MP Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 2 Whole Numbers
Natural Numbers
The counting numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, … are called natural numbers. The collection of natural numbers is denoted by Ni.e. N=(1,2,3,4,…)
Predecessor If we subtract 1 from any natural number, then we get the predecessor of that number.
e.g. 16 – 1 = 15 i.e. 15 is the predecessor of 16.
Successor If we add 1 to any natural number, then we get the successor of that number.
e.g. 10 + 1 = 11 i.e. 11 is the successor of 10.
Note it Every natural number has a successor and every natural number except 1 has a predecessor because 1 is the smallest natural number. There is no last number i.e. we have infinite natural numbers.
Example 1. Write predecessor and successor of the following numbers
(1) 9
(2) 43
(3) 297
(4) 2901
Solution.
(1) Predecessor of 9 = 9 – 1 = 8
and successor of 9 = 9 + 1 = 10
(2) Predecessor of 43 = 43 – 1 = 42
and successor of 43 = 43 + 1 = 44
(3) Predecessor of 297 = 297 – 1 = 296
and successor of 297 = 297 + 1 = 298
(4) Predecessor of 2901 = 2901 – 1 = 2900
and successor of 2901 = 2901 + 1 = 2902
Read and Learn More MP Board Class 6 Maths Solutions
Example 2. Write
(1) a single-digit predecessor of a two-digit number.
(2) a three-digit successor of a two-digit number.
Solution.
(1) 9, which is a predecessor of 10.
(2) 100, which is a successor of 99.
Example 3. Write the next four natural numbers after 6999.
Solution. The next four natural numbers after 6999 are
6999 + 1 = 7000, 7000 + 1 = 7001,
7001 + 1 = 7002, 7002 + 1 = 7003
i.e. 7000, 7001, 7002 and 7003.
MP Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 2 Whole Numbers
The natural numbers along with zero form the collection of whole numbers. The collection of whole numbers is denoted by Wi.e. W = {0,1,2,3,4,…}
All natural numbers are whole numbers but all whole numbers are not natural numbers.
Note it Every whole number has a successor and every whole number except O has a predecessor. There is no last whole number i.e. we have infinite whole numbers.
Example 4. Write the whole number whose successor is 79500.
Solution. The required whole number = Predecessor of
79500 = 79500 – 1 = 79499
Example 5. Write the whole number whose predecessor is 35999.
Solution. The required whole number=Successor of 35999 = 35999 + 1 = 36000
Example 6. Find the number whose successor is 5 more than 364.
Solution. Let the successor be x.
x = 364 + 5 = 369
Hence, the required number is 369-1=368
Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Questions
Example 7. Write the four whole numbers occuring just before 1001.
Solution. The four whole numbers just before 1001 are
1001 – 11000, 1000 – 1 = 999,
999 – 1998, 998 – 1 – 997
i.e. 1000, 999, 998 and 997.
Example 8. How many whole numbers are there between 19 and 33?
Solution. Whole numbers between 19 and 33 are
20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32
Hence, the total number of whole numbers between 19 and 33 is 13.
Example 9. How many 3-digit numbers are there between 88 and 702?
Solution. 3-digit numbers between 88 and 702 are
100, 101, 102,…, 701.
Number of these numbers = 701 – 99 = 602
Note it in the above list, 701 is included and 99 is not included.
Example 10. Write the number which is product of successor and predecessor of 1001.
Solution. Successor of 1001 = 1001 + 1 = 1002
Predecessor of 1001 = 1001 – 1 = 1000
∴ Product of successor and predecessor of 1001 = 1002 × 1000 = 1002000
Example 11. Write all the whole numbers between 99 and 199 which do not change if the digits are written in reverse order.
Solution. All the whole numbers between 99 and 199 which do not change, if the digits are written in reverse order, are 101, 111, 121, 131, 141, 151, 161, 171, 181, 191.
Number Line
To represent whole numbers on a number line, draw a line and mark a point on it and label it 0 (zero).
