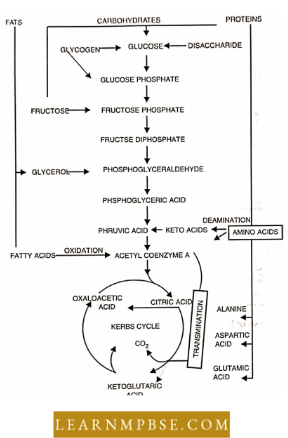
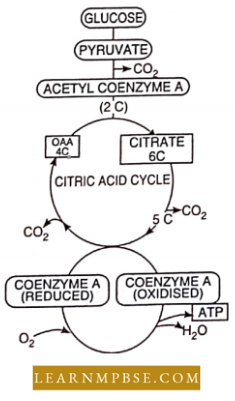
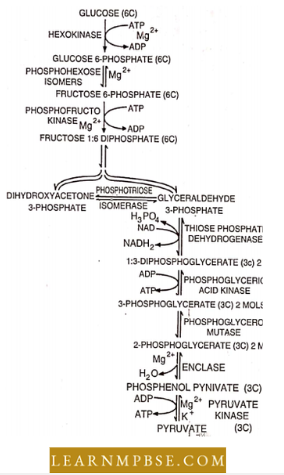
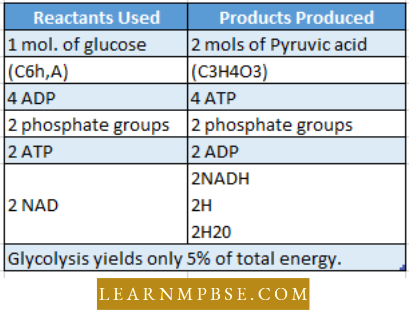
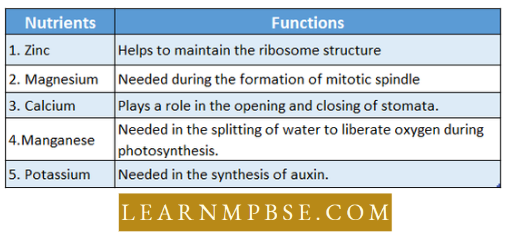
NEET Biology Endocrine System
Hormone (Gk: Hormoein = to excite) is the secretion of the endocrine (Gk. yendon = inside, Krinein = to separate) gland.

- Endocrine Glands. (The Greek word Rendon means inside, and kinesin means to separate) These are endogenously located glands that lack the ducts (so also called ductless glands) and generally secrete their secretions into the blood (so-called glands of internal secretion) for their transportation to target organs (sites of action). Exocrine glands. Secretions of these glands are transported by duct or ductules or directly.
- Heterocrine glands are composed of exocrine and endocrine tissues. The former sends its secretion or product through a duct and the latter discharges its secretion directly into the blood For example. pancreas, gonads.
- The blood contains all the hormones but target organs pick up the required hormones only and ignore all others because target cells have a specific protein called a receptor which has a specific affinity for a particular hormone.
- In man, there are the following endocrine glands: Thyroid, Parathyroid, Thymus, Pituitary, Adrenal, Pineal body, and (pancreas, stomach, intestine, skin, kidney, and gonads mixed glands).
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
NEET Biology Endocrine System Types Of Hormones With Their Function Intracellular Receptors
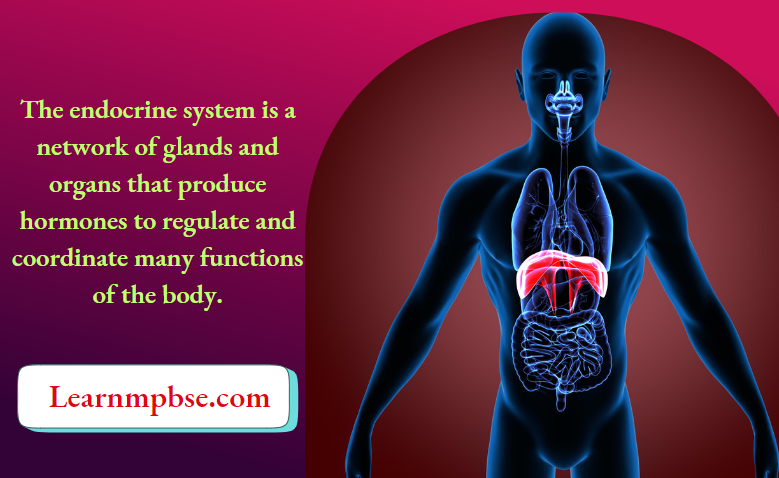
- The steroid and thyroid hormones enter the cell directly and bind to the intracellular receptor proteins in the cytoplasm, this complex enters the nucleus and binds to the specific regulatory sites on the chromosome. This alters the pattern of gene expression initiating its transcription, formation of specific mRNA, and then protein (enzyme).
- Synergic hormone. A pair of hormones work together for a particular function. For example. LH and FSH work together for the maturation of Graafian follicles.
- Antagonistic hormone. A pair of hormones each with opposite function. For example. Insulin and glucagon. Insulin acts as a hypoglycemic factor but glucagon acts as a hyperglycemic factor,
- Tropic hormone. A hormone of one gland activates the secretion of the hormone of another gland. For example.TSH of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland activates the thyroid gland to secrete thyroxine.
- Chalones. These substances inhibit the secretion of other glands. For example, enterogasterone from duodenal mucosa inhibits the secretion of HCI in the gastric juice of the stomach.
Endocrine System NEET Notes

NEET Biology Endocrine System Mechanism Of Hormone Action
Hormones are transported by the bloodstream to the entire body, but they influence only specific cells.
- Cells that respond to a certain hormone possess receptor sites for that hormone. This resembles a lock and key mechanism.
- Should the key be compatible with the lock, the door will unlock. If a hormone binds to the receptor location, an effect will ensue.
- All cells possessing receptor sites for a specific hormone constitute the target tissue for that hormone. In certain instances, the target tissue is confined to a specific gland or organ.
- In other instances, the target tissue is dispersed and disseminated throughout the body, resulting in many locations being impacted. Hormones exert their distinctive impacts on target cells by altering cellular functions.
Proteins, peptides, and modified amino acids
- These hydrophilic (and mostly large) hormone molecules bind to receptors on the sur¬face of ‘ ‘target’ ’ cells: that is, cells able to the presence of the hormone. The receptors are transmembrane proteins. Binding of the hormone to its receptor initiates a sequence of intracellular signals that may :
- alter the behavior of the cell (such as by opening or closing membrane channels) or stimulate (or repress) gene expression in the nucleus by turning on (or off) the promoters and enhancing the action of the genes.
- The hormone binds to a site on the extracellular portion of the receptor.
- The receptors are transmembrane proteins.
- Many (but not all) pass through the plasma membrane 7 times, with their N-terminal exposed at the exterior of the cell and their C-terminal projecting into the cytoplasm.
- Binding of the hormone to the receptor
- Activates a G protein associated with the cytoplasmic C-terminal
- This initiates the production of a “second messenger”. The most common of these are
- cyclic AMP, (cAMP) which is produced by adenyl cyclase from ATP and
- inositol 1,4, 5-triphosphate (IP3)
- The second messenger, in turn, initiates a series of intracellular events such as
- phosphorylation and activation of enzymes
- release of Ca2+ stores within the cytoplasm
- In the case of cAMP, these enzymatic changes activate the transcription factor CREB (cAMP response element binding protein)
- Bound to its response element 5′ TGACGTCA 3′ in the promoter of genes that can respond to the hormone, activated CREB turns on gene transcription.
- The cell begins to produce the appropriate gene products in response to the hormonal signal it has received at its surface.
NEET Biology Endocrine System Steroid Hormones
- Steroid hormones, being hydrophobic molecules, diffuse freely into all cells. However, their “target” cells contain cytoplasmic and/or nuclear proteins that serve as receptors of the hormone.
- The hormone binds to the receptor and the complex binds to hormone response elements – stretches of DNA within the promoters of genes responsive to the hormone. The hormone/receptor complex acts as a transcription factor turning the target gene “on” (or “off”). mRNA is formed and with translation, protein is synthesized. This protein formed is responsible for the biological action of that steroid.
NEET Biology Endocrine System Thyroid Gland
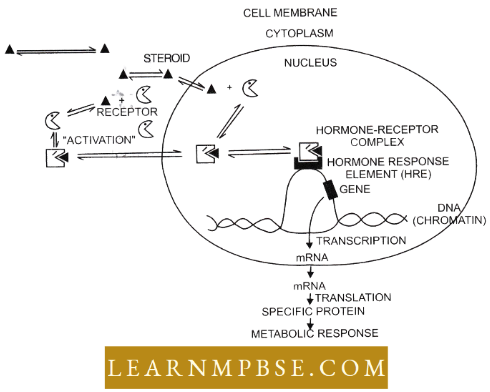
- Discovered by Wharton (1908) it is the largest endocrine gland (3 – 7 cm in diameter and 15-20 gm in weight).
- Situated below the thyroid cartilage of the larynx it is a bilobed structure, connected by an isthmus.
- The only endodermal gland homologous to the endostyle of protochordate develops as a venial outgrowth from the pharyngeal wall.
- Consists of many follicles formed by follicular cells as epithelial parts and interfollicular stroma of areolar connective tissue with parafollicular cells.
Hormones And Their Functions NEET Biology
NEET Biology Endocrine System Parathyroid Gland
Follicular cells are of two types.
- Chief cells. The main secretory cells and Oxyntic cells with eosinophilic granules.
- It secretes Parathormone (PTH or Collip’s hormone), a polypeptide with 84 amino acids which regulate the metabolism of calcium and phosphate;
- Increase plasma Ca++ level by increasing bone dissolution (osteoclastic activity) and enhancing reabsorption through renal tubules and by increasing Ca++ absorption in the gut.
- Thus, the maintenance of proper Ca++ levels in the body is the synergistic effect of calcitonin, PTH, and Vit. D.
- Increases phosphate elimination in urine and consequently lower phosphate concentration in plasma.
NEET Biology Endocrine System Adrenal Gland (OR Suprarenal body)
- A small, yellowish-brown, paired gland situated at the anterior end of each kidney like a cap, is a semicircular structure weighing 3.5 – 4.5 gm (in adults).
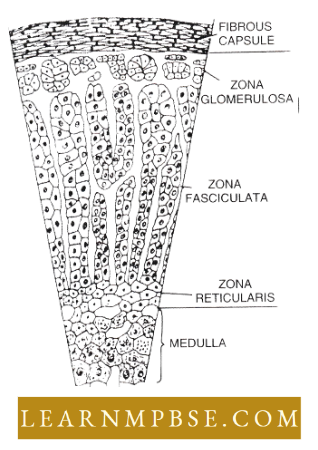
- Covered by a fibrous connective tissue capsule. The structure is internally differentiated as the outer mesodermal cortex and inner ectodermal medulla of nervous origin.
- Cortex. The thick layer constitutes 70 – 75% part of the gland distinct into the following three zones of cells :
- Zona glomerulosa. The outermost layer below the capsule, is made of five layers of small cuboidal basophilic cells densely set along an axis parallel to the surface.
- Zona fasciculata. The thickest and middle parts have large polyhedral cells arranged in radiating columns perpendicular to the surface.
- Zona reticularis. The innermost part has cells arranged in a layer to form a network.
- Medulla. Consists of groups of round granulated cells which are modified postganglionic cells of the sympathetic nervous system having an exclusively secretory function. These are chromaffin cells, distinct in two layers :
- Zona compactum. Densely packed rounded cells with thick plasma membrane, without any intercellular spaces, the average size of cells is 190 – 210 pm (diameter).
- Zona spongiosum. The innermost layer of irregular cells in 5 – 12 layers with large intermolecular spaces with matrix and blood vessels, the average size of cells is 260 pm- 360 pm.
NEET Biology Endocrine System Cortical hormones
About 50 types of steroids have been isolated from the adrenal cortex hence called corticosteroids. But, only a few are biologically active, of the following 3 types.
NEET Biology Endocrine System Mineralocorticoid (Aldosterone)
- A 21-carbon steroid molecule is secreted by zona glomerulosa.
- Increases the reabsorption of Na+ and Cl– by uriniferous tubules, also controls the level of other salts, and thus plays a role in osmoregulation.
- Increase the removal of K+ in urine.
NEET Biology Endocrine System Glucocorticoid (Cortisol or hydrocortisone and Corticosterone)
- A steroid of 20 carbons it is secreted from zona fasciculata and zona reticularis.
- It controls the metabolism of fat and amino acids into carbohydrates, protein, and fat, and stimulates gastric secretions.
- Stimulates the conversion of fat and amino acids into carbohydrates (gluconeogenesis).
- Reduces amino acid levels in tissues, and increases ketone formation in the blood.
- Anti-inflammatory in nature suppresses the WBC movement but increases RBC count.
- Immunosuppressive in nature, hence used for treatment of allergy and in transplantation surgery.
- Dexotes synthesis of collagen, hence cortisole is used for treatment of arthritis or rheumatism.
NEET Biology Endocrine System Sex Corticoid
- Secreted by zona fasciculata and zona reticularis is a 12 carbon steroid.
- Influences sex-related changes in muscles on bone, maintains the normal growth of external sex organs, hair growth, etc., in the pre-puberty stage, and also influences sexual behavior.
- Hypersecretion of this hormone causes gynecomastia in males with female-like characteristics like overgrowth of the mammary gland.
