NEET Biology Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology
It pertains to the industry of advancements in research procedures and instruments within the biological sciences.
- The genesis of biotechnology is rooted in the depths of human history. At the inception of civilization, alcohol derived from fermented steep liquor or plant juices was likely the earliest result of biotechnology.
- Biotechnology is the application of biological organisms or their derivatives in industrial operations.
- Modern biotechnology refers specifically to techniques and production technol
- ogies that entail genetic engineering.
- The European Federation of Biotechnology (EFB) characterizes biotechnology as the amalgamation of natural sciences with organisms, cells, their components, and molecular analogs for the development of products and services; it includes both conventional perspectives and contemporary molecular biology.
Some Of The Biotechnological Products And Processes Are
- Recombinant DNA vaccines.
- Synthesis of a gene and introduction of it into a target cell/organism.
- Gene therapy.
- In vitro fertilization for production of test tube babies.
- Production of many biological compounds such as vaccines, antibodies vitamins, antibiotics, hormones, etc.
The organisms involved in industrial biotechnology may be as complex as cattle or as simple as a single-celled yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae.)
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
Bioreactor: The fermentation tank where fermentation is carried out in the presence of micro-organisms.
Biotechnology is closely linked to the development in the 1970s of genetic engineering (the directed alteration of genetic material). Substances that have been produced in this manner include human interferon (a natural virus-fighting substance), human insulin, and human growth hormone.
- Biotechnology has advanced rapidly in the last two decades due to advances in biology, microbiology, biochemistry, immunology, molecular biology, genetic engineering, and chemical engineering.
- Any organism can be used in biotechnology, for example, cattle, pigs, sheep, horses, monkeys, yeast, and a large number of microorganisms. For better yield, it is imperative to select a suitable strain/variety and evolve a suitable technique for the extraction and purification of the product.
- The first use of biotechnology must have been in pre-historic times when humans discovered the fermentation of alcoholic beverages and dairy products.
Genetic Engineering: It is a technique for artificially and deliberately modifying DNA (genes) to suit human needs. It is also called recombinant DNA technology or DNA splicing. It is a kind of biotechnology.
Principles Of Biotechnology: The two core techniques that enabled the birth of modern biotechnology are
- Genetic engineering technique of altering the nature or genetic material and/ or introducing it into another host organism to change its phenotype.
- Techniques to facilitate tile growth and multiplication of only the desired microbes or cells in large numbers, under sterile conditions for the manufacture of biotechnological products.
Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology NEET
Steps In Genetic Engineering (Recombinant DNA Technology)
- Identification and isolation of agronomically important genes.
- Cloning of isolated genes in a vector.
- Introduction of the gene into plant protoplast cells/tissues with the use of gene transfer method.
- Culture and regeneration of complete plant on suitable selection medium.
- Integration of foreign genes in the transgenic plants by using molecular techniques.
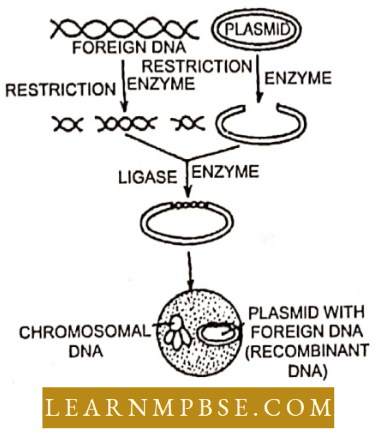
With the help of restriction enzymes DNA is cut at specific sites and then joined with DNA of plasmids or phages. Then these plasmids or phages known as vectors are introduced into a bacterium. The process is known as transformation.
With the division of bacteria, desirable quantities of that particular DNA segment can be obtained. The key tools needed for the recombinant DNA technology to be accomplished are:
- Cell culture with desired DNA
- Restriction enzymes
- DNA polymerase
- Ligases
- Vector (s)
- Host organism/cell.
NEET Biology Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology Cloning Vectors
Vectors And Their Types: A vector is defined as a DNA molecule capable of self-replication and used as the carrier of DNA segments to be cloned (Gene). In an actual sense, it is required for transferring and cloning the gene in a suitable host or bacterium.
- The gene is inserted in the vector forming Recombinant DNA or Recombinant vector. The recombinant vector is also called the hybrid vector or chimeric vector (chimera = a mythological monster with a lion’s head, goat’s body, and serpent’s tail).
- The vectors can be cloning vectors i.e., those which isolate, characterize, and clone genes, or expression vectors i.e., those which not only allow multiplication (cloning) but may also be manipulated in such a way that the inserted gene may express in the host.
- Use Of Plasmids as Genetic Material: Plasmids are obtained from bacteria. They are treated with restriction endonuclease enzyme to obtain the fragments of the desired genome. They are allowed to fuse with the help of DNA ligase enzyme. The recombinant plasmids thus formed are used as genetic material.
- Plasmid: Additional DNA rings present in bacteria can be elaved by R.E. (Restriction Endonuclease), and can be joined with foreign DNA by ligase.
- Ti plasmids of Agrobacterium and Ri plasmid of Agrobacterium rhizogenes are best-known vectors in higher plants.
- The Plasmids Normally Used As The Vectors Are: The size of plasmids ranges from 1 x 106 to 200 x 106 daltons. These can be of the following types
- Single copy plasmids i.e., those which occur one plasmid per cell.
- Multiple copy plasmids i.e., those which occur 10 to 20 copies per cell.
- There are also plasmids that, are under the relaxed replication control, thus permitting their accumulation in very large numbers i.e., up to 1000 copies per cell. These are the plasmids that we use for cloning purposes due to their increased yield potential.
- Bacteriophage DNA: Lambda (X) phage is another very useful vector for Gene cloning in bacteria. Plasmid vectors described above are normally used to clone DNA segments of small size i.e., up to 10 kilo bases.
- However, while preparing a genomic library for a eukaryote with quite large DNA fragments or even whole genomes the requirements of cloning are fulfilled by lambda phage derivatives used for transferring genetic material from one bacterium to the other.
- From these cloning of 20-25 kilobases is possible. These consist of linear double-stranded DNA molecules which have been engineered in a way that their lytic cycle is possible but a lysogenic cycle is not possible.
- The Lambda Phage Genome is λ about 50 kbp circular DNA. It follows either a lytic path or a lysogenic path. Lytic one may be switched towards lysogeny and vice versa. An important feature of the lambda genome is that only about 60% genome is required for the lytic growth of phage and the central 40% can be replaced by foreign DNA.
- The percentage of foreign DNA can be increased also but a maximum up the 75-95% of the wild genome. This is made possible by removing some of the non-essential parts of the phage genome but only up to a certain limit.
