NEET Biology Diversity Of Life Five Kingdoms Of Life And Biological Classification
Kingdom Classification Definition
- Life can be defined as a unique, complex, organization of molecules that acquire and use energy for metabolism, expressing itself through chemical reactions which lead to growth. development, responsiveness, adaptation, and reproduction.
- Aggregation, interaction, equilibrium, and change regulate all types of organizations.
- The cellular organization of the body is the defining feature of all living organisms.
- A group of cells meant to perform a specific function is called tissue.
- A biological organization starts with submicroscopic molecular levels, passes through the microscopic cellular level and microscopic or macroscopic organismal level, and ends in ecosystems and biosphere.
- Reproduction is a characteristic feature of all living organisms and ensures the perpetuation of the species.
- In living organisms, thermal energy is produced during energetic reactions. The ectothermic animals such as fish, amphibians, reptiles, and plants.
- Mammals, birds, and a few fishes instead of losing thermal energy retain it. They are termed endothermic.
- Living organisms maintain their internal organization stable irrespective of changes in the environment. It is termed homeostasis.
- Living systems are open systems.
- Metabolism is the total of all chemical reactions taking place in the body.
- Metabolic reactions are of two types i.e. building up reactions termed anabolism and breaking down reactions as catabolism.
- Consciousness is the defining property of living organisms.
- There are innumerable plants, animals, bacteria, and viruses. Each one differs from the other.
- Biological classification is the art of identifying distinctions among organisms and placing them into groups.
- There is a great diversity among living organisms termed biodiversity. Biologists estimate that about 1.7 million kinds of organisms are living today on the planet Earth. Out of these 1.2 million are animals and 0.5 are million plants.
- About 15000 species are discovered every year.
- Underwater reefs and tropical rainforests possess innumerable undiscovered species.
- About 50-100 times more species are already extinct.
- Total living organisms vary between 5-30 million.
- Out of a million of the known species of animals and insects forms the largest group with 750000 species.
- Many species appeared and disappeared during the 3.5 billion years of long history of life.
- Over half a million species are unexplored.
- Taxonomy is the branch of biology concerned with the relationship between organisms and their classification.
- Taxon. It is any level of grouping of organisms e.g. mammals, roses, poppies.
- Category. Rank in Linnaean hierarchy eg. family Rosaceae, order Rosales class Dicotyledoneae.
- Species is the basic unit of classification.
- Each species is given a unique Iatin binomial, name consisting of genus name and species epithet.
- Species are grouped into progressively more inclusive higher categories.
- The main levels in the taxonomic hierarchy, from most to least inclusive are Kingdom, Phylum/Division, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species.
- Intermediate categories arc super or subdivision. The tribe is a subdivision of a family.
- The binomial system of nomenclature was first used by Linnaeus.
- Species change slowly over generations.
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
NEET Biology Notes
NEET Biology Five Kingdoms Artificial Natural Lmiylocknktic Systems Of Classification
- Systems of classification may be artificial, natural, or pltylogcnclic.
- Artificial System. It is more or less an arbitrary system with only a few characters of the organisms considered, like the grouping of plants into herbs, shrubs, and trees or the sexual system of Linnaeus based on several stamens and styles.
- These characters do not throw any light on the affinities or inter-relationships of plants. Hence closely related plants are placed wide apart.
- The artificial system hence is of help only in finding the name of a plant.
- The best-known artificial system is Linnaeus (1735).
- Natural System. It is a system based on considerations of several important characters and classification is done according to the related characters taking the affinities and inter-relationship into account.
- The system hence reflects the situation thought to exist under natural conditions.
- Some of the Natural systems of classification are of John Ray and Bentham and Hooker.
- Phylogenetic System. The plants are classified according to their evolutionary and genetic affinities.
- However, the fossil record available at present is not sufficient and hence the plants are classified partly on a natural basis and partly on a phylogenetic basis.
Different Classification Systems For Living World
- Takhtajan (1967) in his ‘Flora of Armenia’ has given a phylogenetic classification based on the classification of Bentham and Hooker. His classification is of considerable merit since he has made use of the maximum data available through Morphology, Cytology, Palynology, Anatomy, Embryology, Cytogenetics, Biochemistry, and Palaeobotany in the construction of taxa of various ranks.
