NEET Biology Cell Unit Of Lift And Structural Organization MCQs
Question 1. The part/parts of a cell that can be seen with an electron microscope, but never with a light microscope is/are the:
- Nucleus
- Golgi bodies
- Chloroplasts
- The membrane separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm.
Answer: 4. Membrane separating the nucleus from the cytoplasm.
Question 2. Fundamentally a dead cell differs from a living cell because:
- It has become separated from other cells
- Its vital forces have been destroyed
- A change in its surrounding environment has occurred
- A change in its specific organization has occurred.
Answer: 2. A change in its surrounding environment has occurred
Question 3. Plant cell differs from animal cells by :
- Cell wall absent in animal cell but chloroplast present
- Cell wall and chloroplast absent in animal cell
- Vacuoles only a few and that too contractile are present in plant cell
- Cell walls are present in an animal cells.
Answer: 2. Cell wall and chloroplast absent in animal cell
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question and Answers
Question 4. The organic molecules present in traces in living cells can be detected and isolated by:
- Centrifugation
- Tracer technique
- Chromatography
- Microscopy.
Answer: 3. Chromatography
Cell The Unit Of Life Mcq For Neet
Question 5. The cell theory was proposed by :
- Robert Hooke
- Leuwenhoek
- Schleiden and schwann
- Purkinje.
Answer: 3. Schleiden and schwann

Question 6. 1 A is equal to:
- 10 8 Cm
- 10Acm
- 10-6 Cm
- 10 3 Cm.
Answer: 1. 10 8 Cm
Question 7. Which of the following sets resemble in their basic structure and function:
- Centrioles, cilia and flagella
- DNA, MRNA And TRNA
- Er, Golgi complex and lysosome
- Leucoplast, chloroplast and chromoplasts.
Answer: 1. Centrioles, cilia and flagella
Question 8. How many membranes comprise the nuclear envelope?
- One
- Two
- Three
- None.
Answer: 2. Two
Question 9. Which of the following organelles regularly moves from the nucleus to the cytoplasm?
- Glycogen
- Cholesterol
- RNA
- DNA.
Answer: 3. RNA
Cell The Unit of Life Botany NEET MCQ Question 10. Which of the following cellular organelles breaks down complex macromolecules such as polysaccharides and proteins?
- Golgi complex
- Lysosome
- Mitochondria
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Answer: 2. Lysosome
Question 11. The fuel gen reaction of dna is due to :
- Aldehyde produced by acid hydrolysis
- Removal of RNA but not dna
- Phosphoric acid, carbohydrates and nitrogen bases
- Phosphoric acid.
Answer: 1. Aldehyde produced by acid hydrolysis
Question 12. Which one of the following does not lose living nature even after crystallization?
- Protista
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Parazoa.
Answer: 3. Viruses
Question 13. In prokaryotic cells, the enzymes involved in the oxidation of metabolites is associated with :
- Nucleoid
- Plasma membrane
- Ribosomes
- Plasmosome.
Answer: 2. Plasma membrane
Cell The Unit Of Life Mcq For Neet
Question 14. Which of the following is an exception to cell theory?
- Bacteria
- Protozoans
- Protista
- Viruses.
Answer: 2. Protozoans
Question 15. Which of the following relationships between cell structure and their respective function is not correct?
- Cell wall – support, protection
- Cilia – site for diffusion
- Chromosome – carrier of heredity material
- Mitochondria – a powerhouse of cell1.
Answer: 4. Mitochondria – powerhouse of cel1.
Question 16. A human egg is very large compared to a human sperm. Most of this size differential is due to the difference in their:
- Nucleus
- Membranes
- Cytoplasm
- Both 1 and 3.
Answer: 3. Cytoplasm
Question 17. The cortex of the human brain may consist of :
- Six billion, two hundred million cells
- Seven billion, two hundred million cells
- Eight billion, two hundred million cells
- Nine billion, two hundred million cells.
Answer: 2. Seven billion, two hundred million cells
Question 18. The human body weighs about 50 kg. May consist of:
- 25 X 1015 cells
- 50 X 101s cells
- 100 X 101s cells
- 150 X 101s cells.
Answer: 4. 150 X 101s cells.
Question 19. Nucleoli are rich in :
- Ribose nucleic acid
- Deoxyribose nucleic acid
- Proteins and RNA
- Carbohydrates.
Answer: 3. Proteins and RNA
Question 20. Which of the following phenomena is not found in viruses in the host cell?
- Replication
- Production of energy
- Mutation
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Production of energy
Neet Mcqs On Cell Structure And Function
Question 21. The correct order of sedimentation of subcellular structures during differential centrifugation is as follows:
- Lysosome -+ mitochondria -+ nucleus -l ribosome
- Mitochondria-+ nucleus -+ lysosome -+ ribosome
- Nucleus -+ mitochondria->lysosome + ribosome
- Lysosome -+ ribosome-+ mitochondria –> nucleus.
Answer: 3. Nucleus -+ mitochondria->lysosome + ribosome
Question 22. Which of the following represents the correct sequence of relative sizes in descending order?
- Cell, nucleus, chromosome, water molecule, oxygen atom
- Cell, nucleus, water molecule, oxygen atom, chromosome
- Chromosome, cell, nucleus, water molecule, an oxygen atom
- Cell, nucleus, water molecule, chromosome, oxygen atom.
Answer: 1. Cell, nucleus, chromosome, water molecule, oxygen atom.
Question 23. The activities of all living cells are controlled by :
- Chloroplasts
- Auxins
- Nucleus
- Tonoplast.
Answer: 3. Nucleus
Question 24. Leaf pigments are separated from a mixture by :
- Spectrophotometry
- Autoradiography
- Chromatography
- Microcinematography.
Answer: 3. Chromatography
Question 25. Which of the following sets of cell organelles contains dna?
- Mitochondria, ribosomes and chloroplasts
- Nucleus, ribosomes and chloroplasts
- Nucleus, ribosomes and mitochondria
- Nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Answer: 4. Nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Question 26. Leaving aside water, which of the following constitutes the bulk of an active living cell?
- Ribose nucleic acid
- Deoxyribose nucleic acid
- Proteins
- Carbohydrates.