- Hirsutism (Adrenal Virilism) in females: growth of facial hairs, temporal baldness, enlargement of the clitoris, atrophy of breast, hoarse voice, etc.
- Control of Secretion. ACTH from the pituitary maintains its growth and secretion which in turn is controlled by corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) from the hypothalamus. Secretion of aldosterone is mainly controlled by the renin-angiotensin system.
NEET Biology Endocrine System Hormones Of Adrenal Medulla
- Medullary hormones are formed from the amino acid tyrosine.
- Chromaffin cells take up tyrosine which is first hydroxylated and then decarboxylated to form dopamine which is further hydroxylated to form noradrenaline, this is then methylated to form adrenaline.
- All these, dopamine, noradrenaline, and adrenaline together are called catecholamines which means “catch-all” Adrenaline (or Epinephrine)
- Its secretion (from zona compactum) is stimulated by emergency conditions like fear, anger, accident, injury, stress, etc. hence is also called an emergency hormone. Its effect is like a sympathetic nervous system.
- Norepinephrine (or Noradrenaline).
- Secreted from zona spongiosus it is a polypeptide.
- It is a vasoconstrictor that increases blood pressure (both systolic and diastolic) and controls the normal circulation of blood.
- Control of Adrenal Medulla.
- Its secretion is controlled by the sympathetic (autonomic) nervous system and feedback system through the level of adrenaline and nor-adrenaline in the blood.
Pituitary Gland Hormones NEET Study Material
NEET Biology Endocrine System Thymus Gland
- It is a single, bilobed, flattened, pyramidal gland, situated in the mediastinal space just in front of the heart.
- Grows at an early age and becomes fully developed at 16 years but starts degenerating after 18 years and atrophies after the age of 25 years.
- It is partly endocrine and partly lymphoid, covered by a connective tissue capsule, and consists of two zones: (i) Outer cortex with lymphocyte-like cells; and
- Inner medulla comprising reticular cells. Thymosin is the only hormone secreted from this gland with the following functions :
- Stimulates T-lymphocytes to counter the attack of pathogens and antigens.
- Helps in the development of sex glands.
- Controls the heartbeat through the S.A. node.
NEET Biology Endocrine System Pineal Body
- Situated on the roof of 3rd ventricle (diencephalon), covered by a capsule from which many septa (or trabeculae extend inside dividing it into many lobules; contain 2 types of cells :
- Parenchymal pinealocytes with minute processes; neuroglia with the darkly stained nucleus.
- A few acervuli or brain sand are present within the capsule.
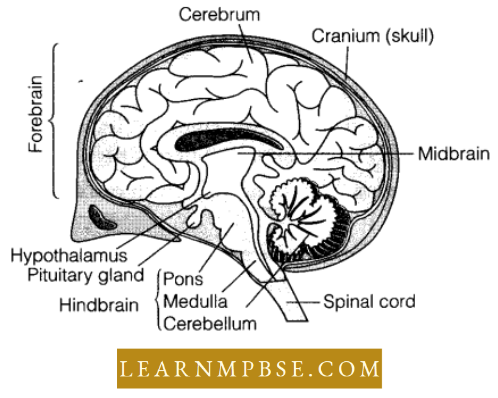
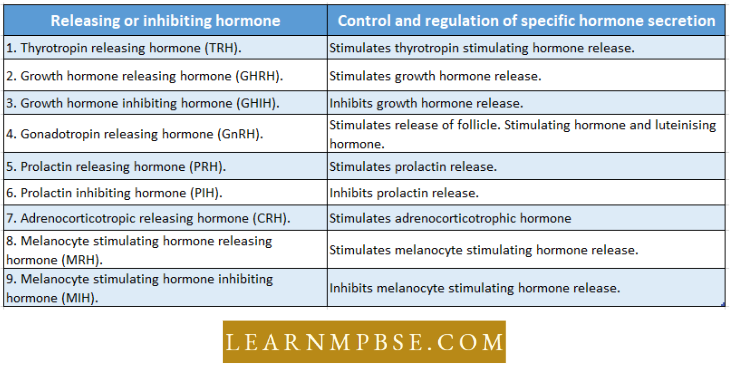
NEET Biology Endocrine System Hypothalamus
- It is the floor of the diencephalon (forebrain) with many neurosecretory cells that secrete a variety of hormones to control the secretion of the pituitary gland.
- It also contains several such nerve cells whose axons terminate into the posterior pituitary and secrete hormones.
- The ability of endocrine secretion in the hypothalamus is to monitor metabolite and hormone levels in the body as per the information gathered by the brain. Hypothalamic hormones released in the blood come to the pituitary through hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal circulation.
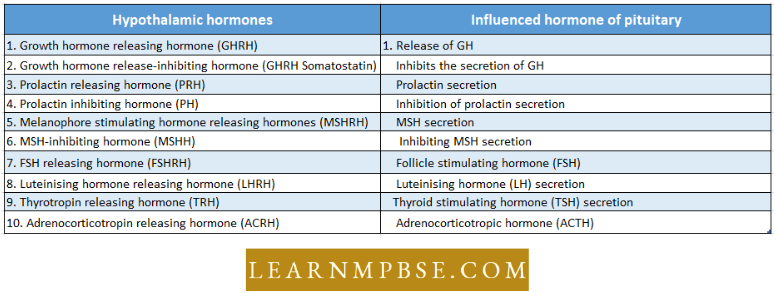
- These include various releasing and inhibiting hormones as follows :
- Hypothalamic hormones Influence hormones of the pituitary
NEET Biology Endocrine System Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
- Located on the ventral aspect of the hypothalamus, this single pea-sized gland was historically regarded as the master gland (Vesalius) because to its regulatory influence over all endocrine glands. However, Webster (1967) rejected this notion.
- It is now referred to as the conductor of an endocrine orchestra.
- Situated in a cavity known as the sella turcica, at the base of the sphenoid bone, it is linked via a stalk termed the infundibulum to the hypothalamus.
- This stalk is lacking in mammals.
Pituitary Gland Hormones NEET Study Material
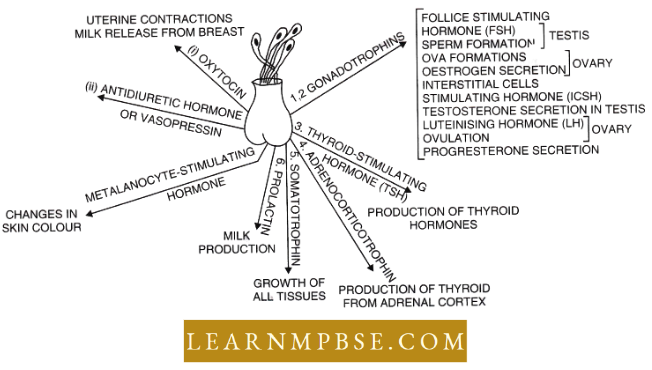
NEET Biology Endocrine System Hormones Of the Posterior Lobe Of the Pituitary Gland
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH or Vasopressin or Pitressin)
- The osmoregulation hormone controls the volume of urine by increasing water reabsorption in nephric tubules.
- Brings back the normalcy in the autonomic nervous system during periods of stress, pain, anger, and excitement.
- Deficiency of its level causes ‘diabetes insipidus’ (drinking disease), an abnormal amount of water is lost in the urine and to compensate for it the patients keep taking equally high amounts of water.
Oxytocin (or Pitocin or labor hormone or birth hormone)
- Secreted from median eminence of pars nervosa hence is the direct secretion of hypothalamus stored in the pituitary.
- Facilitates childbirth by loosening pubic symphysis before the birth of the child causing contraction and relaxation of muscles of the uterus, relaxing vaginal muscles and vestibular sphincter of the vulva
- The release of milk from the mammary gland is made by relaxing the muscles of the nipple.
NEET Biology Endocrine System Islets Of Langerhans (Pancreas)
- The pancreas acts as both an exocrine and endocrine gland and hence is referred to as a heterochrony gland
- The endocrine component of the pancreas Islets of Langerhans was discovered by Langerhans (1950).
NEET Biology Endocrine System Hormones Of Islets Of Langerhans
NEET Biology Endocrine System Insulin
- Isolated by Banting and Best and its primary structure was determined by Sanger(1950).
- Hypersecretion causes hypoglycemia(extreme case insulin shock)
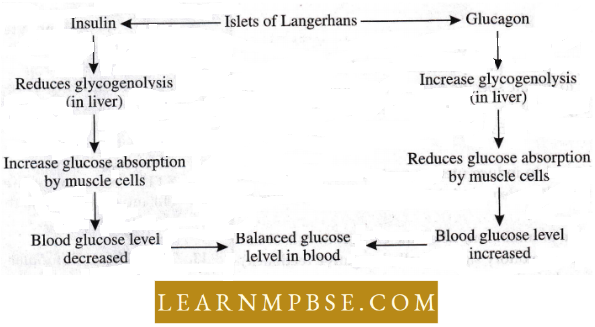
NEET Biology Endocrine System Glucagon
- Discovered by Kimbell and Murlin (1935) a polypeptide with a molecular weight of 2495; comprises 29 amino acids in a single chain.
- Hyperglycemic, by enhancing glycogenolysis in the liver.
- Promotes gluconeogenesis, uptake of amino acids, and its deamination in the liver.
- Lowers blood calcium level by increasing its renal elimination.
- It does not affect muscle glycogen.
- Its hypersecretion causes diabetes mellitus.
NEET Biology Endocrine System Somatostatin
- Secreted from 8 cells, also called a GHH balances the level of glucagon and insulin as per requirement of the body.
NEET Biology Endocrine System GONADS
- Gonads also secrete a variety of hormones.
NEET Biology Endocrine System Testes
- The interstitial cells (or cells of Leydig) in the stroma secrete androgen (steroid) from which the male sex hormone testosterone is synthesized.
- Induces the production of male gametes (sperms) and their morphogenesis.
- Promotes growth and virility of skeleton muscle, external genitalia (accessory sex organs) secondary sex characters in puberty.
- Its hyposecretion causes eunuchoidism, with the following symptoms.
- Less growth of secondary sex organs (prostate, seminal vesicle, penis)
- Improper spermatogenesis (infertility) and loss of secondary sexual characters.
- Extreme hyposecretion causes complete sterility.
- Sertoli cells secrete inhibin hormone that inhibits sperm formation.
Pituitary Gland Hormones NEET Study Material
NEET Biology Endocrine System Ovaries
- Follicular cells and theca of maturing follicles secrete estrogen (17 (J-estradiol), a steroid.
- Stimulates production, growth, and maturation of ovum and functions of secondary sex organs (uterus, fallopian tube, and ducts of mammary glands).
- Maintains external or secondary sexual characters.
- FSH from the anterior pituitary controls the level and functions of estrogen.
- The corpus luteum formed from a ruptured follicle after ovulation secretes another hormone progesterone (a steroid) the pregnancy hormone.
- Helps in the thickening of the uterus wall (endometrium) increasing blood supply to restore normalcy after menstruation.
- Implantation of zygote on uterus wall, and formation of placenta.
- Maintains the level of dissolved 02 in the embryonic fluid.
- It also secretes inhibin hormone that stops follicular maturation.

NEET Biology Endocrine System Memory Points
- Thyroidectomy – removal of thyroid gland.
- Hypophysectomy- removal of the entire pituitary gland.
- Pheromones (Ectohormones). These are intraspecific chemical messengers released by an animal into the air to initiate specific responses in another animal of the same species. These may be signals of food, mate, etc. The term pheromone was coined by Karlson and Butenandt (1959). The first known pheromone is bombycol.
- Synthetic oxytocin is administered to induce uterine contraction in a woman who is exhausted during delivery. It is also administered in female cattle to induce lactation.
- Feedback inhibition. In this type of inhibition, when the end product is at the required level then it gives certain inhibitory signals (called negative feedback) which inhibit the formation of the end product.
- G-proteins are related to the hormonal action of those hormones requiring a second messenger, C-AMP. They link hormone receptors on the outer surface of the cell and the interior of the cell.
- Prostaglandins. These are lipid compounds secreted into the tissue fluid by cell membranes of the glandular cells. These control either contraction/relaxation of smooth muscles or dilation/ contraction of blood capillaries. These were first reported in the semen of men and are produced by the prostate gland.
- Enzyme adenyl cyclase is secreted by the plasma membrane and changes ATP into C-AMP which helps in hormonal action.
- Sutherland first described the role of C-AMP in hormone action and called it the “Second Messenger”
- Origin of endocrine glands. Most endocrine glands are endodermal in origin For example. Thyroid, Parathyroid, Islets of Langerhans, and Gastric glands.
- Intestinal glands, Thymus, etc. while some are ectodermal in origin For example. Pituitary gland, Hypo-thalamus; Pineal body etc. Gonads are mesodermal in origin while the Adrenal gland is ecto-mesodermal in origin.
- The sub-neural gland of Herdmania is homologous to the pituitary of vertebrates. Herring bodies. Structures present in the pituitary and store neurosecretory substances of the hypothalamus.
- The H-shaped endocrine gland is the thyroid.
- The endostyle of lower chordates like Herdmania, Amphioxus, etc. is homologous to the thyroid gland.
- When under stress, adrenaline is secreted directly into the blood.