- Some of the phylogenetic systems are those of Hutchinson, Tippo, and Takhtajan.
NEET Biology Five Kingdoms Modern Trends In Taxonomy
- Taxonomy study aimed at producing a hierarchical system of classification of organisms which Ivst reflects the totality of similarities and differences.
- Systematic It is the system of classification based on evolution and other relationships 01 systematise is the science of the diversity of organisms.
- New systematic taxonomy has become a very interesting subject knitting together all kinds of relationships between various plants.
- Characteristics of “New Systemnllcs.”
New Systematicy. It was introduced by Sir Julian 1luxley ( 1940) to overcome the failures of classical systematicy. It is characterized as follows:
The strictly morphological definition of species has been supplanted by a biological definition incorporating ecology, geography, genetics, cytology, physiology, biochemistry, and behavior.
- The significance of the species itself diminishes since the majority of research focuses on subdivisions, including subspecies and populations.
- Species are considered a dynamic entity rather than the static entity of classical systematics.
- Gross Morphology. Morphological categorization offers the most effective foundation for a comprehensive classification due to the simplicity of its characteristics.
- Anatomical. Tippo has delineated the evolutionary pathways of stem structure, specifically concerning the secondary xylem of angiosperms. Stem anatomy verifies that Magnoliales are the most basic angiosperms.
- Palynological. Woodhouse has demonstrated that one-furrowed pollen grains are primitive and present in Gymnosperms and early angiosperm groups such as Magnoliaceae.
- Pollen morphology of primordial angiosperms indicates the existence of two principal dicot lineages: Magnolian (monocolpate) and Ranalian (tricolpate).
- Cytotaxonomy. Cytotaxonomy refers to the classification of plants and animals based on their cytological structure.
- Biochemical Systematics. The categorization of flora and fauna according to biochemical traits is termed biochemical systematics.
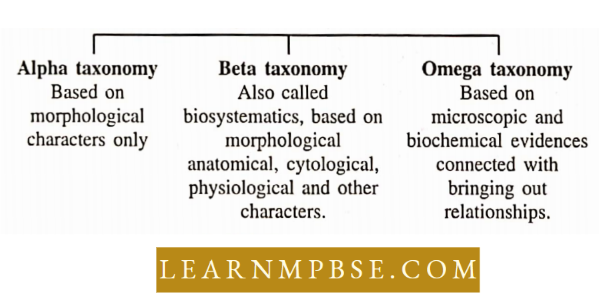
- Alpha Taxoalynology, biochemistry, physiology, etc. (P taxonomy of Turrill).
Turill gave taxonomy in three parts:
NEET Biology Five Kingdoms Binomial Nomenclature
Carl Linnaeus (1758) was the pioneer in the introduction of scientific nomenclature. His nomenclature for animals and plants assigns each a binomial designation.
- The first designation is referred to as the generic name, while the second denotes the species name.
- Generic names may be assigned to multiple animals or plants based on their similarities, whereas a unique and specialized name is designated for each species.
- The specialized name may denote certain qualities such as habitat, behavior, morphology, dimensions, and coloration. Rana tigrina is the designation for a frog species.
- Rana is a generic designation, whereas tigrina refers to a specific species. Tautonyms. If both the generic and particular names are identical, they are referred to as autonyms, a term not widely recognized by contemporary biologists.
Biological Classification NEET Study Material
Type Method Principle:
The application of names of taxa of the rank of family or Mow iv determined using nomenclatural types. The nomenclature type Is a taon with which the name of the taxon Is permanently associated. It is not necessarily the most typical or representative element of a taxon.
- The holotype is the one specimen or another element (description/figure) designated by the author and nomendatuntl type.
- Isotype. Duplicate of the holotype (other specimens collected at the same time)
- Specimen or other element selected from the original material to serve as nomenclatural type when no holotype was designated at the time of publication or it is missing.
- Neotypc. Specimen or other element selected to serve as nomenclatural type as long as all of the material, on which the name of the taxon was based, is missing.
