NEET Biology Nature And Scope
You and alive Being a part of the living world is a wondrous and complicated thing. Biology is the picnic that deals with living things (bios = life and the logie or ology = science of study) .
- Biologists have a tremendous variety of living things and life activities from which to choose as they select their area of study.
- In doing their work, they are like dctecto cs trying to solve a mystery. They try to be observant and alert to new ways of looking at things.
- Lamarck and Trcviranus (1801) were the first to use the term Biology. The branch of biology which deals with the study of animals is called zoology (zoion = an animal; logie or ology = science of study).
- Aristotle is regarded as the Father of Zoology. The study of plants is called Botany (butane = herb). Theophrastus (370-287 B.C.) prepared a list of 500 plants and is called the “Father of Botany”. Pure Science. In pure science research is conducted for the sake of knowledge itself.
- Applied science. It makes practical use of pure science. For example, much basic research has been conducted in recent years on the effects of radiation on living matter.
- It remained for applied science to make use of this knowledge in destroying tissue employing radiation.
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
Nature And Scope Of Biology NEET Notes
Different branches of biology deal with various aspects such as morphology deals with an accurate description of the form and external structure, histology is related to the detailed study of tissue and anatomy is the study of internal structures. Cell biology is the complete study of the structural and functional aspects of a cell.
NEET Biology Nature And Scope Sub Divisions
- Anatomy-It is a branch of science which deals with the study of the internal structure of an organism as revealed by dissection.
- Arthrology- Study of joints.
- Agriology- Study of customs of primitive man.
- Apliidology- Study of flying organisms about other flying objects.
- Agronomy – The management of farms and the science of crop production is called agronomy.
- Anthropology – The science of man and mankind including his physical and mental constitution, cultural development and social conditions of present and past is called anthropology.
- Anthology- It is the study of flowers.
- Agrostology- It is the study of grasses.
- Acarology- Study of order acarina comprising ticks and mites.
- Aerology- The study of ticks and mites is called aerology.
- Aerobiology- Study of airborne organisms and structures such as spores etc. and their distribution.
- Agrobiology – It is the quantitative science of plant life and plant nutrition.
- Agrology – It is the soil science dealing with the production of crops.
- Andrology – It is die study of male reproductive organs.
- Aranrology – It is the study of spiders.
- Arboneulture – The cultivation of trees and shrubs is called arboriculture.
- Agriculture-li dc. iN with the cultivation of crops nml the improved method of farming.
- Actinobiology – Study of radiation effect on living organisms. Angiologx – Studs of Mood vessels.
- Bioinformatics – It is a branch of science concerned with the development and application of computing stem and technology to make novel observations about biological processes.
- Biotechnology- It is the controlled use of biological agents such as microorganisms or cellular components for beneficial use.
- Breeding biology – It is the art and science of changing and improving the heredity of plants and animals.
- Biochemistry- The study of the chemical aspect of living organisms is termed biochemistry.
- Batmchology- It is the study of frogs.
- Bioclimatology- The study of climatic effects on biological processes and organisms.
- Biometrology- Study of effects of atmospheric change on living organisms.
- Bionics- It is the study of solving by humans, and animals and its technical applications.
- Bacteriology- It is the study of bacteria.
- Bryology- It is the study of bryophytes.
- Computational biology – Systematic development, application and validation of computational hardware and software solutions for building simulation models of biological systems.
- Cytology- It deals with the study of the structure and functions of cells.
- Cell Biology – The study of structure and functions, reproduction, energy dynamics, transport mechanism and life history of cells is called cell biology.
- Cryobiology- It is the study of the effect of low temperature on living organisms.
- Chirology-It deals with communication systems with deaf and mute by sign language
- Chromatology- Study of pigments.
- Ctcnology- Study of acquired characteristics of organisms.
- Chorology- Biogeography.
- Chronobiology- Study of the biology of cyclic physiological phenomena.
- Cosmology- Science of structure and evolution of the universe.
- Cnidology- Study of coelenterates (Cnidarians)
- Conchology- Study of shells.
- Chondrology- Study of cartilage.
- Craniology- Study of skull.
- Cardiology- Study of heart.
Nature And Scope Of Biology NEET Study Material
- Dysteleology- It is the study of the appearance of vestigial organs due to evolution.
- Dendrology biology- It deals with the study of processes by which organisms undergo progressive and orderly changes in structure as well as physiology during their entire life cycle.
- Dermatology- Study of skin.
- Developmental morphology- It deals with the developmental aspects of plants.
- Dactylogy- Communication system for the deaf using signs made of fingers.
- Demecology – Population ecology. It is the study of the population with its environment.
- Demography- It is the study of population.
- Dendrology- It is the study of trees and shrubs also called xylology.
- Desmology- Study of structures and anatomy of ligaments.
- Evolution- It is the branch of biology which deals with the study of the descent of present-day complex living organisms (plants and animals) from the living forms of the past.
- Embryology deals with the study of the stages of an organism that occur immediately after fertilization.
- Ecology – It is the study of inter-relationships between living organisms and their environment.
- Aetiology- Study of annual behaviour and conditions of animals.