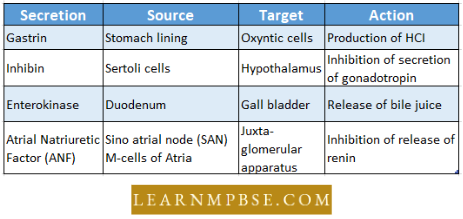
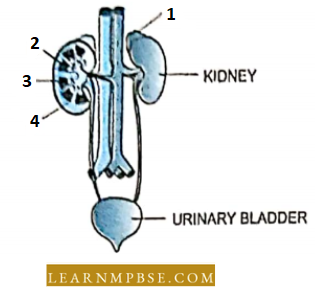
- Many other organs such as the digestive tract secrete hormones, and erythropoietin from the kidney stimulates RBC production. An atrial natriuretic hormone secreted by the heart helps to regulate salt and water balance and blood pressure.
- The iodine content of thyroxine is 65% and is called iodized hormone. Thyroxine contains 80% tetra do thyronine (T4) and 20% triiodo thyroxines (T3) is more active than T4
- Renin. A hormone secreted by the kidney. It helps in erythropoiesis in bone marrow and osmoregulation through the renin-angiotensinogen system. Adiposogenital syndrome of Hypothalamic eunuchoidism. Hypogonadism in males is caused by the genetic inability of the hypothalamus to secrete gonadotrophin-releasing hormones.
- Contraceptive pills. These contain estrogens and progesterone.
- Diseases Due To Deficiency/Excess Of Hormones
- Grave’s disease. (Exophthalmic Goitre)
- Cause: Hypersecretion of thyroxine due to enlargement of the thyroid gland.
- Cretinism. Cause: Hyposecretion of thyroxine in children.
- Myxoedema. Cause. Deficiency of thyroxine in adults
- Symptoms: a. puffy appearance due to accumulation of fats.
- Lack of alertness, and intelligence.
- Slow heartbeat, low BP, decreased body temperature.
- Iodine Def. Goitre: Deficiency of iodine in diet.
- Symptoms: Enlargement of thyroid gland.
- Parathyroid tetany : Cause: Deficiency of Parathormone.
- Symptoms: Sustained contraction of muscles of face, pharynx, hands and feet.
- Addison’s Disease: Cause: Deficiency of mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids.
- Symptoms: a. low blood sugar, low Na+ ion, high K+ ion concentration in blood.
- Bronze-like pigmentation of skin.
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
- Conn’s syndrome (Aldosteronism) Caused due to excessive secretion of aldosterone.
Cushing’s Syndrome. Cause. Excess of cortisol.
- Symptoms, a. High blood sugar, b. Sugar in urine, c. Obesity, d. Wasting of limb muscles
- Adrenal virilism. Excess of sex corticoids in (females) a tendency to develop male characteristics by the female due to imbalances in the secretion of adrenal hormones.
- Dwarfism. Deficiency of GH from early age. It may be Lorrain type, Frohlich type, or Progeria.
- Gigantism. Excess of GH from childhood.
- Acromegaly. Excess of GH after adolescence. The stage is called Acromicria.
- Diabetes Insipidus. Deficiency of ADH.
- Diabetes Mellitus. Deficiency of insulin.
- Eunuchoidism. Failure of testosterone.
- Infantilism. Characteristics of childhood continue beyond the years of puberty. Generally caused due to imbalances in the hormone of the anterior pituitary.
- Diabetes is a disease caused by a deficiency of insulin secreted by the pancreas.
- Hyperglycemia is an increased blood glucose level than the optimum level.
- Hypoglycemia is a lower blood glucose level than the optimum level.
- Osteoporosis is a disease caused by hypersecretion of parathormone.
- Hashimoto’s Disease: Due to a fall in the secretion of thyroxine antibodies start forming against the gland, so the thyroid gets destroyed. It is also known as the suicide of the thyroid.
- Ridding Henson disorder: It is caused by to deficiency of collip’s hormone as a result of which phosphate level in the blood decreases and Ca2+ level increases.
Acidosis. Excessive loss of Na+ is known as acidosis. It may occur due to the hyposecretion of Aldosterone.
Thyroid Gland Disorders NEET Exam Preparation
- Contributors related to Endocrinology
- The first hormone was discovered by William M. Bayliss and Earnest H. Starling (1903).
- The term hormone was introduced by Starling (1905).
- Selye (1948) defined hormone as a functional chemically complex organic compound.
- Berthold laid the foundation for the study of the functions of hormones.
- Scharrer and Scharrer (1936) stated that hormones generally control or regulate reproductive activities, growth, maturation, regeneration, metabolism, and homeostasis. , Huxley called hormones as chemical messengers.
- Thomas Addison is regarded as the father of endocrinology.
- Claude Bernard (1955) established that the nervous system controls the function of endocrine glands.
- The action of insulin hormone was demonstrated by Banting and later by Best. Shaefer (1912) gave the name insulin.
- F. Sanger (1954) worked out the molecular structure of insulin. He established that it is polypeptide and was awarded the Nobel Prize (1958). i
- Human insulin was synthesized by Tsan in 1965.
- Kimball and Murlin discovered glucagon.
- Karlson and Burtenandt coined the term pheromones.
- Kochar (1916) isolated thyroxine (pure form).
- Kendall (1919) obtained a crystallized form of thyroxine.
- Harrington and Barges (1927) worked out the molecular structures of thyroxine.
- Gudernatch (1912) discovered that metamorphosis in a frog’s tadpole begins only when an adequate amount of thyroxine is secreted by the thyroid of the tadpole.
- Aldrich (1901) worked out the molecular structures of adrenaline and noradrenaline.
- Stolz (1904) and Dakin (1905) synthesized adrenaline.
- Enterocrinin. This hormone was isolated by Nasset from both small and large intestinal mucosa
- The nervous system and endocrine system together regulate the working of the body.
- Hormones affect all the cells of a target organ whereas a neuron will affect only a single muscle or fraction of it.
- A hormone is a chemical messenger secreted by the endocrine gland and carried to the target organ by blood.
- The pituitary gland is pea-shaped, 1.3 cm in diameter, and weighs only 0.5 gm.
- The pituitary is attached to the hypothalamus of the brain by a stalk-like structure called the infundibulum.
- Region of pituitary
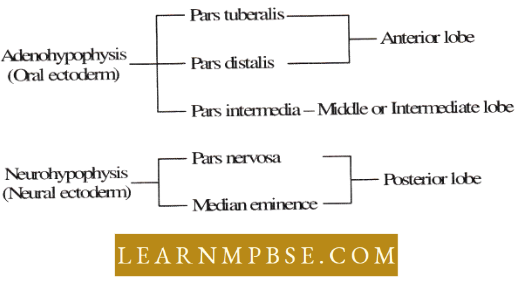
- Anterior lobe (Adenohypophysis)
- Posterior lobe (Neurohypophysis)
- A third region is termed the intermediate lobe or pars intermedia.
- Neurons of the autonomic system stimulate hormone release from some glands. For instance, adrenaline and noradrenaline are released from the adrenal medulla on the arrival of nerve impulses during anxiety, stress, and danger. Thus endocrine system is considered a chemical extension of the nervous system.
- Corticotropes. about 20 % and secrete ACTH.
- Gonadotropes. secrete FSH and LH in female ; and FSH and ICSF1 in male.
- The gastrointestinal lining also secretes several hormones that regulate the secretion of digestive juices.
- Thymosin secreted by the thymus stimulates the maturation of immune system cells. Melatonin controls skin shade in some animals and appears to control annual reproductive cycles. Some hormones, such as steroid hormones, act by binding to DNA and altering gene expression.
- Other hormones bind to membrane receptors, where they either open ion channels (usually Ca2+) or trigger the production of other chemical messengers inside the cell. Typically the receptor activates an enzyme via a G protein intermediate, which generates c AMP, which in turn activates the first step in an enzyme cascade.
- Cellular reactions are faster and more accurate when activity is determined by the ratio of two antagonistic hormones rather than the absolute level of a single hormone.
NEET Biology Endocrine System Quanta To Memory
- Hormonology. Study of hormones.
- Hormonotherapy. Treatment by hormones.
- Largest Endocrine Gland. The thyroid (25 to 40 gms) is the largest endocrine gland in the human body.
- Trophins (Tropins). The hormones which stimulate an endocrine gland to secrete its hormone (s,), For example., thyrotrophic hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete thyroxine.
- All the pituitary hormones are molecules made chiefly of monomers of amino acids
- The anterior pituitary has been called the master gland, because of the tropic hormones it releases. The real master “gland,” however, is the hypothalamus because its hormones regulate the secretory activity of the anterior pituitary.
- Anterior and intermediate lobes of pituitary form adenohypophysis derived from Rathke’s pouch are ectodermal in origin.
- The posterior lobe or neurohypophysis arises from the floor of the hypothalamus.
- Rathke’s pouch: an embryonic outgrowth of the pharynx which forms adenohypophysis of the pituitary gland. Median eminence is a part of the posterior pituitary
- Adenohypophysis gets its blood supply through the circle of Willis
- In comparison with the nervous system, hormones are distributed by blood but slowly.
- Hormonal action is generally less specific in comparison with nervous regulation.
- Kyphosis. Hunched back in the person suffering from acromegaly.
- Lag period. The period between secretion of hormone from the endocrine gland and biological response from the target organ.
- Baldness. It is related to the sex hormones. Male sex hormone promotes baldness, female sex hormones inhibit it.
- Melatonin is a hormone secreted by the pineal body and controls skin pigmentation.
- Sella turcica is the pituitary fossa (a depression in the skull in which the pituitary gland lies).
- Somatotropes are cells of the pituitary gland that secrete growth hormone (also called STH).
- Thymosin is a hormone secreted by the thymus gland and increases the activity of T-lymphocytes.
- Islets of Langerhans. These are approximately 1 to 2 million small clusters of endocrine cells which are named after the name of their discoverer (1869). Prostaglandins and leukotrienes are important eicosanoids.
- These are local hormones and are derived from a 20-carbon fatty acid called arachidonic acid. Contraceptive pills contain the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
- Melanocyte-stimulating hormone is secreted by the middle lobe of the pituitary. It darkens the skin of many animals including fishes and amphibians. It results from the stimulation of the synthesis of melanin in the skin.
- Gravidex test is for detecting the presence of HCG hormone in the urine in case of pregnancy
- Parathormone is a protein hormone consisting of 84 amino acids.
- The British biologist V.B. Wigglesworth discovered, in the 1930s, two hormones that regulate development in insects. One is ecdysone, which promotes growth, molting, and the development of adult traits.
- It is produced by the prothoracic glands in the head or thorax. The other hormone is juvenile hormone which promotes retention of larval characteristics. It is produced by the corpora allata glands in the head.
- Of the two insect hormones discovered by Wiggles Worth, ecdysone has no role in the adult insect, whereas juvenile hormone promotes the development of eggs and sperm.
- Prolactin and oxytocin are being used for increasing milk yield among dairy cattle. Recently genetically engineered Bovine growth hormone (BGH) was also used to boost milk yield in cows but was banned in March 1995.
- The melanocyte-stimulating hormone was previously known as intermedin.
- The adrenal gland is also known as the 3F gland (Fear, Flight, Fright)
- Oral insulin is given as IZS [Insulin zinc suspension] or PZS (Protamine zinc suspension)
- Hassels’ corpuscles are found in the thymus and are known as Thymic cells.
- a-and (3-chains of insulin are connected through disulfide bonds.
- The thymus is associated with our immune system. It acts as a lymphatic gland.
- Humulin is a human insulin, produced by DNA recombinant technology.
- Allaxonic diabetes is due to allaxon which destroys beta cells of the pancreas.
- The adrenal gland is also known as the 3-F gland and the 4-S gland.
- Oral contraceptive pills with a synthetic form of estrogen and progesterone hormones prevent ovulation in the female. Milk secreting hormone is prolactin and milk ejecting hormone is oxytocin.
- The pregnancy hormone is progesterone and the birth hormone is oxytocin.
NEET Biology Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions
Question 1. Hormones Chemically Are :
- Proteins
- Fatty Acid Derivatives
- Steroids
- All The Above.
Answer: 4. All The Above
Question 2. Hormonal Diseases May Be Called :
- Functional Diseases
- Deficiency Diseases
- Infectious Diseases
- All The Above.
Answer: 1. Functional Diseases
Question 3. Which Of The Following Is A Hormonal Disease?
- Measles
- Rabies
- Tuberculosis
- Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica.
Answer: 4. Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica.
Question 4. A Hormone Is A Molecule That:
- Moves Through The Blood Stream And Ducts
- Influences Development
- Has The Same Chemical Activity In A Variety Of Organisms
- Alters The Activity Of Certain Non-Adjacent Cells.
Answer: 4. Alters The Activity Of Certain Non-Adjacent Cells
Adrenal Gland Hormones NEET Biology
Question 5. Adrenaline Is Secreted By :
- Pituitary Gland
- Pineal Gland
- Adrenal Gland
- Thymus Gland.
Answer: 3. Adrenal Gland
Question 6. Corticoids Are Secreted By :
- Thymus
- Adrenals
- Pancreas
- Kidney.
Answer: 2. Adrenals
Question 7. Islets Of Langerhans Secrete :
- Adrenaline
- Acth
- Fsh
- Insulin.
Answer: 4. Insulin.
Question 8. Based on the Chemical Nature Of Hormones, They Are Divided Into :
- Two Categories
- Three Categories
- Five Categories
- Six Categories.
Answer: 4. Six Categories.
Question 9. α-Cells Of Adenohypophysis Secrete Which Hormone?
- ACTH And LH
- GH And LTH
- FSH And LH
- TSH And FSH.
Answer: 2. GH And LTH
Question 10. The Trophic Factors Are Made Up Of Proteins Containing :
- 1 To 4 Amino Acids
- 4 To 10 Amino Acids
- 3 To 15 Amino Acids
- 3 To 20 Amino Acids.