- Paratype. It is a specimen cited with the original description other than the holotype or isotype.
- Syntype. Any ofthe two or more specimens cited by the author when there is no holotype.
Nomenclature
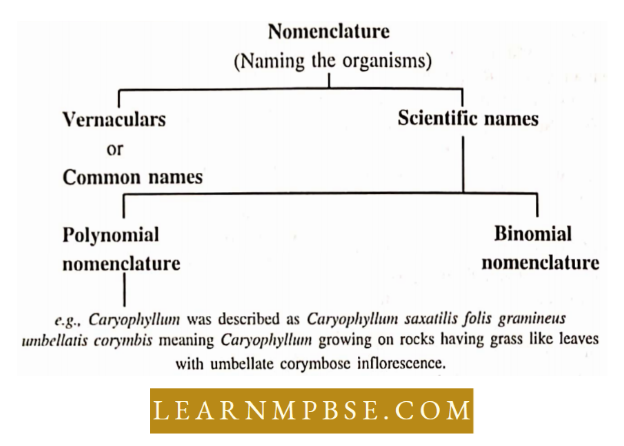
- Some rules of binomial nomenclature were first proposed by Casper & Bauhin in the book Pinax.
- Linnaeus-Karl von Lanne (1707) in Sweden at the age of 22 published a paper ‘Sexuality of Plants’.
- Linnaeus gave some rules of binomial nomenclature in the book Philosophia Botanica (1751), Species Plantarum (1753), and Systema Naturae (1758).
Rules of binomial nomenclature
- All organisms should have distinct and specific names.
- All names given before the 10th edition of Systema Naturae (1758) are discarded except seed plants for whom the date is 1/5/1753.
- If two names are given to the same organism by two different scientists then the name given first after 1/8/1758 will be accepted and the other one will be called as its synonym (by law or rule of priority), e.g. Albugo Candida is a valid name whereas, Cytopus Candida is a synonym.
- If the binomial name is to be printed it should be printed in Italics. If handwritten, genus and species should be underlined separately.
- The name will have two parts genus and species.

NEET Biology Five Kingdoms Classification
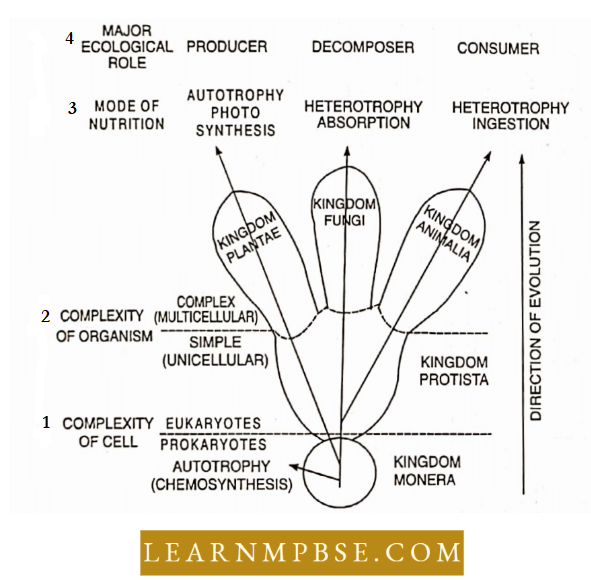
R. H Whittaker divided the living into five kingdoms based on the following criteria:
- The complexity of cell structure, Pmkaryoiie or Eukaryotic.
- Complexity of body structure (level of structural organization). Unicellular and multicellular.
- Mode or nutrition. Autotropliy, heterotrophy (absorptive and digestive).
Geological role. clusters, carnivores, or decomposers. Whittaker’s Five Kingdoms arc :
- Moncra, Protista. Plantac, Fungi and Animalia
- Kingdom Monera. Moncrans arc prokaryotes. Bacteria, Blue-green algae.
- Kingdom Protista. Protists are unicellular eukaryotes that have widely diverse lifestyles.
- Protists form the precursors from which higher forms—Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia— arose on photosynthetic, assimilative, and ingestive lines. Mastigophores, Ciliates, Sarcodines, Spoaizoans, slime molds, diatoms.
