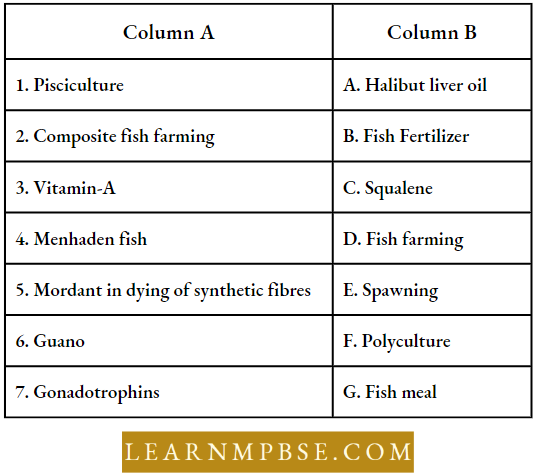
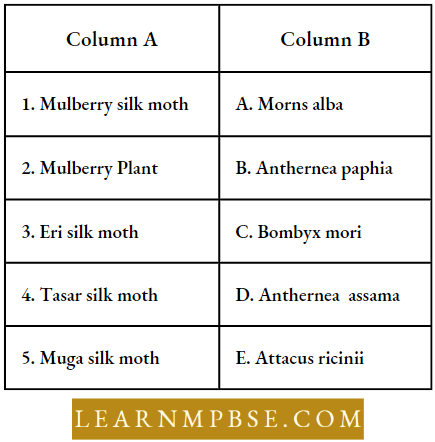
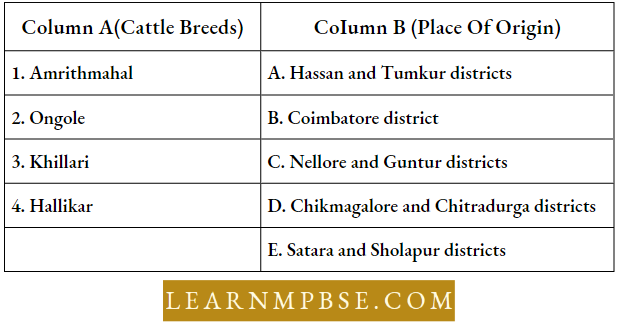
NEET Biology Human Growth Development
- Growth is defined as an irreversible permanent change in the volume or size of a living body accompanied by a change in the dry weight.
- It involves 3 phases i.e. phase of cell division, phase of cell elongation, and phase of cell differentiation.
- Growth is always followed by differentiation and the two phenomena jointly constitute a larger phenomenon called development.
- The growth centers in higher plants are called meristems which may be apical, lateral, or intercalary.
- The growth at the cellular level is initiated by plasmatic growth. A cell passes through 3 phases of growth, differentiated as cell formation, cell elongation, and cell maturation.
- The growth may be measured in terms of fresh weight, dry weight, length, and area.
- Growth in length can be measured by horizontal microscopy, are indicator, or auxanometer. Bose’s crescograph is the finest instrument for measuring growth.
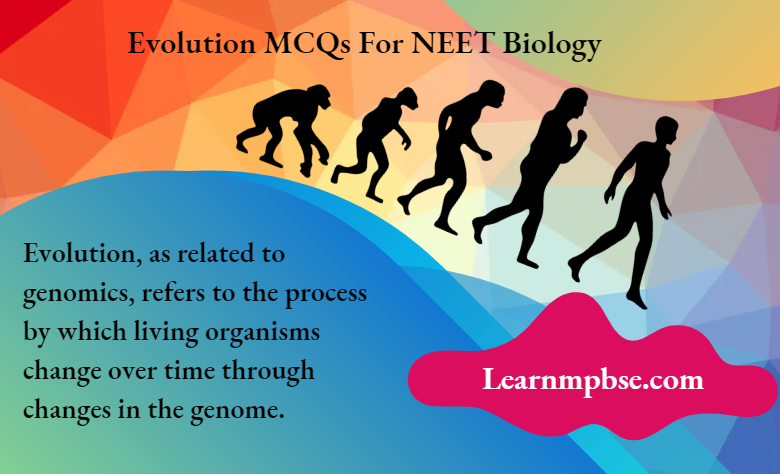
Sachs was the first to plot growth rate i.e., increase of growth per unit of time, and obtained a sigmoid curve.
Neet Biology Human Growth And Development Notes
He differentiated three phases i.e., lag, log or exponential, and steady-state followed by the senescence phase. In some plants, a linear phase is recognized.