Starting from 0 (zero) on the line, mark out the equal intervals (of unit length) to the right of 0 and label them as 1, 2, 3,…. Thus, the distance between these points labelled as 0, 1,… is called as unit distance.
In this way, you can go to any whole number on the right in this manner. Thus, we represent whole numbers on the number line as shown below

Note it Distance between 16 and 17 is same as distance between 35 and 36 which is one unit.
MP Board Class 6 Maths Solutions
Comparison of Two Whole Numbers
On the number line, the number on the right of the other number is the greater number and the number on the left of the other number is the smaller number.
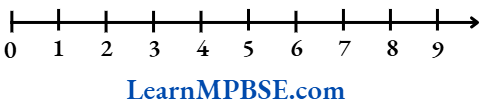
On the number line, 7 is on the right of 5. So, 7 is greater than 5 i.e. 7 > 5.
The number 6 lies on the left of 9. So, 6 is smaller than 9 i.e. 6 < 9.
Example 12. In each of the following pair of numbers, state which whole number is on the right of the other number on the number line. Also write them with the appropriate sign >,<) between them
(1) 627, 613
(2) 157, 168
(3) 6123, 5674
(4) 113295, 1132956
Solution. (1) On the number line, whole number 627 is on the right of 613 because 627 is greater than 613
i.e. 627 > 613
(2) On the number line, whole number 168 is on the right of 157 because 157 is less than 168
i.e. 157 < 168
(3) On the number line, whole number 6123 is on the right of 5674 because 6123 is greater than 5674
i.e. 6123 > 5674
(4) On the number line, whole number 1132956 is on the right of 113295 because 113295 is less than 1132956
i.e.113295 < 1132956
MP Board Class 6 Maths Solutions
Example 13. Represent the successor and the predecessor of 12 and 7 respectively on the number line.
Solution. Place the successor of 12 on the number line.

12 + 1 = 13
Place the predecessor of 7 on the number line.
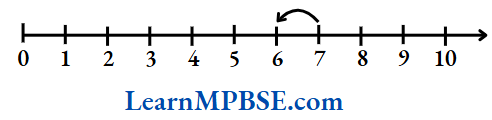
So, 7 – 1 = 6
Addition on the Number Line
When we add any number to a given number, we move towards right on the number line.
e.g. Let us add 3 and 5.
We start from 3 on the number line and make 5 jumps to the right by unit distance each. Then, we reach at 8.
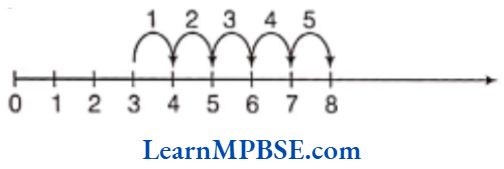
So, 3 + 5 = 8
Subtraction on the Number Line
When we subtract any number from a given number, we move towards left on the number line.
e.g. Let us find 6 – 2.
We start from 6 on the number line and make 2 jumps to the left by unit distance each. Then, we reach at 4.
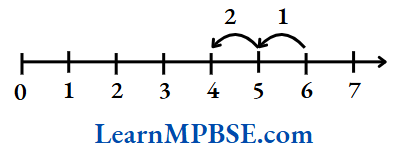
So, 6 – 2 = 4
Multiplication on the Number Line
For multiplication, we make jumps of equal distance starting from origin.
e.g. Let us find 5×3.
We start from 0 (zero) on the number line and move 5 units at a time. After 3 such moves, we reach at 15.
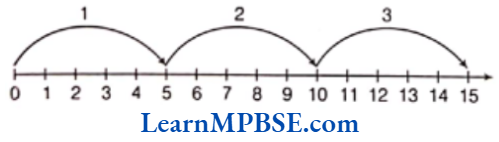
So, 5 x 3 = 15
MP Board Class 6 Maths Solutions
Example 14. Find the value of the following on the number line.