Answer: 4. 3 To 20 Amino Acids.
Question 11. Which One Of The Following Is Not Synthesized In the Pituitary?
- Lactotrophic
- TSH
- ICSH
- ADH
Answer: 1. Lactotrophic
Question 12. Acth Is Secreted By :
- Pineal Body
- Anterior Lobe Of Pituitary Gland
- Posterior Lobe Of Pituitary Gland
- Thymus.
Answer: 2. Anterior Lobe Of Pituitary Gland
Question 13. Adh Is Produced By :
- Pineal Body
- Anterior Lobe Of Pituitary Body
- Thymus
- Posterior Lobe Of Pituitary Body.
Answer: 4. Posterior Lobe Of Pituitary Body.
Question 14. Which Of The Following Substances Is Released In Excess Quantity During Excitement?
- Cortisone
- Serotonin
- Adrenaline
- Nor-Epinephrine.
Answer: 3. Adrenaline
Adrenal Gland Hormones NEET Biology
Question 15. Which Of The Following Structures Act As Temporary Ductless Gland?
- Pancreas
- Pineal
- Parathyroid
- Placenta.
Answer: 4. Placenta
Question 16. Which Of The Following Secretory Glands Acts Both As Endocrine And Exocrine?
- Adrenal
- Parathyroid
- Pancreas
- Pineal.
Answer: 3. Pancreas
Question 17. Like Muscles, Hormones Are Antagonistic In Their Functioning. Mark The Wrong One :
- Calcitonin And Parathormone
- Insulin And Glucagon
- Tsh And Thyroxine
- Somatostatin And Growth Hormone.
Answer: 3. Tsh And Thyroxine
Question 18. The Hormone Released From the Intermediate Lobe Of the Pituitary Is:
- FSH
- LH
- MSH
- ACTH.
Answer: 3. ACTH
Question 19. Secretion Of The Following Hormones Results In Cretinism :
- Thyroxine
- Testosterone
- Calcitonin
- ADH.
Answer: 1. Thyroxine
Question 20. Vasopressin Is Related With :
- Concentration Of Urine
- Dilution Of Urine
- Quick Digestion
- Slow Heart Beat.
Answer: 1. Concentration Of Urine
Question 21. Which Of The Following Statements Is False?
- Hormones Produced In Ovary Affects The Uterine Cycle
- Hormones Produced In Small Intestine Stimulate Heart
- Hormones Produced In Adrenal Medulla Stimulate HeartBeat
- Hormones Produced In Thyroid Stimulate Metabolism.
Answer: 2. Hormones Produced In the Small Intestine Stimulate the Heart
Adrenal Gland Hormones NEET Biology
Question 22. The Target Cells Of A Hormone Always Have :
- Special Receptors To Which The Hormones Bind
- Special Channels Through Which The Hormones Move
- Large Amounts Of Hormones Stored Within Vesicles.
- Undifferentiated Cytoplasm.
Answer: 1. Special Receptors To Which The Hormones Bind
Question 23. The Cells That Produce Glucagon In Pancreas Are :
- α Cells
- β Cell
- ϒ Cells
- Acinar Cells.
Answer: 1. α Cells
Question 24. Calcium Ions Are Important In The Body Because They :
- Are Involved As Co-Factors
- Regulate Many Intercellular Metabolism
- Influence Membrane Permeability
- All The Above.
Answer: 4. All The Above.
Question 25. Fsh Is Produced By :
- Posterior Lobe Of Pituitary Body
- Middle Lobe Of Pituitary Body
- Anterior Lobe Of Pituitary Body
- Adrenal Cortex.
Answer: 3. Anterior Lobe Of Pituitary Body
Question 26. A Short Individual, Fairly Well Proportioned Body, Who Is Mentally And Physically Normal, Developed Due To The Undersecretion Of Growth Hormones, This Stage Is :
- Lorrain’S Type
- Frohlich’S Type
- Acromegaly
- Acromicria.
Answer: 1. Lorrain’s Type
Question 27. Adrenal Medullary Hormones Are Produced When :
- Neurohypophysis Is Stimulated
- Adenohypophysis Is Stimulated To Produce Oxytocin
- Under Stress
- Breeding Phase Starts.
Answer: 3. Under Stress
Question 28. Estrogen Is Necessary For :
- Development And Maintenance Of Uterus
- Proper Functioning Of Fallopian Tube
- Normal Functioning Of The Cervix And Vagina
- Development Of Secondary Sexual Characters In Females.
Answer: 4. Development Of Secondary Sexual Characters In Females.
Question 29. Vasopressin And Oxytocin Are Secreted By :
- Hypothalamic Neurosecretory Cells
- Neurohypophysis
- Medulla
- Pancreas.
Answer: 1. Hypothalamic Neurosecretory Cells
Question 30. Adrenal Cortical Cells Are Stimulated By :
- Corticotropins From The Hypothalamus
- Adreno Corticotropic Hormones
- Corticoids
- Changes In Blood Glucose Level.
Answer: 2. Adreno Corticotropic Hormones
Question 31. Many Hormones Are Initially Synthesised As Biologically Inactive Precursor Molecules Called :
- Ectohormones
- Pheromones
- Endorphins
- Prohormones.
Answer: 4. Prohormones.
Question 32. Rate Of Hormones Synthesis And Secretion Depend Upon :
- Functional Efficiency Of The Feedback
- Amount Of Excitation In Target Tissue
- Degree Of Inhibition Causes
- Functional State Of Tissue.
Answer: 1. Functional Efficiency Of The Feedback
Pancreatic Hormones And Blood Sugar Regulation NEET
Question 33. Thyrotrophic Releasing Hormone Is :
- A Neurosecretion From The Hypothalamus Which Stimulates Anterior Lobe Of Pituitary
- A Secretion Of Pars Distalis
- Elaboration Of Neurohypophysis
- From Thyroid Gland.
Answer: 1. A Neurosecretion From The Hypothalamus that stimulates the Anterior Lobe Of the Pituitary
Question 34. Involvement Of Any Hormone In The Control Of Cellular Function Depends On A Series Of Reactions Involving :
- Synthesis Of Hormone In The Endocrine Cells
- Feedback Control
- Beginning With Hormone Synthesis And Finishing With Feedback Control
- None Of The Above.
Answer: 3. Beginning With Hormone Synthesis And Finishing With Feedback Control
Question 35. Hormones Regulating The Morphogenetic Effects Are :
- Growth Hormone
- Testosterone
- Androgens
- All Of The Above.
Answer: 4. All Of Above.
Question 36. If the Ovaries Of A Lady Are Removed In The Fourth Month Of Pregnancy, The Result Will Be :
- Embryo Will Develop Normally Till Birth
- Abortion Will Occur After Some Time
- Development Of Embryo Become Improper
- None Of The Above.
Answer: 1. Embryo Will Develop Normally Till Birth
Question 37. A Substance Called ADH Is:
- A Hormone That Promotes Glycogenesis In Liver Cell
- An Enzyme Secreted By Cells Of Intestinal Wall; Hydrolyses Dipeptides Into Amino Acids
- A High Energy Compound Involved In Muscle Contraction
- A Pituitary Secretion Which Promotes Reabsorption Of Water From Glomerular Filtrate.
Answer: 4. A Pituitary Secretion that promotes Reabsorption Of Water From Glomerular Filtrate.
Question 38. The Pancreas Is A Mixed Gland In Which :
- All Cells Secrete Enzymes And Hormones
- Most Cells Secrete Hormones
- A Few Cells Secrete Enzymes
- Enzymes And Hormones Are Secreted By Separate Cells.
Answer: 4. Enzymes And Hormones Are Secreted By Separate Cells.
Question 39. Treatment With Alloxan Destroys :
- STH Cells
- β- cells of Islets Of Langerhans
- Cells Of Sertoli
- Cells Of Leydig.
Answer: 2. Islets Of Langerhans
Question 40. Select The Correct Answers To The Followings. Which Of The Following Techniques Should Be Least Likely To Help Elucidate The Function Of A Hormone Produced By An Endocrine Gland?
- Removal Of The Gland And Subsequent Analysis Of What Functions Are Lost
- Transplantation Of The Gland Into An Animal That Lacks The Gland
- Transfusion Of Blood From An Animal Lacking The Gland Into An Animal That Has The Gland And Observation Of Its Effects
- Observing Effects Of Gland Extract On Various Tissues Grown In Culture.
Answer: 3. Transfusion Of Blood From An Animal Lacking The Gland Into An Animal That Has The Gland And Observation Of Its Effects
Question 41. All The Following Commonly Serve As Signals Stimulating Hormone Secretion Except:
- Conditions Outside The Body
- Rising Levels Of Another Hormone
- Rising Levels Of The Hormone In Question
- Falling Levels Of The Hormone In Question.
Answer: 3. Rising Levels Of The Hormone In Question
Pancreatic Hormones And Blood Sugar Regulation NEET
Question 42. Hormones Are Known To Cause All The Following Changes In Target Cells Except:
- Changes In Genetic Make-Up
- Change In Permeability
- Change In Metabolic Rate
- Increase In Cyclic Amp Concentration.
Answer: 1. Changes In Genetic Make-Up
Question 43. An Advantage Of Having The Endocrine System As Well As The Nervous System Involved In The “Fight Or Flight” Response:
- The Endocrine System Responds Faster
- The Endocrine Response Usually Lasts Longer
- The Endocrine System Is Turned More Precisely To The Degree Of Need
- The Endocrine System Affects Only The Target Organ Whose Response Is Needed To Meet The Emergency.
Answer: 4. The Endocrine System Affects Only The Target Organ Whose Response Is Needed To Meet The Emergency.
Question 44. In Case Of Hypersecretion Of A Parathormone, Some Cells Of the Body Become Overactive. These Cells Are :
- Ependymal Cells
- Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
- Osteoclasts
- Osteocytes.
Answer: 3. Osteoclasts
Question 45. Hormones Controlling Expression Of Secondary Sexual Characters Are Secreted By Which Of These Cells In The Testis?
- Sertoli Cells
- Spermatogonia
- Leydig’S Cells
- Primary Spermatocytes.
Answer: 3. Leydig’s Cells
Question 46. Hormones Which Helps In The Implantation Of Embryo In Uterus Is :
- Estrogen
- Thyroxine
- Relaxin
- Progesterone.
Answer: 4. Progesterone
Question 47. In The Areas Of Destruction In The Bones, Fibrous Cysts Develop However The Parathyroid Becomes Overactive. This Is The :
- Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica
- Polydipsia
- Osteomalacia
- None.
Answer: 1. Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica
Question 48. Anti-Allergic Hormone Is :
- Epinephrine
- Non-Epinephrine
- Gluco-Corticoid
- Mineralo-Corticoid.
Answer: 3. Gluco-Corticoid
Question 49. Cretinism Is Due To :
- Hypothyroidism In Children
- Hypothyroidism In Adults
- Hyperthyroidism In Children
- Hyperthyroidism In Adults.
Answer: 1. Hypothyroidism In Children
Pancreatic Hormones And Blood Sugar Regulation NEET
Question 50. Which Of The Following Is Not Necessarily Property Of All Hormones?
- Carrying Information
- Secreted In Small Amounts
- Short Half-Life
- Proteinic Nature.
Answer: 4. Proteinic Nature.
Question 51. One Of The Following Hormones Is Not Produced By Alimentary Canal. Select?
- Insulin
- Cholecystokinin
- Secretin
- Gastrin.
Answer: 1. Insulin
Question 52. The True Proteinaceous Hormones Are Secreted By :
- Pancreas
- Anterior Lobe Of Pituitary
- Posterior Lobe Of Pituitary
- Thyroid.
Answer: 2. Anterior Lobe Of Pituitary
Question 53. What Does The Growth Hormone Do When the Growth Period Is Over:
- Regulates Metabolism
- Promotes Reproductive Activities
- Stimulates Growth Of Secondary Sexual Characters
- Stimulates Gametogenesis.
Answer: 1. Regulates Metabolism
Question 54. Strong Emotional Attachment To The Young Ones Is Due To:
- Emotional Hormones Like Epinephrine And Gluco-Corticoids
- Luteotropic Hormone (Lth)
- Lh
- All.
Answer: 2. Luteotropic Hormone (Lth)
Question 65. Secretion Of Vasopressin Is :
- Acyclic And Not Affected By Seasonal Changes
- Cyclic Phenomenon With Seasonal Changes
- Effect Of Exercise
- A Regular And Constant Feature.
Answer: 1. Acyclic And Not Affected By Seasonal Changes
Question 66. Precursor Chemical For Steroid Hormones Are:
- Cholesterol
- Nucleic Acid
- Amino Acid
- Mucoprotein.
Answer: 1. Cholesterol
Question 67. Function Of Progesterone Is :
- Preparation Of Uterus For Pregnancy
- To Maintain The Pregnancy
- To Complete The Formation Of Milk In The Mammary Glands
- Both 1 And 2.
Answer: 2. To Maintain The Pregnancy
Endocrine System NEET Notes
Question 68. A New Menstrual Cycle Starts When :
- Pituitary Resumes Lh Production In The Absence Of Fsh And Progesterone
- Ovary Resumes Progesterone Production In the Presence Of Lh
- Ovary Resumes Estrogen Production In The Presence Of Fsh
- Pituitary Resumes Lh Production In The Presence Of Fsh And Progesterone.
Answer: 3. Ovary Resumes Estrogen Production In The Presence Of Fsh
Question 69. Diabetes Mellitus Is Caused By Deficiency Of:
- Secretin
- Adrenaline
- Insulin
- Prolactin.