- The arithmetic growth of the root can be put as Lt = Lo +rt, where Lo is the length at zero time, Lt at time t, and r is the growth rate.
- Maintenance of the ratio between the growth rates of different parts is called allometric growth. The growth shows a diurnal rhythm. They are partly endogenous and partly governed by external factors.
- The growing shoot tip follows a helical path and the phenomenon is called circumnutation. Many phases of plants operate by a ‘biological clock’.
- When a distinct juvenile phase is identified in the life history, the development is said to be heteroblastic. Such phases have been seen in many plants. Example: BatrachosperDuan, Hedera, Citrus, Quercus, etc.
The juvenility may be due to arrested development or low light intensity. In Acacia melamoxylon, it recapitulates phylogeny.
Human Growth And Development NEET Notes
NEET Biology Notes On Human Growth Development Factors Affecting Growth
The growth of plants is fundamentally regulated by genetic factors via the production of several enzymes. Multiple environmental elements affect growth, including flight, temperature, CO2 levels, moisture, nutrition, and pollution.
- Plants growing in darkness exhibit etiolation. Light intensity influences leaf orientation, chlorophyll synthesis, and other factors. Sun leaves differ from shadow leaves.
- Optimal growth is observed under red light, while minimal growth occurs under green light among monochromatic lights. Gamma, ultraviolet, and X-rays are detrimental to plants. The length of light influences flowering.
- The temperature thresholds for the growth phase are 5°C, 20-30°C, and 35-40°C. They respond to diurnal (photo-temperature) and nocturnal temperatures. This occurrence is referred to as thermoperiodicity.
- Exposure to severe temperatures results in harm to plants. For instance, desiccation, refrigeration, and cryopreservation.
- To endure these challenges, a plant exhibits both internal and external adaptations.
An elevation in CO2concentration from 300 to 1000 ppm enhances net respiration (NR) and relative growth rate (RGR) in certain plant species. Moisture stress may cause the RGR to decline to zero. - The growth of plants is affected by mineral deficiencies, specifically nitrogen, calcium, iodine, and boron.
- Growth is significantly impacted by contaminants including fluorine, ozone, and ethylene.
Human Growth And Development NEET Notes
NEET Biology Notes On Human Growth Development Growth regulators
- Growth is regulated not only by environmental factors like light and temperature but also by certain chemical substances within the plants.
- These substances are known as plant hormones, growth hormones, phytohormones, or growth regulators.
- A plant hormone can be defined as a chemical substance, which is capable of translocation and regulating one or more physiological reactions, when present in low concentrations.
- The plant hormones can have a positive effect on a process and thus promote it, or they have a negative effect and cause inhibition. A particular hormone may promote certain processes, or inhibit some other processes.
Human Growth And Development NEET Notes
NEET Biology Notes On Human Growth Development Auxins
- Auxins (auxin = to grow) are a class of phytohormones that promote longitudinal growth in plants.
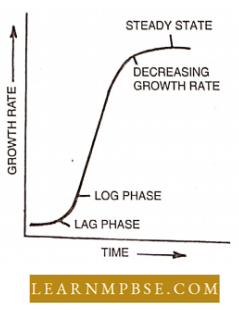
- Auxins that occur in plants are called natural auxins eg.- indole-3-acetic acid, Indolc- 3-acetaldehyde, and Indolc-3-pyruvic acid.
- Synthetic auxins are synthesized artificially and have properties like auxins, eg.- Naphthalene Acetic Acid (NAA), Indole Butyric Acid (IBA), Indole Propionic Acid (IPA), 2, 4-Dichlorophenoxy acetic acid (2,4-D).
- The biosynthesis of auxin has been traced back from the amino acid tryptophan.
- The movement of auxins is polar and basipetal in most plants.
- Auxins can be degraded by the enzyme system IAA oxidase and also by light. They can be inactivated by X-rays UV-rays and gamma rays.
- Auxins are synthesized in the apices ol‘ the stem.
- The most characteristic action of auxin is to promote cell enlargement.
- Auxins cause growth in leaves, roots, stems, etc. by Indicating cell enlargement and cell elongation.
- The cell enlargement is due to ;
- Increase in osmotic content of the cell.
- increase in cell permeability to water. ,
- Reduction in wall pressure,
- Increase in wall synthesis and,
- Synthesis of specific RNA and proteins which increase cell wall plasticity.