Answer: 3. Proteins
Question 27. Which one of the following is incorrect?
- All cells do not contain a true nucleus
- All living plant cells contain chlorophyll
- Cell rivals are generally made up of cellulose
- Respiration occurs in mitochondria.
Answer: 2. All living plant cells contain chlorophyll
Question 28. The endoplasmic reticulum often contains :
- Ribosomes
- Golgi bodies
- Centrioles
- Lysosomes.
Answer: 1. Ribosomes
Neet Mcqs On Cell Structure And Function
Question 29. The fine network of membranes distributed extensively throughout the cytoplasm in a cell is referred to as:
- Golgi bodies
- Peroxisome
- Lysosome
- Endoplasmic reticulum.
Answer: 4. Endoplasmic reticulum.
Question 30. The endoplasmic reticulum occurs in the form of:
- Cisternae only
- Vesicles only
- Tubules only
- All the above.
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 31. The endoplasmic reticulum in the cells of adipose tissue is in the form of:
- Vacuoles
- Sacs
- Tubules
- All the above.
Answer: 1. Vacuoles
Question 32. When the region of the endoplasmic reticulum is studded with ribosomes on the outer surface of the cisternae. It is called:
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- Granular endoplasmic reticulum
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Granular endoplasmic reticulum
Question 33. The principal site of the synthesis of ribosomal RNA is the :
- Mitochondria
- Golgi bodies
- Nucleolus
- Lysosomes.
Answer: 3. Nucleolus
Question 34. During active protein synthesis, some ribosomes seem to occur in groups and are collectively known as :
- Bound ribosomes
- Polyribosomes
- Lysosomes
- Dictyosomes.
Answer: 2. Polyribosomes
Question 35. Ribosomes are present in the cytoplasm as minute particles:
- Associated with er and are sites for protein synthesis
- Associated with mitochondria are the sites of glucose oxidation
- On the cell surface and are concerned with protein synthesis
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Associated with er and are sites for protein synthesis
Neet Mcqs On Cell Structure And Function
Question 36. Which of the following are prokaryotes?
- Viruses and rickets
- Bacteria and archaebacteria
- Cyanobacteria and mycoplasma
- Both 2 and 3.
Answer: 4. Both 2 and 3.
Question 37. Ribosomes originate from:
- Nucleus
- Er
- Nucleolus
- Mitochondria.
Answer: 3. Nucleolus
Question 38. Ribosomes present in a prokaryotic cell are :
- 70 S type
- 60 S type
- 80 s type
- Both 70s and 80s type.
Answer: 1. 70 S type
Question 39. Sphaerosomes have an affinity for :
- Sudan black
- Eosin stains
- I Leishman’s stain
- Giemso’s stain.
Answer: 1. Sudan black
Question 40. Ribosomes are :
- Positively charged
- Negatively charged
- Amphoteric
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Negatively charged
Question 41. Golgi apparatus is present in :
- Phanerogams
- Cryptogams
- All eukaryotes
- Vertebrates.
Answer: 3. Vertebrates.
Cell The Unit Of Life Neet Previous Year Questions
Question 42. Dictyosome is also known as :
- Respiratory particle
- Ribosome
- Golgi bodies
- Peroxisome.
Answer: 3. Peroxisome.
Question 43. Golgi bodies are related to:
- Excretion
- Energy liberation
- Pinocytosis
- Secretions.
Answer: 3. Pinocytosis
Question 44. Golgi bodies are maximum in :
- Calyptrogen
- Root cap
- Both 1 and 2.
- Root tip.
Answer: 4. Root tip.
Question 45. Which of the following cell organelles are considered to be rich in catabolic enzymes?
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Lysosomes
- Golgi bodies
- Mitochondria.
Answer: 2. Lysosomes
Question 46. Which of the following is widely distributed in a cell?
- Chromoplasts
- Chloroplast
- RNA
- DNA.
Answer: 3. RNA
Question 47. Membranes are found within :
- Chromosomes, nuclei and mitochondria
- Cytoplasm, chloroplasts and mitochondria
- Cytoplasm, nuclei and starch grains
- Chromosomes, chloroplasts and starch grains.
Answer: 2. Cytoplasm, chloroplasts and mitochondria
Cell The Unit Of Life Neet Previous Year Questions
Question 48. Most of the hydrolytic enzymes of lysosomes function at :
- Acidic ph (ph =5)
- Basic ph
- Neutral ph
- Any ph.
Answer: 1. Acidic ph (ph =5)
Question 49. The secretory material is discharged by the Golgi vesicles, from the surface of the cell membrane by:
- Pinocytosis
- Endocytosis
- Reverse pinocytosis
- Dissolving the cell membrane.
Answer: 3. Reverse pinocytosis
Question 50. Mitochondrial DNA differs from nuclear DNA in:
- Being linear
- Having a=tandc: g
- Being highly twisted
- Lacking binding with the histones.
Answer: 4. Lacking binding with the histones.
Question 51. In the nucleon ema of the nucleus, particles 150- 2004 are seen which resemble:
- Ribosomes
- Lysosomes
- Mitochondria
- Sphaerosomes.
Answer: 1. Ribosomes
Question 52. Mitochondria can be distinguished from similar-looking particles in living cells by their affinity for a dye called:
- Acetocarmine
- Janus green.
- Eosin
- Methylene blue.
Answer: 2. Janus green
Question 53. Which of the following observations most strongly support the view that mitochondria contain electron transfer enzymes aggregated into compact association?
- Mitochondria have a highly folded inner wall
- Disruption of mitochondria yields membrane fragments which can synthesize ATP
- Mitochondria in animal embryos tend to concentrate in cells which become a part of the locomotory structure
- A contractile protein capable of utilising ATP has been obtained from mitochondria.
Answer: 2. Disruption of mitochondria yields membrane fragments which can synthesize ATP
Question 54. Within the cell, the site of respiration is:
- Nucleus
- Mitochondrion
- Ribosome
- Lysosome.
Answer: 4. Lysosome.