Answer: 3. Insulin
Question 70. The Growth Of Facial And Body Hair In Male Is Stimulated By :
- Pituitary Hormones
- Thyroxine
- Parathyroid
- Androgenic Hormones.
Answer: 4. Androgenic Hormones.
Question 71. The Phenomenon Of ‘Heat’ Or Oestrus In Females Is Due To The Hormones Secreted By :
- Pituitary
- Thyroid
- Interstitial Cells Of Testes
- Ovarian Follicles.
Answer: 4. Ovarian Follicles.
Question 72. Hyperadrenalism Is Called :
- Cushing’S Disease
- Addison’S Disease
- Simmond’S Disease
- None.
Answer: 1. Cushing’s Disease
Question 73. Which Of The Pituitary Hormones Is Responsible For The Secretion Of Milk By The Mammary Glands In Females?
- ACTH-RH
- LH And Prolactin
- LTH-RH
- TH.
Answer: 2. LH And Prolactin
Question 174. Which One Of The Endocrine Glands Shrinks After The Start Of Adolescence?
- Pituitary Body
- Pineal Glands
- Hypothalamus
- Thymus Glands.
Answer: 4. Thymus Glands.
Question 75. The Hormone That Regulates The Growth Of The Skeleton And The Body As A Whole Is :
- Thyroxine
- Parathormone
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
- Human Growth Hormone.
Answer: 4. Human Growth Hormone.
Question 76. Which One Of The Following Has an Anti-Insulin Effect?
- Calcitonin
- Cortisol
- Oxytocin
- Aldosterone.
Answer: 2. Cortisol
Question 77. Which Of The Following Hormones Is Proteinic In Nature But May Be Secreted By An Organ Which Normally Secretes Steroids Under Special Conditions Is :
- Relaxin
- LH
- Estrogen
- Oxytocin.
Answer: 1. Relaxin
Question 78. The Addison’s Disease Is Caused By The :
- Hyposecretion Of Cortical Hormones
- Hypersecretion Of Cortical Hormones
- Hypersecretion Of Pituitary Hormones
- Enlargement Of Thyroids.
Answer: 1. Hyposecretion Of Cortical Hormones
Question 79. The Determination And Masculinisation Of Female May Be Done By :
- Ovary
- Medulla Of Adrenals
- Cortex Of Adrenals
- Parathyroids.
Answer: 3. Cortex Of Adrenals
Question 80. Select The Odd One :
- Insulin
- Oxytocin
- Thyroxine
- Ecdysone.
Answer: 4. Ecdysone.
Question 81. Progesterone Is A / An :
- Enzyme
- Protein
- Hormone That Relaxes Uterus During Birth
- Hormone Responsible For Growth And Maintenance Of Foetus.
Answer: 4. Hormone Responsible For Growth And Maintenance Of Foetus.
Question 82. Which Hormone Of The Following Endocrine Glands Lacks Peptide, Amines And Sulphur?
- Hormones Of the Anterior Lobe Of the Pituitary
- Hormones Of the Posterior Lobe Of the Pituitary
- Hormones Of Thyroids And Adrenal Gland
- Hormones Of Gonads.
Answer: 4. Hormones Of Gonads.
Endocrine System NEET Notes
Question 83. Which Endocrine Gland Stores Its Secretion In The Extracellular Space Before Discharging It Into The Blood?
- Adrenal
- Pancreas
- Testis
- Thyroid.
Answer: 4. Thyroid.
Question 84. According To The Accepted Concept Of Hormone Action, If Receptor Molecules Are Removed From Target Organs :
- The Target Organ Will Continue To Respond To The Hormone Without Any Difference
- The Target Organ Will Continue To Respond To The Hormone But Will Require Higher Concentration
- The Target Organ Will Not Respond To The Hormone
- The Target Organ Will Continue To Respond To The Hormone But In The Opposite Way.
Answer: 3. The Target Organ Will Not Respond To The Hormone
Question 85. Oxytocin Is A :
- Parathormone
- Small Peptide
- Fatty Acid Residue
- Sugar Molecule.
Answer: 2. Small Peptide
Question 86. The Hormone that elevates Blood Calcium And Phosphorus levels is:
- Parathormone
- Calcitonin
- Thyroxine
- Triiodothyronine.
Answer: 1. Parathormone
Question 87. The Hormone Which Stimulates Milk Production In Mammals Is Known As:
- Glucagon
- Prolactin
- Progesterone
- Oestrogen.
Answer: 2. Prolactin
Question 88. Which Of The Following Is Not a Steroid?
- Testosterone
- Oestradiol-17b
- Progesterone
- Prolactin.
Answer: 4. Prolactin.
Question 89. Which Of The Following Hormones Stimulate the Conversion Of Proteins Into Amino Acids Particular During Fasting Or Hibernation?
- Glucocorticoids
- Secretin
- Adrenaline
- Enterogastrone.
Answer: 1. Glucocorticoids
Question 90. Growth Hormone Is Secreted By :
- Hypothalamus
- Thyroid Glands
- Pituitary Gland
- Pineal Body.
Answer: 3. Pituitary Gland
Question 91. The Hormone In the Pineal Gland Is Called :
- Melatonin
- Melatonin
- Serotonin
- Pincolin.
Answer: 1. Melatonin
Question 92. The Pineal Gland :
- Is A Photoreceptor
- Responds To Smell
- Responds To Sound
- Is Sensitive To Light Stimulus.
Answer: 4. Is Sensitive To Light Stimulus.
Endocrine System NEET Notes
Question 93. Endocrinology Term Was Proposed By :
- Pande
- Hardy
- Sutherland
- All Of These.
Answer: 1. Pande
Question 94. Hormones Are Needed In :
- Gms.
- Milligrams
- Nanograms
- Kilograms.
Answer: 3. Nanograms
Question 95. Pheromones Are :
- Hormones Of Insects
- Peripheral Hormones
- Both 1 And 2
- None.
Answer: 3. Both 1 And 2
Question 96. The Total No. Of Hormones Produced By Adrenal Cortex Is 20 But They Are Grouped Under :
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four.
Answer: 3. Three
Question 97. Calcitonin, Which Reduces The Excessive Amount Of Calcium Of The Blood, Is Secreted By The :
- Hypothalamus
- Parathyroid
- Thyroid
- Adrenal.
Answer: 3. Thyroid
Question 98. The Vesicles Of The Thyroid Gland Are Lined By :
- Epithelium Which Is Single Layered
- A Double Layer Of Epithelium
- A Single Layer Of Endothelium
- A Double Layer Of Endothelium.
Answer: 1. Epithelium Which Is Single Layered
Question 99. The Moulting In Insects Is Triggered Off By :
- Thyroxine
- Ecdysone
- Juvenile Hormone
- Pheromone.
Answer: 2. Ecdysone
Question 100. The Hormones Secreted By Hypothalamus Are Carried To The Pituitary Gland By :
- Hypophyseal Stalk
- Hypophyseal Portal System
- Neural Complex
- Neuro-Hypophyseal Portal System.
Answer: 2. Hypophyseal Portal System
Question 101. Cretinism In Children Is Caused By :
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypopituitarism
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Hypo-Insulin-Secretion.
Answer: 1. Hypothyroidism
Hormones And Their Functions NEET Biology
Question 102. Mammalian Thymus Is Mainly Concerned With :
- Regulation Of Body Growth
- Regulation Of Body Temperature
- Immunological Functions
- Secretion Of Thyrotropins.
Answer: 3. Immunological Functions
Question 103. Insulin Was Extracted First By :
- Flemming
- Khorana
- Watson And Crick
- Banting And Best.
Answer: 4. Banting And Best.
Question 104. The Effect Of Different Hormones On The Body Can Be Best Said To Bring About:
- Stimulation Of Organs
- Release Of Inherent Capacities
- Proper Growth
- Coordination Of Functions.
Answer: 4. Coordination Of Functions.
Question 105. Which Hormone Has The Anti-Insulin Effect?
- Calcitonin
- Cortisol
- Oxytocin
- Glucagon.
Answer: 2. Cortisol
Question 106. Hypoparathyroidism Results Due To :
- Upset In Metabolism
- Improper Gonadial Function
- Convulsions And Tetany
- Nervousness And Wasting.
Answer: 3. Convulsions And Tetany
Question 107. The Secretion From Which Of The Following Controls Wall Balance In The Body?
- Cerebellum
- Cerebrum
- Pineal Body
- Pituitary.
Answer: 4. Pituitary.
Question 108. Hypothyroidism In Adult Causes :
- Cretinism
- Exophthalmic Goitre
- Myxoedema
- Graves’s Disease
Answer: 3. Myxoedema
Question 109. Insulin Promotes :
- Glycogenesis
- Glycolysis
- Glyconeogenesis
- Glycogenolysis.
Answer: 1. Glycogenesis
Question 110. Mark The Gland In Whose Presence Sex Glands Fail To Develop :
- Adrenal
- Pituitary
- Pineal
- Thyroid.
Answer: 3. Pineal
Question 111. The Anterior Lobe Of Pituitary Affects :
- Protein Metabolism
- Fat Metabolism
- Carbohydrate Metabolism
- All Of The Above.
Answer: 4. All Of The Above.
Question 112. Survival Time Can Be Minimized If We Remove:
- Adrenal
- Pituitary
- Thymus
- Thyroid.
Answer: 1. Adrenal
Question 113. Testis Secretes Androgen, It Is :
- Testosterone
- Androsterone
- Progesterone
- Aldosterone.
Answer: 1. Testosterone
Question 114. Which Of The Following Causes Ageing?
- Islets Of Langerhans
- Parathyroid
- Thyroid
- Thymus.
Answer: 4. Thymus.
Hormones And Their Functions NEET Biology
Question 115. Breast Development During Pregnancy Is Induced By :
- Estradiol
- Progesterone
- Relaxin
- None Of These.
Answer: 2. Progesterone
Question 116. Which Of The Following Is Helpful For An Asthma Patient In Exhaling The Air?
- Adrenaline
- Insulin
- Oxytocin
- Thyroxine.
Answer: 1. Adrenaline
Question 117. Which Of The Following Controls Thirst?
- Adrenal
- Pituitary
- Parathyroid
- Thyroid.
Answer: 2. Pituitary
Question 118. Complete Failure Of Adenohypophysis Of Pituitary In Adult Women Causes :
- Addison’S Disease
- Cushing’S Disease
- Dwarfism
- Simmond’s Disease.
Answer: 3. Dwarfism
Question 119. Oxytocin Is Secreted By :
- Adenohypophysis
- Neurohypophysis
- Hypophyseal Stalk
- Only Pregnant Women.
Answer: 2. Neurohypophysis
Question 120. Fsh Is Produced By :
- Adrenal
- Thyroid
- Anterior Lobe Of Pituitary
- Posterior Lobe Of Pituitary.
Answer: 3. Anterior Lobe Of Pituitary
Question 121. Which Of The Following Hormones Is From the Parathyroid Gland?
- Epinephrine
- Gastrin
- Noradrenaline
- Parathormone.
Answer: 4. Parathormone.
Question 122. Thyroxine Is Produced Through :
- Chlorination Of Serine
- Iodination Of Isoleucine
- Iodination Of Tyrosine
- Phosphorylation Of Amino Acids.
Answer: 3. Iodination Of Tyrosine
Question 123. Which Of The Following Is Related To The Production Of Lymphocytes And Antibodies?
- Thymus
- Hypothalamus
- Thyroid
- Leydig Cells.
Answer: 1. Thymus
Question 124. Addison’s Disease Is Due To the Malfunctioning Of the:
- Adrenal Cortex
- Parathyroid
- Pineal Gland
- Pancreas.
Answer: 1. Adrenal Cortex
Question 125. The Recently Reported Hormone, Angiotensin Is Secreted By :
- Liver
- Kidney
- Pancreas
- Placenta.
Answer: 1. Liver
Question 126. Thyroxine Plays Significant Effect On :
- Carbohydrate Metabolism
- Protein Metabolism
- Vitamin Metabolism And Central Nervous System
- All Of The Above.
Answer: 3. Vitamin Metabolism And Central Nervous System
Question 127. Continued Secretion Of Milk Is Maintained By :
- Prolactin
- Progesterone
- Oestrogen
- Relaxin.
Answer: 1. Prolactin
Question 128. The Over-Secretion Of Which Of The Following Pituitary Hormones Causes Acromegaly (Irregularly Development Of Bones)?
- ACTH
- LH
- GTH
- STH Or GH.
Answer: 4. STH Or GH.
Question 129. Hormone Responsible For The Implantation Of Embryo In Uterus And Formation Of Placenta Is :
- Adrenaline
- Progesterone
- Estradiol
- FSH.
Answer: 2. Progesterone
Question 130. The Pituitary Gland’s Posterior Lobe Produces Two Hormones Called :
- Cortisone And Corticosterone
- Progesterone And Estradiol
- Testosterone And Androsterone
- Vasopressin And Oxytocin.
Answer: 4. Vasopressin And Oxytocin.
Question 131. According To Recent Knowledge, The Pineal Body Is Considered As :
- An Organ Of Intelligence
- An Endocrine Gland
- A Vestigial Organ
- An Organ Of Involuntary Action.
Answer: 2. An Endocrine Gland
Pituitary Gland Hormones NEET Study Material
Question 132. Which Hormone Is Responsible For The Relaxation Of The Ligaments Of The Pelvic Girdles In Females At The Time Of Birth?
- Corpus Luteum
- Gastrin
- Estradiol
- Relaxin.