- Eugenics – It is the science dealing with the improvement of the human race through the application of the law” of heredity.
- Entomology- Study of insects.
- Exobiology- The study of the kind of life that may exist in outer space is called exobiology.
- Aetiology- It is the study of the causes of diseases.
- Exobiology- Study of adaptations with habitat.
- Ecophysiology- Physiological adaptations in response to environment.
- Epigenetics- It is the study of mechanisms by which genes and, their products bring about phenotypic expression.
- Ethnobotany- It is the relationship between primitive humans and plants.
- Ethnology- It is science dealing with different races of mankind. Economic botany- It deals with the study of various uses of plants and their products.
- Environmental management- It is the assessment of the environment, finding out the ways and means to remedy environmental problems and food conservation of biodiversity to maintain the balance in nature.
- Forensic science – Application of science for identification of various facts about blood groups, hair, poisons, narcotics, fingerprints, and DNA fingerprinting for solving civilian and criminal cases.
- Food technology – The study of the processing and preservation of food is called food technology.
- Forestry or silviculture- It deals with the development of forests and the utilization of their products.
- Gynaecology- Study of female reproductive organs.
- Gerontology- It is a branch of developmental biology which deals with the study of ageing.
- Genetics is the study of genes and concerned with heredity and variations.
- Gynaecology- Study of the genetic make-up of species or populations about habitat.
- Genetic engineering – The methods of artificial synthesis of new genes and their subsequent recombination in the genome of an organism or methods of correcting defective genes are called genetic engineering.
- Geology-It deals with the study of the earth and its life as recorded in the rocks.
- Genecology-It deals with the study of the genetic composition of a population of the environment.
- Horticulture- It deals with the study of plants cultivated in gardens and orchards.
- Hypnology- Science dealing with sleep including the one from hypnosis.
- Helminthology- Study of parasitic worms.
- Herpetology- Study of reptiles.
- Hepatology- Study of the liver.
- Haematology- Study of blood.
- Histology -> The study of the structure and chemical composition of animal and plant tissue as related to the function.
- Heredity- It is the study of the inheritance of characters from parents to offspring.
- Ichthyology- Study of fishes and amphibians.
- Internal morphology- It deals with the internal structure of plant parts and is also called anatomy.
- Ichnology- It is a branch of palaeontology which deals with fossil foot parents.
- Kalology- Study of human beauty.
- Lepidepteriology- Study of butterflies and moths.
- Leprology- It is the study of leprosy its cause and cure.
- Umnobiology -It is the study of fresh water.
- Limnology- the study of freshwater ecology study of snails.
- Lichcnology – It is the Mud of lichens.
- Molecular biology – Studs of living organisms at the tncolcculnr level.
- Morphology – It deals with the study of the form and structure of animals.
- Mammalogy – Stusly of mammals.
- Microbiology – Study of microscopic organisms.
- Malariology – Study of malaria.
- Myremecohgy- The study of ants is termed myrmecology.
- Malacology – Study of molluscs.
- Myology arcology) – Study of muscles.
- Mastology- The study of breasts including teats is
- called mastology.
Mycology- It is the study of fungi.
Scope Of Biology NEET
- haematology- Study of nematodes (roundworms).
- Nephrology- Study of the kidney.
- Neonatology- It is the science of the study of new bombs up to twenty-eight days in humans.
- Neurology – Study of the nervous system.
- Nidology- Study of nests of birds.
- Ornithology- Study of birds.
- Ophthalmology- Study of eyes.
- Osteology- Study of bones.
- Organocology- Study of the development of organs under embryology.
- Olericulture- It is the branch of agriculture dealing with the cultivation of vegetables.
- Odontology- Study of teeth and gums.
- Oto-larynology- Study ofear and larynx.
- Palaeontology- It is the study of the origin of plants and animals as shown by fossil records.
- Palacozoology- It is the study of animal fossils. Phenology- Study of organisms as affected by seasonal climates e.g. bird migration, opening of flowers etc.
- Physiology- The study of functions of various parts of the body is called physiology.
- Parasitology- Study of parasites.
- Protozoology- Study of unicellular organisms, i.e. protozoans.
Parazoology- Study of sponges. - Pathology- Nature, symptoms, causes, effects, prevention and suggestive cure of disease is called pathology.
- Plant physiology is the study of various functional aspects or life processes of plants.
- Plant taxonomy- It is the study of identification, nomenclature and classification of plants.
- Palaeobotany- It is the study of fossils of prehistoric plants.
- Plant ecology- The study of the relationship of plants with the environment is termed plant ecology.
- Plant geography- The study of the distribution of plants over the surface of the earth.
- Phycology- It is the study of algae.
- Plant pathology- It is the study of plant diseases, their causes, symptoms and methods of control.
- Pteridology- It is the study of pteridophytes.
- Palynology- It is the study of pollen grains.
- Pomology- It is the study of fruits.
- Protology- It is the study of the hindgut including the rectum and anus.
- Physiotherapy- The treatment of defects by physical remedies is called physiotherapy.
- Protistology- It is the study of protists.
- Phenology- Study of periodicity phenomenon of organisms e.g. Bird Migration.