Cell The Unit Of Life Neet Previous Year Questions
Question 55. Cristae refer to :
- Infolding of the inner membrane of mitochondria
- Infolding of the outer membrane of mitochondria
- Branches of endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus.
Answer: 1. Infolding of the inner membrane of mitochondria
Question 56. A mitochondrion possesses a :
- Single membrane
- Double membrane
- Three-layered membrane
- Four-layered membrane.
Answer: 2. Double membrane
Question 57. The existing evidence favours that mitochondria arise;
- From precursors in the cytoplasm
- From non-mitochondrial membranes
- By growth and division of pre-existing mitochondria
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. None of the above.
Question 58. The Golgi apparatus present in cells synthesizes:
- Cellulose
- Hemicellulose
- Pectin
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 59. The Golgi apparatus is bounded by :
- Single unit membrane
- Cellulose layer
- Plasma membrane
- The double unit membrane of lipoproteins.
Answer: 1. Single-unit membrane
Question 60. Which one of the following is responsible for the breakdown of parts of the cell and foreign particles in the cell?
- Ribosome
- Centrosome
- Lysosome
- Golgi apparatus.
Answer: 3. Lysosome
Cell Biology Mcqs With Answers For Neet
Question 61. The percentage of mitochondrial DNA in the cells is:
- 10% Of total cellular DNA
- L% of total cellular DNA
- 2.5% of total cellular DNA
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. L% of total cellular DNA
Question 62. Secondary lysosomes give rise to:
- Residual bodies
- Tertiary lysosomes
- Peroxisome
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Residual bodies
Question 63. Lysosomes are considered suicidal bags because they:
- Kill the neighbouring cells
- Kin the engulfed bacteria
- Are responsible for intracellular digestion
- Oxidise the food in the cells.
Answer: 3. Are responsible for intracellular digestion
Question 64. Lysosome along with the food contents is :
- Primary lysosome
- Secondary lysosome
- Residual bodies
- Cytosome.
Answer: 2. Secondary lysosome
Question 65. Peroxisomes are bounded by :
- Single membrane
- Double membrane
- Triple membrane
- No membrane.
Answer: 1. Single membrane
Question 66. Peroxisomes do not have :
- O-amino acid oxidase
- B-hydroxy acid oxidase
- Urate oxidase
- DNA synthetase.
Answer: 4. DNA synthetase.
Question 67. Bone cells containing lysosomes are:
- Osteofibrils
- Osteoclasts
- Osteoblasts
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Osteoclasts
Question 68. Sphaerosomes arise from;
- Mitochondrion
- Lysosome
- E.r.
- Ribosome.
Answer: 3. E.r.
Cell Biology Mcqs With Answers For Neet
Question 69. Sphaerosomes are mostly present in :
- All cells
- Prokaryotic cells
- Lipid secreting and storing cells.
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Lipid secreting and storing cells.
Question 70. The cellular role of the lysosome is not :
- Ingestion of foreign bodies
- Digestion of aged organelles
- Cell destruction during development
- Osmoregu location.
Answer: 4. Osmoregu lation.
Question 71. The first scientist to say that plants purify air in the presence of light was:
- Van Belmont
- Priestley
- Ingenhousz
- Blackman.
Answer: 3. Ingenhousz
Question 72. Thylakoids are presenl in plasrids of :
- Bacteria
- Cyanobacteria
- Higher plants
- All the above.
Answer: 3. Higher plants
Question 73. The main types of plastids meant for photosynthesis are:
- Leucoplasts
- Chromoplasts
- Chloroplasts
- None of them.
Answer: 3. Chloroplasts
Question 74. Isolated chloroplasts can synthesize :
- RNA
- DNA
- Proteins
- None of the above.
Answer: 4. None of the above.
Question 75. DNA genetic material occurs by itself in lower organisms and is combined with proteins as nucleoproteins in higher organisms. The nucleoprotein is organized in higher looms to form:
- Chromosome
- Nucleolus
- Nucleotides
- Nucleoside.
Answer: 1. Chromosome
Question 76. The nucleus was first discovered by :
- Walson and crick
- Bowman
- Roberr brown hooke.
- Hooke
Answer: 3. Roberr brown hooked.
Cell Biology Mcqs With Answers For Neet
Question 77. A nucleus which involves the duplication of chromosomes but fails to divide is known as :
- Endomitosis
- Restitution nucleus
- Euploidy
- Polyploidy.
Answer: 2. Restitution nucleus
Question 78. Which stain gives purple or violet colour to the chromosome?
- Feulgen
- Acetocarmine
- Acetocein
- Safranin.
Answer: 1. Feulgen
Question 79. The structure of the nuclear membrane facilitates:
- Organization of spindle
- Synapsis of homologous chromosomes during meiosis
- Nucleo-cytoplasmic exchange of materials
- Anaphasic separation of daughter chromosomes.
Answer: 3. Nucleo-cytoplasmic exchange of materials
Question 80. The pores of the nuclear membrane have a diameter of :
- 400Å to 1000Å
- 600Å to 900Å
- 100Å to 200Å
- 700Å to 760Å
Answer: 4. 700Å to 760Å
Question 81. If the nucleus represents its large size in proportion to the cytoplasm of the cell, it indicates that:
- The cell is dying
- The nucleus is in the resting phase
- The nucleus has entered the s-phase of the interphase
- The cell is about to die.
Answer: 3. The nucleus has entered the s-phase of the interphase
Question 82. An acentric chromosome at metaphase will be :
- Condensed and lie near the equator
- Irregularly shaped and lying at one of the poles
- Condensed and lie at poles
- Coiled and attached to spindle fibre.
Answer: 1. Condensed and lie near the equator
Question 83. Cytochromes present in the cells are :
- Electron acceptors
- Carbon acceptors
- Hydrogen acceptors
- Nitrogen acceptors.
Answer: 1. Electron acceptors
Question 84. The parallel layering of membranes in chloroplast is suited for:
- Maximum light absorption
- Maximum exposure to enzymes
- Minimum light absorption so that the cells can maintain their temperature
- All the above.
Answer: 1. Maximum light absorption
Cell Organelles Mcq For Neet
Question 85. Non-photosynthetic plastids are :
- Amyloplasts
- Chromoplasts
- Chloroplasts
- Both 1 and 2.