Answer: 4. Relaxin.
Question 133. Who Studied The Effect Of Thyroxine On Metamorphosis :
- Huxley
- Starling
- Kendall
- Gudernatsch.
Answer: 4. Gudernatsch.
Question 134. Correct Hormonal Sequence In The Increase Of Menstruation Is:
- Estrogen, Fsh And Progesterone
- Estrogen, Progesterone And Fsh
- Fsh, Progesterone And Estrogen
- Fsh, Estrogen And Progesterone.
Answer: 4. Fsh, Estrogen And Progesterone.
Question 135. Hormone Secreted By Posterior Lobe Of Pituitary Is Concerned With :
- Metabolism Of Carbohydrates
- Stimulation Of Thyroid
- Secondary Sexual Characters
- Contraction Of Uterus.
Answer: 4. Contraction Of Uterus.
Question 136. Hormone-secreting cells, Called Neurosecretory Cells, Are Abundant In The following:
- Hypothalamus
- Amygdala
- Cerebral Cortex
- Medulla Oblongata.
Answer: 1. Hypothalamus
Question 137. Oxytocin And Antidiuretic Hormone Reach The Posterior Pituitary By Way Of :
- The Anterior Pituitary Gland
- Lymphatic Vessels
- Blood Vessels
- Axons.
Answer: 4. Axons.
Question 138. Oxytocin And Antidiuretic Hormone Reach Their Target Cells By Way Of :
- The Anterior Pituitary Gland
- Lymphatic Vessels
- Blood Vessels
- Axons
Answer: 3. Blood Vessels
Question 139. The Luteinising Hormone Is Secreted By :
- Lactotrophs
- Gonadotrophs
- Thyrotrophs
- Neurohypophysis.
Answer: 2. Gonadotrophs
Question 140. Hypothalamic Releasing Hormones Reach The Anterior Pituitary Gland By Way Of:
- The Posterior Pituitary Gland
- Lymphatic Vessels
- Blood Vessels
- Axons.
Answer: 3. Blood Vessels
Question 141. Excessive Production Of Growth Hormone During Adulthood Can Lead To :
- A Pituitary Giant
- A Pituitary Dwarf
- Disproportionately Large Hands, Feet And Jaw
- Deterioration Of The Bones.
Answer: 3. Disproportionately Large Hands, Feet And Jaw
Question 142. In Mammals, Prolactin Stimulates The Production Of :
- Progesterone
- Mucus In The Digestive Tract
- Digestive Enzymes In The Small Intestine
- Milk.
Answer: 4. Milk.
Question 143. Cushing’s Syndrome Is Associated With the:
- Glucocorticosteroids
- Mineralo Corticosteroids
- Sex Corticosteroids
- Gene Mutation.
Answer: 1. Glucocorticosteroids
Question 144. If A Person Is Subjected To Stress (Like Heat, Cold, Loud Noise, etc.) Continuously, Which Organ Will Undergo Hypertrophy :
- Adrenal
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Salivary Glands.
Answer: 1. Adrenal
Question 145. Addison’s Disease Is Caused By the:
- Hyposecretion Of Corticosteroid
- Oversecretion Of Corticosteroid
- Hyposecretion Of Lh
- Oversecretion Of Lh.
Answer: 1. Hyposecretion Of Corticosteroid
Pituitary Gland Hormones NEET Study Material
Question 146. The Adrenal Glands Are Located Adjacent To The :
- Larynx
- Urinary Bladder
- Kidneys
- Gonads.
Answer: 3. Kidneys
Question 147. The Fight-Or-Flight Response Is Developed By Hormones Of The :
- Hypothalamus
- Adrenal Medulla
- Adrenal Cortex
- Adreno-Pancreatic Complex.
Answer: 2. Adrenal Medulla
Question 148. The Main Function Of Norepinephrine Is To Increase :
- Blood Pressure
- Urine Production
- Cellular Respiration
- The Release Of Epinephrine.
Answer: 1. Blood Pressure
Question 149. Epinephrine And Norepinephrine Function As Both Hormones And :
- Fuel For Cellular Respiration
- Neurotransmitters
- Ions To Promote Action Potentials
- Solutes To Promote Osmotic Flow.
Answer: 2. Neurotransmitters
Question 150. All The Hormones Of The Adrenal Cortex Are Synthesized From:
- Tyrosine
- Glycoproteins
- Cholesterol
- Fats.
Answer: 3. Cholesterol
Question 151. Disease Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica Is Related With :
- Hyposecretion Of Parathyroid Hormone
- Hypersecretion Of Parathyroid Hormone
- Hypersecretion Of Mineralocorticosteroids
- Hyposecretion Of Glucocorticosteroids.
Answer: 2. Hypersecretion Of Parathyroid Hormone
Question 152. The Part Of The Brain With the Greatest Influence Over The Endocrine System Is The :
- Hypothalamus
- Amygdala
- Cerebral Cortex
- Medulla Oblongata.
Answer: 1. Hypothalamus
Question 153. Which Of The Following Groups Of Arthropoda Has a Well-Developed Endocrine System?
- Arachnida
- Crustacea
- Insecta
- All Classes Of Arthropoda.
Answer: 4. All Classes Of Arthropoda.
Question 154. If Adenohypophysectomy Is Done In Adults, Then Which Of The Following Is The Correct Statement:
- Acromegaly
- It Will Affect the Function Of the Testis And Ovary
- Gigantism
- B.M.R. Will Be Affected.
Answer: 2. It Will Affect the Function Of the Testis And Ovary
Question 155. The Moult Of An Insect Is Triggered By :
- Thyroxine
- Ecdysone
- Juvenile Hormone
- A Pheromone.
Answer: 2. Ecdysone
Question 156. The Development Of Adult Characteristics In A Moulting Insect Is Promoted By :
- Thyroxine
- Ecdysone
- Juvenile Hormone
- A Pheromone.
Answer: 2. Ecdysone
Question 157. The Retention Of Larval Characteristics In A Moulting Insect Is Promoted By :
- Thyroxine
- Ecdysone
- Juvenile Hormone
- A Pheromone.
Answer: 3. Juvenile Hormone
Question 158. A Male Moth Finds A Mate Using:
- Thyroxine
- Ecdysone
- Brain Hormone
- Pheromone.
Answer: 4. Pheromone.
Question 159. Diabetes Mellitus Develops Only When :
- α Cells Of the Pancreas Are In Excess
- α Cells Of the Pancreas Are Not Functioning
- β Cells Of Pancreas Are In Excess
- β Cells Of the Pancreas Are Not Functioning.
Answer: 4. 3 Cells Of Pancreas Are Not Functioning
Question 160. The Target Cells Of A Hormone Always Have :
- Special Receptors To Which The Hormone Binds
- Special Channels Through Which The Hormone Moves
- Large Amounts Of The Hormone Stored Within Vesicles
- Undifferentiated Cytoplasm.
Answer: 1. Special Receptors To Which The Hormone Binds
Question 161. The Hormone Which Is Related To The Urine Concentration In Mammals :
- Antidiuretic Hormone Only
- Antidiuretic Hormone And Oxytocin
- Antidiuretic Hormone And Aldosterone
- Testosterone Only.
Answer: 3. Antidiuretic Hormone And Aldosterone
Pituitary Gland Hormones NEET Study Material
Question 162. Which Of The Following Hormones Is A Steroid?
- Prostaglandin
- Estrogen
- Epinephrine
- Thyroxine.
Answer: 2. Estrogen
Question 163. In A Male Heavy Voice And Growth Of Beard And Moustaches Is Due To Oversecretion Of :
- Androgen
- Estrogen
- Adrenaline
- Estrogen And Progesterone.
Answer: 1. Androgen
Question 164. A Steroid Hormone Typically Alters The Activity Of Its Target Cells By :
- Digesting Holes In The Cell’s Plasma Membrane
- Entering The Cell And Altering Gene Expression
- Passing Its Message To An Intracellular Messenger
- Digesting Holes In The Cell’s Lysosomes.
Answer: 2. Entering The Cell And Altering Gene Expression
Question 165. Which Of The Following Hormones Is A Modified Amino Acid?
- Prostaglandin
- Estrogen
- Epinephrine
- Progesterone.
Answer: 3. Epinephrine
Question 166. A Peptide Hormone Typically Alters The Activity Of Its Target Cells By :
- Digesting Holes In The Cell’s Plasma Membrane
- Entering The Cell And Altering Gene Expression
- Passing Its Message To An Intracellular Messenger
- Digesting Holes In The Cell’s Lysosomes.
Answer: 3. Passing Its Message To An Intracellular Messenger
Question 167. Animal Tissues That Synthesize Hormones Are Closely Associated With, And Sometimes Resemble, Cells Of The :
- Immune System
- Embryonic Mesoderm
- Circulatory System
- Nervous System.
Answer: 4. Nervous System.
Question 168. Which One Of The following is Not Under Direct Control Of Pituitary Gland?
- Adrenal Cortex
- Adrenal Medulla
- Thyroid
- Testis.
Answer: 2. Adrenal Medulla
Question 169. If Thyroidectomy Of Tadpole Is Performed, Moulting Will Take Place :
- Potassium Iodide Treatment
- Fed On Adult Sheep Thyroid
- Moulting Will Never Take Place
- Normal Moulting Will Take Place.
Answer: 2. Fed On Adult Sheep Thyroid
Question 170. Spermatogenesis In the Mammalian Testis Is Controlled By :
- FSH
- LH
- Progesterone
- ICSH.
Answer: 1. FSH
Question 171. Vasopressin Is Related With :
- Dilution Of Urine
- Increased Heart Beat
- Concentration Of Urine
- Decreased Heart Beat.
Answer: 3. Concentration Of Urine
Question 172. The Part Of The Brain With The Greatest Influence Over The Endocrine System Is The :
- Hypothalamus
- Cerebellum
- Cerebral Cortex
- Medulla Oblongata.
Answer: 1. Hypothalamus
Question 173. Metabolic Rate In Mammals Is Controlled By :
- Pancreas
- Liver
- Pituitary
- Thyroid.
Answer: 4. Thyroid.
Question 174. Hypothalamo-Hypophyseal System Is Derived From :
- Rathke’S Pouch
- Neuroectoderm
- Rathke’s Pouch And Neuroectoderm
- None Of The Above.
Answer: 3. Rathke’s Pouch And Neuroectoderm
Question 175. The Cells Of the Pancreas That Produce Glucagon Are :
- Alpha Cells
- Gamma Cells
- Acinar Cells
- Beta Cells.
Answer: 1. Alpha Cells
Question 176. The First Hormone To Be Isolated (In 1902) Was :
- Thyroxine
- Testosterone
- Epinephrine
- Secretin.
Answer: 4. Secretin
Question 177. The Mammalian Thyroid Gland Is Located Adjacent To The
- Adenoids
- Trachea
- Kidneys
- Pancreas.
Answer: 2. Trachea
Question 178. Thyroxine And Triiodothyronine, Produced By The Thyroid Are Synthesized From Iodine And :
- Phenylalanine
- Cholesterol
- Glycoproteins
- Tyrosine.
Answer: 4. Tyrosine.
Pituitary Gland Hormones NEET Study Material
Question 179. The Parathyroid Glands Are Located Adjacent To The :
- Adenoids
- Thyroid Gland
- Adrenal Glands
- Pancreas.
Answer: 2. Thyroid Gland
Question 180. Progesterone Is Secreted By :
- Corpora Allata
- Corpus Albicans
- Corpus Luteum
- None Of These.
Answer: 3. Corpus Luteum
Question 181. Which Of The Following Statements is correct?
A. Endocrine Control Is Integrated With Neural Control At The Level Of The Hypothalamus.
B. Thyroid Hormones Are Required For Normal Prenatal Brain Development.
C. Glucocorticoids Are Anabolic Steroids.
D. Adrenal Medulla Releases Adrenaline And Noradrenaline In A Ratio Of Approximately 10:1:
Choose The Correct Answer
- A And D
- A And C
- A And B
- B And C
Answer: 3. A And B
Question 182. Which Of The Following Statement Is Correct?
- Testosterone Is Not Water-Soluble And Acts Via Receptors On The Plasma Membrane Of The Target Cells.
- Hypoglycemia Occurs Most Commonly In Diabetic Patients.
- Oxytocin Is Released In Response To Mechanical Stimulation Of The Breast Nipple
- Cellular Reactions Are Slow And More Accurate When Activity Is Determined By Two Antagonistic Hormones.
Answer: 2. Hypoglycemia Occurs Most Commonly In Diabetic Patients.
Question 183. The Posterior Pituitary :
- Produces Oxytocin
- Is Under The Control Of the Hypothalamic Releasing Neurohormone
- Secretes Trophic Hormones
- Secretes Neurohormones.
Answer: 1. Produces Oxytocin
Question 184. Parathyroid Hormone :
- Is Produced By The Thyroid Gland
- Is Released When Blood Calcium Levels Fall
- Stimulates Osteoblasts To Lay Down New Bone
- Stimulates Calcitonin Release.
Answer: 2. Is Released When Blood Calcium Levels Fall
Question 185. Steroid Hormones :
- Have Only Cell Surface Receptors
- Are Lipophobic
- Act Through Altering The Activity Of Proteins In The Target Cell
- Are Produced By The Adrenal Cortex.