Human Growth And Development NEET Notes
NEET Biology Notes On Human Growth Development Gibberellins
They are weakly acidic plant growth hormones that possess a gibbon ring, structure, and can bring about cell elongation of both leaves and stems in general, and intermodal length of genetically dwarf plants in particular.
- They are named after the fungus Gibberella (= Fusariitm moniliform) which produces balance (foolish seedling disease) in rice. The hormone was discovered by Yabuta and Suniiki. Yabuta (1935) coined the term gibberellin.
- About 100 gibberellins are known, GA or gibberellic acid is the commonest. GA4 and GA2 are also commercially used. Gibberellins are synthesized in plants in the leaves of buds, developing embryos, and root tips.
- GA3 promotes intermodal elongation and flowering.
- They promote stem growth by activating the subapical meristem of the stem tip.
- The elongation of internodes before flowering in rosette plants is called bolting.
- Applications of gibberellins induce bolting.
- Gibberellins induce flowering in long-day plants during short-day conditions, e.g.- cabbage, Rudbeckia.
- Gibberellins induce flowering in plants that require cool winter nights before flowering (i.e., they substitute the cold treatment, vernalization).
- Gibberellins break the dormancy in buds and seeds.
- Gibberellins promote the germination of cereal grains such as barley, wheat, rice, etc.
- Gibberellins promote the development of parthenocarpic fruits in tomatoes, apples, almonds, etc.
- The size of the fruits and seeds also increases due to gibberellin treatment.
- When giberellins are sprayed on plants their leaves become expanded. It increases the total photosynthetic area and biomass.
- Gibberellins inhibit the formation of adventitious roots from the cut end of the stem.
- Parthenocarpy. They can induce parthenocarpy in several plants.
- Maleness. Gibberellins stimulate maleness.
- Fruit Yield. Gibberellin application increases the number and size of fruits, e.g., grapes.
- Malt. There is increased malt production when gibberellins are provided to germinating barley grains (due to greater production of a-amylase).
- Sugarcane. GA application increases the sugar yield of sugarcane by promoting intermodal length.
NEET Human Growth And Development Chapter Notes
NEET Biology Notes On Human Growth Development Cytokinins
Cytokinins are slightly basic growth hormones, often derivatives of amino-purine (sometimes adenine), that stimulate cell division in plants. The initial cytokinin was identified by Miller et al. (1955) via the autoclaving of Herring sperm DNA.
- The substance is a synthetic compound known as kinetin. It is 9-furfurylaminopurine. The initial natural cytokinin was identified by Letham et al. (1963). It was satin fabric. Approximately 18 cytokinins have been identified, including dihydrozeatin, IPA, and benzyl adenine.
- Cytokinins are crucial for cytokinesis via chromosomal duplication and may occur in their absence.
- Cytokinins induce division in permanent cells in the presence of auxin.
- Cytokinins, like to auxin and gibberellins, induce cell elongation.
- Buds arise when cytokinins are in surplus, but roots develop when their ratios are inverted (Skoog and Miller, 1957).
- Cytokinins promote plastid differentiation, lignification, and the development of interfascicular cambium.
- Cytokinins postpone the senescence of leaves and other tissues. They also enhance resilience to harsh temperatures and diseases.
- They function antagonistically to auxin, which facilitates apical dominance.
Similar to gibberellins, they mitigate seed dormancy. - They facilitate phloem movement.
- Cytokinins, similar to auxins and ethylene, facilitate the development of female characteristics in flowers.
Human Growth And Development Class 12 Notes For NEET
NEET Biology Notes On Human Growth Development Ethylene
- Ethylene (CH2 = CH2) is a volatile gas present in the atmosphere and as a component of smoke and other industrial gases. Ethylene is formed by incomplete combustion of carbon-rich compounds such as coal, petroleum, and natural gas.
- Soon after the introduction of illuminating gas (produced from coal) for home and street lighting, evidence of plant damage was observed. Physiological studies confirmed that plants produce ethylene by metabolic process during growth and development.
- Ripening fruits in particular synthesize quantities of ethylene that build up to rather high concentrations within intercellular spaces of fruit tissue. The most important effect of ethylene on fruit ripening is that it is produced in large amounts which coincides with the respiratory climacteric.
- Excess of auxin causes ethylene synthesis.
- In the presence of ethylene, roots become apogeotropic while stems turn positively geotropic.