(1) 3 + 6
(2) 8 + 2
(3) 6 – 3
(4) 6 x 3
(5) 2 x 5
Solution. (1) To find 3 + 6
Let us start from 3. Since, we have to add 6 to this number, we make 6 jumps to the right of 3. Each jump being equal to 1 unit. After six jumps, we reach at 9. 1 2 3 4 5 6
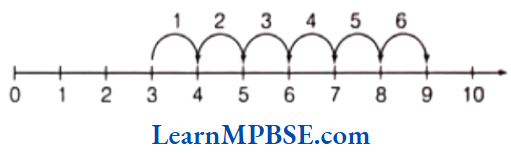
So, 3 + 6 = 9
(2) To find 8 + 2
Let us start from 8. Since, we have to add 2 to this number, we make 2 jumps to the right of 8. Each jump being equal to 1 unit. After two jumps, we reach at 10.

So, 8 + 2 = 10
(3) To find 6 – 3
Let us start from 6 and make 3 equal jumps to the left of 6. Each jump is equal to 1 unit. Now, we reach at 3.
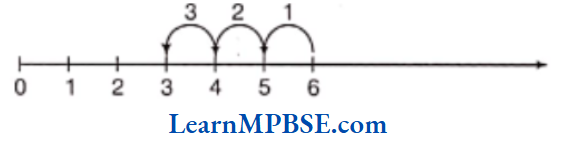
so, 6 – 3 = 3
(4) To find 6 x 3
We have to multiply 6 by 3 i.e. 6 units x 3 (or 6 units 3 times).
Let us start from 0, move 6 units to the right of 0, 31 times.

After moving 3 such moves, we reach at 18.
So, 6 x 3 = 18
(5) To find 2 x 5
We have to multiply 2 by 5 i.e. 2 units x5 (or 2 units 5 times).
Let us start from 0, move 2 units to the right of 0, 5 times.
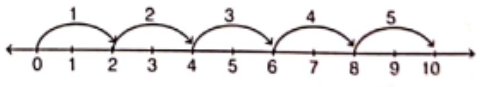
After moving 5 such moves, we reach at 10.
So, 2 × 5 = 10
Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Questions
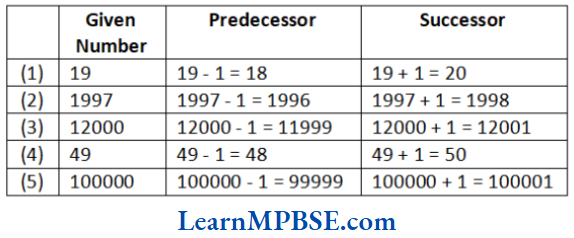
Question 1. Write the predecessor and successor of 19, 1997, 12000, 49 and 100000.
Solution.
Question 2. Is there any natural number that has no predecessor?
Solution. Yes, the smallest natural number I has no predecessor because predecessor of 1 is (1-1=0) zero and zero is not a natural number.
Question 3. Is there any natural number which has no successor? Is there a last natural number?
Solution. No, there is no natural number which has no successor because each natural number has a successor.
e.g. Successor of 4=4+1=5 Successor of 5=5+1=6 and so on.
Also, there is no last natural number because natural number starts from 1 and goes upto infinite.
Question 4. Are all natural numbers also whole numbers?
Solution. Yes, all the natural numbers are also whole numbers.
Question 5. Are all whole numbers also natural numbers?
Solution. No, all whole numbers are not natural numbers because 0 is a whole number but it is not a natural number.
Question 6. Which is the greatest whole number?
Solution. Since, every whole number has a successor. So, there is no greatest whole number.
Question 7. Find the sum, using the number line.
(1) 4+5
Solution. (1) To find 4 + 5
Let us start from 4. Since, we have to add 5 to this number, we make 5 jumps to the right of 4. Each jump being equal to 1 unit. After five jumps, we reach at 9.
