NEET Biology Plant Water Relation Water Relations Of A Cell Multiple Choice Question and Answers
Question 1. The bullion cells of monocotyledon leaves show
- Tropic movement
- Autonomic movement
- Nastic movement
- Turgor movement.
Answer: 4. Turgor movement.
Question 2. Water will be absorbed by the root hairs when :
- Plants are rapidly respiring
- The concentration of salts in the soil is high
- The concentration of solutes in the cell sap is high
- They are separated from the soil by a permeable membrane.
Answer: 3. Concentration of solutes in the cell sap is high
Question 3. In which of the following plants would metabolism be hindered if the leaves are coated with wax on their upper surface?
- Vallisneria
- Pistici
- Lotus
- Hydrilla.
Answer: 3. Lotus
Question 4. Stomata open at night and close during the daytime in
- Succulents
- Mesophytes
- Hydrophytes
- Herbs.
Answer: 1. Succulents
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question and Answers
Question 5. During the rainy season, doors made up of wood generally swell up due to :
- Osmosis
- Had workmanship
- Imbibition
- Bad quality of wood.
Answer: 3. Imbibition
Plant Water Relation MCQs
Question 6. Dumb-bell shaped guard cells are characteristics of:
- Herbs
- Dicot leaf
- Isobilateral leaf
- Scale leaf.
Answer: 3. Isobilateral leaf
Question 7. The closing and opening of stomata is due to an influx of:
- K+ ions
- Na ions
- Fe ions
- Mg ions.
Answer: 1. K+ ions
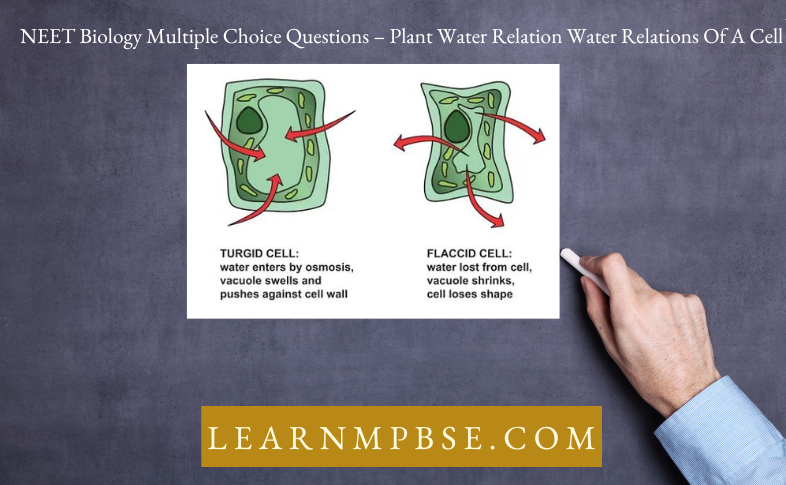
Question 8. Pure water has a water potential which is :
- zero
- Negative
- High
- Very low.
Answer: 1. zero
Question 9. The amount of water absorbed to compensate for the loss of transpiration is measured by :
- Potometer
- Crescograph
- Manometers
- Auxanometers.
Answer: 1. Potometer
Plant Water Relation MCQs
Question 10. The inward pressure exerted on the cell contents by the stretched cell wall is termed :
- Osmosis
- Wall pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure.
Answer: 2. Wall pressure
NEET Questions Botany Transport in Plants Question 11. The form and structure of a growing cell is maintained due to :
- Atmospheric pressure
- Plasmolysis
- Turgidity
- Wall pressure.
Answer: 3. Turgidity
Question 12. The water potential and osmotic potential of pure water are :
- 100 and zero
- Zero and Zero
- 100 and 100
- Zero and 100.
Answer: 2. Zero and Zero
Question 13. The membrane that allows certain molecules to enter into the cell and prevents others is known as:
- Impermeable membrane
- Permeable membrane
- Selectively permeable membrane
- Unit membrane.
Answer: 3. Selectively permeable membrane
Plant Water Relation MCQs
Question 14.” The vacuolar membrane is known as :
- Cell membrane
- Plasmalemma
- Chromoplast
- Tonoplast.
Answer: 4. Tonoplast.