- Abscission of various parts (leaves, flowers, fruits,) is stimulated by ethylene which induces the formation of hydrolases.
- Ethylene promotes apical dominance and prolongs the dormancy of lateral buds.
- In low concentrations ethylene helps in root initiation, growth of lateral roots, and root hairs.
NEET Biology Human Growth And Development Revision Notes
NEET Biology Notes On Human Growth Development Abscisic Acid (Aba)
- It is also called stress hormone or dormant because the production of hormones is stimulated by drought, water logging, and other adverse environmental conditions.
- The hormone is an inhibitor that counteracts the influence of growth-promoting hormones (auxin, gibberellins, and cytokinins), induces dormancy, and helps overcome conditions of stress. The hormone was discovered by Addicott et al in 1963.
- It is commonly formed inside chloroplasts either from mevalonic acid or xanthophyll-like violoxanthin.
- It is known as dormant as it induces dormancy in buds, underground stems, and seeds.
- This hormone was first isolated by Addicott et al (1963) from cotton balls.
- It is produced in many parts of the plants but more abundantly inside the chloroplasts of green cells.
- The hormone is formed from mevalonic acid or xanthophylls.
- It is transported to all parts of the plant through diffusion as well as transport channels (phloem and xylem).
- Abscisic acid induces dormancy of buds towards the approach of winter.
- The buds as well as seeds sprout only when abscisic acid is overcome by gibberellin.
- The formation of abscisic acid stops mitosis in the vascular cambium towards the approach of winter.
- Abscisic acid promotes the abscission of flowers and fruits.
NEET Biology Notes Oon Human Growth Development Calines
- The effect of auxin on root, stem, and leaves is not an isolated reaction but involves other natural hormones called canines which are of three types :
- Rhizocaline: It is a special root-forming honnone produced by the leaves and transported in a polar manner down the stem.
- Caulocaline: It is a stem-forming hormone synthesized in roots from where it is translocated to its site of activity in the stem. ,
- Phyllocaline: It stimulates mesophyll development in leaves. It is synthesized only in the presence of light and the actual site of its synthesis is not known.
NEET Biology Human Growth And Development Important Points
NEET Biology Notes On Human Growth Development Florigen
It is a floral hormone that is produced in photo-induced leaves and translocated to apical and lateral meristems where flower formation is initiated
NEET Biology Human Growth And Development Important Points
NEET Biology Notes On Human Growth Development Useful Information
- Went is credited with the discovery of auxins.
- Hitchcock and Zimmerman showed that flowering in Nicotiana can be accelerated by auxins.
- Auxins prevent premature leaf fall by arresting the formation of the abscission layer.
- Snow (1933) showed that the reactivation of the cambial cells in the spring season is due to auxins.
- Went named the growth-promoting substance Auxin (auxin = to grow)
- Kogl and Haagen Smith isolated three chemicals from human urine and named them auxin a, auxin b, and heteroauxin.
- IAA was first discovered by KogI et al in 1934.
- Letham et al obtained the first naturally occurring cytokinin from unripe maize grain called Zeatin (6 hydroxy, 3 methyl trans, 2 butenyl amino purine).
- Crookes et al recognized ethylene as a plant hormone. r4 Cams and Addict (1961) extracted abscisin-1 and abscisic-II from old cotton bolls and young cotton bolls respectively.
- Knott (1934) found that the locus for photoperiodic induction occurs in the leaves.
- Wellensick (1964) found that the locus for perception of cold treatment is the mer- istematic cells, especially the shoot apex.
- Yabuta (1935) separated the hormone and named it Gibberellin.
- O Yabuta (1938) prepared a crystalline form of Gibberellin.
- Hitchcock and Zimmerman showed that flowering in Nicotiana can be acceler¬ated by auxins.
- Snow (1933) showed that the cambial cells become activated in spring due to auxins.
- Brain et al (1955) isolated GA3 in pure form.
- Cross et al (1961) worked out the structure of Gibberellin or GA3. It is chemically CL 19 ^22
- The first cytokinin was discovered by Miller et al and called Kinetin.
- Draghett (1933) used the term crypto vegetation to signify a state of vegetation maintained by certain plants under low-temperature conditions of winter.
- Peter Ray et al showed that IAA promotes the liberation of a water-soluble xyloglucan from the cell wall.
- Boysen Jensen (1931) while working on coleoptiles of oats (Avena saliva), concluded that growth triggering substance is synthesized in the coleoptile tips.