- The Lambda Cloning Vectors Are Of Two Types:
- The insertion vector, which accepts inserts only 2 kbp long at a single multiple cloning site λ gt 10 and λ gt 11 vectors.
- The replacement vectors, which accept inserts 9-23 kbp long with involvement of replacement of a non-essential part (stuffer) of the genome, for example, EMBL3 and EMBL4 vectors.
- Plant And Animal Vectors.
- Jumping Genes (Transposons)
- Artificial Chromosomes Of Bacteria, Yeast, And Mammals.
- Cosmids: These are the vectors that can accommodate DNA segments up to 45 kbp. These are actually plasmid particles to which specific DNA sequences, namely those for the cos sites are inserted.
- Since the cos sites enable the DNA to be packed in the phage (λ) particle we can say that cosmids allow the packaging of DNA in phage in vitro thus permitting their purification.
- Like plasmids, these cosmids also perpetuate in bacteria. The advantage of cosmids for cloning is that its efficiency is high enough to produce a complete genome library of 106 – 107 clones from a mere Img of insert DNA. The disadvantage is its inability to accept more than 40- 50 kbp of DNA.
- Phagemids: These arc plasmids with a fragment of filamentous phage DNA, thus combining the desirable features of both.
- Segments of foreign DNA cloned in them are multiplied as plasmid vectors, but when these plasmid vectors are infected with a filamentous phage called helper phage, the phagemid genome present already behaves like a phage.
- As a result of this the phagemid generates multiple copies of one strand of it and the associated DNA inserted in it.
- The single strand can be purified from these phage particles and used for:
- Sequencing
- Site-directed mutagenesis
- Synthesis of strand-specific probes
Phagemids have been developed by inserting intergenic regions of a variety of filamentous phages into plasmids.
Origin Of Replication (Ori)
- This is a sequence of base pairs on DNA where replication starts.
- Any piece of DNA linked to this sequence can be made to replicate within the host cells.
- This sequence is also responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA.
Process Of Biotechnology NEET
Selectable Marker
- A marker is a gene that helps in selecting those host cells that contain the vector (transformant) and eliminating the non-transformants.
- Common selectable markers for E. coli include the genes encoding resistance to antibiotics such as ampicillin. chloramphenicol, tetracycline, and kanamycin or the gene for β galactosidase which can be identified by a color reaction.
Enzymes Used In Genetic Engineering: The following Enzymes are used
- Lysing Enzyme: It is used to open up cells to get DNA for genetic experiments. Lysoenzyme and Lysozyme arc are commonly used to dissolve bacterial cell walls.
- Cleaving enzymes to break DNA molecules; of 3 types
- Exonuclease cuts off nucleotides from 5′ or 3′ end.
- Endonuclease cleaves DNA at any point except ends.
- Restriction Endonuclease. It cleaves DNA duplex at specific points → Discovered by Arbern Nathans and Smith (1962) in Bacteria.
- Uses Of Restriction Enzymes
- Restriction enzymes are used to cut a source DNA into small fragments for the isolation of a desired gene to be cloned.
- They are used to cut the vector DNAs at well-defined sites for cloning purposes.
- They are used to cut out unwanted sequences from natural vector DNAs to construct active vectors.
- They are used to cut a large DNA into small fragments for nucleotide sequencing.
- They are used to construct restriction maps of DNAs.
- They are used to cut DNAs to determine variant sequences among the DNAs of closely related individuals by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RELP).
- DNA Polymerase. Help in the formation of DNA strands on DNA template.
- Joining Enzyme (Ligase): Join and reseal the gaps in DNA fragments.
Fragmentation DNA: Fragmentation of DNA is carried out by incubating the purified. DNA molecules with suitable restriction enzymes at optimal conditions of temperature anil pH.
Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology NEET
Isolation Of DNA (Gene) Of Interest
- The fragments of DNA are separated by a technique called gel electrophoresis.
- The DNA is cut into fragments by restriction endonucleases.
- These fragments are separated by a technique called gel electrophoresis.
- Agarose, a natural polymer obtained from seaweeds is used as the matrix.
- DNA fragments being negatively charged, are separated by forcing them to move through the matrix towards the anode under an electric field.
- The DNA fragments separate/resolve according to their size.
- The separated molecules are stained by ethidium bromide and visualized by exposure to UV- radiation, as bright orange colored bands.
- The separated bands of DNA (on the gel) are cut from the gel and extracted from the gel piece (elution).
- Such DNA fragments are purified and used for constructing recombinant DNA by joining them with cloning vectors.
Amplification Of The DNA/Gene Of Interest.
- Amplification refers to the process of making multiple copies of the DNA segment in vitro.
- It employs polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
- The process was designed by K. Mullis.
- This technique involves three main steps :
- Denaturation
- Primer annealing and
- Extension of primers.
- The double-stranded DNA is denatured by using high temperatures.
- Two sets of primers are used; primers are the chemically synthesized short segments of DNA (oligonucleotides), that are complementary to the segment of DNA (of interest).
Ligation Of The DNA Fragment With The DNA Of The Vector.
- After cutting the source DNA segment and the vector DNA (to make the space for source DNA), the two are mixed and incubated with ligase under suitable conditions.
- This results in the formation of recombinant DNA (rDNA)
Transfer Of Recombinant DNA Into The Host.
- The bacterial cells must be made competent to take up DNA; this is done by treating them with a specific concentration of calcium, that increases the efficiency with which DNA enters the cell through the pores in its cell wall.
- Recombinant DNA can then be forced into such cells by incubating the cells with recombinant DNA on ice followed by placing them at 42°C and then putting them back on ice.
- Microinjection is a method in which the recombinant DNA is directly injected into the nucleus of the animal cell with the help of microneedles or micropipettes.
- Gene gun or biolistics is a method suitable for plant cells, where cells are bombarded with high-velocity microparticles of gold or tungsten coated with DNA.
- Disarmed pathogens are used as vectors; when they are allowed to infect the cell, they transfer the recombinant DNA into the host.
Culturing The Transgenic Cell.
- The cell containing the foreign gene (transgene) is cultured on a suitable medium.
- The cells multiply and make clones.
Extraction Of The Desired Product.
- The transgene expresses itself in the form of protein (s) under appropriate conditions.
- The product (s) can be extracted from the medium by employing a suitable procedure.
- Bioreactors are used for processing large volumes of culture to obtain the product of interest in sufficient quantities.
Biotechnology Principles And Processes NEET Study Material
Downstream Processing
- The product obtained is subjected to a series of processes (collectively called downstream processing) before it is made into a finished product ready for marketing.
