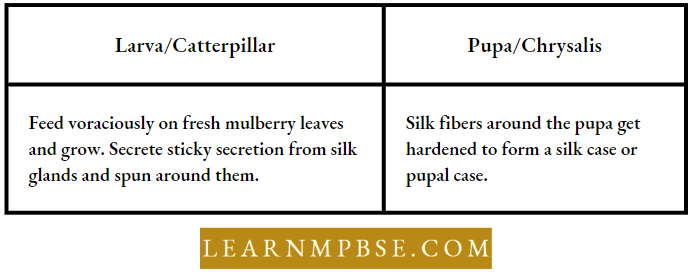
Silk Extraction
- After one or two days of cocoon formation pupa are either killed by boiling or drying in the Sun.
- The raw silk fibers from the cocoon are then reeled into silk thread.
- Pupa are killed before they emerge into adulthood as the long silk fibers are broken and can thin and only be spun like cotton can not reel.
- Few cocoons or seeds are kept to develop into adults to continue generation.
Silk Extraction Important Points
- Composition of silk.
- Protein fibroin (75 – 80%) and Sericin (20 – 25%)
- The intestine of silkworm – Gut, used in fishing and some surgical work.
- Bombyrmori: China silk worm – Mulberry silk – Best silk.
- The disease of the silkworm is Pebrine caused by Nosema bombycis.
- Silkworm Bombyx mori is reared on mulberry leaves.
- Caterpillars are very active feeders.
- The hard covering of silk fibers around the worm is called a cocoon, A silkworm with a cocoon is known as a pupa.
- Pupae are killed to get silk thread because the emergence of an adult breaks the thread.
NEET Biology Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Lac Culture
The zoological name of the lac insect is Laccifer lacca or Tachardia lacca.
- Lac insect belongs to the order Homoptera.
- Lac is a resinous substance secreted from the hypodermal glands of the body of the larval stage and females.
- Lac insects usually build lac houses for the protection of host plants like Butea monosperma (palas), Shorea robusta, (sal), Acacia nilotica (Babul), Mangifera indica (mango), etc.
- Male and female insects live separately in lac capsules
- After copulation male dies, female lays about 200-300 eggs.
- The larvae (nymphs) are red-colored and suck the plant sap by boring the tender twigs.
- The secretion of the lac glands covers the body of the insect, it joins the cover of the insect with a twig of tree.
Dairy And Poultry Management NEET
Lac Culture Uses
- Lac in the form of shellac is used as sealing material.
- Lac is also used in the printing industry, preparation of gramophone records, electrical appliances, varnish, polish paints, toys, bangles, buttons cosmetics, etc.
Hybrid Breeds Of Livestock. Karanswiss was developed at NDRI Kamal while Sunandini was developed at NDRI Kerala.
Broiler. Chicken reared for meat.
Fish Gauno. Dried refuse after extraction of oil.
Honey is aromatic, viscid, and sweet-material. The color and flavor of honey depend upon the source of nectar.
The Honey consists of:
- Fish Liver Oil. It is extracted from the liver of fish. It is the main source of Vitamin-A though the liver oil of some fishes also contains vitamins C, D, and E. For example, the liver oil of certain fishes like Tuna, Halibut, etc. is rich in vitamin D.
- Vitamin- E (a-tocopherol) acts as an anti-oxidant of vitamin A. Cod liver oil contains about 60-75% of oil contents but a low percentage of vitamin A, while Tuna and Halibut liver oil contain a lower (4 to 28%) percentage of oil Fut higher percentage of vitamin -A.
- Fish Protein. It is in the form of white powder extracted from fish wastes by removing the fat and contains 80 to 90% soluble proteins. It is used in the preparation of ice cream, pharmaceuticals, paints, varnishes, textiles, paper, and cosmetics.
- Fish Protein Concentrate (FPC) has been defined as a stable product prepared from whole fish or parts thereof, by the removal of water and, in certain cases, oil, bones, and other materials.
- Milk Yield/Cow/Yr. 4250 kg in the U.S.A. and 220 kg in India. Tassar Silk. Besides Anthenea roylei, other species are A- paphia, A. perenyi, and A. mylitta.
- Arnadi Silk is obtained from the cocoon of the Eri silkworm—Altacus ricin
- Muga Silk is obtained from cocoons of muga silkworm Anthenea assama.
- Pashmina. Under the fur of Kashmiri goat
- Angoora Wool. From Angoora rabbit.
- An insecticide used to control external parasites, like lice on cattle is lindane.
- Yak – Lahaul Spiti, Leh, Ladhakh, Garhvval, Sikkim
NEET Biology Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production Synopsis
Animal Husbandry. Agricultural practice of breeding and raising livestock like buffaloes, cows, pigs, horses, cattle, sheep, camels, goats etc. It also includes poultry farming and fisheries.
Strategies For Enhancement In Food Production NEET Question Bank
Dairy Farm Management: Management of animals for milk and its products
- Selection of high-yielding breeds.
- Resistance to diseases
- Cleanliness and hygienic shelter
- Regular inspection
- Proper record
- Quality and quantity of fodder
- Water
- Milking, storage of milk and products.
Poultry Farm Management
- Management of domesticated fowls (birds) used for food and eggs.
- All facts about dairy farm management + Eradication dispersing of vims affected birds.
Apiculture (Beekeeping Maintenance of hives of honey bees for obtaining honey and wax.
- Successful bee-keeping
- Knowledge of nature and habits of bees
- Selection of suitable location for keeping beehives.
- Catching and hiving of swarms.
- Management of beehives during different seasons.
- Handling and collection of honey and of bees wax.
Fisheries. Catching, processing, selling of fish, and shellfish or other aquatic animals;
- Freshwater fishes
- Catla, Rohu and Carps
- Marine fishes
- Hilsa, Sardine, Mackerel Pomffet