Question 15. Due to osmosis, water enters into a cell and results in hydrostatic pressure. This is known as :
- Osmotic pressure
- Wall pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Low pressure.
Answer: 3. Turgor pressure
Question 16. The plasmalemma, cytoplasmic film, and the vacuolated membrane in an osmotic system of a vacuolated cell constitute the :
- Permeable membrane
- Impermeable
- Electively permeable membrane
- Unit membrane.
Answer: 3. Electively permeable membrane
Plant Water Relation MCQs
Question 17. Exosmosis takes place when a plant cell is put in :
- Hypertonic solution
- A hypotonic solution
- An isotonic solution
- Non-ionic solution.
Answer:1. Hypertonic solution
Question 18. Endosmosis occurs when a plant cell is put in :
- A hypertonic solution
- Hypotonic solution
- An isotonic solution
- Non-ionic solution.
Answer:2. Hypotonic solution
Question 19. If there is no net movement of water into a cell from the outside medium, the medium is :
- Isotonic to the cell sap
- Hypertonic
- Hypotonic
- Non-ionic.
Answer: 1. Isotonic to the cell sap
Question 20. During absorption of water by roots, the water potential of cell sap is lower than that of:
- Pure water and soil solution
- Neither pure water nor soil solution
- Soil solution but higher than that of pure water
- Pure wafer but higher than that of soil solution.
Answer: 1. Pure water and soil solution
Question 21. When a cell is fully turgid, it:
- O.P. = D.P.D.
- OP = Zero
- DCP.D = zero
- D.P.D. = O.P.
Answer: 3. DCP.D = zero
Water Relations Of A Cell NEET
Question 22. A cell increases in volume when placed in a solution which is:
- Isotonic
- Hypotonic
- Hypertonic
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Hypotonic
Question 23. DPD stands for:
- Diffusion pressure deficit
- Diffusion pressure demand
- Daily photosynthetic depression
- Daily phosphorus demand.
Answer:1. Diffusion pressure deficit
Question 24. The force responsible for water entry into the cell is :
- Diffusion
- DPI
- Osmotic pressure
- Wall pressure.
Answer: 2. DPI
Question 25. Minerals are absorbed by the plants from the soil ;
- By a process independent of water absorption
- Independently of water
- Only when soil solution is hypertonic to cell sap
- Only when soil solution is hypotonic to cell sap.
Answer: 1. By a process independent of water absorption
Question 26. The osmosis means :
- Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration into an area of lower concentration
- Uptake of water by plant roots
- Passage of solvent from a weak solution to a strong solution when the two are separated by a semi-permeable membrane
- Passage of solute from a weak solution to a strong solution when the two are separated by a semi-permeable membrane.
Answer: 3. Passage of solvent from a weak solution to a strong solution when the two are separated by a semi-permeable membrane
Question 27. Starch is changed to organic acids during :
- Stomatal initiation.
- Stomatal closure
- Stomatal opening
- Stomatal growth.
Answer: 3. Stomatal opening
Water Relations Of A Cell NEET
Question 28. Selective permeability is the main property of:
- Osmosis
- Diffusion
- Active transport
- Imbibition.
Answer: 3. Active transport
Question 29. When placed in water seeds swell, due to :
- Hydrolysis
- Osmosis
- Imbibition
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Imbibition
Question 30. Most of the physiological reactions in plants occur at a pH of:
- 4.0
- 8.0
- 7.0
- 14.0.
Answer: 3. 7.0
Question 31. The movement of water from one cell of the cortex to the adjacent one in the roots is due to :
- Accumulation of inorganic salts in the cells
- Water potential gradient
- Accumulation of organic salts in the cells
- Chemical potential gradient.
Answer: 2. Water potential gradient
Question 32. Which of the following factors is most important in the regulation of transpiration?
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Light
- Wind.
Answer:2. Humidity
Water Relations Of A Cell NEET
Question 33. If the volume of a cell decreases after being placed in a solution, the solution is :
- Isotonic
- Hypertonic
- Hypotonic
- Normal.
Answer: 2. Hypertonic
Question 34. If cell A with, DPD, 4 bars are connected to cells B, C, and D whose OP and TP are respectively 4 and 4, 10 and 5, and 7 and j bar, the flow of water willies-
- C to A, B, and D ‘
- A and D to B and C
- A to B, C, and D ‘
- B to A, C, and D.