- Kingdom Fungi. Fungi are eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms with assimilative nutrition. Rhizopus, Agaricus.
- Kingdom Plantae. Plantae includes eukaryotic multicellular, photosynthetic organisms.Grcen multicellular plants.
- Kingdom Animalia. Animals are eukaryotic, multicellular consumers characterized by ingestive nutrition. Non-chordates and chordates.
Important Contributors
- Carl. P Linnaeus. The Father of Taxonomy gave an artificial system of classification. He introduced Binomial nomenclature. He wrote “Systema Naturae”, “Species Plantarum” and “Philosophia Botanica” Genera Plantarum -4 Bentham & Hooker,
- John Ray. Introduced the term species. He wrote a book titled “Historia Generalis Plantarum”.
- Pliny the F.lder (28-79). Introduced the first system of artificial classification. He wrote a book titled “Historia Naturalis.”
- Aristotle was the first to classify organisms as “Aristoria Animalia”.
- Charaka. (An Indian) classified plants of medicinal value and wrote “Charaka Samhita”. He described 200 kinds of animals and 340 kinds of plants.
- Parasara (An Indian) described plants of medicinal value in his book “Vrikashayurveda”.
- J. K. Maheshwari described plants of Delhi in his book “Flora of Delhi”
- J. D. Hooker wrote “Flora of British India”
- Diocorides described plants in his hook “Mntcrla Mctllcn”
- Kmst Meyer gave the biological species concept based on reproductive Isolation Fuller and Tippo introduced partly natural and partly artificial systems of classification.
- J.I. Cuvier used the term phylum.
- R. If. Whittaker. Imposed five kingdom classification.
- Turrill (1938). He gave a-Taxonomy and P-Taxonomy.
- Turner wrote a book titled ‘Herbnll’
- Lindley wrote a book titled “The Vegetable Kingdom”.
Botanical gardens are sufficiently large tracts where plants of different types and different areas are grown for scientific and educational purposes.
Five Kingdom Classification Notes
One of the important herbaria in India are Central National Herbarium. Kolkata and Herbarium of FRI, Dehradun.
- Royal Botanical Garden, Kew, England extends over 250 acres of land. Botanical gardens keep records of local flora.
- There is a big Botanical Garden in Kolkata having the Great Banyan Tree.
- The herbarium is a collection of well-dried and nicely preserved plants that are correctly identified and arranged according to an approved system of classification.
- The herbarium serves as the reference material for modern taxonomical research and education.
- The collection of plants is the first step in the direction of making a herbarium.
- The collected plants are pressed immediately between sheets of newspapers or blotting papers to dry them. After drying the plant materials are mounted on her barium sheets.
- Herbaria can be classified into three categories:
- National
- Regional and
- Local
- One of the important herbaria in India are Central National Herbarium. Kolkata and Herbarium of FRI, Dehradun.
- The term “wildlife” generally gives an impression of large and ferocious animals living in jungles or water bodies and may include lions, tigers, elephants, rhinoceros, crocodiles, and whales.
- But actually, wildlife refers to any type of living organism (plant or animal or microbes), in a natural habitat other than cultivated plants and domesticated animals.
- Zoological Park (Zoo). It is an area where many kinds of living animals are kept so that people can look at them or study them.
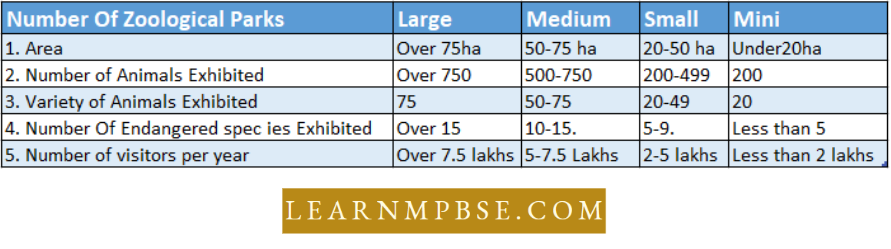
- There are over 300 zoological parks in India.