- Pharmacology- It is the study of medicine or drug plants.
- Plant breeding – ll is the study of genetics Concerning selective crossing and reproduction between different plants.
- Plant agronomy- It is the science of soil management and the production of crops.
- Pharmacognosy- It is the scientific study of structural, physical, chemical and sensory characteristics of plants, cultivation, collection and other particulars relating to their uses.
- Pharmacology- Study of synthesis and effect of medicines on organisms.
- Phrenology- Study of mental faculties of the brain including feelings. Plant Morphology- the study of form and structure of plant organs is called morphology.
- It generally includes external morphology which refers to gross structure visible to the naked eye.
- Pedology- Paedology = Edaphology -the study of soil.
- Quantitative zoology- Study of biometric data in animals.
- Radiation biology- The study of the effects of radiation on living organisms is termed radiation biology (Actinobiology) Rhinology- Study of the nose and olfactory organs.
- Serology- Study of serum; interaction of antigens and antibodies in the blood.
- Splanchnology- Study of the visceral cavity and its organs.
- Soil Science- The study of soil involving its structure, type and dynamics is called soil science Sedimentology- Study of rocks and fossils.
- Space biology-It is the study problem of survival of living organisms in outer space.
- Herpetology (Ophiology)- Study of snakes.
- Saurology- Study of lizards.
- Sitology- Science of food, diet and nutrition.
- Stomatology is the study of the foregut.
- Speciology- Study of species.
- Sarcology is a branch of anatomy which deals with flesh parts of the body.
- Spelaeology- Study of caves and cave life.
- Teratology – It is a branch of developmental biology which deals with the study of developmental abnormalities during embryonic stages. Taxonomy deals with the principle of identification, nomenclature and classification of the animals.
- Torentology- It is the study of diseases of embryos.
- Taphonomy deals with the study of conditions conducive to the fossilization of organisms in the plant.
- Tricology- The study of hairs is called tricology.
- Trophology- The study of nutrition is called trophology.
- Toxicology- Study of narcotic effect on animals.
- Therapeutics- Study of healing.
- Tectology- It is the study of the structural organisation of animals.
- Traumatology- Study of injuries and wounds.
- Urology- Study of the excretory system.
- Virology- It is the study of viruses.
- Xenology- It is the study of hosts concerning the life history of parasites.
- Zoo-geography-It is the study of the distribution of animals in different geographic regions.
- Zoopathology- Study of diseases of animals.
- Zymology- The study of fermentation is called zymology.
- Zootechny- Science of breeding and domesticating animals.
- Zoonosology- It is the study of handicapped animals.
NEET Biology Nature And Scope Fathers In The Field
- Father of Biology: Aristotle
- Father of Botany: Theophrastus
- Father of Zoology: Aristotle
- Father of Plant Physiology: Stephan Maids
- Father of Taxonomy: Carl Linnaeus
- Father of Genetics: G.J. Mendel
- Father of Experimental Genetics: Morgan
- Father of Bryology: Johannn Hcdwig
- Father of Modem Cytology: Carl P. Swanson
- Father of Microscopy: Marcello Malpighi
- Father of Plant Anatomy: N. Grew
- Father of Histology: Francis Bichet
- Father of Mycology: Micheli
- Father of Palynology: Erdtman
- Father of Eugenics: Francis Galton
- Father of Biochemical Genetics: Archibald Garro
- Father of DNA fingerprinting: Lorentz
- Father of Ethology: Addison
- Father of Endocrinology: Lipmann
- Father of ATP cycle: Hans Selye
- Father of stress physiology: Korenchevsk
- Father of gerontology: R. Mihsra
- Father of Indian ecology: Bason George Curvier
- Father of Comparative Anatomy: Andras Vesalius
- Father of Modem Anatomy: Galen
- Father of Experimental Physiology: William Harvey
- Father of Study of circulation of Blood: Empedocles
- Father of Evolutionary ideas: K.V. Baer
- Father of Modem Embryology: Charaka
- Father of Ayurveda: L. da Vinci
- Father of Palaeontology: Hippocrates
- Father of Medicine: E.J. Butler
- Father of Indian Mycology: Robert Koch
- Father of Bacteriology: LOusis Pasteur
- Father of Microbiology: Hugo De Viruses
- Father of Mutation: Father Suarez
Nature And Scope Of Biology NEET Exam Preparation
- Father of Special Creation Theory: Edward Jenner
- Father of Immunology: Edward
- Father of Modem Genetics: Bateson
- Father of Blood groups: C. Land Steiner
- Father of genetic engineering: Paul Berg
- Father of biochemistry: Leibig
- Father of ECG: Einthoven
- Father of conditioned reflex: Pavlov
- Father of Polygenic inheritance: Kolreuter
- Father of epidemiology: John Snow
- Father of plant pathology: de Bary
- Father of Antiseptic surgery: Joseph Lister
- Father of Antibiotics: Alexander Flemming
- Father of Radiation genetics: H.J. Muller
NEET Biology Nature And Scope Scientific Method
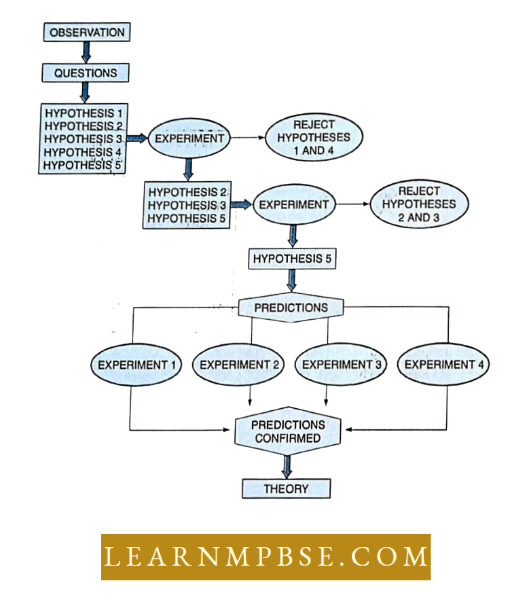
Most biological Investigations start with an observation. Raising questions such as what, how and why of an observation and defining the problem constitute an important step in this method. To arrive at an answer to such questions, the scientist gathers as many relevant facts as possible and then formulates a hypothesis.