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2.
Question 86. The organelles which occur outer to the cell membrane but inner to the cell wall are :
- Sphaerosomes
- Lomasomes
- Glyoxisomes
- Peroxisomes.
Answer: 2. Lomasomes
Question 87. Centrioles are :
- Cylindrical structures
- Rectangular structures
- Cuboidal structures
- Square structures.
Answer: 1. Cylindrical structures
Question 88. The fruits on ripening become coloured, it is due to the:
- Disintegration of chloroplasts and development of chromoplasts
- Conversion of chloroplasts to chromoplasts
- Conversion of chlorophyll into anthocyanin pigment
- All the above.
Answer: 1. Disintegration of chloroplasts and development of chromoplasts
Question 89. Mitochondria and chloroplasts are believed to be bacterial endosymbionts of cells because:
- They have their nucleic acids
- Their inner membrane resembles those of bacteria
- They do not arise de novo
- They have all the above attributes.
Answer: 4. They have all the above attributes.
Question 90. Which of the following shows a 9 + 0 arrangement?
- Centriole
- Cilia
- Cilia + centriole
- Cilia + centriole + flagellum.
Answer: 1. Centriole
Question 91. Cilia and flagella are responsible for :
- Respiration
- Locomotion
- Co-ordination
- Lipid formation.
Answer: 2. Locomotion
Cell Organelles Mcq For Neet
Question 92. Microfilaments are long. Thin fibres 40-60 a :
- Myosin
- Actin
- Tubulin
- Both 1 and 2.
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2.
Question 93. The cellular role of the microtubule is not :
- Protein synthesis
- Int racell ulai communication
- Movement
- Formation of mitotic spindle.
Answer: 1. Protein synthesis
Question 94. One centriole is composed of:
- Nine triplet peripheral microtubules
- Nine doublet peripheral microtubules
- Nine singlet peripheral microtubules
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Nine triplet peripheral microtubules
Question 95. Chromosomes having equal arms are known as :
- Metacentric
- Acrocentric
- Telocentric
- Acentric.
Answer: 1. Metacentric
Question 96. Prokaryotic flagella possess :
- A helically managed protein molecule
- Protein membrane-bound libres
- Unit membrane-enclosed fibre
- Microtubular “9 + 2” membrane-enclosed structure.
Answer: 1. Helically managed protein molecule
Question 97. The nucleolus is a :
- Distinct membrane-bound organelle
- Spheroid ribonucleoprotein only
- Parr of chromosome
- All of the above.
Answer: 2. Spheroid ribonucleoprotein only
Cell Organelles Mcq For Neet
Question 98. Perinuclear space is the space lying :
- Outside and around the nuclear membrane
- Inside and around the nuclear membrane
- Between the two nuclear membranes
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Between the two nuclear membranes
Question 99. An October of four histones complexed with dna is called:
- Nucleosome
- Centrosome
- Chromosome
- Endosome.
Answer: 1. Nucleosome
Question 100. The core of nucleosome is made up of :
- H1.h2, a, h,b,h3
- H1,h2, a,h,b, h4
- H2 a, h2 b,h3,h1
- H2 a, h2 b,h3,h4
Answer: 4. H2 a, h2 b,h3,h4
Question 101. Nucleoli are not present in the cells of :
- Eukaryotes
- Blue-green algae
- Maize plant
- Pancreas.
Answer: 2. Blue-green algae
Question 102. Chromosomes can be specifically stained by :
- Safranin
- Acetocarmine
- Janus green
- Amine blue.
Answer: 2. Acetocarmine
Question 103. Mature mammalian white blood cells are :
- Without nuclei
- With four nuclei
- Without nucleoplasm
- With nuclei.
Answer: 4. With nuclei.
Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cell Mcq Neet
Question 104. The undifferentiated fibrillar nucleus is found in :
- Eukaryotes
- Cells of higher organisms
- Prokaryotes
- Higher animals.
Answer: 3. Prokaryotes
Question 105. Which of the following has a nucleus?
- Cork cell
- Sieve tubes
- Companion cell
- Vessels.
Answer: 3. Companion cell
Question 106. What will happen if the nucleus is removed?
- The metabolism will increase
- The cell will die
- The metabolism will decrease
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. The cell will die
Question 107. The process by which dna of the nucleus passes genetic information to mRNA is called :
- Translocation
- Transportation
- Translation
- Transcription.
Answer: 4. Transcription.
Question 108. The beaded appearance of the chromosome is known as:
- Centromere
- Chromomere
- Centriole
- Centrosphere.
Answer: 2. Chromomere
Question 109. In mitochondria, cristae act as sites for :
- Phosphorylation of flavoproteins
- Protein synthesis
- Oxidation reduction reactions
- Breakdown of macromolecules.
Answer: 3. Oxidation-reduction reactions
Question 110. Raphides found in asparagus are crystals of :
- Calcium carbonate
- Calcium Citrate
- Magnesium oxalate
- Calcium oxalate.
Answer: 4. Calcium oxalate.
Question 111. Chromosome puffs in salivary gland chromosomes are the sites of :
- Translation
- Transcription
- DNA synthesis
- DNA replication.
Answer: 2. Transcription
Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cell Mcq Neet
Question 112. The fuel-gen nuclear reaction includes the following :
- Reaction of deoxyribose with leuco fuschin to give purple colour to DNA
- The reaction of ribose with leuco fuschin to give pink colour to rna
- Removal of purine at the level of the purine deoxyribose glycosidic bond of DNA by acid hydrolysis.
- All the above.
Answer: 3. Removal of purine at the level of the purine deoxyribose glycosidic bond of dna by acid hydrolysis.
Question 113. The chromosome number in plants can be increased by
- Colchicine treatment
- Heat treatment
- Hormonal treatment
- Breeding with their wild varieties.
Answer: 1. Colchicine treatment
Question 114. Balbiani rings are the characteristics of :
- Polytene chromosomes
- Sex chromosomes
- Ring chromosomes
- Lampbrush chromosomes.
Answer: 3. Ring chromosomes
Question 115. Chromosomes are made of structural units called
- Nucleoli
- Nucleosome
- Base
- Centromere.