- These are classified as large, medium, small, and mini based on the area, variety of animals exhibited, number of endangered species exhibited, and number of visitors visited per year.
- For the conservation of wildlife rare species of plants and animals have been categorised as endangered, vulnerable, and rare according to the degree of danger facing them.
- National parks, biosphere reserves, and sanctuaries will form the refuge for wild plants and animals in the years to come.
- Protected area. It is the area created for the protection, preservation, and propagation of the varied natural bounty.
- The government of India passed the Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972, under which national parks and sanctuaries could be created as protected areas.
- National park. It is an area that is strictly reserved for the betterment of wildlife and where activities such as forestry, and grazing cultivation are not permitted. There are 66 national parks in the country which are spread over an area of 33,988.14 sq. km. (Nearly 1% of total geographical area)
- Sanctuary. In a sanctuary, protection is given only to animal life. In such areas, private ownership is allowed. Harvesting timber, and collection of forest products are permitted so long as they do not interfere with the well-being of animal life.
- There are 368 sanctuaries spread over an area of 1,07,310,13 square kilometers (Nearly 3.2 percent of the total geographical area). about 1000 pillar-like aerial roots which provide support to the canopy. It is about 100 feet in height and is supposed to be the largest living creature in the world houses. They are elegant metal structures covered with wire netting.
- A large number of pretty creepers are grown over the structures whose foliage provides the shade for the growth of rare palms, ferns, and other shade-loving plants. Over forty species of palms are grown in¬ including the rare branching palm Hyphaene thcbaiai.
- Museums perform the following functions: Acquisition of materials,
- Recording of materials preservation of materials reearch exhibition of materials education. Key. A scheme for the identification of plants and animals.
- Taxonomic keys are based on contrasting characters. Generally, keys are of two types i.e. Yorked or Indented key and Bracketed key.
NEET Biology Five Kingdoms Quanta To Memory
- Unique features of living organisms are growth, reproduction, ability to sense the environment and respond.
- Metabolism, the ability to self-replicate, self-organize, and interact are other features of life.
- Photoperiods affect reproduction in seasonal breeders in both plants and animals.
- Biology is regarded as the story of life and evolution of living organisms on earth.
- There are about 1.7 to 1.8 million species that are known to be described. It refers to biodiversity. Founder of Taxonomy/Father of Biology/Father of Zoology—Aristotle.
- Father of Botany—Theophrastus.
- In the Biological Taxonomic hierarchy from species to kingdom, the number of common characteristics goes on decreasing.
- Species is the basic unit of taxonomy.
- Species include interbreeding, reproductively isolated organisms. But the idea of species is discarded on the basis that species are nothing but man-made, which is wrong. Species are not fixed as the process of evolution is continuous and natural selection always works on organisms.
- The fossil study shows that earlier simpler organisms gradually evolved into complex ones. The earliest fossils, about 3.1 billion years old, resemble the existing bacteria.
Classification Of Mango
- Kingdom: Plantae
- Division: Spennatophyta (Erabryophyta Siphonogama)
- Subdivision: Angiospemiae
- Class: Dicotylcdoneae
- Order: Sapindales
- Family: Anacordiaccae
- Germs: Mangifcra
- Species: Indica
Classification Of Tiger
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Division: Chordata
- Subdivision: Vertebrata
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Carnivora
- Family: Felidae
- Germs: Panthera
- Species: Tigris
Suffixes. According to the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature, the names of different ranks must end in the following standard endings (suffixes)—
- Rank— Suffix
- Division — phyla (Example; Bryophyta)
- Subdivision — physical (Example; Pterophytina)
- Class — apsidal (Example; Lycopsida)
- or ae (Example; Magnolioatae)
- or phytate (Example; Chlorophyceae)
- Order—ales (Example; Volvocales)
- Suborder— lineae (Example; Malvineae)
- Family— Poaceae (Example; Malvaceae)
- Subfamily— ideas (Example; Mimosoideae)
- Trade-in
Five Kingdoms Of Classification NEET
Biological classification is not rigid and is subject to modification as more and more is learned about organisms.
- The phylogenetic classification reflects the evolutionary relationships of organisms. The organisms related to evolution are usually similar morphologically also.