Answer: 3. A to B, C and D ‘
Question 35. The energy source that drives the upward flow of water is:
- Temperature
- Sucrose
- Solar energy
- ATP.
Answer: 4. ATP.
Water Relations Of A Cell NEET
Question 36. To initiate cell plasmolysis, the salt solution should be
- Isotonic
- Hypertonic
- Hypotonic
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Hypertonic
Question 37. Plant cells submerged in distilled water will become :
- Turgid
- Flaccid
- Plasmolyzed
- Impermeable.
Answer:1. Turgid
Question 38. Which of the following plant cells has more negative water potential?
- Cell with high osmotic pressure
- Cell with high turgor pressure
- Cell with high wall pressure
- Cell with low osmotic pressure.
Answer:1. Cell with high osmotic pressure
Question 39. Protoplasm is :
- True solution
- Colloidal solution
- Suspension
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Colloidal solution
Question 40. Plasma membrane helps :
- In protein synthesis
- Regulates the passage of water only.
- Regulates the passage of water and dissolved Substances into and out of cells
- Protects the cell.
Answer: 3. Regulates the passage of water and dissolved Substances into and out of cells
Question 41. The cell wall is permeable and can be observed from the passage of water and minerals from’?”
- Root hair into cortical cells
- Cortical cells into endodermis
- Soil into root hairs
- Cortical cells into pericycle.
Answer: 3. Soil into root hairs
Question 42. Deplasmolysis into the cell occurs which is placed in:
- Isotonic solution
- hypotonic solution
- Hypertonic solution
- None of these.
Answer:2. hypotonic solution
Water Relations Of A Cell NEET
Question 43. Purple cabbage leaves do not lose their color in cold water but do so in boiling water because :
- The plasma membrane becomes permeable in boiling water and pigments come out
- Hot water can enter the cells readily
- The pigment is not soluble in cold water
- The cell wall is killed by boiling water.
Answer: 1. The plasma membrane becomes permeable in boiling water and pigments come out
Question 44. Osmosis is defined as the process by which :
- Water diffuses from lower concentration to higher concentration
- Solutes diffuse from lower concentration to higher concentration
- Active transport of ions takes place
- Passive transport of ions takes place.
Answer:1. Water diffuses from lower concentration to higher concentration
Question 45. Water potential in the leaf tissue is positive (+ve) during :
- Excessive transpiration
- Low absorption
- Low transpiration
- Guttation.
Answer: 3. Low transpiration
Question 46. With the increase in turgidity of a cell surrounded by water the wall pressure will:
- Increase
- Decrease
- Fluctuate
- Remain unchanged.
Answer: 1. Increase
Question 47. The ultimate cause of water movement against gravity is :
- Osmosis
- Imbibition
- Transpiration pull
- Respiration.
Answer: 3. Transpiration pull
Water potential NEET MCQs
Plant Water Relations MCQ Question 48. When a plant wilts, what will be a sequence of events :
- Exosmosis, deplasmolysis, plasmolysis, temporary and permanent wilting
- Exosmosis, plasmolysis, temporary and permanent wilting
- Exosmosis, plasmolysis, deplasmolysis, temporary and permanent wilting
- Endosmosis, plasmolysis, temporary and permanent wilting.
Answer: 2. Exosmosis, plasmolysis, temporary and permanent wilting
Question 49. The process of osmosis stops when:
- The solution is not isotonic
- Water concentration becomes equal
- There is no light
- The leaves fall.
Answer: 2. Water concentration becomes equal
Question 50. The rate of absorption of water is slow at temperatures near the freezing point:
- It is mainly a metabolic process
- Cell membrane becomes more viscous
- The growth of cells stop
- Transpiration is retarded.
Answer: 4. Transpiration is retarded.
Water potential NEET MCQs
Question 51. The outward pressure exerted on the cell wall by the fluid contents of the cell wall is called:
- Turgor pressure
- Wall pressure
- Osmosis
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Turgor pressure
Question 52. Dixon and Jolly’s are associated with :
- Aerobic respiration
- Calvin cycle allision
- Cohesion theory of ascent of sap
- Light reaction.