- The two main processes are (1) separation and (2) purification.
- The product is then formulated with suitable preservatives.
- Such formulations have to undergo clinical trials, in the case of drugs.
Restriction Enzymes, Their Source, And The Target DNA Sequence With Cleavage Site

NEET Biology Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology Steps Of Genetic Engineering (RDNA Technology)
Isolation Of DNA
- DNA has to be isolated in pure form for the action of restriction enzymes.
- DNA can be released from the cells by digesting the cell envelope by the use of enzymes like lysozyme for bacterial cells, chitinase for fungal cells, and cellulose for plant cells.
- Since DNA is intertwined with histone proteins and RNAs, proteins are removed by treatment with proteases and RNAs by ribonucleases. o Other impurities are removed by employing suitable treatments.
- The purified DNA is precipitated by the addition of chilled ethanol; it is seen as a fine thread in suspension.
Importance Of Genetic Engineering Includes The Following :
- Gene Splicing: In Eukaryote, DNA is made up of exon (coding segment) and intron (Non-coding segment) or junk gene. This is also called the concept of split genes. It was discovered by RJ. Roberts and Phillip Sharp Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine (1993).
- As far as transcription is concerned, entire DNA is transcribed to form mRNA. (heterogeneous) mRNA : (heterogeneous mRNA); If segments of mRNA corresponding to intron are removed, and remaining mRNA segments (corresponding to exon) are joined together, the mRNA (fully translatable) is called processed or spliced RNA.
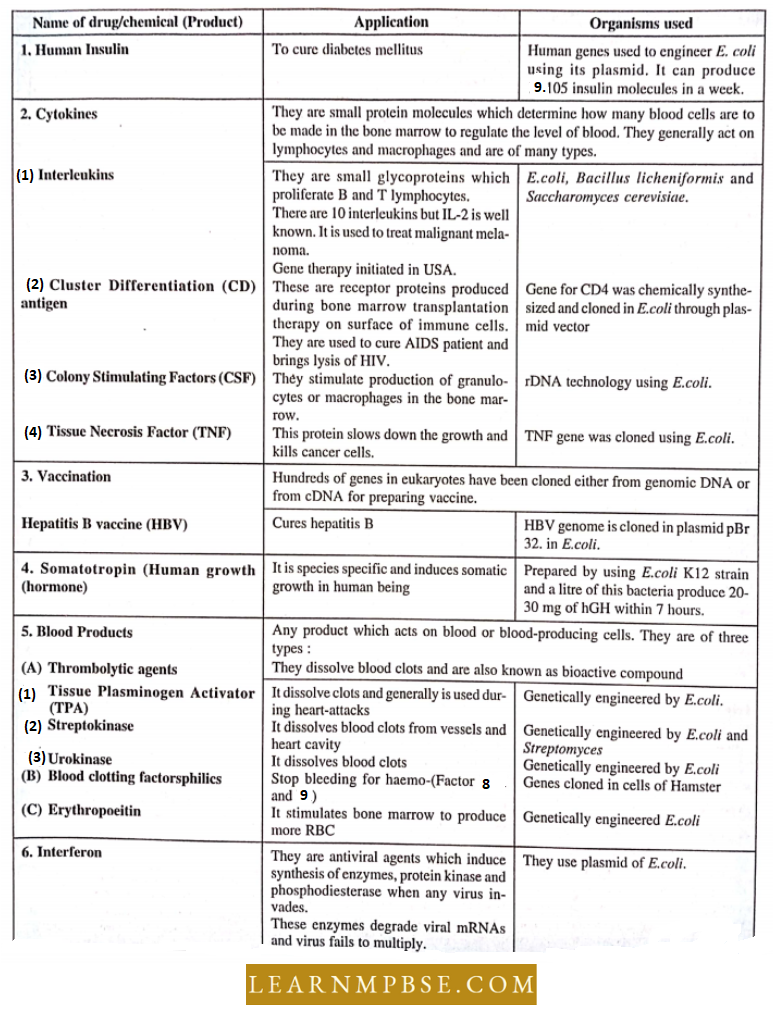
NEET Biology Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology Production Of Various Drugs And Chemicals
Numerous medications, vaccines, pharmacological agents for the treatment of diverse ailments, and hormones have been created via genetic engineering (recombinant DNA technology), with several currently undergoing release.
A few are described below:
NEET Biology Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology DNA Cloning
To clone a specific gene, namely a DNA segment, it is essential to possess a pure fragment of DNA that encompasses that gene. There are various methods to acquire DNA. Single-stranded mRNA undergoes enzymatic conversion to double-stranded DNA. The resultant double-stranded DNA is termed complementary DNA (cDNA).
Process Of Biotechnology NEET
Clone DNA Can Be Obtained By
- Separation of those segments of DNA which are to be cloned.
- λ phage is used to join the DNA segment vector.
- To get more of isolated clones these vectors and DNA segment is inserted in the host cell where the division it provides many copies of the wanted DNA segment.
- Selection of wanted clone.
- Store the clones in the Gene Bank.
- It is easy to prepare a clone when the size of DNA segment is 10kb or more otherwise recombination is difficult.
- According to Boffey (1987), to get a segment of 10kb DNA 1.5 x 103 colonies are to be raised of the E. coli genome and in Homo sapiens, 2 x 106 colonies are to be raised.
- To get more number of clones host cells are cultured in a culture medium and the wanted gene is separated by the use of a restriction enzyme and then stored.
- If a particular gene is needed, it is taken from the gene bank inserted into the vector, and taken to the host cell.
NEET Biology Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology Organism Cloning
Production of individuals having identical genetic makeup from one parent through asexual reproduction is the cloning of organisms. Clones are exact genetic replicas of an individual. Clones of plants, bacteria, and protozoa can be easily obtained by vegetative propagation and asexual reproduction.