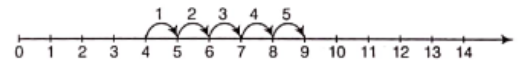
∴ 4 + 5 = 9
Question 8. Find the difference, using the number line.
(1)8-3
Solution. (1) To find 8 – 3
Let us start from 8 and make 3 equal jumps to the left of 8. Each jump is equal to 1 unit. Now, we reach at 5.

∴ 8 – 3 = 5
Question 9. Find using the number line.
(1) 2×6
Solution. (1) To find 2×6
We have to multiply 2 by 6
i.e. 2 units x 6 (or 2 units 6 times).
Let us start from 0, move 2 units to the right of 0.
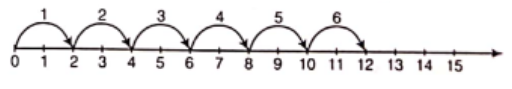
After making 6 such moves, we reach at 12.
∴ 2 × 6 = 12
MP Board Class 6 Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Exercise 2.1
Question 1. Write the next three natural numbers after 10999.
Solution. 11000, 11001 and 11002.
Question 2. Write the three whole numbers occurring just before 10001.
Solution. 10000, 9999 and 9998.
Question 3. Which is the smallest whole number?
Solution. The smallest whole number is zero (0).
Question 4. How many whole numbers are there between 32 and 53?
Solution. Whole numbers between 32 and 53 are as follows
33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51 and 52.
Hence, the total number of whole numbers between 32 and 53 is 20.
Mp Board Class 6 Maths Important Questions
Question 5. Write the successor of
(1) 2440701
(2) 100199
(3) 1099999
(4) 2345670
Solution. The successor of given numbers are as follows
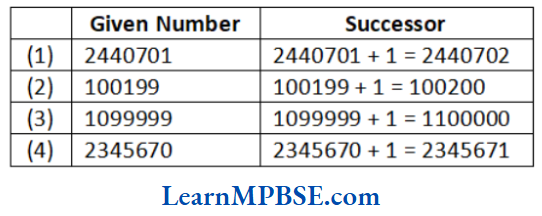
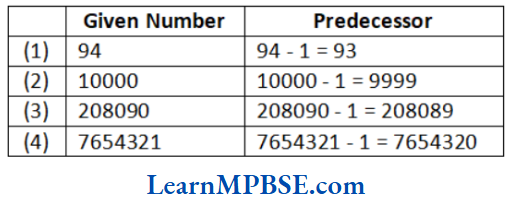
Question 6. Write the predecessor of
(1) 94
(2) 10000
(3) 208090
(4) 7654321
Solution. The predecessor of given numbers are as follows
Question 7. In each of the following pairs of numbers, state which whole number is on the left of the other number on the number line. Also, write them with the appropriate sign (>, <) between them.
(1) 530, 503
(2) 370, 307
(3) 98765, 56789
(4) 9830415, 10023001
Solution.
On the number line, whole number 503 is on the left of 530 because 530 is greater than 503 i.e. 530 > 503.
On the number line, whole number 307 is on the left of 370 because 370 is greater than 307 i.e. 370 > 307.
On the number line, whole number 56789 is on the left of 98765 because 98765 is greater than 56789 i.e. 98765> 56789.
On the number line, whole number 9830415 is on the left of 10023001 because 9830415 is less than 10023001 i.e. 9830415 < 10023001.
Mp Board Class 6 Maths Book Pdf
Question 8. Which of the following statements are true (T) and which are false (F)?
Zero is the smallest natural number.
400 is the predecessor of 399.
Zero is the smallest whole number.
600 is the successor of 599.
All natural numbers are whole numbers.
All whole numbers are natural numbers.
The predecessor of a two-digit number is never a single digit number.
1 is the smallest whole number.
The natural number 1 has no predecessor.
The whole number 1 has no predecessor.
The whole number 13 lies between 11 and 12.
The whole number 0 has no predecessor.
