NEET Biology Elements Of Heredity Multiple Choices Questions
Question 1. When one member of a pair of allelic genes expresses itself as a whole, it is a case of:
- Dominance
- Co-dominance
- Incomplete dominance
- None of these.
Answer: 1. Dominance
Question 2. The first generation of a given cross is known as :
- F2 generation
- F2 generation
- F1 generation
- None of these.
Answer: 3. F1 generation
Question 3. Gamete is:
- Diploid sex cell
- Haploid cell
- Diploid somatic cell
- Triploid somatic cell.
Answer: 2.Haploid cell
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question and Answers
Question 4. The genotype of the individual is :
- Genetic constitution
- Genetic setup
- Both of these
- None of these.
Answer: 3. Both of these
Principles of Inheritance And Variation MCQs NEET
Question 5. Fraternal twins air produced when :
- Two ova are fertilized simultaneously
- Single fertilised ovum gets fertilised again
- Two ova develop paitlicnogcnclically
- Single ovum fertilized by two sperms.
Answer: 1. Two ova are fertilized simultaneously

Question 6. “Theory of pangenesis” to explain the mechanism of heredity was given by :
- Mendel
- Darwin
- Lamarck
- Cuvier.
Answer: 2. Darwin
Question 7. The I.Q. of a genius ranges from :
- 70-80
- 90-109
- 110-139
- 140 and more.
Answer: 1. 70-80
Question 8. The genetic setup is termed as :
- Dominant
- Genotype
- Phenotype
- Alleles.
Answer: 3. Phenotype
Question 9. It is the ratio of mental age to :
- Chronological age × 100
- Chronological age + 100
- Chronological age — 100
- Chronological age ÷ 100.
Answer: 1. Chronological age × 100
Principles of Inheritance And Variation MCQs NEET
Question 10. The sex of an unborn mammal can be predicted by :
- Placental biopsy
- Examining the chorion
- Amniocentesis
- Examine the mother’s blood.
Answer: 3. Amniocentesis
Question 11. Criminal syndrome :
- XXY
- XO
- XYY
- XY.
Answer: 3. XYY
Question 12. Gallon is associated with :
- Eugenics
- Euthenics
- Genetics
- Human genetics.
Answer: 1. Eugenics
Question 13. The term gene refers to :
- The sequence of amino acid
- A linkage group
- A part of tRNA
- A portion of DNA.
Answer: 4. A portion of DNA.
Principles of Inheritance And Variation MCQs NEET
Question 14. Who connected cytology with genetics :
- Morgan
- Sutton
- Bridges
- Mendel.
Answer: 4. A portion of DNA.
Question 15. The total of genes in a population is known as :
- Gene bank
- Gene linkage
- Gene pool
- Genome.
Answer: 3. Gene pool
Question 16. Which is the wholly genetic trail?
- Diphtheria
- Leucoderma
- Albinism
- Tuberculosis.
Answer: 3. Albinism
NEET Biology Inheritance And Variation Questions
Question 17. The wife is a PTC non-taster and the husband is a PTC taster. Their son is a taster but daughters are non-tasters. This is not a sex-linked trait. Which pedigree is correct ?
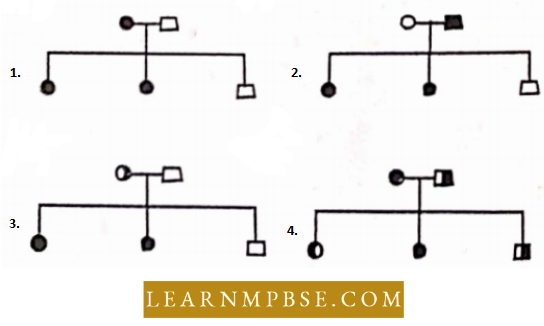
Answer: 1
Question 18. Predict from the following chart
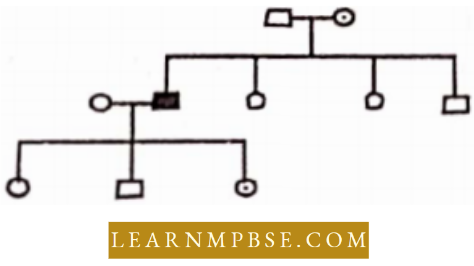
- Character is dominant and carried by X chromosome
- Carried by Y chromosome
- Character is sex-linked recessive
- Character is recessive autosomal.
Answer: 3. Character is dominant and carried by X chromosome
Question 19. From the pedigree of a family given below, it is clear that the trait is inherited as a dominant autosomal trail. What will be the genotype of the mother and father?
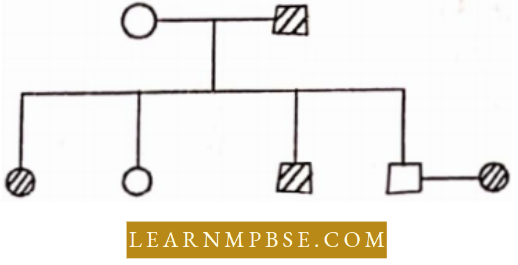
- Mother is aa and father is Aa
- Father is AA and mother is aa
- Father is Aa and mother is Aa
- None of die above.