Answer: 3. Cohesion theory of ascent of sap
Question 53. Which plants do not generate root pressure?
- Monocot grasses
- Perennial shrubs
- Conifer trees
- Seasonal herbs.
Answer: 3. Conifer trees
Water potential NEET MCQs
Question 54. Transpiration cohesion tension theory operates in :
- Active absorption
- Passive absorption
- Both active and passive absorption
- None of the above.
Answer:2. Passive absorption
Question 55. Which plant is used for demonstrating plasmolysis in the laboratory?
- Tropeolum
- Patience balsamic
- Tradescantia
- All the above.
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 56. Transpiration takes place from :
- Leaves
- Stem
- All aerial parts of the plant
- All parts of the plant body.
Answer: 3. All aerial parts of the plant
Question 57. Much of transpiration takes place through :
- Epidermis
- Lenticels
- Stomata
- Cuticle.
Answer: 3. Stomata
Plant Water Relation MCQs
Question 58. Transpiration from plants will be more rapid when :
- The atmosphere is saturated with water
- There is excess water in the soil
- Environmental conditions are dry
- Air is still.
Answer: 3. Environmental conditions are dry
Question 59. Guttation takes place through :
- Stomata
- Hydathodes
- Lenticels
- Cuticle.
Answer: 2. Hydathodes
Plant Water Relation MCQs
Question 60. If cohesion-tension transpiration theory is correct then a break in the water column in xylem vessels :
- This should cause the mesophyll cells to become flaccid and result in the wilting of leaves.
- Should increase the water contents of leaves
- Should have no effect at all
- Should increase the rate of photosynthesis.
Answer: 1. This should cause the mesophyll cells to become flaccid and result in the wilting of leaves.
Question 61. According to Scarth, opening and closing of stomata is controlled by :
- Enzymes
- pH value
- NADP
- Hormones.
Answer:2. pH value
Question 62. Stomata are bounded by guard cells and open when the cells are :
- Turgid
- Flaccid
- Green
- Small.
Answer: 1. Turgid
Question 63. Stomata open during the time because the guard cells :
- Photosynthesize and produce osmotically active sugars
- Are thick-walled
- Are bean-shaped
- Have to help in gaseous exchange.
Answer: 1. Photosynthesize and produce osmotically active sugars
Question 64. Which one is not related to transpiration?
- Bleeding
- Circulation of water
- Absorption and distribution of mineral salts
- Regulation of plant body temperature.
Answer:1. Bleeding
Question 65. A small mesophytic twig with green leaves is dipped into water in a big beaker under sunlight. It demonstrates :
- Photosynthesis
- Respiration
- Transpiration
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Transpiration
Plant Water Relation MCQs
Question 66. The phytohormone which is supposed to be one of the factor responsible for regulating the opening and closing of stomata:
- ABA
- GA
- IBA
- Kinetin.
Answer: 1. ABA
Question 67. Which of the following changes in the cell sap of the guard cell is responsible for keeping stomata open during the daytime?
- Decrease in both osmotic and turgor pressure
- Increase in both osmotic pressure and turgor pressure
- Increase in osmotic pressure but decrease in turgor pressure
- Decrease in osmotic pressure but increase in turgor pressure.
Answer: 2. Increase in both osmotic pressure and turgor pressure
Question 68. Guard cells differ from epidermal cells in having :
- Mitochondrion
- Chloroplast
- Vacuole
- Cell wall.
Answer: 2. Chloroplast
Question 69. If the C02 concentration of the atmosphere were to increase :
- Stomata will close partially
- Respiration will decrease
- Stomata will open
- Photorespiration will increase.
Answer: 1. Stomata will close partially
Question 70. Which one of the following factors is most important in the regulation of transpiration?
- Light
- Humidity
- Temperature
- Wind.
Answer: 1. Light
Plant Water Relation MCQs
Question 71. Which of the following is the most likely cause for the wider opening of stomata?
- The atmosphere outside the stoma is becoming less humid
- Secretions of salt molecules by the adjacent guard cells take place
- Water molecules enter the guard cells
- The night temperature is going to fall.