- Water lily has 81 Dutch names, 44 French names, and 15 English names.
- Atharva Veda mentions 108 plants with powers to heal wounds, skin grafting, hair growth, increased milk yield, bone setting, etc.
- The terms prokaryotes and eukaryotes were coined by Folt.
- S. Prusiner was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1997 for his contribution to infectious agents called Prions which are made up of proteins without any nucleic acids. Numerical taxonomy is the same as phenetic taxonomy.
- It emerged in 1950. It employs numerical methods for the evaluation of similarities and differences between species.
- In this method as many characteristics as possible are used for their comparisons, without extra emphasis being given to anyone.
- Such a comparison is possible due to the availability of sophisticated machines and computers.
- This system is considered better because it uses a large number of comparable characters. A family tree based on numerical phenetic taxonomy is called a dendrogram.
NEET Biology Five Kingdoms Classification Questions From Competitive Examinations
Question 1. Phenolic classification is based on:
- Sexual characters
- The ancestral lineage of existing organisms
- Observable characteristics of existing organisms
- Dendrograms based on dna characteristics.
Answer: 3. Observable characteristics of existing organisms
Question 2. In which kingdom would you classify the archaea and nitrogen-fixing organisms in the five-kingdom system of classification
- Monera
- Plantae
- Fungi
- Protista.
Answer: 1. Monera
Question 3. Species are considered as:
- Real units of classification devised by taxonomists
- The real basic unit of classification
- The lowest unit of classification
- The artificial concept of the human mind cannot be defined in absolute terms.
Answer: 2. The real basic unit of classification
Question 4. Plants reproducing by spores such as mosses and ferns are grouped under the general term:
- Thallophytes
- Cryptogams
- Bryophytes
- Sporophytes.
Answer: 2. Cryptogams
Question 5. Which pair of examples will correctly represent the grouping of Spermatophyta according to one of the schemes of classifying plants?
- Ginkgo, Pisum
- Acacia, sugarcane
- Pinus, cycas
- Rhizopus, triticum.
Answer: 1. Ginkgo, Pisum
Question 6. From the point of tiger reserve and state which one of the following groups is correct?
- Corbett-Madhya Pradesh
- Palamu-Orissa
- Manas-Assam
- Bandipur-tamil nadu.
Answer: 3. Manas-Assam
Question 7. Who wrote ‘species plantarum’ and provided a basis for the classification of plants:
- Av. Leeuwenhoek
- Charles Darwin
- Carl Linnaeus
- Robert Hooke.
Answer: 3. Carl Linnaeus
Question 8. Which of the following animals is protected in Kaziranga sanctuary in Assam?
- Indian lion
- Indian bison
- Indian elephant
- Indian rhinoceros
Answer: 4. Indian rhinoceros
Five Kingdom Classification Chart
Question 9. The species whose number has been reduced considerably and are on the verge of extinction, are called:
- Vulnerable
- Rare
- Endangered
- Threatened.
Answer: 1. Vulnerable
Question 10. Which one of the following is a pair of endangered species?
- Garden lizard and Mexican poppy
- Rhesus monkey and sal tree
- Indian peacock and carrot grass
- Hombill and indian aconite.
Answer: 4. Hombill and Indian aconite.
Question 11. The Bengal tiger becomes extinct:
- Hyaenas and wolves will become scarce
- Its gene pool will be lost forever
- The wild areas will be safe for man and domestic animals
- The populations of beautiful animals like deer will get stabilized.
Answer: 2. Its gene pool will be lost forever
Question 12. Which of the following is not true for a species?
- Members of a species can interbreed
- Variations occur among members of a species
- Each species is reproductively isolated from every other species
- Gene flow does not occur between the populations of a species.
Answer: 4. Gene flow does not occur between the populations of a species.
Question 13. One of the most important functions of botanical gardens is that:
- One can observe tropical plants there
- They allow ex-situ conservation of germplasm
- They provide the natural habitat for wildlife
- They provide a beautiful area for recreation.
Answer: 2. They allow ex-situ conservation of germplasm
Question 14. The outer protein covering of the virus is :
- Virion
- Viroid
- Capsid
- Coat.