- A hypothesis supported by experiments or repealed observation is called a theory.
- Theories are subject to change.
- The universally accepted theory is called law or principle.
- When discoveries are made unexpectedly or by accident phenomenon is called serendipity.
- The method of science is not limited to the laboratory and often forms a part of our everyday life.
- Generalized approach in science.
Emergence of biology in ancient India
- The people of Vedic ages (2500 BC to 650 BC) recorded about 740 plants and 250 animals.
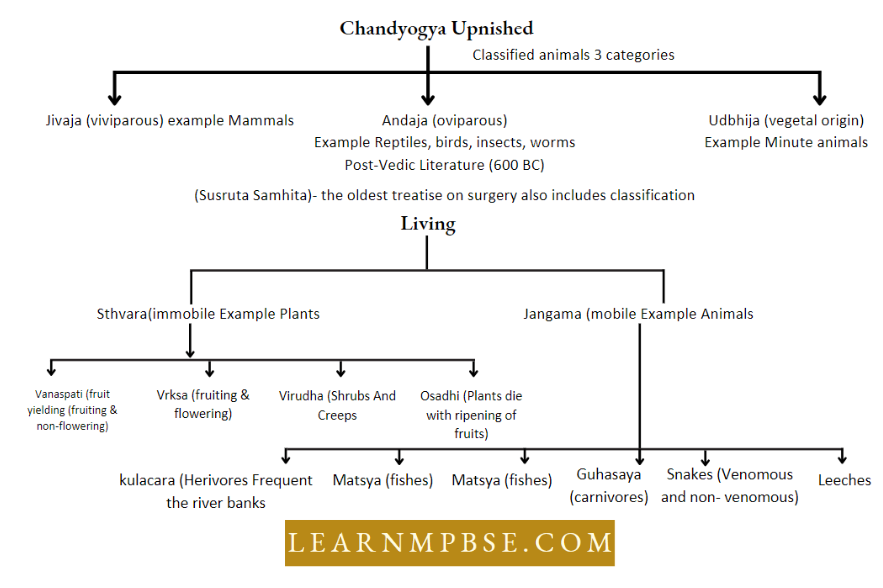
- In Chandogya Upanishad animals were organised into 3 categories i.e. Jivaja, Andaja and Udbhija.
- Post-Indian literature (Susruta Samhita) (600 BC) classified substances into two sthavara (immobile-plants) and jangama (mobile-animals). This literature further also classified plants and animals.
Importance Of Biology NEET
Classification of organisms as proposed by Susruta Samhita
- As in our Vedic literature, people of that time (2500 BC to 650 BC) used to observe plants and animals and recorded 740 plants and 250 animals.
- Susruta described in detail parts of plants such as Ankura (sprout) Kanda (Bulb or stem) Puspa (flower) Mula (root) Patra (leaf) Phala (fruit).
- Susruta Samhita also mentioned the classification of animals, such as Kulacara (those herbivores who frequent the river banks, e.g. elephant, buffalo, etc.), Matsya (fish), Janghala (wild herbivorous quadrupeds, e.g. deer), Guhasaya (carnivorous quadrupeds like tiger, lion, etc.) Susruta Samhita also records some observations on snakes (both venomous and nonvenomous) and leeches.
- Six elements comprise humans according to Charahra Samhita Charahra Samhita ancient Indians mentioned that all humans and the visible world are composed of the following six elements.
- Prithvi (earth), ap (water or liquid), Tejas (fire), Vayu (air) and akasa (ether), The sixth element, the spirit or self in the individual, is equivalent to Brahma in the universe.