Answer: 3. Act Through Altering The Activity Of Proteins In The Target Cell
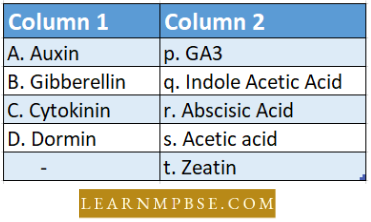
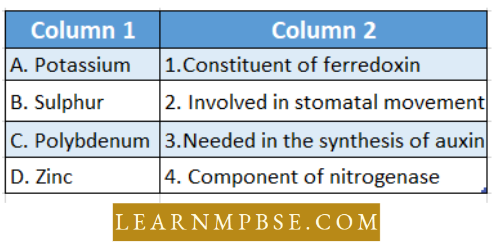
Question 186. Match The Definitions Of Column 1 With the Appropriate Term Of Column 2
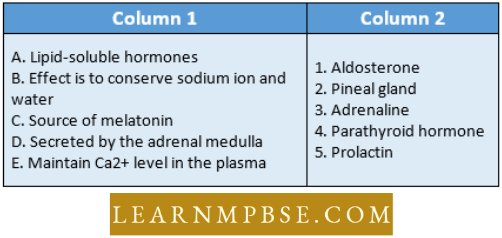
- 1 2 4 3 5
- 5 1 2 3 4
- 5 1 3 4 2
- 5 1 2 4 3.
Answer: 2. 5 1 2 3 4
Question 187. Both Adrenaline And Cortisol Are Secreted In Response To Stress; Which Of The Following Statement Is Also True For Both Of These Hormones?
- They Act To Increase Blood Glucose
- They Are Secreted By The Adrenal Cortex
- Their Secretion Is Stimulated By Adrenocorticotropin
- They Are Secreted Into The Blood Within Seconds Of The Onset Of Stress.
Answer: 1. They Act To Increase Blood Glucose
Question 188. Which Of The Following Is Not Inhibitory Hormone?
- PIH
- GHIH
- MIH
- GI.
Answer: 4. GI.
Question 189. Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone Is Secreted By Which Cell Type Of Pituitary Gland?
- Somatotroph
- Thyrotroph
- Corticotroph
- Gonadotroph.
Answer: 3. Corticotroph
Question 190. Which Of The Following Can Cause the Release Of Oxytocin Hormone In A Lactating Mother?
- Sight Of Baby
- Sound Of Baby
- Both 1 And 2
- None Of Above.
Answer: 3. Both 1 And 2
Question 191. Which Of The Following Hormone Is Not Present In Both Sexes?
- Oxytocin
- ADH
- FSH
- ICSH.
Answer: 4. ICSH.
Question 192. About A Million Islets Of Langerhans Each With Approximately 3000 Cells Comprise What Percentage Of Pancreas?
- 1
- 1-5
- 2
- 2-5.
Answer: 2. 1-5
Question 193. Which Of The Following Statement Is Incorrect?
- Somatostatin Inhibit The Secretion Of Insulin And Glucagon
- Cortisol Hormone Has No Role During And After Danger
- Hypoglycemic Results From Hypersecretion Of Insulin
- Human Placental Lactogen Stimulate Mammary Growth.
Answer: 2. Cortisol Hormone Has No Role During And After Danger
Thyroid Gland Disorders NEET Exam Preparation
Question 194. Which Of The Following Is A Function Of Calcitonin?
- Regulation Of Metabolic Rate
- Maintenance Of Body Temperature
- Regulate The Development Of Mental Faculties
- All Of The Above.
Answer: 4. All Of Above.
Question 195. Hypophysectomy Results In Diminution Of All Except One Of The Following Hormones.
- Acth (Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone)
- Growth Hormone
- Prolactin
- Tsh (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone).
Answer: 3. Tsh (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone).
Question 196. The Glucocorticoids Are Mainly Responsible For :
- Enhancement Of Glucose Formation
- Diminution Of Glucose Formation
- Excretion Of Sodium By Kidney
- Retention Of Sodium By Kidney.
Answer: 1. Enhancement Of Glucose Formation
Question 197. Insulin Deficiency Produces :
- Increased Entry Of Glucose Into Cells
- Reduced Entry Of Glucose Into Cells
- Decreased Release Of Glucose From Liver
- No Effect On Carbohydrate Metabolism.
Answer: 2. Reduced Entry Of Glucose Into Cells
Question 198. Hormones Based On Fatty Acids Are :
- Small In Size And Variable In Structure
- Small In Size And Constant In Structure
- Large In Size And Variable In Structure
- Large In Size And Constant In Structure.
Answer: 2. Small In Size And Constant In Structure
Question 199. A Disease Which Is Caused By The Under-Secretion Of Adrenal Cortex Is :
- Grave’s Disease
- Addison’s Disease
- Cushing’s Syndrome
- Acromegaly.
Answer: 2. Addison’s Disease
Question 200. A Hormone Which Helps In The Implantation Of Embryo In Uterus Is :
- Oestrogen
- Relaxin
- Progesterone
- Thymosin.
Answer: 3. Progesterone
NEET Biology Endocrine System Questions From Competitive Examination
Question 1. Myxoedema Is Due To :
- Decreased Production Of Thyroxine
- Increased Production Of Thyroxine
- Excess Gh
- Decreased Insulin.
Answer: 1. Decreased Production Of Thyroxine
Question 2. Injection Of Glucagon Will :
- Cause Hypoglycemia
- Cause Galactosemia
- Increase Blood Sugar
- Cause Goitre.
Answer: 3. Increase Blood Sugar
Question 3. Goitre Influences :
- Speech
- Excretion
- Metabolism
- Vision.
Answer: 3. Metabolism
Question 4. Pheromones Are :
- Produced By Endocrine Glands
- Mrnas
- Chemicals Used In Animal Communication
- Proteins.
Answer: 3. Chemicals Used In Animal Communication
Question 5. Which Is Not Involved In Endocrine Secretion?
- Ley Dig Cell
- Lutein Cell
- Para-Follicular Cells Of Thyroid
- Kupffer Cells.
Answer: 4. Kupffer Cells
Thyroid Gland Disorders NEET Exam Preparation
Question 6. Gh Affects Growth By Controlling Production Of:
- mRNA
- tRNA
- rRNA
- None Of The Above.
Answer: 1. mRNA
Question 7. If the Receptor Molecule Is Removed From the Target Organ For Hormone Action, The Target Organ Will:
- Continue To Respond But Requires Higher Concentration Of Hormone
- Continue To Respond But In Opposite Way
- Continue To Respond Without Any Difference
- Not Respond To Hormone.
Answer: 4. Not Respond To Hormone.
Question 8. Melatonin Is Produced By :
- Thymus
- Skin
- Pituitary
- Pineal Gland.
Answer: 2. Skin
Question 9. On Seeing A Tiger, The Heart Beat And Blood Pressure Increase Due To Release Of Hormone :
- Adrenaline
- Thyroxine
- Parathormone
- Corticoids.
Answer: 2. Thyroxine
Question 10. A Person Has Protruding Eyes, Tachycardia, And Higher Body Temperature. He Is Suffering From :
- Cretinism
- Hyperthyroidism
- Diabetes
- Acromegaly.
Answer: 2. Hyperthyroidism
Question 11. Match The Endocrine Gland, Given Under Column 1 With Their Respective Position In The Body, Given Under Column 2. Choose The Answer Which Gives The Correct Combination Of Alphabets Of Two Columns :
- A – S, B = T, C = P, D= Q
- A = Q, B = S, C = T, D= P
- A = T, B = R, C = P, D= Q
- A = P, B = Q, C = R, D= T.
Answer: 3. A = T, B = R, C = P, D= Q
Question 12. Match The Hormone Listed Under Column 1 With The Roles Given Under Column 2. Choose The Choice In Which The Alphabets Of The Two Columns Are Correctly Matched :
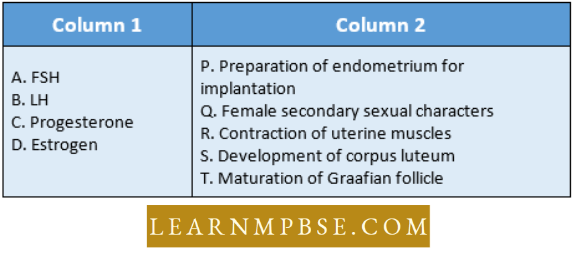
- A = Q, B = S, C = P, D- R
- A – T, B = P, C = S, D= Q
- A = R, B = T, C = S, D= Q
- A = T, B – S, C = P, D= Q.
Answer: 4. A = T, B – S, C = P, D= Q.
Question 13. Autoimmune Hypothyroidism Is :
- Hashimoto Disease
- Cushing Syndrome
- Myxoedema
- Addison’s Disease.
Answer: 1. Hashimoto Disease
Question 14. Steroids Are Precursors Of:
- Progesterone
- Oestrogen
- Testosterone
- All Of the Above.
Answer: 4. All Of Above
Thyroid Gland Disorders NEET Exam Preparation
Question 15. Thyrotropin – Releasing Factor (Trf) Is Produced By :
- Cerebrum
- Optic Lobe
- Cerebellum
- Hypothalamus.
Answer: 4. Hypothalamus.
Question 16. Tetany Is Caused By :
- Hypothyroidism
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Hyperparathyroidism.
Answer: 3. Hypoparathyroidism
Question 17. Mainly Which Type Of Hormones Control The Menstrual Cycle In Human Beings :
- FSH
- Progesterone
- FSH, LH, Estrogen
- LH.
Answer: 3. FSH, LH, Estrogen
Question 18. When Both Ovaries Are Removed From the Rat Then Which Hormone Is Decreased In Blood?
- Oxytocin
- Gonadotrophic Releasing Factor
- Estrogen
- Prolactin.
Answer: 3. Estrogen
Question 19. Which One Of The Following Pairs Correctly Matches A Hormone With A Disease Resulting From Its Deficiency?
- Insulin -Diabetes Insipidus
- Relaxin -Gigantism
- Prolactin -Cretinism
- Parathyroid Hormone -Tetany.
Answer: 4. Parathyroid Hormone -Tetany
Question 20. Synthesis Of Testosterone By Leydig Cells Is Stimulated By :
- FSH
- ICSH
- LTH
- TSH
Answer: 2. ICSH
Question 21. Which One Of The Following Hormones Is A Modified Amino Acid?
- Prostaglandin
- Estrogens
- Epinephrine
- Progesterone.
Answer: 3. Epinephrine
Question 22. Which One Of The Following Pairs Correctly Matches A Hormone With A Disease Resulting From Its Deficiency?
- Thyroxine-Tetany
- Parathyroid Hormone-Diabetes Mellitus
- Luteinizing Hormone-Failure Of Ovulation
- Insuhn-Diabetes Insipidus.
Answer: 3. Luteinizing Hormone-Failure Of Ovulation
Question 23. Chemically The Hormones Are :
- Proteins Only
- Steroids Only
- Biogenic Amines Only
- Proteins, Steroids And Biogenic Amines.
Answer: 3. Biogenic Amines Only
Question 24. Which Of The Following Hormones Is Not A Secretion Product Of the Human Placenta?
- Estrogens
- Progesterone
- Hcg
- Prolactin.
Answer: 4. Prolactin.
Question 25. Damage To the Thymus In A Child May Lead To :
- A Reduction In Haemoglobin Content Of Blood
- A Reduction In Stem Cell Production
- Loss Of Antibody-Mediated Immunity
- Loss Of Cell-Mediated Immunity.
Answer: 4. Loss Of Cell-Mediated Immunity.
Question 26. Parkinson’s Disease (Characterized By Tremors And Progressive Rigidity Of Limbs) Is Caused By Degeneration Of Brain Neurons That Are Involved In Movement Control And Make Use Of Neurotransmitters:
- Acetylcholine
- Norepinephrine
- Dopamine
- Gaba.
Answer: 3. Dopamine
Question 27. Fsh Is Secreted By :
- Anterior Lobe Of Pituitary
- Hypothalamus
- Gonads
- Posterior Lobe Of Pituitary
Answer: 1. Anterior Lobe Of Pituitary
Question 28. Which One Of The Following Four Glands Is Correctly Matched With The Accompanying Description?
- Thyroid – Hyperactivity In Young Children Causes Cretinism
- Thymus – Starts Undergoing Atrophy After Puberty
- Parathyroid – Secrete Parathormone Which Promotes the Movement Of Calcium Ions From Blood Into Bones During Calcification
- Pancreas – Delta Cells Of The Islets Of Langerhans Secrete A Hormone That Stimulates Glycolysis In the Liver.
Answer: 2. Thymus – Starts Undergoing Atrophy After Puberty
Thyroid Gland Disorders NEET Exam Preparation
Question 29. The Hormone That Controls The Level Of Calcium And Phosphorus In The Blood Is Secreted By :
- Thyroid
- Parathyroid
- Pituitary
- Thymus.
Answer: 2. Parathyroid
Question 30. Which Of The Following diseases is Not Related To Thyroid Gland?
- Myxoedema
- Cretinism
- Acromegaly
- Goitre.
Answer: 3. Acromegaly
Question 31. Grave’s Disease Is Due To :
- Hyperactivity Of the Thyroid Gland
- Hypoactivity Of Adrenal Cortex
- Hyperactivity Of the Adrenal Medulla
- Hypoactivity Of Islets Of Langerhans.
Answer: 1. Hyperactivity Of Thyroid Gland
Question 32. Hassal’s Bodies/Corpuscles Are Found In :
- Liver
- Thymus
- Thyroid
- Adrenal.