The successor of a two-digit number is always a two-digit number.
Solution.
- False, because zero is not a natural number. It is a whole number.
- False, because predecessor of 399 is 399-1=398.
- True, because whole numbers start with zero (0).
- True, because successor of 599 is 599 + 1 = 600.
- True.
- False, because 0 is not a natural number.
- False, because predecessor of 10 is 10 – 1 = 9, which is a single digit number.
- False, because 0 is the smallest whole number.
- True, because, if we subtract 1 from 1, then we get 0 (1-10), which is not a natural number.
- False, because predecessor of 1 is 1-1=0 and 0 is a whole number.
- False, because 13 is greater than 12.
- True.
- False, because successor of two-digit number 99 is 99+1=100, which is a three-digit number.
MP Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. The product of non-zero whole number and its successor is always
- an even number
- an odd number
- a prime number
- divisible by 3
Answer. 1. an even number
Question 2. The whole number which has no predecessor is
- 1
- 0
- 2
- 3
Answer. 2. 0
Question 3. The predecessor of 1 lakh is
- 99000
- 99999
- 999999
- 100001
Answer. 2. 99999
Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Solutions
Question 4. The successor of 1 million is Competency Based Question
- 2 million
- 1000001
- 100001
- 10001
Answer. 2. 1000001
Question 5. The product of two whole numbers is always a
- natural number
- even number
- odd number
- None of the above
Answer. 4. None of the above
Question 6. The greatest number which always divides the product of the predecessor and successor of an odd natural number other than 1, is
- 6
- 4
- 16
- 32
Answer. 2. 4
Question 7. Which of the following is right side to 10 on the number line?
- 8
- 9
- 18
- 0
Answer. 3. 18
MP Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Questions
Question 1. Assertion (A) 1 is a natural number.
Reason (R) Every natural number is a whole number.
(a) A is false but R is true.
(b) A is true but R is false.
(c) Both A and R are true.
(d) Both A and R are false.
Answer. c. Both A and R are true.
Question 2. Assertion (A) 70 is greater than 50.
Reason (R) 70 is the left side to 50 on the number line.
(a) A is false but R is true.
(b) A is true but R is false.
(c) Both A and R are true.
(d) Both A and R are false.
Answer. b. A is true but R is false.
Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Mp Board Solutions
Question 3. Assertion (A) 27 is the successor of 26.
Reason (R) Any natural number, you can add 1 to that number and get the next number i.e. you get its successor.
(a) A is false but R is true.
(b) A is true but R is false.
(c) Both A and R are true.
(d) Both A and R are false.
Answer. c. Both A and R are true.
MP Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Fill in the Blanks
Question 1. 300 is the predecessor of ……
Solution. 301
Question 2. 450 is the successor of ……
Solution. 449
Question 3. ……… is the successor of the largest 3-digit number.
Solution. 1000
Question 4. The smallest 6-digit natural number ending in 5 is …….
Solution. 100005
Question 5. Addition corresponds to the …… on the number line.
Solution. Right
MP Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 2 Whole Numbers True/False
Question 1. Successor of 1-digit number is always a 1-digit number.
Solution. False
Question 2. Successor of 3-digit number is always a 3-digit number.
Solution. False
Question 3. Every whole number except zero is the successor of another whole number.
Solution. True
Question 4. Sum of two whole numbers is always less than their product.
Solution. False
Question 5. There is a whole number which when added to a whole number, gives the second whole number.
Solution. True
MP Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Match the Columns
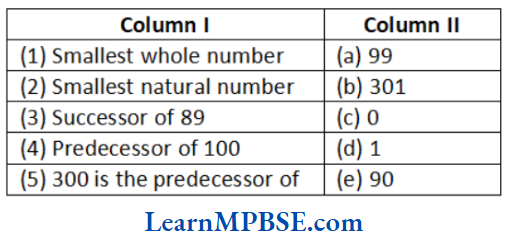
1. (1) → (c), (2) → (d), (3) → (e), (4) → (a), (5) → (b)
MP Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. How many natural numbers are there between 60 and 72?