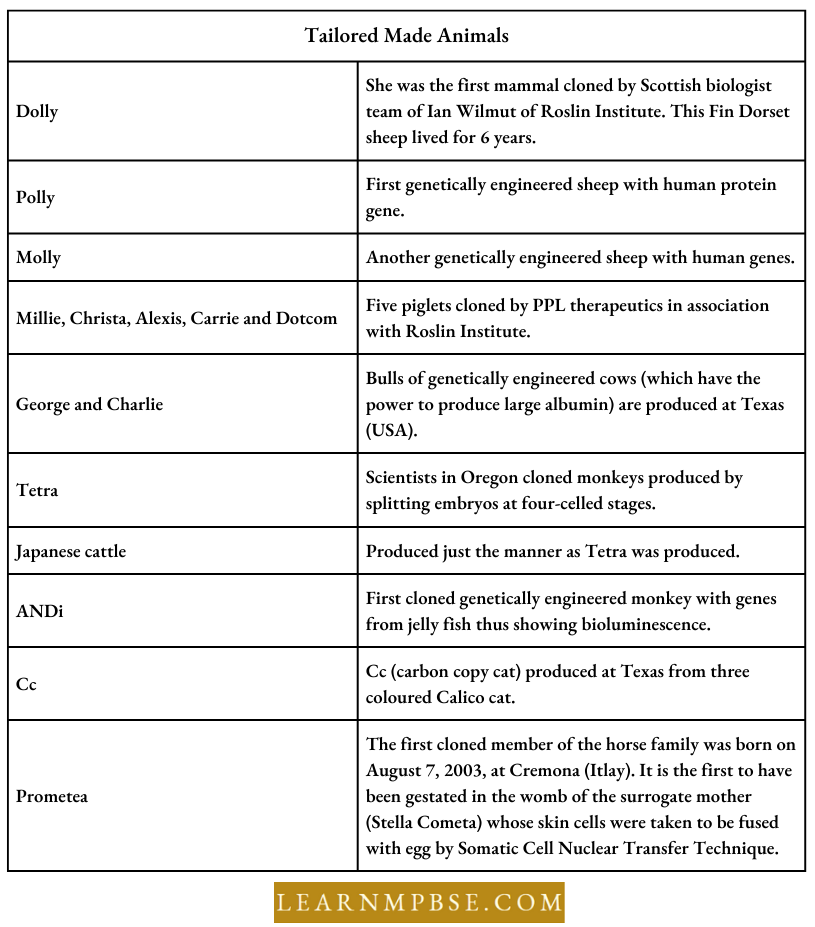
The technique involves the artificial transplantation of the diploid nucleus into enucleated egg cells. These cells grow and develop into a young one similar to the parent whose diploid nucleus was transplanted.
Importance Of Cloning
- New organisms with high and desired characteristics can be obtained in pure form.
- Specific compounds for medicines that are made available by the specific organism can be obtained in high amounts by cloning.
- Organs could be formed by cloning methods for transplantation so that they can be accepted by the human system without any rejection.
- The main organs of transplantation are the Liver, Cornea, Heart, Kidney Skin, etc.
- The success of animal cloning also has some adverse effects. Man has thought of producing human clones which is unethical and has adverse society, religion, and the law would not permit this as they are afraid of the time when a man can clone a criminal then what be the fate of society?
Biotechnology Principles And Processes NEET Question Bank
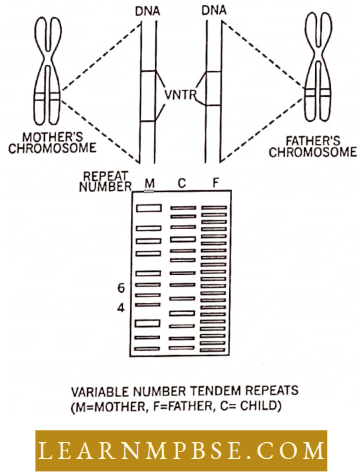
VNTRs (Variable Number Tandem Repeats). The VNTRs of two persons may be of the same length in the sequence at certain sites but vary at others. Half of the VNTRs of the child resemble that of the mother and the other half with that of the father.
- Gene Cloning: A foreign DNA (useful in genetic engineering) is combined with a vector and multiplied faithfully.
- Organism Cloning Nucleus of the ovum (IN) is removed and replaced by the nucleus of the diploid cell of the same organism. Now the egg with 2N nucleus is trans¬ferred to the uterus of the mother to have a normal pregnancy and delivers a clone of itself.
- Dr. Steven Stice and James of Advanced Cell Technology Corporation, Texas (USA), developed a technique for cloning genetically engineered calves that will be able to produce medicines for humans in their milk: The first cloned calves; George and Charlie were born in January 1998. Thus cloned cows are called Living Pharmaceutical factories (L.P.F.)
NEET Biology Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology Genomics
The term genomics was introduced by Thomas Roderick to describe the scientific discipline of mapping, sequences, and analysis of genes. In fact genomics is the study of genomes. All the DNA in the cells of an organism, say for our cells from skin or muscle or brain and everything including genes, is its genome.
Our body contains 100 million cells of over 260 different kinds. However, in most cases complete set of instructions in each is the same, needed to make a whole new human being. In all, there are 23 different chromosomes containing packed DNA in a haploid set of the human genome. Additional DNA is in the cell’s mitochondria which is inherited from one’s mother.
- Genomics is subdivided into structural genomics and functional genomics.
- Structural Genomics is the study of genome structure and deals with the complete nucleotide sequences of organisms.
- Functional Genomics is the study of genome function which includes transcriptome and proteome.
- Transcriptome is a complete set of RNAs transcribed from a genome.
- The proteome is a complete set of proteins encoded by a genome and aims at the deter¬mination of the structure and functions of all the proteins in living organisms.
- The nucleotide sequences of the genomes of two subspecies of rice were published in April 2002.
- The human body contains 100 million cells of over 260 different kinds.
- There is a complete set of instructions in each of the cells needed to make a whole new human being.
- There are 23 different chromosomes containing packed DNA in a haploid set of the human genome.
- Additional DNA is in the cell’s mitochondria which is inherited from one’s mother.
Revelations Of Genome: The details of the findings of our genome have revealed some startling facts. Being the most complex organism, we were expected to have more than 100,000 genes. Instead, the human gene count is much lower than expected, approximately 30,000 to 40,000 genes
Additional DNA is in the cell’s mitochondria which is inherited from one’s mother.
Principles Of Biotechnology NEET Notes
Revelations Of Genome: The details of the findings of our genome have revealed some startling facts. Being the most complex organism, we were expected to have more than 100,000 genes. Instead, the human gene count is much lower than expected, approximately 30,000 to 40,000 genes.
- Bacteriophage: 10 thousand base pairs.
- Escherichia coli: 4,7 million base pairs 4,000 genes.
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae: 2 million base pairs 6,000 genes
- Caenorhabditis elegans: 97 million base pairs 18,000 genes
- Drosophila melanogaster: 180 million base pairs 13,000 genes
- Human: 3 billion base pairs cells 30,000 genes
- Lily: 106 billion base pairs per cell.
NEET Biology Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology Human Genome Protect
Additional DNA is in the cell’s mitochondria which is inherited from one’s mother. Many countries are working together with the National Institute of Health and Department of Energy USA., to decipher the human genome to know the position and function of each and every gene of the genome.
- Jean Dausset 1983 first thought about the human genome project. He worked on the Human Leucocyte antigen system (HLAS) helping in organ transplantation.