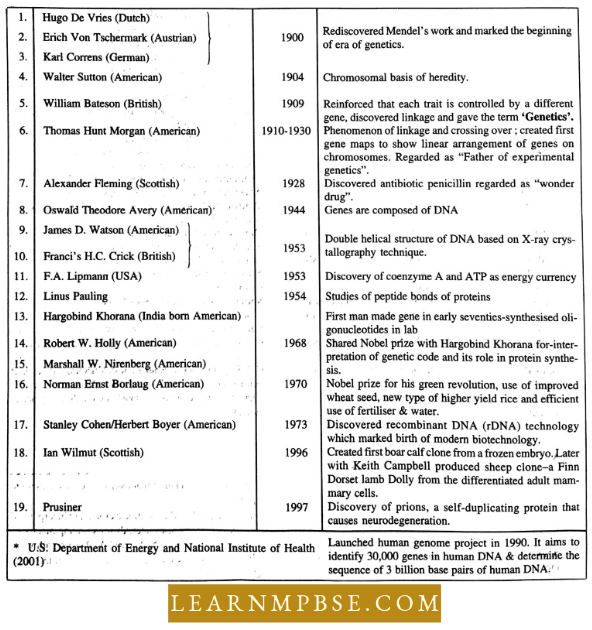
- Green revolution. Norman Ernst Borlaug won the Nobel Prize for the Green Revolution. It involves the use of improved wheat seed, new types of higher-yield rice and more efficient use of fertiliser and water.
- It resulted in higher yield of wheat crops. Modern plant and animal breeders can now produce new forms of life with almost any mix of characteristics by altering the genes in DNA.
- Genetically modified crops are prepared by using recombinant DNA technology. In this case by manipulation of genes new crops are produced, which can give higher yield and resistance to pests.
NEET Biology Nature And Scope Of Biology
Amniocentesis. It is the technique of the removal of amniotic fluid via a needle inserted through the maternal abdomen into the uterus and amniotic sac, to gain information about the foetus. The amniotic fluid contains cells (“amniocytes”) of the amniotic membrane and some foetal skin cells.
These cells are then cultured and stimulated to grow. After a few days, the cells are broken to release the chromosomes which are stained counted and compared with the 23 pairs of normal human chromosomes to detect missing or extra pieces.
It helps in detecting foetal abnormalities, even the test could reveal the sex of the foetus. It has resulted in female foeticides.
Bioweapons. The development of antibiotic-resistant microorganisms with increased infectivity. For example, anthrax is an acute infectious disease caused by the spore-forming bacterium Bacillus anthracis.
Spores of B anthracis can be produced and stored in a dry form keeping them liable for decades in storage or after release. A cloud of anthrax spores, if released at a strategic location to be inhaled by the individuals under attack may act as an agent of effective weapon of bioterrorism.
Branches Of Biology NEET Notes
An attack with bioweapons using antibiotic-resistant strains would, thus, initiate the incidence and spread of communicable diseases, such as anthrax and plague, on either an endemic or epidemic scale.
NEET Biology Nature And Scope Science Of Contemporary
1. Aristotle (384-322 BC)- Greek.
- Classified animal species and arranged them in hierarchies
2. Andreas Vesalius (1514-1564).
- Belgian; “Father of Anatomy’’. Book: De Humani Corporis Fabrica (The structure of the human body).
3. William Harvey (1578-1657).
- British; demonstrated blood circulation pumped by the heart.
Book: Anatomical Exercise on the Motion of the Heart and Blood. Also contributed to the field of reproduction and embryonic development of chicks.
4. Robert Hooke (1635-1703) British;
- First studied cell under microscope Book; Micrographia. Coined the term ‘cellulite’.
5. Antony Von Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723).
- Dutch draper-turned-scientist, Observed living cells with his own invented simple microscope, e.g. protozoans, human sperm, eggs and blood corpuscles of invertebrates, Hydra, about compound eyes of insects and many other animal structures.
- First to draw a diagram of bacteria (1683) from his observations of bacterial cells under a microscope.
6. Carolus Linnaeus – (1707-1778)
- Swedish naturalist. Introduced Binomial nomen clature.
Book: Species Plantarum (1753) registers about 6000 sps. of plants.
System a Naturae (1758)- recorded about 4000 sps. of animals.
7. Georges Leopold Cuvier (1769- 1832)
- French palaeontologists Rejected the traditional ‘scala naturae’ as a unifying concept of evolution.
- First, it identified the fossils of extinct birds like reptiles and laid the foundation of palaeontology.
- First to give the concept of comparative anatomy of chordates.
8. Jean Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829)
- French naturalists; discarded the idea of the fixity of species.
Book: Philosophic Zoologique (1809)
9. Matthias SchIeiden-( 1804-1881)
- Studied plant cells and proposed cell theory- (1838) German Botanist
Branches Of Biology NEET Notes
10. Theodor Schwann-(1810-1882)
- Studied animal cells and proposed cell theory along with Schleiden – (1839) German Zoologist
11. Charles Robert Darwin-British naturalist (1809-1882).
- Book On the origin of species by natural selection: The Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life-1859.
- Established that Natural Selection is the agent that brings about cliimÿcs to result in the Origin of Species by evolution.
12. Lousis Pasteur (1822 – 1895) Prench scientist.
- Discovered the concept of spontaneous origin of life Prosed fermentation is caused by living organisms Case Genu Theory of diseases, and developed the scientific basis of immunity on cholera bacteria in chicken.