Answer: 2. Thymus
Question 33. Choose The Correct Combination Of Labelling In The Hormonal Control Of the Female Reproductive System
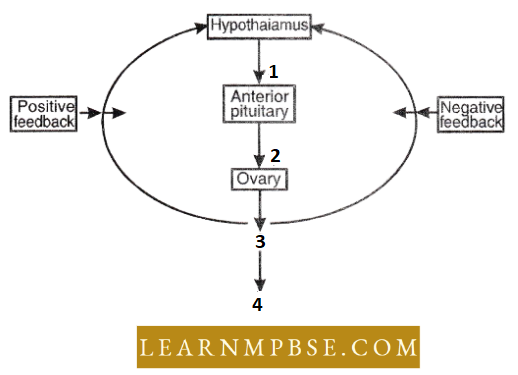
- A-GnRH, B-Tsh, C- Lth, D-Uterus
- A-Gnrh, B-Fsh/Lh, C – Estrogen Of Progesterone, D- Utrerus
- A-Gnrh, B-Sth, C-Lh, D-Uterus
- A-Gnrh, B-Acth, C-Lh, D-Uterus.
Answer: 2. A-Gnrh, B-Fsh/Lh, C – Estrogen Of Progesterone, D- Utrerus
Question 34. Which Of The Following Is Not Paired Correctly?
- Myxoedema – Swollen Facial Tissues
- Cretinism – Mentally Retarded
- Grave’s Disease – Exophthalmos
- Insulin – Raise Blood Glucose.
Answer: 4. Insulin – Raise Blood Glucose.
Question 35. Match Item In Column 1 With Those Given In Column 2.
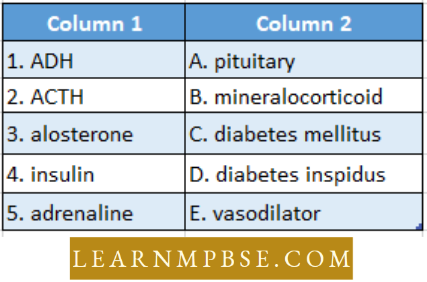
- 1 – A, 2 – D, 3 – B, 4 – C, 5 – E
- 1 – D, 2 – B, 3 – A, 4 – C, 5 – E
- 1 – D, 2 – A, 3 – B, 4 – C, 5 – E
- 1 – D, 2 – A, 3 – C, 4 – B, 5 – E.
Answer: 3. 1 – D, 2 – A, 3 – B, 4 – C, 5 – E
Question 36. If the Receptor Molecule Is Removed From the Target Organ For Hormone Action, The Target Organ Will:
- Continue To Respond But Require Higher Concentration Of Hormone
- Continue To Respond But In Opposite Away
- Continue To Respond Without Any Difference
- Not Respond To Hormone.
Answer: 4. Not Respond To Hormone.
Question 37. Match The List 1 Wish List 2
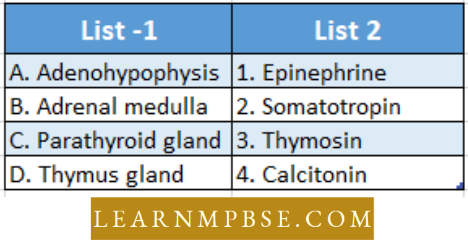
- A : 3, B:1, C: 4, D: 2
- A: 1, B: 2, C : 3, D: 4
- A: 2, B: 1, C: 4, D : 3
- A: 4, B : 3, C: 2, D: 1.
Answer: 3. A:2, B: 1, C: 4, D: 3
Question 38. A Patient Of Diabetes Mellitus excretes glucose In Urine Even When He Is Kept on a carbohydrate-free diet. It Is Because :
- Fats Are Catabolised To Form Glucose
- Amino Acids Are Catabolised In Liver
- Amino Acids Are Discharged In Blood Stream From Liver
- Glycogen From Muscles Are Released In The Blood Stream.
Answer: 1. Fats Are Catabolised To Form Glucose
Question 39. Sertoli Cells Are Regulated By The Pituitary Known As:
- Prolactin
- LH
- FSH
- GH.
Answer: 3. FSH
Question 40. A Steroid Hormone Which Regulates Glucose Metabolism Is :
- 11-Deoxycorticosterone
- Cortisone
- Cortisol
- Corticosterone.
Answer: 3. Cortisol
Question 41. Which One Of The Following Is Not A Second Messenger In Hormone Action?
- Sodium
- Camp
- Cgmp
- Calcium.
Answer: 1. Sodium
Question 42. Which One Of The Following Statements Is Correct?
- Neurons Regulate Endocrine Activity, But Not Vice Versa
- Endocrine Glands Regulate Neural Activity, But Not Vice Versa
- Neither Hormones Control Neural Activity Nor The Neurons Control Endocrine Activity
- Endocrine Glands Regulate Neural Activity, And Nervous System Regulates Endocrine Glands.
Answer: 4. Endocrine Glands Regulate Neural Activity, And Nervous System Regulates Endocrine Glands.
Question 43. Which Hormone Causes Dilation Of Blood Vessels, Increased Oxygen Consumption And Glucogenesis?
- Adrenalin
- ACTH
- Glucagon
- Insulin.
Answer: 1. Adrenalin
Question 44. Withdrawal Of Which Of The Following Hormones Is The Immediate Cause Of Menstruation?
- FSH
- Progesterone
- Estrogen
- FSH-RH.
Answer: 2. Progesterone
Question 45. Which Is Not A Symptom Of Hypothyroidism?
- Lethargy
- Mental Retardation
- Oedema
- Rise In Blood Urea.
Answer: 4. Rise In Blood Urea
Question 46. Flyposecretion Of Which Of The Following Can Cause Diabetes Insipidus?
- Insulin
- Thyroxine
- Glucagon
- ADH.
Answer: 1. Insulin
Question 47. The Hormones That Initiate Ejection Of Milk, Stimulate Milk Production And Growth Of Ovarian Follicles Are Respectively Known As
- PRL, OT, And LH
- OT, PRL And FSH
- LH, PRL, And FSH
- PRH, OT, And LH
- PRH, OT, And FSH
Answer: 2. OT, PRL And FSH
Question 48. Hypothyroidism In Adults And Hyperparathyroidism Will Respectively Lead To :
- Myxoedema And Cretinism
- Grave’s Disease And Hashimoto’s Disease
- Myxoedema And Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica
- Addison’s Disease And Cretinism
- Cretinism And Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica.
Answer: 3. Myxoedema And Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica
Question 49. Which One Of The Following Endocrine glands functions As A Biological Clock And A Neurosecretory Transducer?
- Adrenal Gland
- Thyroid Gland
- Pineal Gland
- Thymus Gland
- Pituitary Gland.
Answer: 3. Pineal Gland
Question 50. Match The Hormone In Column 1 With Their Function In Column 2.
- A-5, B-4, C-L, D-2
- A-4, B-5, C-2, D-1
- A-4, B-3, C-2, D-5
- A-5, B-1, C-2, D-4
- A-4, B-2, C-3, D-5.
Answer: 1. A-5, B-4, C-1, D-2
Question 51. In The Homeostatic Control Of Blood Sugar Level, Which Organs Function Respectively As Modulator And Effector?
- Liver And Islets Of Langerhans
- Hypothalamus And Liver
- Hypothalamus And Islets Of Langerhans
- Islets Of Langerhans And Hypothalamus.
Answer: 3. Hypothalamus And Islets Of Langerhans
Question 52. Column 1 Lists The Endocrine Structure And Column 2 Lists The Corresponding Hormones. Match The Two Columns. Identify The Correct Option From Those Given.
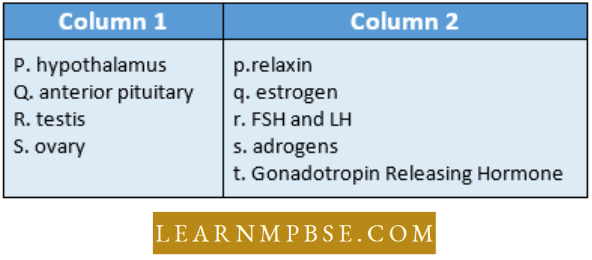
- P = t, Q = r, R = s, S = q
- P = t, Q = r, R = q, S = s
- P = p, Q = q, R = s, S = r
- P = r, Q,= t, R = s, S = q.
Answer: 1. P = t, Q = r, R = s, S = q
Question 53. Which Of The Following Hormones Are Produced In The Hypothalamus And Stored In The Posterior Pituitary?
- FSH And LH
- ADH And Oxytocin
- TSH And STH
- ACTH and MSH.
Answer: 2. ADH And Oxytocin
Question 54. Parathyroid :
- Increases Blood Ca Level
- Decreases Blood Ca Level
- Promotes Collagen Synthesis By Osteoblasts
- All Of The Above.
Answer: 1. Increases Blood Ca Level
Question 55. Which Part Of the Ovary In Mammals Acts As An Endocrine Gland After Ovulation?
- Stroma
- Germinal Epithelium
- Vitelline Membrane
- Graffian Follicle.
Answer: 4. Graffian Follicle.
Question 56. A Person Is Having Problems With Calcium And Phosphorus Metabolism In His Body. Which One Of The Following Glands May Not Be Functioning Properly?
- Parotid
- Pancreas
- Thyroid
- Parathyroid.
Answer: 4. Parathyroid.
Question 57. Feeling The Tremors Of An Earthquake A Scared Resident Of the Seventh Floor Of A Multistoryed Building Starts Climbing Down The Stairs Rapidly. Which Hormone Initiated This Action?
- Adrenaline
- Glucagon
- Gastrin
- Thyroxine.
Answer: 1. Adrenaline
Question 58. Match List With List Ii And Select The Correct Option.
- A – 2, B – 5, C – 4, D – 1, E – 3
- A – 3, B – 4, C – 5, D -3, E – 2 ‘
- A – 5, B – 3, C – 2, D – 4, E – 1
- A – 2, B -3, C – 4, D – 5, E – 1
- A – 5, B – 3, C – 4, D – 2, E – 1.
Answer: 1. A – 2, B – 5, C – 4, D – 1, E – 3
Question 59. Which One Of The Following Pairs Of Organs Includes Only The Endocrine Glands?
- Thymus And Testes
- Adrenal And Ovary
- Parathyroid And Adrenal
- Pancreas And Parathyroid.
Answer: 3. Parathyroid And Adrenal
Question 60. Which One Of The Following Is An Amine Hormone?
- Insulin
- Oxypurin
- Thyroxine
- Progesterone.
Answer: 3. Thyroxine
Question 61. The Blood Calcium Level Is Lowered By The Deficiency Of :
- Thyroxine
- Calcitonin
- Parathormone
- Both Calcitonin And Parathormone.
Answer: 3. Parathormone
Question 62. In Human Adult Females Oxytocin :
- Is Secreted By the Anterior Pituitary
- Stimulates Growth Of Mammary Glands
- Stimulates Pituitary To Secrete Vasopressin
- Causes Strong Uterine Contractions During Parturition.
Answer: 4. Causes Strong Uterine Contractions During Parturition.
Question 63. Match The Source Gland With Its Respective Hormone As Well As The Function.
Answer: 2. Posterior- Vasopressin- Stimulates resorption Of Water In the Distal tubules in the nephron
Question 64. Given Below Is An Incomplete Table About Certain Hormones, Their Source Glands, And One Major Effect Of Each On The Body In Humans. Identify The Correct Option For The Three Blanks A, B, And C.
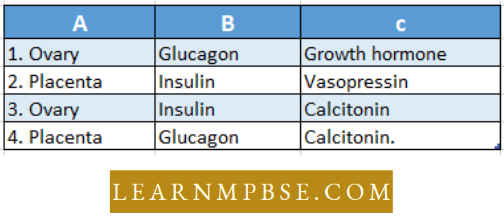
Answer: 1. A- Ovary, B- Glucagon, C- Growth Hormone
Question 65. Which One Of The Following Statements Is Incorrect?
- Glucagon Is Secreted By Pancreas.
- Androgen Is Produced By Ovary.
- Thyroxine Is Secreted By Thyroid.
- Oxytocin Is Secreted By the Pituitary.
Answer: 2. Androgen Is Produced By Ovary.
Question 66. Which Of The Following Statements Is Correct To The Endocrine System?
- Organs In The Body Like the Gastrointestinal Tract, Heart, Kidney, And Liver Do Not Produce Any Hormones.
- Non-Nutrient Chemicals Produced By The Body In Trace Amount That Act As Intercellular Messenger Are Known As Hormones.
- Releasing And Inhibitory Hormones Are Produced By The Pituitary Gland.
- Adenohypophysis Is Under Direct Neural Regulation Of The Hypothalamus.
Answer: 2. Non-Nutrient Chemicals Produced By The Body In Trace amounts that Act As Intercellular Messengers Are Known As Hormones.
Question 67. A Pregnant Female Delivers A Baby Who Suffers From Stunted Growth, Mental Retardation/Low Intelligence Quotient And Abnormal Skin. This Is The Result Of :
- Low Secretion Of Growth Hormone
- Cancer Of The Thyroid Gland
- Oversecretion Of Pars Distalis
- Deficiency Of Iodine In Diet.
Answer: 4. Deficiency Of Iodine In Diet.
68. Select The Answer Which Correctly Matches The Endocrine Gland With The Hormone It Secrets And Its Function/Deficiency Symptom :
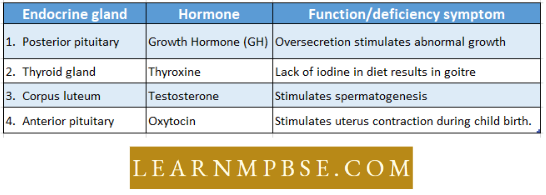
Answer: 2.