- Paal (1919) confirmed that growth-promoting substance is synthesized in the stem tips only.
- Went extracted the substance from Avena coleoptile tip and observed its effects
on the stump. He named the substance as auxin. - Kogl, Erxlaben, and Haagen-Smit isolated heteroauxin from human urine which was chemically Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). The term auxin was coined by KogI.
Human Growth And Development NEET Exam Preparation Notes
NEET Biology Notes On Human Growth Development Photoperiodism
- Light is of crucial significance in the flowering of plants. The response of a plant to the Native lengths of light and dark periods is called photoperiodism and the length of the daylight required by the plant to flower is called photoperiod.
- Garner and Allard (1920) classified plants into three groups according to their photoperiods.
- Short-dav plants (SDP or long-night plants): These plants flower when the day length is less than a certain critical length (critical day length is the photoperiod required to induce flowering) say 12 hours. Some examples of short-day plants are tobacco, soybean, Xanlhium, and Chrysanthemum. etc.
- Long-day plants: These plants flower when the day length is greater than a certain critical length example. Spinach, sugarbeet, radish, henbane, potato etc.
- Day-neutral plants: These plants flower in all possible photoperiods e.g. tomato, four o’clock, cotton, cucumber, balsam, maize, etc.
- The photoperiodic stimulus is received by a pigment called phytochrome present in leaves. This pigment is a protein with a chromophore prosthetic group. It seems to be localized in the cell membranes. Phytochrome exists in two interconvertible forms i.e. Pr and Pfr.
- The Pr form of phytochrome absorbs red light (660 nm) and is converted into Pfr form while Pfr forms absorb far-red light (730 nm) and are converted into Pr form. Under continuous darkness, the Pfr form of phytochrome gradually changes to Pr form which promotes the formation of flowering stimulus in short-day plants.
- If the long dark period is interrupted by red light, the Pr form is converted into Pfr form which inhibits the formation of flowering stimulus in short-day plants. In long-day plants, the flowering is promoted by the Pfr form of phytochrome as the long light period favors the conversion of Pr to the Pfr form of phytochrome.
- It is. therefore, concluded that flowering in short-day plants is promoted by the Pr form and inhibited by the Pfr form whereas in long-day plants, flowering is promoted by the Pfr form of phytochrome and inhibited by the Pr form.
- The floral stimulus is a floral hormone. Butler and others isolated the phytochrome pigment responsible for the above change. It is a glycoprotein having a molecular weight of 1,25,000 and located in the plasma membrane. It occurs in two forms PR and Pp^ which are interconvertible as under :
- The photo-induced leaves synthesize this floral hormone called florigen which is translocated to the site of flower formation. Cajlachjan (1958) suggested that there are two steps involved in the flowering process, the first mediated by gibberellin and the second by the flowering factor called ‘adhesive.’
- Together, gibberellin and anthesine constitute the true florigen.
Photoperiodism and C/N Ratio: Kraus and Kraybill, 1918, while working with tomato plants discovered an interesting correlation. They found that different levels of carbohydrate and nitrate supply produce different responses in the plant. Broadly speaking there are four possibilities.
- Very high C/N Ratio → Plants remain weakly vegetative and no flowering is observed.
- High C/N Ratio → Plants show less vegetative growth but flower profusely.
- Low C/N Ratio→ Plants show luxuriant vegetative growth but no flowering is observed.
- Very low C/N Ratio → Plants show weak vegetative growth but fail to produce flowers.
- The Day neutrals or photo neutrals do not need any specific photoperiod for flowering example, Cucumis, Gossypium, impatiens, Lycopersicon, Zea, Mirabilis, etc.
- The photoperiod needed for flowering is called a critical day length. In short-day plants, it indicates the minimum period whereas in long-day plants, it tells the maximum photoperiod.
- Based on experiments Knott, and Cajlachjan confirmed that photoperiodic and photoperiodic stimulus is captured by leaves of cotyledons. The experiments were conducted on loin pioups of plants of Chrysanthemum.
The photoperiodic stimulus may be systemic (Xanthium) or localiscil ((cosmos), Host flowering ooouis in red wavelength. poor flowering under blue and no flowering occurs in green.
Human Growth And Development NEET Exam Preparation Notes
NEET Biology Notes On Human Growth Development Vernalization
- Many species, especially biennials and perennials, arc induced or promoted to flower by low temperatures. Vernalization is the low-temperature treatment given to water-soaked seeds, slightly germinated seeds, or seedlings to hasten the time of plants that will develop from them.