- Discovered vaccine against anthrax caused by Bacillus anthracis in cattle.
- His technique of killing germs (or sterilisation) is Pasteurization.
13. Gregor Johann Mendel (1822-1884)
- Austrian monk; discovered (1865) the Principles of inheritance which remained unknown to the world till 1900.
14. August Wcismnnn (1834-I914)-
- German biologist; gave the theory of germplasms (1892).
NEET Biology Nature And Scope Scientists Of The Twentieth Century
- Contribution of Aristotle (384-322 B.O.). a great philosopher of Greece, belongs to an ancient time when biology as a science was poorly developed. About 90% of his writings are on scientific subjects, mostly on biological ones. A few important contributions of Aristotle are noted below:
- Aristotle classified animal species and arranged them into hierarchies. His classification was reasonable and strikingly modern.
- Formulated the Great Chain of Being or Seala Naturae —a chain of progressive change in nature. This corresponds to a sort of evolution.
- Dealt with five hundred types of animals and dissected nearly 50 of them.
- He studied the developing embryo of the chick and reported that sharks give birth to live young but do not develop a placenta like mammals. He is regarded as the founder of embryology.
- He observed the placenta in dolphins and on a placental basis classified dolphins with mammals.
- He is regarded as the “Father of Biology.” Charles Darwin (1809-1882) put forward the ‘Theory of Natural Selection which explains the mechanism of evolution.
- Andreas Vesalius is regarded as the Father of Anatomy
- Jean Baptiste Lamarck in his book ‘Philosophic Zoologique (1809)’ gave the idea of “fixity of species.”
Leeuwenhoek (1670) observed the living cell for the first time. - Schleiden and Schwann proposed cell theory based on studies of plant and animal tissues. c1 Charles Darwin published his work in his monumental treatise “On the Origin of Species through Natural Selection or The Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life.”
- Natural selection is the agent that brings about changes to result in the origin of species by evolution.
- Louis Pasteur established the germ theory of disease. Cuvier was the first to identify fossils. F.H. Janssen and Z. Janssen prepared the first bright field compound microscope.
- Faber coined the term ‘microscope.’
- Tolies developed a polarizing microscope.
- Zsigmondy invented a dark field microscope.
Branches Of Biology NEET Notes
- Knoll and Ruska invented the electron microscope.
- Zerinke developed a phase contrast microscope.
- Caspersson invented the UV microscope.
- Gregor Johann Mendel worked for eight long years on Pisum sativum and discovered the principles of inheritance.
- Darwin’s Theory of Pangenesis, suggests that gemmules were carried through the blood from every organ of the body and collected into the gametes.
- A. Weismann after his experiments on rats proposed the
Theory of continuity of germplasm. - De Vries, Tschermak and Correns rediscovered Mendel’s work and formulated Mendel’s laws.
- Bateson described genes, discovered linkage and introduced the term genetics.
- Sutton along with Boveri proposed the Chromosome Theory of heredity.
- T.H. Morgan, regarded as the father of experimental genetics, described linkage, crossing over, sex linkage and prepared chromosome (linkage) maps.
NEET Biology Nature And Scope Quanta To Memory
- The tissue culture technique is useful in the study of genetic enginnering, ageing and nutritional requirements of cells.
- Tissue Culture. Harrison (1907) was the first to use the tissue culture technique.
- All land animals drink water but kangaroo rat never drinks it. It obtains water from dry seeds during metabolism.
- Teleology. It is a belief that events occur in response to specific needs.
- Autoradiography: Radioactive isotopes are incorporated in intermediate or raw materials for studying metabolic pathways including D.N.A. R.N.A. Protein pathways. 14C was used to study the path of carbon assimilation by Calvin (1955).
- 13N was employed by Taylor (1958) for studying chromosome implication.
- 3-D images are obtained with the help of a scanning electron microscope and X-ray microscope. All others give 2-D images.
- American salamander (Ambystoma triturus) has an aquatic larva called axolotl larva which can develop sex organs and produce young ones the phenomenon is called Neoteny.
- Vital stains arc dyes which are used to stain living material c.g. Janus green to study mitochondria neutral red. methylene blue.
- Fuelgcn stain is basic Fuchsin which is specific for D.N.A. (Fuelgen/Schiff’s reaction developed by Fuelgen and Rossenbeck 1924).
- Acid Fuchsin is used for staining cellulose cell walls. Azure B for RNA, Sudan for lipids, Millon’s reaction for protein and iodine for starch.
- Microsomes are new products in cell fractionation
techniques. - Cell fractionation. Cell fractionation is a combination of processes by which a tissue or cell suspension is disrupted and the various cell components, the organelles and the macromolecules like proteins are separated for their subsequent biochemical analysis.
- The tissue is dipped in 0.25 M sucrose solution and kept at a low temperature. In sucrose solution, cell organelles do not change their properties.
- It involves the separation of cells into components so that their structure and function can be separated. It involves two steps:
- Homogenization
- Centrifugation.
- Ultraccntrifugc was developed by Svcdbcrg (1938). It has more than 50,000 rpm. It is used to separate constituents of cells. Fluorochromes are the dyes which produce fluore-sccncc.