Answer: 2. Nucleosome
Question 116. One of the following serves as a temporary storage place for proteins and other compounds synthesized by the endoplasmic reticulum :
- Lysosomes
- Dictyosomes
- Sphaerosome
- Microsome.
Answer: 4. Microsome.
Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cell Mcq Neet
Question 117. Polytene chromosomes are formed when :
- Chromosome divides but the nucleus does not divide
- The nucleus divides but the cell does not divide
- Chromatids divide but the chromosome does not divide
- The chromosome assumes a lampbrush shape.
Answer: 3. Chromatids divide but the chromosome does not divide
Question 118. Micrococcal nuclease enzyme :
- Cuts the DNA from a specific site
- Joins the DNA segment
- Cuts the DNA at the junction between nucleosome
- Binds the DNA with histone.
Answer: 3. Cuts the DNA at the junction between nucleosome
Question 119. Cenffomere is required for :
- Replication of DNA
- The poleward movement of chromosome
- Cytoplasmic cleavage
- Chromosome segregation.
Answer: 2. Poleward movement of chromosome
Cell The Unit Of Life Mcq For Neet
Question 120. To determine the ultrastructure of cell organelles, the most likely method of successful observation would be:
- Phase contrast microscopy
- Light microscopy
- Electron microscopy
- Autoradiography.
Answer: 3. Electron microscopy
Question 121. Mitochondria in a cell are concerned with the formation of:
- ATP From ADP
- ATP From Pyruvic Acid
- Lactic Acid From Citric Acid
- ADP From ATP.
Answer: 1. ATP From ADP
Question 122. Which of the following representations correctly explains the function of mitochondrion?
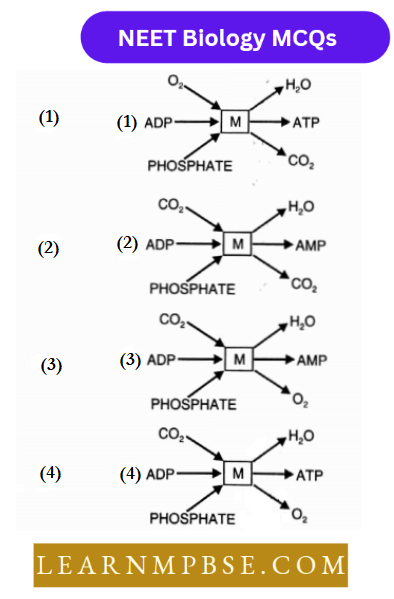
Answer: 1.
Question 123. Who was awarded the Nobel Prize for the synthesis of RNA in 1959 :
- S. Ochoa
- A. Korenberg
- Nirenberg
- H.G. Khorana.
Answer: 1. S. Ochoa
Question 124. Chlorophyll a is characterized by the side group :
- Methyl
- Aldehyde
- Phytol
- Ketone.
Answer: 1. Methyl
Cell The Unit Of Life Mcq For Neet
Question 125. Endoplasmic reticulum was first discovered by :
- Bell
- Porter
- Golgi
- Altrnan.
Answer: 2. Porter
Question 126. The centrosome is rich in :
- DNA
- RNA
- ATP
- Enzymes.
Answer: 2. RNA
Question 127. ‘Protein factories’ of the cell to be effective, need :
- Fe++
- Cu++
- Mg++
- Ca++
Answer: 3. Mg++
Question 128. In a eukaryotic cell, the region between the nucleus and plasma membrane is called :
- Junction
- Nucleoplasm
- Cytoplasm
- Lumen.
Answer: 3. Cytoplasm
Question 129. Vacuoles are considered as living organelles because they:
- Are membrane-bound
- Have hormones
- Store enzymes
- Can arise de novo.
Answer: 1. Are membrane-bound
Question 130. Which of the following is not the correct pairing of structure with function :
- Golgi complex: breakdown of complex molecules
- Chloroplast: photosynthesis
- Mitochondria: production of ATP
- Sphaerosome: synthesis and storage of fat.
Answer: 1. Golgi complex: breakdown of complex molecules
Question 131. Proteins that are to be utilized outside the cell are synthesized :
- In the mitochondria
- On the rear
- On the ser
- On free ribosomes.
Answer: 2. On the rear
Neet Mcqs On Cell Structure And Function
Question 132. Plant cells are connected by channels through their walls called :
- Plasmodesmata
- Desmosomes
- Tight junction
- Desmotubules.
Answer: 1. Plasmodesmata
Question 133. Haploid plants can be obtained by culturing :
- Root tips
- Young leaves
- Endosperm
- Pollen grains.
Answer: 4. Pollen grains.
Question 134. Pyrenoids are centres for:
- Fat production
- Starch formation
- Protein formation
- Enzyme foundation.
Answer: 2. Starch formation
Question 135. Bacteria are examples of :
- Prokaryotic cell
- Eukaryotic cell
- Organelles
- Plastids.
Answer: 1. Prokaryotic cell
Question 136. Which of the following is not found in prokaryotic cells?
- Plasma membrane
- Cell wall
- Nuclear envelope
- Ribosomes.
Answer: 3. Nuclear envelope
Question 137. How many membranes comprise the nuclear envelope?
- None
- One
- Two
- Three.
Answer: 3. Two
Question 138. Which of the following moves regularly frorn the nucleus to the cytoplasm?
- Glycogen
- Rna
- DNA
- Cholesterol.
Answer: 2. Rna
Question 139. The plastids that give fruits and flowers their orange and yellow colour are the :
- Leucoplasts
- Chloroplasts
- Chromoplasts
- Protoplasts.
Answer: 3. Chromoplasts
Neet Mcqs On Cell Structure And Function
Question 140. The types of cellular organelles that transform energy are :
- Chromoplasts and leucoplasts
- Mitochondria and chloroplasts
- Mitochondria and chromoplasts
- Chloroplasts and leucoplasts.
Answer: 3. Mitochondria and chromoplasts
Question 141. Lysosomes contain enzymes capable of:
- Aerobic cellular respiration
- Digesting part of the cell
- Synthesizing proteins
- Synthesizing lipids.