Answer: 3. Water molecules enter the guard cells
Question 72. Cohesion tension theory of water transport is based on :
- Root pressure
- Activity of parenchyma to the proximity of conducting vessels and tracheids.
- Activity of phloem
- Transpiration pull.
Answer: 4. Transpiration pull
Question 73. The value of water potential (yw) can be obtained by :
- π+WP
- ψs+ψp
- ψ + WP
- ψ + TP.
Answer: 2. ψs+ψp
Question 74. The bulliform cells of leaves lose their turgidity during excessive :
- Assimilation
- Transpiration
- Photosynthesis
- Respiration.
Answer: 2. transpiration
Question 75. A freshly cut potato chip is put into a strong solution of sugar. Later it is found to be :
- Flaccid
- Longer
- Turgid
- More full of starch.
Answer:1. Flaccid
Question 76. Which of the following processes in excess causes temporary wilting?
- Respiration
- Transpiration
- Photosynthesis
- Imbibition.
Answer: 2. Transpiration
Question 77. Osmotic pressure is responsible l\>v tho turgidity of plant colls which;
- Causes cell elongation
- Causes opening to stomata
- Prevents willing to leave
- All the three above,
Answer: 4. All the three above,
Question 78. Hydathodes are present:
- On the upper sin face of the leaf
- On the lower surface of the leaf
- At the tip of the vein of the leaf
- At the base of the veins of the leaf.
Answer: 3. At the tip of the vein of the leaf
NEET MCQs On Plant Physiology
Question 79. The cohesion theory of the ascent of sap was given by ;
- Sachs
- Dixon and Jolly
- Bose
- Robert Brown,
Answer: 2. Dixon and Jolly
Question 80. Spraying of phenyl mercuric
- Increases transpiration
- Reduces transpiration
- Increases rate of photosynthesis
- Causes guttation.
Answer: 2. Reduces transpiration
Question 81. Silicone emulsions when used:
- Increase transpiration
- Reduce transpiration
- Increase rate of photosynthesis
- Cause guttation.
Answer: 2. Reduce transpiration
Question 82. With the increase in turbidity of a cell surrounded by water. the wall pressure will?
- Increase
- Decrease
- Fluctuate
- Remain unchanged.
Answer: 1. Increase
NEET MCQs On Plant Physiology
Question 83. Transpiration is:
- Not necessary for plants
- Necessary for plants
- Avoidable
- A necessary evil.
Answer: 4. A necessary evil.
Question 84. A plasmolyse cell can be plasmolyse by placing it in :
- Pure water or hypotonic solution
- Hypertonic solution
- Isotonic solution
- Saturated solution.
Answer: 1. Pure water or hypotonic solution
Question 85. Leaves of xerophytes have thick cuticle, hairs, fewer and sunken stomata in order to :
- Facilitate transpiration
- Slop transpiration
- To minimize excessive transpiration
- Store water.
Answer: 3. To minimize excessive transpiration
Question 86. The rate of transpiration is regulated by the movement of:
- Epidermal cells of the leaves
- Guard cells of the stomata
- Mesophyll tissue of the leaves
- Cuticle.
Answer: 2. Guard cells of the stomata
Question 87. The low atmospheric pressure :
- Increases the rate of transpiration
- Decreases the rate of transpiration slowly.
- Doesn’t affect the rate of transpiration rapidly
- Decreases the rate, of transpiration rapidly.
Answer: 1. Increases the rate of transpiration
Question 88. If alcohol treated cell is kept in a hypertonic solution it:
- Bursts
- Plastnolysed
- Remains same
- None.
Answer: 3. Remains same
NEET MCQs On Plant Physiology
Question 89. The distribution of stomata per unit area of leaf and their size affects the rate of:
- Respiration
- Transpiration
- Guttation
- Absorption.
Answer:2. Transpiration
Question 90. In a dorsiventral leaf, the number of stomata is:
- Same on both sides
- Large on the upper epidermis
- Huge on the lower epidermis
- Lesser on lower than upper epidermis.
Answer: 3. Huge on the lower epidermis
Question 91. The restoration of turgidity in a plasmolyse cell, when placed in a hypotonic solution is caused by :
- Hydration
- Electrolysis
- Plasmolysis
- Deplasmolysis
Answer: 4. Deplasmolysis
Question 92. Water In plants is transported by (Ascent of sap takes placed through)?