- Spectrophotometry In this case solution having dissolved cellular chemicals is exposed to selected wavelengths of light and the absorption spectrum is recorded. Now, it is compared with the absorption spectra of different molecules to know the exact composition of the solution.
- The radioactive substances used are Tritium (‘ll), Carbon (UC), Phosphorus (P3Z) N15, K42 Ca4 Fcw S35 O18 Na25Cl36. N 15 and 018 are heavy isotopes. N” is used to study the replication of DNA.
- H3 was used by Taylor to study the duplication of chromosomes and locate DNA in the nucleus.
- Cl36, Na25, and Ca43 are used in the study of salt metabolism. Tritium or carbon labelled thiamine is used for synthesis of DNA and Carbon labelled uridine is used for studying the synthesis of RNA. 4C02 is used for studying the photosynthesis (Calvin cycle) of glucose in plants.
- Autoradiography is employed to study dynamic aspects of cells, their constituents and various metabolic pathways.
Nature And Scope Of Biology NEET Question Bank
- ELISA test is the first test to screen HIV cases. It tests antibodies. Western blotting techniques confirm HIV. Here antibodies are tested as per the molecular weight of antigens.
- A few other tests of HIV are 1FA (Immunii fluorescent assay), RIPA (Radio immunoprecipitation assay), B2 macroglobulin and Serum neopterin.
- Units of size used in microscopy
- 1 metre (m) = 100 centimetres (cm) = 39.4 inches
- 1 cm = 10 millimetres (mm)
- 1 mm = 10-3 m = 103 micrometres (pm)
- (Micrometres were formerly known as microns, denoted by the Greek letter, p pronounced “mew”.)
- 1pm = 10″6 m= 104= 103 nanometres (nm)
- 1nm= 10″6 m= 10-7 cm = 10 Angstroms (A)
- 1A = 10″10 m = 10’8 cm = 10’1 nm
- Angstrom was named after J. Angstrom
- (1814-1874 is spectroscopist)
- (Most biologists have now abandoned
- the use of Angstrom units, which still, however, be encountered in older books.
- Ontogeny deals with embryonic history and phylogeny deals with evolutionary history.
- The study which deals with the preservation of dead bodies in liquid by chemicals is called neurobiology.
- Cheetahs can run at the speed of 1 12.00 km/hour. Young lions, tigers, bears and wolf is called cubs and young horses are known as colts or foals.
- Proteins form 15% of body weight and are essential for growth, repair wound healing etc.
- Survival of Anopheles depends on mammalian blood from which it obtains protein required for its egg production.
- The total number of bones in man is 206. The smallest bone is the stapes (middle ear) and the longest bone is called the femur (thigh bone).
- Elephant has the sharpest memory.
NEET Biology Nature And Scope Questions From Competitive Examinations
Question 1. Resolving the limit of our eyes is
- 1/60
- 1/60
- 1
- 1″
Answer: 1. 1/60
Question 2. Which of the following sequences is correct?
- Observation, hypothesis, problem defining, experiment
- Observation, problem defining, hypothesis, experiment
- Problem defining, hypothesis, observation, experiment
Answer: 2. Observation, problem defining, hypothesis, experiment
Question 3. Match the correct pair:
- Silviculture—silkworm
- Pisciculture—lac insect
- Apiculture—honey bee
- Sericulture—fish
Answer: 3. Silviculture—silkworm
Question 4. Match column i with column ii and give the correct choice :

- 1-q,2-s,3-r,4-t
- 1-p,p-s,3-r,4-t
- 1-s,2-p,3-t,4-r
- 1-s,2-t,3-p,4-r
Answer: 3. 1-s,2-p,3-t,4-r
Question 5. The most abundant organic compound on planet Earth is
- Proteins
- Cellulose
- Lipids
- Steroids
Answer: 2. Cellulose
Nature And Scope Of Biology NEET Mcqs
Question 6. The term ‘biocoenosis’ was coined by
- Charles Darwin
- Karl Mobius
- Ernst Haeckel
- E.p Odum.
Answer: 2. Karl Mobius
Question 7. Match the names of branches of biology listed under the column with the field of study given under the column; choose the answer which gives the correct combination of the alphabets of the two columns :
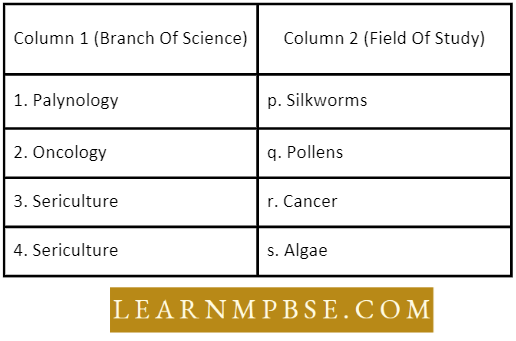
- 1-r,2-q,3-s,4-p
- 1-s,2-r,c-q,d-p
- 1-q,2-r,3-s,4-p
- 1-s,2-q,c-r,4-p
Answer: 3. 1-q,2-r,3-s,4-p
Question 8. The electron microscope was invented by :
- Robert Hooke
- Louis Pasteur
- Knoll and Ruska
- Schwann and schlcidcn
Answer: 2. Louis Pasteur
Introduction To Biology NEET Notes
Question 9. The branch of biology dealing with the process of improvement of the human race by selective breeding is known as
- Euthenics
- Eugenics
- Eupthenics
- Obstetrics
Answer: 2. Eupthenics
Question 10. Biosystematics aims at:
- Identification and arrangement of organisms based on their cytological characteristics
- The classification of organisms based on broad morphological characters
- Delimiting various taxa of organisms and establishing their relationship
- The classification of organisms based on their evolutionary history and establishing their phylogeny on the totality of various parameters from all fields of studies.