- The easiest way of getting DNA is by taking blood samples.
- The genome project was carried out by DNA mapping, DNA sequencing, and functional analysis of DNA.
- DNA mapping is done by using molecular markers. The simple sequence repeat is prepared and known as Sequence Tagged Site.
- DNA sequencing is known by the DNA sequence of the mouse. Small segments of DNA are taken and sequenced.
- Functional analysis of DNA is carried out by cDNA analysis of brain tissue, by computerized analysis of the sequence of genes, and by fixing the function of genes in the effect of mutation.
- The human genome has 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes. The genes are present in linear positions on chromosomes and approximately 1,00,000 genes are present in the genome.
- Renato Dulbecco (Virologist) of Italy started work on a human genome project in 1986.
- Nobel laureate Jean Dausset for the first time produced a genome map under a human genome project in 1994.
- The human genome is nearly deciphered by now (2000).
- Human beings are 99.9 percent identical with each other at the DNA level.
- Every alive human being is exactly the same and even bacteria are our cousins in code.
- Different human genes vary widely in length often over thousands of base pairs.
- While b-globin and insulin genes are less than 10 kilobase pairs, the gene responsible for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy on ‘X’ chromosome is made up of 2400 kilo-base pairs which is probably the longest gene known.
- Though the lily plant produces fewer proteins than human beings, it has 18 times more DNA.
- Only less than 2 percent of the genome is known to include the exons, the protein-coding sequences.
- Approximately 1 million copies of short 5 to 8 base pair repeated sequences clustered around the centromeres and near the ends of the chromosomes represent ‘the junk DNA’.
NEET Biology Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology Gene Bank And Genomic Library
It is the collection of cloned DNA segments obtained from the complete genome. Gene bank is prepared by Shotgun experiments where the whole cell is stored as a random and unknown clone.
NEET Biology Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology Protein Engineering
The ability to change the amino acid sequence of a protein by altering the sequence of its cDNA is known as protein engineering.
- By site-directed mutagenesis technique, a new cDNA is created which is identical to the natural one except for changes designed by man.
- This DNA is used to generate protein in bacteria to transfect cell lines, or to create transgenic organisms.
- Protein engineering is used to study the proteins, to compare the catalytic properties of the normal and mutated form of an enzyme, etc.
- This technique is used to identify the particular charged amino acid residue responsible for the selectivity of ion channels.
- Nowadays protein engineering is used to generate a number of new proteins as a tool for scientific research, medical, and industrial purposes.
Biotechnology Principles And Processes NEET Mcqs
NEET Biology Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology Hybridoma Technology
Hybridoma is a hybrid cell obtained by the fusion of B-lymphocyte and cell (cell of antibody system of B-lymphocyte).
- Hybridoma cells can grow for an indefinite period and can produce antibodies because of the B-lymphocyte genome.
- Monoclonal antibodies are obtained from the in vitro culture of hybridoma cells.
- Hybridoma technology is developed in 1975 by G. Kohler and C. Milstein for which they were awarded the Nobel Prize in 1984.
- Antibodies obtained by this process are antigen-specific.
NEET Biology Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology DNA Fingerprinting
DNA Fingerprinting technique was developed by Alec Jeffreys (1985, 86) at Leicester University, United Kingdom.
Inheritance of DNA is very stable, Every person has a specific pattern of DNA sequence which shows a combination of the DNA sequence of both mother and father. The study of DNA fingerprints helps in the establishment of the identity of a person, the identification of criminals in case of murder or rape, and paternity tests in case of disputed parentage.
Principle of DNA Fingerprinting. It has been established that the DNA of a person carries some specific sequences of nucleotides that do not carry any information for proteins. Important for DNA typing profiling or fingerprinting are short nucleotide repeats that vary in number from person to person, but are inherited.
- These are the Variable Number Tandem Repeats or VNTRs. The VNTRs of two persons may be of the same length and sequence at certain sites but vary at others.
- In this example, a child might inherit a chromosome with six tandem repeats from the mother and the same tandem repeated four times in the homologous chromosome inherited from the father. Note that the half of VNTR alleles of the child resemble that of the mother and half that of the father.
- For DNA fingerprinting, DNA is isolated from any body cell or even from blood stains, semen stains, or hair roots. These cells are subjected to Southern blotting.
- In India first test of DNA fingerprinting was done in June 1989 to settle a disputed parentage in Madras. The laboratory for DNA fingerprinting is situated in Hyderabad at the Centre for Cell and Molecular Biology (CCMB).
Southern Blotting: A mixture of DNA fragments is separated by gel electrophoresis. DNA bands are denatured into single strands by an alkali solution. These DNA strands are fixed on the nitrocellulose membrane. This DNA is used for hybridization with the help of specific labeled DNA probes.
Then membrane is washed for any unbound DNA autoradiographs are taken and studied and DNA hybridization is done with the help of specific DNA probes. Polymorphism of DNA is revealed which shows very stable inheritance and is used for identification of a person.
Principles Of Biotechnology NEET Notes
Application Of DNA Fingerprinting
- Identify criminals in forensic laboratories.
- Determine paternity, who is the true biological father or mother of a child?
- Verify whether a hopeful immigrant is, as he or she claims, really a close relative of already an established resident.
- Identify racial groups to rewrite biological evolution.
DNA Footprinting. It is done to determine the location and lengths of binding sites of various proteins that bind to DNA. It is also possible to determine the sequence of the binding sites.
NEET Biology Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology Questions From Competitive Examinations
Question 1. Restriction endonucleases are used as:
- Molecular build-up at nucleotides
- Molecular degradation to DNA breakup
- Molecular knives for cutting DNA at specific sites
- Molecular cement to combine DNA sites.
Answer: 3. Molecular knives for cutting DNA at specific sites
Question 2. A somatic plant cell has the potential to develop into a full plant. This is called
- Totipotency
- Gene cloning
- Tissue culture
- Regeneration.
Answer: 1. Totipotency
Question 3. Enzymes breaking nucleic acids into nucleotides are called:
- Hydrolases
- Amylases
- Nucleic acids
- Nucleases.
Answer: 4. Nucleases.
Applications of Biotechnology NEET
Question 4. Recombinant DNA technology is related with:
- Stanley Cohen and Harbert Boyer
- Bateson and Punnet
- Huxley and Harvey
- Schleiden and Schwann.
Answer: 1. Stanley Cohen and Harbert Boyer
Question 5. Cosmid is:
- Extragenetic material in Mycoplasma
- Circular DNA in bacteria
- Extra DNA in bacteria
- Fragment of DNA inserted in bacteria for forming copies.