Answer: 2. Digesting part of cell
Cell The Unit of Life NEET Questions Question 142. Mitochondria are found :
- In all cells
- Only in plant cells
- Only in animal cells
- All eukaryotic cells.
Answer: 4. All eukaryotic cells.
Question 143. Which of the following observations most strongly supports the view that mitochondria contain electron transfer enzymes aggregated into compact association :
- Mitochondria have a highly folded inner wall
- Disruption of mitochondria yields membrane fragments which can synthesise ATP.
- Mitochondria in animal embryos tend to concentrate in cells which become part of locomotory structures.
- A contractile protein is capable of utilisation atp has been obtained from mitochondria.
Answer: 2. Disruption of mitochondria yields membrane fragments which can synthesise ATP
Question 144. Hydrogenosomes (identified in 1997) have double membrane help in energy generation in :
- Dinoflagellates
- Trichomionids
- Diatoms
- All eukaryotes.
Answer: 2. Trichomionids
Question 145. Human sperm cells move by :
- Cilium
- Flagellum
- Basal body
- Hair.
Answer: 2. Flagellum
Question 146. Plant cells are connected by channels through their walls called:
- Plasmodesmata
- Desmosomes
- Tight junctions
- Gap junctions.
Answer: 1. Plasmodesmata
Cell The Unit of Life NEET Questions Question 147. Glycolysis is a process found in :
- Eukaryotic cell
- Anaerobic bacteria
- Most muscle cells
- Virtually all cells.
Answer: 4. Virtually all cells.
Question 148. The protoplasm is:
- True solution
- Emulsion
- Suspension
- Reversible colloidal solution.
Answer: 4. Reversible colloidal solution.
Question 149. The cell organelle common in protista and monera is :
- Lysosome
- Chloroplasts
- Ribosome
- Vacuole.
Answer: 3. Ribosome
Question 150. A striking difference between a plant cell and an animal cell is the presence of the former:
- Chloroplast
- Cell wall
- Centrosome
- Plasmalemma.
Answer: 2. Cell wall
Cell Biology Mcqs With Answers For Neet
Question 151. In which component of a mitochondrion atp is synthesized
- Crista
- Matrix
- Fo-fr complex
- Plasmalemma.
Answer: 3. Fo-fr complex
Question 152. Photorespiration occurs in plant cells in :
- Dictyosome
- Glyoxisome
- Peroxisomes
- Endoplasmic reticulum.
Answer: 3. Endoplasmic reticulum.
Question 153. Golgi apparatus is lacking in :
- Liver cells
- Higher plants
- Blue-green algae
- Yeasts.
Answer: 3. Blue-green algae
Question 154. Polysome is a chain of :
- Pinosome
- Ribosomes
- Phagosomes
- Lysosomes.
Answer: 2. Ribosomes
Question 155. Lysosomes containing inactive enzymes are called :
- Autophagosomes
- Residual bodies
- Secondary lysosomes
- Primary lysosomes.
Answer: 4. Primary lysosomes.
Cell The Unit of Life Biology NEET Question 156. The chloroplast thylakoids are in the form of;
- Interconnected sacs
- Independent discs
- Interconnected tubules
- Stacked discs.
Answer: 1. Interconnected sacs
Question 157. The pattern of microtubule organization in a centriole is:
- 9+0
- 9+1
- 9+2
- 9+3.
Answer: 1.9+0
Question 158. In man the amount of water is about :
- 35%
- 55%
- 1O%
- 90%.
Answer: 1. 35%
Question 159. The basal body could be another name for centriole given internal structures when :
- It gives rise to spindle fibres
- Lt divides during mitosis
- It gives rise to cilia or flagella
- Lt gives basic reactions.
Answer: 3. It gives rise to cilia or flagella
Question 160. How much energy is released for each molecule of oxygen used in :
- 114.5 kcal
- 124.5 kcal
- 134.5 kcal
- 144.5 kcal.
Answer: 3. 134.5 kcal
Question 161. What would be a good example of the occurrence of three types of plastids in a developing organ?
- Radish
- Turnip
- Brinial
- Tomato.
Answer: 4. Tomato.
Question 162. Which of the following is the chief energy food in a cell?
- Carbohydrates
- Nucleotides
- Lipids
- Proteins.
Answer: 1. Carbohydrates
Question 163. Water enters the cell by :
- Endosmosis
- Pinocytosis
- Phagocytosis
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 164. Golgi apparatus resembles :
- Ser
- Rer
- Nuclear envelope
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Ser
Question 165. Materials enter the Golgi complex at :
- Cis region
- Trans region
- Medial region
- Trans golgi reticulum.
Answer: 1. Cis region
Question 166. The enzyme peptidyl transferase is present in :
- Smaller subunit of the ribosome
- Larger subunit of ribosome
- Groove between smaller and larger subunits
- In the cytoplasm.
Answer: 2. Larger subunit of ribosome
Question 167. Autophagic vacuoles (vesicles) digest :
- Pinosome content
- Phagosome content
- Cell organelles
- Microorganisms.
Answer: 3. Cell organelles
Cell Biology Mcqs With Answers For Neet
Question 168. Lysosomes help in :
- Fertilization
- Insulin processing
- Contraception
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 169. F is composed of :
- Five polypeptides
- 3 Polypeptides
- 3 Polypeptides and accessory polypeptides
- A, b, c, d and e polypeptides.
Answer: 4. A, b, c, d and e polypeptides.
Question 170. A quant some contains :
- 250 Chlorophyll molecules
- 350 Chlorophyll molecules
- 450 Chlorophyll molecules
- 245 Chlorophyll molecules.
Answer: 1. 250 Chlorophyll molecules
Question 171. The flagellum of a eukaryotic cell shows :
- 9 + 0 Arrangement
- 9 + 2 Arrangement
- 1 + 2 Arrangement
- 2 + 9 Arrangement.
Answer: 2. 9 + 2 Arrangement
Question 172. Select the self-duplicating organelle :
- Mitochondria
- Plastids
- Centriole
- All of these.
Answer: 4. All of these.
