Class 11 Chemistry Hydrogen Question And Answers
Question 1. Name the isotopes of hydrogen and state their mass ratio.
Answer:
The three isotopes of hydrogen are:
Protium (H or H),
Deuterium (4H or D) and
Tritium (4H or T).
Their mass ratio is protium: deuterium: tritium =1:2:3.
Question 2. What is the source of solar energy?
Answer:
The main source of solar energy is the given nuclear fusion reaction: 4H —> 2He + 2+1e° (positron) + Energy
Question 3. Although Fe is placed above hydrogen in the electrochemical series, dihydrogen is not obtained by its reaction with nitric acid. Explain with reasons.
Answer:
HNO3 being a strong oxidizing agent oxidizes dihydrogen into the water and itself gets reduced to nitrogen dioxide;\(\mathrm{Fe}+6 \mathrm{HNO}_3 \rightarrow \mathrm{Fe}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_3+3 \mathrm{NO}_2+3 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)
Question 4. Give an example and formula of a compound which on electrolysis liberates dihydrogen at the anode.
Answer:
Calcium hydride (CaH2) on electrolysis, liberates dihydrogen at the anode.
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |
Hydrogen Class 11 Chemistry Notes
Question 5. How can one prepare H2 gas from water by using a reducing agent?
Answer:
Reaction between metals such as Na or. JC (strong reducing agents) and water produce hydrogen gas.
⇒ \(2 \mathrm{Na}+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{H}_2 \uparrow\)

Question 6. Name two compounds, in one of which hydrogen is in +1 and in the other in -1 oxidation state.
Answer:
In HCl, hydrogen is in a +1 oxidation state and in NaH it is in a -1 oxidation state.
Question 7. Holli dihydrogen and carbon monoxide burn in the air with blue flame. How will you distinguish between them?
Answer:
Dihydrogen burns with a blue flame in the air to form water vapor which turns white anhydrous CuSO4 into hydrated copper sulfate (CuSO4-5H2O). However, carbon monoxide on combustion forms CO2 which does not bring about any change in CuSO4.
Question 8. What characteristics do you expect from an electron-deficient and an electron-rich hydride with respect to their structures?
Answer:
Electron-deficient hydrides function as electron acceptors, serving as Lewis acids, while electron-rich hydrides operate as electron donors, acting as Lewis bases. B2H6 functions as a Lewis acid, whereas NH3 acts as a Lewis base.
Question 9. Why the boiling point of HF is higher than that of other hydrogen halides?
Answer:
Due to the formation of strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding, the boiling point of HF is higher than that of other hydrogen halides.
Hydrogen Class 11 Chemistry Notes
Question 10. How can you separate H2 or D2 from He?
Answer:
Palladium, heated to a high temperature, is cooled in a helium environment mixed with hydrogen or deuterium. As a result, substantial quantities of H2 or D2 are absorbed by palladium, whereas He is not. Upon heating palladium, occluded H2 or D2 gels are released as free hydrogen or deuterium.
Question 11. Why ionic or salt-like hydrides are used to dry organic solvents?
Answer:
Ionic or salt-like hydrides are used to dry organic solvents because they readily react with water to form the corresponding metal hydroxide along with the evolution of H2O as- The solvent is then separated from the metallic hydroxide by distillation.
Question 12. Why concentration of D20 increase when electrolysis of water is carried out for a long period of time?
Answer:
Electrolysis of H20 occurs at a faster rate than D2O because the bond dissociation energy of the O—H bond is greater than that of the O—D bond. So, electrolysis of ordinary water for a prolonged period of time results in an increase in the concentration of D2O.
Question 13. How would you prepare deuterium peroxide (D2O2)?
Answer:
Deuterium peroxide (D2O2) can be prepared by the reaction between barium peroxide (BaO2) and deuterosulphuric acid (D2SO4).
⇒ \(\mathrm{BaO}_2+\mathrm{D}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \rightarrow \mathrm{BaSO}_4+\mathrm{D}_2 \mathrm{O}_2\)
Question 14. How will you prepare deuteroammonia (ND3) from N2?
Answer: Magnesium burns in nitrogen to produce magnesium nitride which further reacts with D2O to produce ND3 (deuteroammonia)
⇒ \(\begin{gathered} 3 \mathrm{Mg}+\mathrm{N}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{Mg}_3 \mathrm{~N}_2 \\ \mathrm{Mg}_3 \mathrm{~N}_2+6 \mathrm{D}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow 3 \mathrm{Mg}(\mathrm{OD})_2+2 \mathrm{ND}_3 \end{gathered}\)
Question 15. How will you prove that hypophosphorous acid (H3PO2) is a monobasic acid?
Answer:
When H3PO2 is treated with D2O, only one of its hydrogen atoms is replaced by D. So, it can be said that only one H-atom remains attached to O-atom in hypophosphorous acid (H3PO2). Therefore, it is a monobasic acid.
Mpbse Class 11 Chemistry Hydrogen Solutions
Question 16. Sodium chloride is less soluble in heavy water than ordinary water—why?
Answer:
As the dielectric constant of D2O is less than that of H2O, NaCl (sodium chloride) is less soluble in heavy water than ordinary water. +
Question 17. Explain why the water obtained after passing hard water through cation exchange resins is acidic.
Answer:
When hard water traverses an organic ion exchange resin, the resultant water is acidic due to the exchange of all metal ions in the water with H+ ions from the resin. Consequently, the resultant water is devoid of cations and possesses a high concentration of H+ ions. The water converts blue litmus paper to crimson.
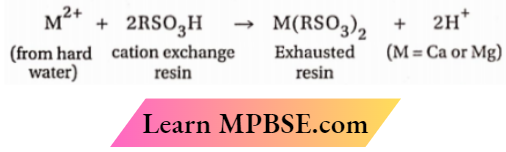
Question 18. A sugar solution prepared in distilled water is passed successively through cation and anion exchange resins. What will be the taste of the collected water and why?
Answer:
Ion-exchange resins cannot remove sugar(non-electrolyte) from water. Therefore, when a sugar solution is passed successively through cation and anion exchange resins, after being collected tastes sweet.
Question 19. The hardness of the water in a tube well is 300 ppm. What do you mean by this statement?
Answer:
The statement means that in million parts by mass of the sample of water from the tube, well contains salts causing its hardness which are equivalent to 300 parts by mass of calcium carbonate.
Question 20. Will the water obtained by passing hard water through anion exchange resin, form lather with soap? Why?
Answer:
As the sample of water is not free from Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions, it will not form a lather with soap easily.
Question 21. A sample of water contains MgS04 and urea. How can they be eliminated easily?
Answer: They can be eliminated by a simple distillation method.
Hydrogen Important Questions Class 11
Question 22. It is better to preserve H202 in a polythene bottle than in a glass bottle—why?
Answer:
The decomposition of H2O2 is accelerated by the presence of glass, sunlight, and basic substances. So, H2O2 is preserved in polythene bottles rather than glass bottles.
Question 23. What do you understand by the expression ’30 volume H2O2 solution’?
Answer:
’30 volume H2O2 solution’ means that 1 mL of that solution yields 30 mL of oxygen at STP as a result of its complete decomposition.
Question 24. What do you mean by 20% H2O2 solution?
Answer:
20% H2O2 solution means that momT. of that solution contains 20g of H2O2.
Question 25. Calculate the percentage strength of 6.588 volume H2O2.
Answer:
Percentage strength of solution \(=\frac{\text { volume strength } \times 34}{11.2 \times 10}\)
\(=\frac{6.588 \times 34}{11.2 \times 10}=1.99\)