Answer: 4. Fragment of DNA inserted in bacteria for forming copies.
Question 6. Match the correct one
- RNA Polymerase-RNA primer
- Respiration-lysosome
- Restriction enzyme-genetic engineering
- Central dogma-DNA structure.
Answer: 3. Restriction enzyme-genetic engineering
Question 7. Plasmid is used as a carrier because:
- It has both ends with replicating points
- It has no free ends
- It is circular DNA with the capacity to bind, with eukaryotic DNA
- All Of the above.
Answer: 3. It is circular DNA with a capacity to bind, with eukaryotic DNA
Question 8. The Ti plasmid used in genetic engineering is obtained from:
- Bacillus thuringeinsis
- Agrobacterium rhizogenes
- Agrobacterium tumifaciens
- Escherichia coli.
Answer: 3. Agrobacterium tumefacient
Biotechnology Principles And Processes NEET Previous Year Questions
Question 9. The function of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is:
- Translation
- Transduction
- DNA amplification
- None of these.
Answer: 3. DNA amplification
Question 10. The genetically engineered bacterium used in the production of:
- Thyroxine
- Human insulin
- Epinephrine
- Cortisol.
Answer: 2. Human insulin
Question 11. Abnormal gene is replaced by normal genes through:
- Gene Therapy
- Medicines
- Cloning
- Radiation.
Answer: 1. Gene Therapy
Question 12. In genetic engineering, the term vector is applied to:
- Plasmid
- Sources of DNA
- Cell which receives
- Virus.
Answer: 1. Plasmid
Question 13. Gene therapy involves
- Introducing a normal gene in a cell
- Eliminating defective and useless genes
- Treating of defective genes with radiation
- Replacement of defective genes with normal ones.
Answer: 4. Replacement of defective genes by normal ones
Question 14. Which of the following enzymes is used in genetic engineering?
- Translocase
- Topoisomerase
- DNAse
- Restriction endonuclease.
Answer: 4. Restriction endonuclease.
Question 15. The transgenic animals are those which have:
- Foreign RNA in all its cell
- Foreign DNA in all its cells
- Foreign DNA in some of its cells
- Both 1 and 3
Answer: 2. Foreign DNA in all its cells
Question 16. The known sequence of DNA that is used to find complementary DNA strands is:
- Vector
- Plasmid
- DNA probe
- Recombinant DNA.
Answer: 3. DNA probe
Question 17. Totipotency in the cell is:
- Flower in a culture medium
- Development of fruit from a flower in a culture medium
- Development of an organism from a cell in a culture medium
- Development of all tissues of all kinds from a cell in a culture medium.
Answer: 3. Development of an organism from a cell in a culture medium
Steps In Biotechnology Process NEET
Question 18. The nuclease enzyme, which begins its attack from the free end of a polynucleotide, is?
- Exonuclease
- Kinase
- Polymerase
- Endonuclease.
Answer: 1. Exonuclease
Question 19. DNA fingerprinting method is very useful for:
- DNA tests for identity and relationships
- Forensic studies
- Polymorphism
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 20. Reverse transcriptase:
- Disintegrates host DNA
- Translates host DNA
- Transcribes viral RNA to DNA
- Polymerises host DNA.
Answer: 3. Transcribes viral RNA to DNA
Question 21. Boviene spongiform encephalopathy disease is equal to:
- KalaAzar
- Parkinson’s disease.
- Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease
Question 22. A clone of sheep Dolly has been made by :
- Gene transfer
- Somatic cell cloning
- Nucleus transfer
- Germinal cell cloning.
Answer: 3. Nucleus transfer
Question 23. Which one of the following bacteria has found extensive use in genetic engineering work in plants?
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- Clostridium septicum
- Xanthomonas citri
- Bacillus coagulens.
Answer: 1. Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Question 24. Improvement of the genotype of an organism by the addition of some foreign genes is:
- Genetic diversity
- Gene handling
- Tissue culture
- Genetic engineering.
Answer: 1. Genetic diversity
Question 25. A variable number of tandem repeats (VTNRs) in the DNA molecule are highly useful in:
- Monoclonal antibody production
- DNA fingerprinting
- Recombinant DNA technology
- Stem cell culture.
Answer: 2. DNA fingerprinting
Question 26. The first clone animal of the world is:
- Molly sheep
- Polly sheep
- Dolly sheep
- Molly goat.
Answer: 1. Molly sheep
Question 27. In transgenics, the expression of transgene in the target tissue is known by:
- Enhancer
- Transgene
- Promoter
- Reporter.
Answer: 4. Reporter
Question 28. DNA fingerprinting is related to:
- Molecular analysis of profiles of DNA samples
- Analysis of DNA samples using imprinting devices
- Techniques used for molecular analysis of different specimens of DNA
- Techniques used in the identification of fingerprints of different persons.
Answer: 1. Molecular analysis of profiles of DNA samples
Question 29. Which of the following is specifically used in genetic engineering?
- Ligase
- Gyrase
- DNA polymerase
- Restriction endonuclease.
Answer: 4. Restriction endonuclease
Question 30. Molecular scissors, which cut DNA at specific sites:
- Ligase
- Cellulase
- Pectinase
- Polymerase.
- Restriction endonuclease.
Answer: 3. Polymerase
Question 31. Plasmids are extrachromosomal circular DNA molecules:
- Which have their own point of replication and can replicate independently
- Which have their own point of replication but cannot replicate independently
- Which do not have their own point of replication and cannot replicate independently of bacterial chromosomal DNA
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Which have their own point of replication and can replicate independently
Steps In Biotechnology Process NEET
Question 32. Identify the plasmid:
- Alu I
- Hindffl
- Eco RI
- pBR 322.
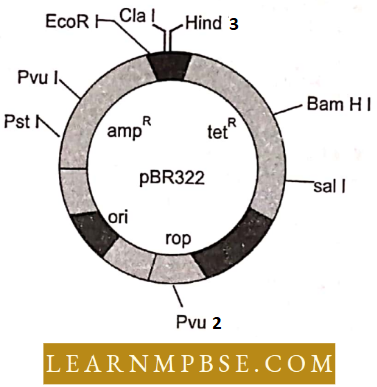
Answer: 4. pBR 322.
Question 33. Natural genetic engineer is:
- Bacillus subtillis
- Pseudomonas spp.
- Escherichia coli
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
Answer: 4. Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Question 34. The most thoroughly studied of the known bacteria-plant interaction is the:
- Plant growth simulation by phosphate-solubilising bacteria
- Cyanobacterial symbiosis with some aquatic ferns
- Gall formation on certain angiosperms by Agrobacterium
- Nodulation of Sesbania stems by nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
Answer: 3. Gall formation on certain angiosperms by Agrobacterium
Question 35. What does Bt stand for the popular crop Bt cotton?