- Cambium
- Epidermis
- Xylem or Xylem vessel elements
- Phloem
Answer: 3. Xylem or Xylem vessel elements
Question 93. The principal pathway by which water is translocated in angiosperms is:
- xylem and phloem together
- sieve tube members of phloem only
- sieve cells of the phloem
- xylem vessels system,
Answer: 4. xylem vessels system
Question 94. For conducting a girdling experiment:
- The cortex is removed
- The cortex anil primary phloem arc removed
- All tissue up to the xylem is removed
- Bark alone is removed.
Answer: 3. All tissue up to the xylem is removed
Question 95. Active absorption of ions is facilitated by :
- Oxygen
- ATP
- More effective plasma membrane
- Slightly higher temperature.
Answer: 2. ATP
Question 96. Levitt’s explanation for stomatal action is due to the:
- Increase in sugar content of guard cells
- Variations in pH value
- Starch is converted into organic acids
- Light causes opening and darkness closure.
Answer: 3. Starch is converted into organic acids
Question 97. Stomatal aperture is measured by ;
- Micrometer
- Potometer
- Photometer
- Luxometer.
Answer: 1. Micrometer
Water Relations Of A Cell NEET
Question 98. The loss of water through the cuticle may reach up to:
- 5%
- 10%
- 20%
- 40%.
Answer: 2. 10%
Question 99. Which of the following walls is of the guard cell is thick:
- Outer
- Inner
- Sidewall
- All the walls,
Answer: 2. Inner
Question 100. The chief role of transpiration in plants is to cause :
- The rapid rise of minerals
- The rapid ascent of sap
- Cooling of plants
- Loss of surplus waiter.
Answer: 2. The rapid ascent of sap
Question 101. The stomata are widely open in :
- Red light
- Blue and red light
- Greenlight
- Yellow light.
Answer: 2. Blue and red light
Question 102. At Full turgor in a cell:
- ψ=0 and hence ψs= ψw
- ψa= 0
- ψp = ψw
- ψp = – ψs and ψw =0
Answer: 4. ψp = – ψs and ψw =0
Question 103. Positive root pressure can be demonstrated :
- At noon
- The early morning
- In the evening
- Only during the night.
Answer: 4. Only during the night.
Water Relations Of A Cell NEET
Question 104. The plant is said to be wilted permanently when it:
- Fails to revive at all
- Revives if the soil is watered
- Revives if kept in a saturated atmosphere
- Revives when it is fanned.
Answer: 1. Fails to revive at all
Question 105. The movement of water up through a tree trunk depends on:
- The high boiling point of water
- Exclusion of air molecules from the sap solution
- The vapor pressure of water
- Attraction between water molecules.
Answer: 4. Attraction between water molecules.
Question 106. The girdling experiments performed by Malpighii supported the theory that:
- Water moves in a tree by the root pressure mechanism
- Water moves in a tree by a transpiration-cohesion mechanism /V.
- The xylem is primarily responsible for conducting water from the roots to the leaves
- Phloem is primarily responsible for conducting organic solutes.
Answer: 3. The xylem is primarily responsible for conducting water from the roots to the leaves
Question 107. The osmotic potential of a solution is denoted by the symbol :
- ψx
- Δψ
- ψp
- ψs.
Answer: 4. ψs.
Question 108. Osmosis is defined as :
- The flow of solvent molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane
- The flow of low-concentration liquid
- The flow of solvent molecules from a higher concentration to a lower concentration region
- The flow of solvent molecules from a lower concentration to a higher concentration region.
Answer: 1. The flow of solvent molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane
Question 109. A root concentrates minerals by :
- Active transport
- Facilitated diffusion
- Osmosis
- Diffusion.
Answer: 1. Active transport
Water potential NEET MCQs
Question 110. A cell placed in a hypertonic solution will:
- Initially gets plasmolysed but later becomes turgid if actively metabolising
- Get plasmolysed and die
- Remain turgid if treated with auxin
- All the above.