Answer: 3. Capsid
Question 15. The modem system of classification classified the organisms into kingdoms.
- One
- Two
- Four
- Five.
Answer: 4. Five.
Question 16. In the kingdom system of classification of r.h. Whittaker, how many kingdoms contain eukaryotes?
- Four kingdoms
- One kingdom
- Two kingdoms
- Three kingdoms.
Answer: 1. Four kingdoms
Question 17. Englar and Prantle published a phylogenetic system in the monograph.
- Die naturlichen pflanzen familien
- Historia planlanim
- Species planlanim
- Genera planlanim.
Answer: 4. Genera planlanim.
Question 18. Two species are ntoiphologicully almost do not, such species are called:
- Evolutional species
- Sibling species
- Polyty pic species
- Sympatric species
Answer: 4. Sympatric species
Question 19. Reproduction can occur within members of a:
- Species
- Genus
- Order
- Family
Answer: 1. Species
Question 20. Binomial nomenclature was given by:
- Lamarck
- Linnaeus
- Darwin
- Tijo and Levan.
Answer: 2. Linnaeus
Five Kingdom Classification Chart
Question 21. Classification based on chromosome number is called :
- Numerotaxonomy
- Cytotaxonomy
- Chemotaxonomy
- None of these.
Answer: 2. Cytotaxonomy
Question 22. Select the false statement:
- Scientists who study and contribute to the classification of organisms are known as systematists
- Carolus Linnaeus developed the first scientific system of naming species
- A five-kingdom arrangement of organisms was introduced by R.H. Whittaker
- A genus is a group of species that are related and have fewer characters in common as compared to species
- Phycomycetes are called club fungi because of a club-shaped end of mycelium known as basidium
Answer: 1. Scientists who study and contribute to the classification of organisms are known as systematists
Question 23. Which of the following is not correctly matched?
- Chlamydomonas – unicellular flagellated
- Laminaria – flattened leaf-like thallus
- Chlorella- filamentous non-flagellated
- Spirogyra- filamentous structure
- Volvox- colonial form non-flagellated
Answer: 5. Volvox- colonial form non-flagellated
Question 24. Which of these is mismatched?
- Phaneros- visible
- Kryptos- concealed
- Gymno- naked
- Bryon- liverworts
- Trachea- windpipe.
Answer: 5. Bryon- liverworts
Question 25. In the classification of plants, the term cladistics refers to the:
- Phylogenetic classification
- Sexual classification
- Classification
- Classification
- Binomial classification,
Answer: 1. Phylogenetic classification
Question 26. Identify from the following, the only taxonomic category that has a real existence.
- Genus
- Species
- Phylum
- Kingdom.
Answer: 2. Species
Question 27. Icbn stands for:
- International code of botanical nomenclature
- International congress of biological names
- Indian code of botanical nomenclature
- Indian congress of biological names.
Answer: 1. International code of botanical nomenclature
Question 28. Two plants can be conclusively said to belong to the same species if they:
- Have more than 90 percent similar genes
- Iook similar and possess identical secondary metabolites.
- Have the same number of chromosomes
- Can reproduce freely with each other and form seeds.
Answer: 4. Can reproduce freely with each other and form seeds.
Question 29. New systematics introduced by Sir Julian Huxley is also called:
- Phenetics
- Cladistics
- Biosystematics
- Numerical taxonomy
- Chemotaxonomy.
Answer: 3. Biosystematics
NEET Biology Handwritten Notes
Question 30. Which one of the following animals is correctly matched with its particular taxonomic category?
- Tiger – Tigris, the species
- Cuttlefish – Mollusca, a class
- Humans – primates, the family
- Housefly – Musca, an order.
Answer: 1. Tiger – Tigris, the species
Question 31. Which one of the following is not a correct statement?
- Botanical gardens have a collection of living plants for reference.
- A museum has a collection of photographs of plants and animals
- The key is taxonomic aid for the identification of specimens.
- Herbarium houses dried pressed and preserved plant specimens.
Answer: 2. A museum has a collection of photographs of plants and animals