Answer: 1. Mother is aa and father is Aa
Mendelian Inheritance MCQs For NEET
Question 20. When an individual possesses both alleles of its phenotypically dissimilar parent, it is called:
- Homozygous
- Mother is aa and father is Aa
- Dioecious
- Monoecious.
Answer: 2. Mother is aa and father is Aa
Question 21. In a pig dominant allele B produces black colour and its recessive allele b produces white. What would be the probable genotype of the offspring when a cross is made between individuals heterozygous for colour?
- BB
- Bb
- bb
- All of these.
Answer: 4. All of these.
Question 22. When the phenotype and genotypic ratio resemble the E, generation, it is an example of:
- Incomplete dominance
- Dihybrid cross
- Cytoplasmic inheritance
- Linkage.
Answer: 1. Incomplete dominance
Mendelian Inheritance MCQs For NEET
Question 23. Word heredity is derived from the Latin word ‘Hereditas’ which means :
- Heirship
- Ancestral property
- Blood relations
- All the above.
Answer: 1. Heirship
Question 24. Which of the following explains the law of dominance?
- The expression of only one of the parental characters in a monohybrid cross in the F( generation
- The expression of both in the F2 generation
- The proportion of 3:1 obtained in the F2 generation
- All of above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 25. Starch grain size in pea seed is an example of:
- Incomplete dominance
- Multiple alleles
- Pleiotropism
- Polygenic inheritance
Answer: 1. Incomplete dominance
Question 26. In family. father had traits but their mother did not. All that ‘one and daughter bail this hail The same hail wav lound in some granddaughters, though daughter married lo normal persons.
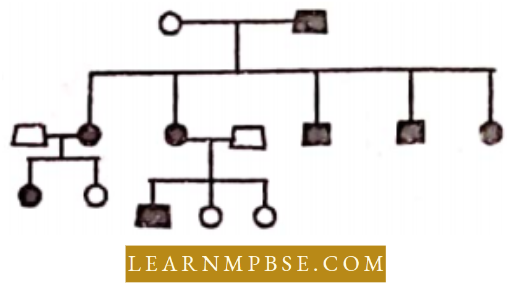
In this pedigree the genotypes of lather, mother and husbands of daughters am
- The father is AA, the mother is aa, husband are aa
- Father is AA, mother is aa, and husbands are AA
- Father is aa, mother is Aa, husband Aa
- Father is AA. mother AA, one husband Aa and second husband aa.
Answer: 4. Father is AA. mother AA, one husband Aa and second husband aa.
Question 27. In sweet pea, genes C and P are necessary for colour in flowers. The flowers are white in the absence of either or both the genes. What will be the percentage of coloured flowers in the offspring of the cross Ccpp x ccPp?
- 25%
- 50%
- 75%
- 100%.
Answer: 1. 25%
Question 28. Polymorphism is mainly due to :
- Monogenic inheritance
- Polygenic inheritance
- Both of the above
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Both of the above
Chapter-wise MCQs On Genetics And Heredity NEET
Question 29. Continuous genetic variations are produced by :
- Independent assortment
- Mutations
- Climatic changes
- Interspecific hybridization.
Answer: 2. Mutations
Question 30. The alleles that produce independent effects in heterozygous conditions are called:
- Supplementary alleles
- Codominant alleles
- Epistatic genes
- Complementary alleles.
Answer: 1. Supplementary alleles
Question 31. In the following pedigree chart, the mutant trait is shaded black. The gene responsible for the trait is:
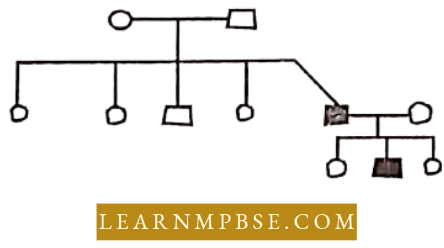
- Dominant and sex-linked
- Dominant but autosomal
- Recessive and sex-linked
- Recessive and autosomal.
Answer: 2. dominant but autosomal
Chapter-wise MCQs On Genetics And Heredity NEET
Question 32. In the given pedigree, indicate whether the shaded symbols indicate a dominant or recessive allele.
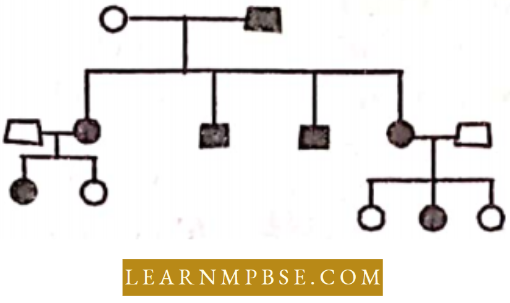
- Dominant
- Recessive
- Codominant
- It can be recessive or dominant.
Answer: 3. recessive
Question 33. A dominant lethal gene Is that which
- Allows nil organotin to survive and to tepfodiite
- Allows an organism to sin vibe lull does not allow il to reproduce
- Suppress the sex of the holder organism
- Kills the organism in which it is present.