Solution. Given numbers are 60 and 72.
Hence, natural numbers between 60 and 72
= (72 – 60) – 1 = 11
Question 2. Write the smallest natural number.
Solution. 1 is the smallest natural number.
Question 3. Write the two immediate predecessors of 2945.
Solution. Given number is 2945.
Immediate predecessors are 2944 and 2943
Question 4. Write the three immediate successors of 3956.
Solution. Given number is 3956.
So, three immediate successors of 3956 are 3957, 3958 and 3959.
Mp Board Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Solutions
Question 5. Write a double digit predecessor of three-digit number.
Solution. 99 is a double digit predecessor of 100.
Question 6. Write a triple digit successor of two-digit number.
Solution. 100 is a triple digit successor of 99.
Question 7. Write two whole numbers occuring just before 1001.
Solution. 1000 and 999.
Question 8. Write three whole numbers occuring just after 1000.
Solution. 1001, 1002, 1003
Question 9. Write down the two whole number which are on the right of 3 and on the left of 6.
Solution. 4 and 5 are right of 3 and left of 6.
Question 10. Write the next three consecutive whole numbers of 89.
Solution. The next three consecutive whole numbers of 89 are 90, 91 and 92.
MP Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Write the predecessor of the following
(1) 96
(2) 9998
Solution. (1) Predecessor of 96 = 96 – 1 = 95
(2) Predecessor of 9998 = 9998 – 1 = 9997
Question 2. Determine the sum of the four numbers as given below
- Successor of 32
- Predecessor of 49
- Predecessor of the predecessor of 56
- Successor of the successor of 67
Solution. Successor of 32 = 32 + 1 = 33
Predecessor of 49 = 49 – 1 = 48 Predecessor of 56 is 55
So, predecessor of the predecessor of 56 = 55 – 1 = 54
Successor of 67 is 68
So, successor of the successor of 67 = 68 + 1 = 69
Hence, the sum of four numbers = 33 + 48 + 54 + 69 = 204
Question 3. Write the predecessor of the sum of 345,287 and 368.
Solution. Sum of 645, 287 and 368 is 1300, whose predecessor
= 1300 – 1 = 1299
Question 4. Write the successor of the difference of 145 and 46.
Solution. Difference of 145 and 46 is 99, whose successor
= 99 + 1 = 100
Mp Board Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Solutions
Question 5. Find the number whose predecessor is 3 more than 456.
Solution. Let the predecessor be x.
x = 456 + 3 = 459
The required number is 459 + 1 = 460
Question 6. Find the whole number x, when
(1) x – 9 = -9
(2) x – 0 = 1
Solution. (1) x – 9 = -9
⇒ x = -9 + 9
⇒ x = 0
(2) x – 0 = 1
⇒ x = 1
Question 7. Write all the whole numbers between 200 and 300 which do not change if the digits are written in reverse order.
Solution. All the whole numbers between 200 and 300 which do not change, if the digits are written in reverse order are
202, 212, 222, 232, 242, 252, 262, 272, 282, 292
Question 8. Find the number whose successor is 3 more thatn 450.
Solution. Let the number be x.
Then, x + 1 = 450 + 3
x = 452
∴ The number = 452
Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Questions
Question 9. In each of the following pairs of numbers, state which whole number is to the left of the other on the number line. Use appropriate symbol (> or <).
(1) 497, 495
(2) 3059, 3096
Solution. We know that the number which lies to the right of other is a greater number.
(1) 495 lies to the left of 497, so, 497 > 495
(2) 3059 lies to the left of 3096, so 3059 <3096
Question 10. There are two whole numbers which when multiplied by itself gives the same number. What are they?
Solution. If we multiply 0 by itself, it gives same number i.e. 0 x 0 = 0, and similarly, 1 x 1 = 1.
∴ The required whole numbers are 0 and 1.