Answer: 4. The classification of organisms based on their evolutionary history and establishing their phylogeny on the totality of various parameters from all fields of studies.
Question 11. Aristotle is connected with :
- Catastrophism
- Scala Naturae
- Biogenetic law
- Parallelism
Answer: 2. Scala Naturae
Question 12. Amniocentesis is employed for the diagnosis of ;
- Brain disorders
- Hereditary defects
- Spina bifida
- Coronary disorders.
Answer: 2. Hereditary defects
Nature and Scope Of Biology NEET Notes
Question 13. Which one of the following is correctly matched regarding an institute and its location?
- National Institute of virology-Pune
- National institute of communicable diseases- Lucknow.
- Central drug research institute-Kasauli
- National Institute of nutrition-Mumbai
Answer: 1. National Institute of virology-Pune
Question 14. The study of the kind of life in outer space is known as ;
- Exobiology
- Ecology
- Evolution
- Anthropology
- Entomology
Answer: 1. Exobiology
Question 15. Amniocentesis is used to determine;
- Heart disease
- Brain disease
- Hereditary disease of the embryo
- All of above
- None of these.
Answer: 3. Hereditary disease of the embryo
Question 16. The name of norman borlaug is associated with :
- Green revolution
- Yellow revolution
- White revolution
- Blue revolution.
Answer: 1. Green revolution
Question 17. The branch of biology dealing with the study of rudimentary organs is :
- Dysicliology
- Dermatology
- Etiology
- Chirology
Answer: 1. Dysicliology
Question 18. Is hirudin is :
- A protein produced by Hordeum vulgar which is rich in lysine
- A toxic molecule isolated from Gossypium which reduced human fertility
- A protein produced from transgenic brassica napus, which prevents blood clotting
- An antibiotic produced by a genetically engineered bacterium. Escherichia coli
Answer: 3. A protein produced from transgenic brassica napus, which prevents blood clotting
Question 19. When children play barefooted in pools of dirty water and flood water, they may suffer from diseases like :
- Leptospirosis and bilharzia
- Malaria, amoebic dysentery and leptospirosis bilharzia, infective hepatitis and diarrhoea
- Guinea worm infection, elephantiasis and amoebic dysentery
Answer: 3. Malaria, amoebic dysentery and leptospirosis bilharzia, infective hepatitis and diarrhoea
Question 20. The biological organisation starts with :
- Cellular level
- Organismic level
- Atomic-level
- Submicroscopic molecular level.
Answer: 4. Submicroscopic molecular level.
Question 21. Living organisms can be unexceptionally distinguished from non-living things based on their ability for:
- Interaction with the environment and progressive evolution
- Reproduction
- Growth and movement
- Responsiveness to touch.
Answer: 2. Reproduction
Question 22. In September 2001, which of the following was used as a bioweapon agent in America?
- Poliovirus
- Aids virus
- Clostridium botulinum
- Bacillus anthracis
Answer: 4. Bacillus anthracis
Nature and Scope Of Biology NEET Notes
Question 23. T bioweapon agents are very convenient for use because they ;
- Cause far more casualties than chemical or conventional weapons
- Low-cost weapons
- Are invisible
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Nature And Scope Of Biology NEET Previous Year Questions
Question 24. Identify the correct set from the following.
- The application of mathematics of biology of biometry
- The study of genetics that deals with the systematic treatment of genetic disorders is euphenics
- The branch of biochemistry concerned with the study of transformation and use of energy of living cells of organisms is biotechnology
- The study deals with the application of statistical methods for computation and analysis of biological data in bioinformatics.
Choose the correct answer
- 1 and 3
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 4
Answer: 4. 1 and 4
Question 25. The study of the growth of a part of the body relative to that of other parts or the whole body is termed.
- Allopatric
- Allometry
- Aliogamy
- Allelopathy.
Answer: 2. Allometry
Question 26. The test which is misused for sex identification for an unborn baby is:
- Angiogram
- Clotting test
- Amniocentesis
- Erythroblastosis.
Answer: 3. Amniocentesis
Question 27. Edaphology is the study of :
- Snakes
- Elephants
- Amphibians
- None of these.
Answer: 4. None of these.
Importance Of Biology NEET
Question 28. The study of the ecology of the population is called :
- Ecotype
- Autecology
- Dermatology
- Synecology.
Answer: 3. Demecology