Answer: 4. Kills the organism in which it is present.
Question 34. In humans, an example of a sex-linked trail is:
- Sickle-cell anaemia
- Curly hair
- Down’s syndrome
- Data are insufficient.
Answer: 1. Sickle-cell anaemia
Question 35. If the cell of an organism heterozygous for two pairs of genes represented by Aa, undergoes meiosis, then the possible genotypic combination of gametes will be:
- AB, aB, Ah. ab
- All, ab
- Aa, Bb
- Data are insufficient.
Answer: 3. Aa, Bb
Non-Mendelian Inheritance NEET MCQs
Question 36. To determine whether variations of a character in a population were genetically controlled, the most appropriate procedure will be lo :
- Measure the variations and see if they are continuous or discontinuous
- Crossing individuals of both extremes and sec if the offspring and parents show the same range of variations
- Count the chromosomes and find out the variations in their number in the population
- Examine the DNA of F| progeny in a cross between AA and aa.
Answer: 2. Crossing individuals of both extremes and sec if the offspring and parents show the same range of variations
Question 37. If Mendel had studied the 7 traits using a plant with 12 chromosomes instead of 14, in what way would his interpretation have been different?
- He could have mapped the chromosome
- He would have discovered blending or incomplete dominance
- He would not have discovered the law of independent assortment
- He would have discovered sex linkage.
Answer: 3. He would not have discovered the law of independent assortment
Biology MCQs with Answers Question 38. How many different types of genetically different gametes will be produced by a heterozygous plant having the genotype: AAB b Cc?
- Nine
- Two
- Four
- Six.
Answer: 3. Four
Question 39. Human skin colour is controlled by several gene pairs. Let us assume here that there are just three gene pairs on different chromosomes and that for each pair there are two alleles – an incompletely dominant one that codes for melanin deposition and an incompletely recessive one that codes for no melanin deposition. If a very dark-skinned person marries a very light-skinned woman, what will be the chance that their offspring will have very dark skin?
- 0
- 1/4
- 5/8
- 9/64
- 3/64.
Answer: 1. 0
Question 40. The F2 generation offspring in a plant showing incomplete dominance, exhibits’
- Variable genotypic and phenotypic ratios
- A genotypic ratio of 1: 1
- A phenotypic ratio of 3:1
- Similar phenotypic and genotypic ratios of 1: 2: 1.
Answer: 4. Similar phenotypic and genotypic ratios of 1: 2: 1.
Non-Mendelian Inheritance NEET MCQs
Question 41. Two pea plants were subjected to cross-pollination. Of the 183 plants produced in the next generation, 94 plants were found to be tall and 89 plants were found to be dwarf. The genotypes of the two parental plants are likely to be :
- TT and It
- Tt and Tt
- Tt and tt
- TT and TT.
Answer: 3. Tt and tt
Question 42. Gametes are never hybrid? It is a statement of the law of:
- Dominance
- Segregation
- Independent assortment
- Random fertilization.
Answer: 2. Segregation
Biology MCQs with Answers Question 43. Which is correct about the traits chosen by Mendel?
- The terminal pod is the dominant
- The constricted pod is the dominant
- Green coloured pod is the dominant
- Tall plants are recessive.
Answer: 3. Green coloured pod is the dominant
Question 44. In a certain plant, red fruit (R) is dominant over yellow fruit (r) and tallness (T) is dominant over shortness (t). If a plant with an RRTt genotype is crossed with a plant rrtt genotype, what will be the percentage of tall plants with red fruits in the progeny?
- 50%
- 100%
- 75%
- 25%
Answer: 1. 50%
Question 45. Mendel obtained wrinkled seeds in pea due to the deposition of sugars instead of starch. It was due to which enzyme?
- Amylase
- Invertase
- Dataset
- Absence of starch branching
Answer: 4. Absence of starch branching
Question 46. The ratio of complementary genes is :
- 9 : 3: 4
- 12:3:1
- 9 : 3 : 3: 4
- 9:7
Answer: 4. 9:7
Question 47. When dominant and recessive allele express itself together, it is called :
- Co-dominance
- Dominance
- Amphidominance
- Pseudodominance.
Answer: 1. Co-dominance
Question 48. What is correct for blood group ‘O’?
- No antigens but both a and b antibodies are present
- An Antigen and b antibody
- Antigen and antibody are both absent.
- A and B antigens and a, b antibodies.
Answer: 1. No antigens but both a and b antibodies are present
Question 49. Sickle cell anaemia induces to:
- Change of Amino Acid in α-chain of haemoglobin
- Change of Amino Acid in β-chain of Haemoglobin
- Change of Amino Acid in both a or β chain of Haemoglobin
- Change of Amino Acid either a or β chain of Haemoglobin
Answer: 2. Change of Amino Acid in the β-chain of Haemoglobin
Question 50. Independent assortment of genes does not take place when :
- Genes are located on homologous chromosomes
- Genes are linked and located on the same chromosome
- Genes are located on non-homologous chromosomes
- All the above.
Answer: 2. Genes are linked and located on the same chromosome