Question 173. Peroxisomes and glycosomes are :
- Energy transducers
- Membrane-less organelles
- Microsomes
- Microbodies.
Answer: 4. Microbodies.
Question 174. Lysosomes with cell organelles are called :
- Primary lysosomes
- Secondary lysosomes
- Autophagosomes
- Residual bodies.
Answer: 3. Autophagosomes
Question 175. Golgi bodies are involved in :
- Excretion
- Secretion
- Atp synthesis
- Rna synthesis.
Answer: 2. Secretion
Question 176. The chloroplasts develop limo :
- Er
- Dictyosome
- Nuclear membrane
- Proplastids.
Answer: 4. Proplastids.
Question 177. The supporting framework of a cell consists of :
- Microfilaments
- Microtubules
- Both of these
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Both of these
Question 178. A chromosome having equal arms is called :
- Metacentric
- Submetacentric
- Acrocentric
- Telocentric.
Answer: 1. Metacentric
Question 179. Chromosomes are stained with :
- Eosin
- Safranin
- Acetocarmine
- Borax carmine.
Answer: 3. Acetocarmine
Question 180. Golgi apparatus is most abundantly found in :
- Muscle cells
- Neurons
- Red blood cells
- Pancreatic cells.
Answer: 4. Pancreatic cells.
Question 181. Mechanical support to the cell is provided by :
- Golgi bodies
- Microfibrils
- E.r.
- Chromatin.
Answer: 3. E.r.
Question 182. The function of the centrosome is :
- Initiation of cell division
- Inhibition of cell division
- Termination of cell division
- None of the above.
Answer: 4. None of the above.
Cell Biology Mcqs With Answers For Neet
Question 183. A chromosome having a subterminal centromere is :
- Telocentric
- Acrocentric
- Submetacentric
- Metacentric.
Answer: 2. Acrocentric
Question 184. Which structure is present in animal cells but is absent in plant cell?
- Centrioles
- Golgi apparatus
- Mitochondria
- Endoplasmic reticulum.
Answer: 1. Centrioles
Question 185. The smallest cell organelle is :
- Mitochondria
- Microfilament
- Microtubule
- Ribosome.
Answer: 4. Ribosome.
Question 186. Which of the following is the vacuolar membrane?
- Cell membrane
- Tonoplast
- Karyotheca
- Er.
Answer: 4. Er.
Question 187. Select the amphipathic organic compound :
- Fibroin.
- Proteins
- Phospholipids
- Nucleotides.
Answer: 3. Phospholipids
Question 188. The plastids present in red algae are :
- Chloroplast
- Rhodoplasts
- Phaeoplasis
- Leucoplasts.
Answer: 2. Rhodoplasts
Question 189. Dark reactions of photosynthesis occur in :
- Stroma
- Inter membrane space
- Thylakoids
- Axe of above.
Answer: 1. Stroma
Question 190. Microtubules were first seen in :
- Medullated nerve fibre
- Muscle fibre
- Non-medullated nerve fitrre
- Cellulose fibre.
Answer: 1. Medullated nerve fibre
Question 191. Maps are found in :
- Microtubules
- Intermediate filament
- Microfilg+ents
- Microtrabeculae.
Answer: 1. Microtubules
Cell Organelles Mcq For Neet
Question 192. Turgor pressure in plant cells is generally, between:
- 5 And 20 atm
- 20 And 40 atm
- 10 And 30 atm
- 1 And 5 atm.
Answer: 1. 5 And 20 atm
Question 193. Hydrogenosomes are found in certain :
- Amoebae
- Flagellates
- Ciliates
- Sporozoans.
Answer: 2. Flagellates
Question 194. The nucleus has ribosomes attached to :
- Inner membrane
- Outer membrane
- Chromatin fibres
- All of the above.
Answer: 2. Outer membrane
Question 195. Which of the following is a major component of the nucleus?
- DNA
- Lipids
- Rna
- Proteins.
Answer: 4. Proteins.
Question 196. The nucleolus is especially rich in :
- DNA and proteins
- Rna and proteins
- DNA and proteins
- Rna and lipids.
Answer: 3. DNA and proteins
Question 197. Chromosomes are best seen in :
- Interphase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase.
Answer: 3. Anaphase
Question 198. In spermatogenesis, the acrosome of the sperm is formed by:
- Mitochondria
- Nucleus
- Lysosome
- Golgi complex.
Answer: 3. Lysosome
Question 199. Polytene chromosomes were first seen in :
- Drosophila
- Fruit fly
- Chironomus larva
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Chironomus larva
Question 200. Synaptonemal complex is associated with :
- Polytene chromosome
- Lampbrush chromosome
- Mitotic chromosome
- Paired meiotic chromosomes.
Answer: 4. Paired meiotic chromosomes.
Question 201. The beaded areas on chromosomes are known as :
- Centromere
- Cristae
- Chromomeres
- Cistron.
Answer: 3. Chromomeres
Question 202. Stem cells is an alternative term for :
- Dedifferenriared cells
- Redifferentiated cells
- Undifferentiated cells
- Differentiated cells.
Answer: 3. Undifferentiated cells
Question 203. Cell biology is the study of :
- Cell structure
- Cell Function
- Cell division
- Cell structure and function.
Answer: 4. Cell structure and function.
Question 204. Which of the following is time?
- A cotton fibre is made up of 1500 fibrils
- A fibril has 250 microfibrils
- A microfibril has 20 micelles
- All of above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 205. Channel has been discovered by :
- Singer and Nicholson
- Garnier
- Robinson and brown
- Nehar and salesman
Answer: 1. Singer and Nicholson
Question 206. Pelviz et al discovered :
- Microtubules
- Microfilaments
- Centriole
- Peroxisome.
Answer: 1. Microtubules
Question 207. Nucleoplasmin occurs inside :
- Chromatin
- Nucleolus
- Nucleoplasm
- Nucleopores.
Answer: 4. Nucleopores.