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 111. When a bottle of perfume is placed in one corner of a room and the lid is opened, the scent spreads all over the room after some time. This happens by the process of :
- Plasmolysis
- Diffusion
- Endosmosis
- Transpiration.
Answer: 2. Diffusion
Question 112. The path of water and solutes from the soil to the conducting tissue of the root is :
- Soil → root hair→ cortex→ endodermis →pericycle protoxylem →phloem
- Soil → root hair → cortex →A pericycle → endodermis →protoxylem → metaxylem
- Soil epidermal cell of the root cortex → endodermis → pericycle → protoxylem → metaxylem → secondary xylem
- Soil → root hair → cortex → endodermis → pericycle → protoxylem → metaxylem.
Answer: 4. Soil → root hair → cortex → endodermis → pericycle → protoxylem → metaxylem.
Question 113. Capillarity is regarded as relatively unimportant as a possible cause of sap rise because :
- Vessels do not show capillarity
- Capillarity would cause sap to rise only a few inches or a few feet
- The tracheids and vessels are very narrow
- Absorption between xylem walls and water molecules is very low.
Answer: 2. Capillarity would cause sap to rise only a few inches or a few feet
Question 114. What will be the nature of the sugar solution, if the cell of an epidermal peal of Rhoeo discolor shows plasmolysis :
- Hydrophobic
- Hypertonic
- Isotonic
- Hypotonic.
Answer: 2. Hypertonic
Question 115. Xylem channels of the rootlets maintain a low water potential due to :
- Maintenance of high salt content
- Presence of negative pressure of water tension
- Both A and B
- Occurrence of positive pressure.
Answer: 3. Both A and B
Question 116. Water and minerals move towards the vascular cylinder of a root, they must enter the cytoplasm of :
- Xylem cells
- Cortex cells
- Endodermal cells
- Pericycle cells.
Answer: 3. Endodermal cells
Question 117. Most vascular plants increase the absorption of minerals by:
- Mycorrhizae
- Convertible phloem
- Casparian channels along the phloem
- Companion cells.
Answer: 1. Mycorrhizae
Question 118. Endosmosis of water occurs when in comparison with the outer solution, the water potential of cell sap is :
- Higher
- Lower
- Equal
- None of the above.
Answer:2. Lower
Question 119. If the cell (X) with DPD = 5 atm. is surrounded by many cells with DPD = 4 atm :
- The net movement of water will be from cell X to the surrounding cells
- The net movement of water will be from the surrounding cells to cell X
- Water will not move at all
- Water movement will depend on other unknown factors.
Answer: 2. Net movement of water will be from the surrounding cells to cell X
Question 120. Uptake of mineral ions into the xylem is controlled by:
- Epidermal cells
- Cortex cells
- Endodermal cells
- Xylem cells.
Answer: 3. Endodermal cells
Water potential NEET MCQs
Question 121. The opening and closing of stomata in leaves of mesophytic plants is reduced by :
- Changes in C02, K ions, and ABA concentration, with simultaneous changes in the turgidity/ flaccidity of guard cells.
- Changes in the starch sugar concentration in the guard cells
- Changes in the H+ concentration in the guard cells
- Differential thickening of walls of the guard cells.
Answer: 1. Changes in C02, K ions, and ABA concentration, with simultaneous changes in the turgidity/ flaccidity of guard cells.
Question 122. Tick the correct statement:
- The amount of water absorbed by closely packed and loosely packed imbibing will depend upon the temperature of the medium
- Both will imbibe the same amount of water
- The closely packed imbibing will imbibe less water than the loosely packed one
- The closely packed imbibing will imbibe more water than the loosely packed one.
Answer: 3. The closely packed imbibing will imbibe less water than the loosely packed one
Question 123. Mark the correct statement:
- The value of TP remains the same at the time of limiting, incipient, and evident plasmolysis
- The value of T.P. becomes zero at the time of limiting plasmolysis and below zero during incipient and evident plasmolysis
- The value of T.P. becomes below zero at the time of limiting plasmolysis and zero at the time of incipient and evident plasmolysis
- The value of T.P. becomes negative in all the stages of plasmolysis. “
Answer: 2. The value of T.P. becomes zero at the time of limiting plasmolysis and below zero during incipient and evident plasmolysis