- Best
- Best type
- Biotechnology
- Bacillus tomentosa.
- Bacillus thuringiensis.
Answer: 5. Bacillus thuringiensis
Question 36. DNA fingerprinting technique was first developed by:
- Jeffreys, Wilson, and Thein
- Schleiden and Schwann
- Edward and Steptoe
- Boysen and Jensen.
Answer: 1. Jeffreys, Wilson and Thein
Question 37. What is the first step in the Southern Blotting technique?
- Isolation of DNA from a nucleated cell such as the one from the scene of crime
- Denaturation of DNA on the gel for hybridization with a specific probe
- Production of a group of genetically identical cells
- Digestion of DNA by restriction enzyme.
Answer: 4. Digestion of DNA by restriction enzyme
Question 38. An example of gene therapy is:
- Production of injectable hepatitis b vaccine
- Production of vaccines in food crops like potatoes which can be eaten
- Production of test tube babies by artificial insemination and implantation of fertilized eggs
- Introduction of the gene for adenosine deaminase in persons suffering from severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID).
Answer: 4. Introduction of gene for adenosine deaminase in persons suffering from severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)
Question 39. The total number of nitrogenous bases in human ge¬nome is estimated to be about:
- 35 million
- 3.1 billion
- 3.5 million
- 35 thousand.
Answer: 2. 3.1 billion
Question 40. The name of the drug used in cancer treatment produced by using biotechnology is:
- HGH
- TSH
- Insulin
- Interferon
- Terramycin.
Answer: 4. Terramycin
Biotechnology Principles And Processes NEET Notes
Question 41. Which of the following pairs is correctly matched?
- Central dogma-Codon
- Okazaki fragments-Splicing
- RNA polymerase-RNA primer
- Restriction enzymes- Genetic engineering.
Answer: 2. Okazaki fragments-Splicing
Question 42. Tj plasmid is used for making transgenic plants. It is obtained from:
- Azotobacter
- Agrobacterium
- Rhizobium in leguminous root
- Yeast.
Answer: 2. Agrobacterium
Question 43. Somaclonal variation can be obtained by:
- Hybridization
- Tissue culture
- Application of colchicine
- Irradiation with gamma rays.
Answer: 2. Tissue culture
Question 44. The enzyme used for cutting DNA segments in genetic engineering is:
- ATPase
- Ligase
- DNA polymerase
- Restriction endonuclease.
Answer: 2. Restriction endonuclease
Question 45. Widely used tools in the genetic engineering of crop plants is:
- Protoplast fusion
- Transposon
- Microinjection
- Agrobacterium mediation.
Answer: 4. Agrobacterium mediation
Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology NEET
Question 46. Which one of the following hydrolyses internal phosphodiester bonds in a polynucleotide chain?
- Lipase
- Protease
- Exonuclease
- Endonuclease.
Answer: 4. Endonuclease
Question 47. There is a restriction endonuclease called £coRI. What does the “co” part in it stand for?
- Coli
- Coelom
- Coenzyme
- Colon.
Answer: 1. Coli
Biotechnology Principles And Processes NEET Study Material
Question 48. Agarose extracted from seaweeds finds use in:
- Spectrophotometry
- Tissue culture
- Gel electrophoresis
- PCR.
Answer: 3. Gel electrophoresis
Question 49. Given below is a sample of a portion of the DNA strand giving the base sequence on the opposite strands. What is so special shown in it?
5′ _____ GAATTC _______ 3′
3′ ______ CTTAAG _______ 5′
- Replication completed
- Deletion mutation
- Start codon at the 5’ end
- The palindromic sequence of base pairs.
Answer: 4. Palindromic sequence of base pairs
Question 50. In DNA fingerprinting which of the following is true?
- VNTR is used as a probes
- Specific metabolic genes are used as probes
- Housekeeping or luxury genes are used as probes
- All of the above.
Answer: 1. VNTR is used as probes
Question 51. The matching sequence of DNA between two pieces of evidence, one of the criminals with the suspect is known as:
- DNA fingerprinting
- DNA amplification
- Gene mapping
- DNA resolution.
Answer: 1. DNA fingerprinting
Question 52. A technology which has found immense use in solving cases of disputed parentage is:
- DNA fingerprinting
- Polymerase chain reaction
- Recombinant DNA technology
- Monoclonal antibody production.
Answer: 1. DNA fingerprinting
Question 53. The first hormone prepared by genetic engineering is:
- Insulin
- Oxytocin
- Adrenaline
- Somatotropin.
Answer: 1. Insulin
Question 54. The first biochemical to be produced commercially by microbial cloning and genetic engineering is:
- Interferon
- Penicillin
- Human insulin
- Fertility factors.
Answer: 3. Human insulin
Question 55. Which of the following statements is true?
- In the historic cloning experiment of Dr. Wilrnut, the transplanted nucleus was taken from an udder cell
- Mammalian characters appeared first in dinosaurs
- The heart of mammals is incapable of being in vitro
- The pyramid of biomass is upright in the pond ecosystem.
Answer: 1. In the historic cloning experiment of Dr. Wilrnut, the transplanted nucleus was taken from an udder cell
Question 56. Protoplasts of two different species are fused in:
- Dona propagation
- Organography
- Micropropagation
- Somatic hybridization.
Answer: 4. Somatic hybridization
Biotechnology Principles And Processes NEET Question Bank
Question 57. cDNA probes are copied from the messenger RNA molecules with the help of:
- Restriction enzymes
- Reverse transcriptase
- DNA polymerase
- Adenosine deaminase.
Answer: 4. Adenosine deaminase
Question 58. The electroporation procedure involves:
- Fast passage of food through sieve pores in phloem elements with the help of electric stimulation
- Opening of stomatal pores during the night by artificial light
- Making transient pores in the cell membrane to introduce gene constructs
- Purification of saline water with the help of a membrane system.
Answer: 3. Making transient pores in the cell membrane to introduce gene constructs
Question 59. Which one of the following is a correct statement
- “Bt” in “Bt-cotton” indicates that it is a genetically modified organism produced through biotechnol¬ogy
- Somatic hybridization involves the fusion of two complete plant cells carrying desired genes
- The anticoagulant hirudin is produced from transgenic Brassica napus seeds
- The “Flavr Savr” variety of tomatoes has enhanced the production of ethylene which improves its taste.
Answer: 3. The anticoagulant hirudin is being produced from transgenic Brassica napus seeds
Question 60. A tumor-inducing plasmid widely used in the production of transgenic plants in that of:
- Escherichia coli
- Bacillus thuringiensis
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
Answer: 4. Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Question 61. The common bacterium used in genetic engineering is:
- E. coli
- Diplococcus
- Rhizobium
- Spirillium.