Question 208. Match the items of column 1 with the items of column 2
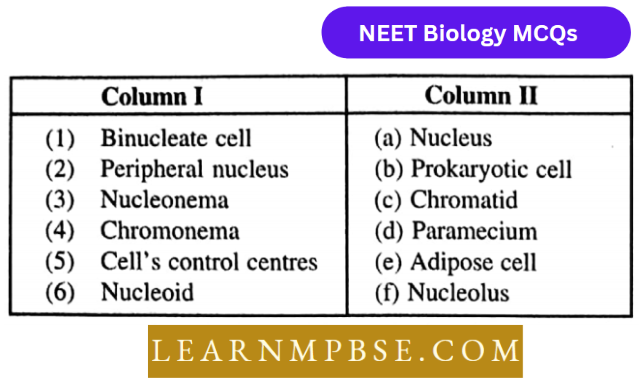
- (1-D), (2-E), (3-F), (4-A) (5-B), (6-C)
- (1-D), (2-E), (3-A), (4-F), (5-B), (6-C)
- (1-D), (2-E) (3-F), (4-C) (5-A), (6-B)
- (1-D), (2-F), (3-C), (4-E), (5-A), (6-B).
Answer: 3. (1-D), (2-E) (3-F), (4-C) (5-A), (6-B)
Question 209. Match the items of column 1 with column 2
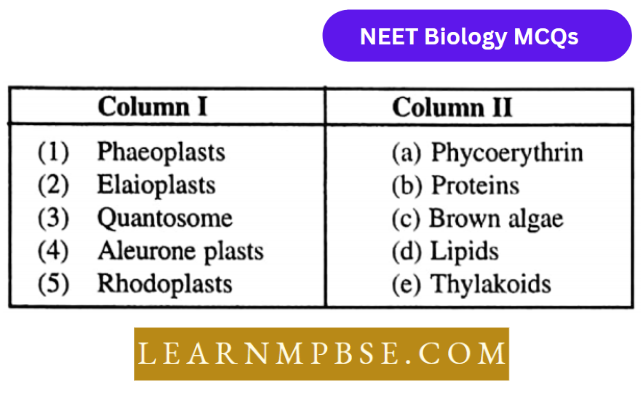
- (1- c), (2- d), (3- e), (4- b), (5- a)
- (1- c), (2- d), (3- b), (4- c), (5- a)
- (1- c), (2-d), (3- a), (4-b), (5- e)
- (1 – c), (2- d), (3- e), (4- a). (5- b).
Answer: 1. (1- c), (2- d), (3- e), (4- b), (5- a)
Question 210. Match the items of column 1 with the items of column 2
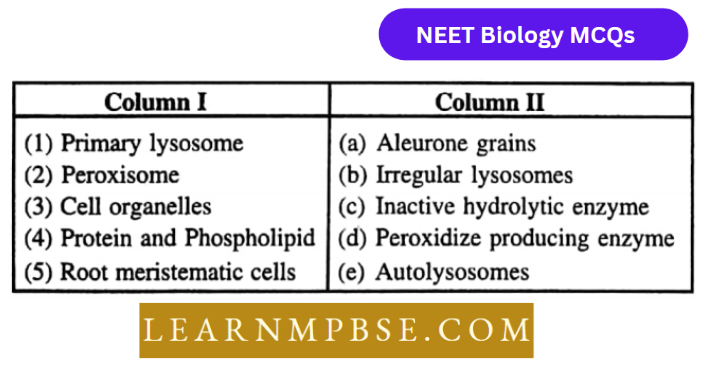
- (1 – C), (2 – d), (3 – a), (4 – b), (5 – e)
- (1- C), (2 – a), (3 – d), (.4 – e), (s – b)
- (1- C), (2 – d), (3 – e), (4 – a), (5 – b)
- (1- C), (2 – d), (3 – b), (4 – a), (5 – e).
Answer: 3. (1- C), (2 – d), (3 – e), (4 – a), (5 – b)
Question 211. Match the terms in column a with suitable terms
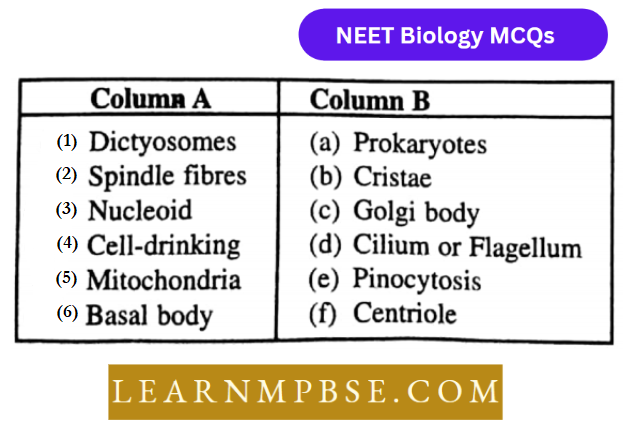
- (1-c), (2-f), (3-a), (4-e) (5-b),(6-d)
- (1-c), (2-f), (3-a), (4-b), (5-d),(6-e)
- (1-c), (2-f) (3-a), (4-e) (5-d),(6-b)
- (1-c), (2-d), (3-a), (4-e), (5-b),(6-f)
Answer: 1. (1-c), (2-d), (3-a), (4-b) (5-e)
Question 212. Enzymes associated with converting fats to carbohydrates are located in which organelle?
- Liposomes
- Golgi bodies
- Glyoxysomes
- Microsomes.
Answer: 3. Glyoxysomes
Question 213. Which of the following is covered by a single membrane?
- Nucleus
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
- Sphaerosomes.
Answer: 4. Sphaerosomes.
Question 214. Dna is ‘mainly’ found in :
- Nucleus only
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus and cytoplasm
- All the above.
Answer: 1. Nucleus only
Question 215. What is common between chloroplasts, chromoplasts and leucoplasts?
- Presence of pigements
- Possession of thylakoids and Gama
- Storage of starch, proteins and lipids
- Ability to multiply by a fission-like process.
Answer: 4. Ability to multiply by a fission-like process.
Question 216. Organelle connected with glycoside
- Ribosome
- E.r.
- Mitochondrion
- Chloroplast.
Answer: 2. E.r.
Question 217. The Centre of phosphorylation is :
- Ribosome
- Oxisome
- Peroxisome
- Sphaerosome.
Answer: 3. Peroxisome