- a = 3, b = 1, c = 5, d = 4
- a = 1, b = 2,c = 3, d = 4
- a = 2, b = 1, c = 3, d = 4
- a = 4, b = 3, c = 1, d = 2
- a = 3, b = 1, c = 5, d = 2.
Answer: 1. a = 3, b = 1, c = 5, d = 4
Question 62. Match The following and choose the correct combination from the options given:
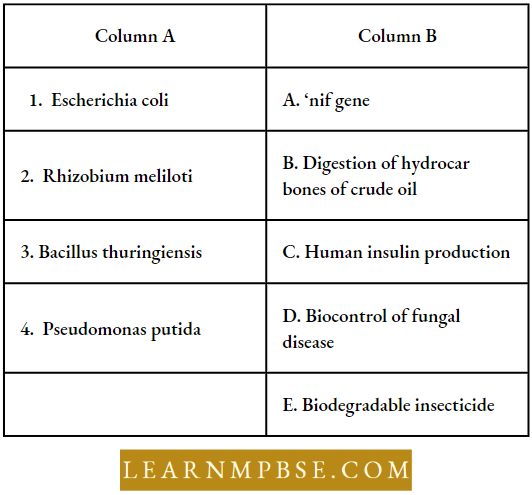
Answer: 5
Question 63. Choose the correct statement with reference to ‘Dolly’:
- She was created by taking the nucleus from unfertilized eggs and cytoplasm from unfertilized eggs
- She was created by taking the nucleus from udder cells and cytoplasm from unfertilized eggs
- She was created by taking cytoplasm from udder cell and nucleus from unfertilized eggs
- She was created by taking cytoplasm from udder cell and nucleus from fertilized eggs
- She was created inside the test tube.
Answer: 2. She was created by taking the nucleus from udder cells and cytoplasm from unfertilized eggs
Question 64. Find the incorrect statement:
- Gene therapy is a genetic engineering technique used to treat disease at the molecular level by replacing defective genes with normal genes
- Calcitonin is a medically useful recombinant product in the treatment of infertility
- Bt toxin is a biodegradable insecticide obtained from Bacillus thuringiensis
- Trichoderma sp. is a biocontrol agent for fungal diseases of plants
- Totipotency is the potential ability of a cell to develop into a complete plant.
Answer: 2. Calcitonin is a medically useful recombinant product in the treatment of infertility
Question 65. Production of a human protein in bacteria by genetic engineering is possible because:
- Bacterial cell can carry out the rna splicing reactions
- The human chromosome can replicate in bacterial cell
- The mechanism of gene regulation is identical in humans and bacteria
- The genetic code is universal.
Answer: 4. The genetic code is universal
Question 66. Two microbes found to be very useful in genetic engineering are:
- Diplococcus sp. and Pseudomonas sp.
- Crown gall bacterium and Caenorhabditis elegans
- Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Answer: 3. Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Principles And Processes Of Biotechnology NEET
Question 67. What is the function of Restriction endonuclease?
- Restricts the synthesis of DNA inside the nucleus
- Synthesizes DNA
- Cuts the DNA molecule randomly
- Cuts the DNA molecule at specific sites.
Answer: 4. Cuts the DNA molecule at specific sites
Question 68. A genetically engineered micro-organism used successfully in bioremediation of oil spills is a species of:
- Trichodenna
- Xanthomonas
- Bacillus
- Pseudomonas.
Answer: 4. Pseudomonas
Question 69. The construction of the first recombinant DNA was done by using the native plasmid of:
- E.coli
- Salmonella typhimurium
- B.thuringiensis
- Yeast
- Agrobacterium.
Answer: 2. Salmonella typhimurium
Question 70. The basis of DNA fingerprinting is:
- The double helix
- Errors in the base sequence
- Polymorphism in sequence
- DNA replication
- DNA coiling.
Answer: 3. Polymorphism in sequence
Question 71. The linking of antibiotic resistance gene with the plasmid vector became possible with:
- DNA ligase
- Exonucleases
- Endonucleases
- DNA polymerase.
Answer: 1. DNA ligase
Question 72. Gel electrophoresis is used for:
- Isolation of DNA molecule
- Cutting of DNA into fragments
- Separation of DNA fragments according to their size
- Construction of recombinant DNA by joining with cloning vectors.
Answer: 3. Separation of DNA fragments according to their size
Question 73. Which one of the following palindromic base
- 5′ _______ GATATG ______ 3′
3′ _______ CTACTA ______ 5′ - 5′ _______ GAATTC ______ 3′
3′ _______ CTTAAG ______ 5′ - 5′ _______ CACGTA ______ 3′
3′ _______ CTCAGT ______ 5′ - 5′ _______ CGTTCG ______ 3′
3′ _______ ATGGTA ______ 5′
Answer:
2. 5′ _______ GAATTC ______ 3′
3′ _______ CTTAAG ______ 5′
Question 74. An improved variety of transgenic basmati rice:
- Gives a high yield and is rich in Vitamin A
- Is completely resistant to all insect pests and diseases of paddy
- Gives a high yield but has no characteristic aroma.
- Does not require chemical fertilizers and growth hormones.
Answer: 1. Gives high yield and is rich in Vitamin A
Question 75. Genetic engineering has been successfully used to produce:
- Transgenic models for studying new treatments for certain cardiac diseases
- Transgenic cow-Rosie which produces high-fat milk for making ghee
- Animals like bulls for farm work as they have superpower.
- Transgenic mice for testing the safety of the polio vaccine before use in humans.
Answer: 4. Transgenic mice for testing the safety of polio vaccine before use in humans
Question 76. The genetically modified (GM) brinjal in India has been developed for:
- Enhancing shelf life
- Enhancing mineral content
- Drought-resistance
- Insect-resistance.
Answer: 4. Insect-resistance
Question 77. PCR and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism are the methods for:
- Genetic transformation
- DNA sequencing
- genetic fingerprinting
- Study of enzymes.
Answer: 4. Study of enzymes
Question 78. For transformation, microparticles coated with DNA are to be bombarded with gene guns made up of:
- Platinum or Zinc
- Silicon or Platinum
- Gold or Tungsten
- Silver or Platinum.
Answer: 3. Gold or Tungsten
Question 79. Which of the following is not correctly matched for the organism and its cell wall degrading enzyme?
- Plant cells – Cellulase
- Algae – Methylase
- Fungi – Chitinase
- Bacteria – Lysozyme
Answer: 2. Algae – Methylase