- So, vernalization can best be defined as “The acquisition or acceleration of tire ability to flower by a chilling treatment.’’ (Chounrd 1960).
- T.D Lysenko used the term vernalization as a low-temperature promotion of flowering in plants, The low-temperature requirement for flowering was first noticed by lvlippart (1837) while working with two varieties of wheat, the winter wheat and the spring wheat.
- He concluded that winter wheat requires low treatment (0 – 5° C) for subsequent flowering, a tire phenomenon now called vernalization. It is an aerobic process.
- Plains, in nature, requiring vernalization commonly behave as biennials. The biennials complete their life cycle in two years. They germinate and grow vegetatively in the first year and produce flowers in the second year of growth.
- These fulfill their cold requirement during winter.
- Russian scientists recognized the following two phrases in vernalization.
- Thermophase. It requires a temperature varying between 10 – 20° C together with some moisture and oxygen (so that the embryo wakes up from the dormancy).
- This phase has to be completed before the initiation of the primordia of reproductive organs. The period of low-temperature treatment varies from four days to three months in different plants. Thermophase can take place during the day as well as at night.
- Photophase. A thermophase has to be followed by a period of illumination (i.e., photoperiod) and a period of relatively high temperature.
- This low-temperature treatment given to the seeds to reduce the vegetative growth period and accelerate flowering is called vernalization or Yarovization. The site of vernalization is believed to be the growing point (apical bud).
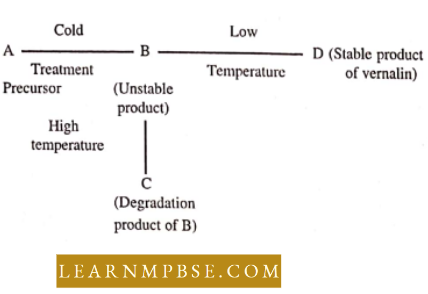
- The German botanist, Melchers (1939) demonstrated that the product of vernalization could be transmitted from a vernalized to an unvernalized Hyoscyamus plant through a graft union. He named this substance vernalin which is a hypothetical one and has not been isolated yet.
- The vernalization effect is reversible and the process is called deyernalization. If the vernalized seeds are kept at high temperatures or under anaerobic conditions, they revert to their normal nature and produce biennial plants.
Human Growth And Development NEET Chapter Summary
Human development NEET notes Mechanism Of Vernalization
- To explain the mechanism of vernalization in physiological terms, three different hypotheses have been put forward.
- Antagonism between vegetative and reproductive growth. According to this theory, vegetative growth and flowering are antagonistic to each other. Thus any means of repressing vegetative growth would result in flowering.
- Phasic development hypothesis. Lysenko (1932) emphasized the distinction between growth (quantitative change or increase in size) and development (a qualitative change or progressive change in the characteristics of new organs produced in cell division) and opined what has become known as the ‘Phasic development theory’.
- According to this theory, the process of development of an annual seed plant consists of a series of phases that must occur in some predetermined sequence. When the proceeding phase is completed, the onset of any one phase will only take place.
- Flower-producing substances hypothesis—Regarding the role of flower-producing substances during vernalization in cereal plants, Purvis (1961) has proposed a scheme. According to Purvis’s scheme, B is some compound that is part of a reaction system leading to flowering.
Human Growth And Development NEET Chapter Summary
NEET growth and development Biology Factors Affecting Vernalization
- Water and Oxygen. Dry seeds cannot be vernalized. Seeds need to imbibe about 30¬40% moisture before they can be vernalized. Although moisture may be present, in the absence of air or oxygen, seeds or plants cannot be vernalized.
- In other words, active respiration is essential. This is supported by the fact that the inhibitors of respiration such as cyanide and dinitrophenol prevent vernalization even when other conditions are favourable.
- Temperature. The seeds of plants can be vernalized by exposing them to low temperatures. Usually, a temperature in the range of 1-7° C is equally effective. Vernalization, although weak, is still possible at temperatures lower than this range up to-4 °C and the higher range up to 12°C. Temperature beyond 12°C does not cause vernalization.
- Food Substances. If vernalization has to take place, there should be a source of carbohydrates. Isolated embryos of cereals cannot be vernalized till these are supplied with sucrose and minerals.
- Effect of Light. Light does not affect the process of vernalization. Many plants like carrots and hyoscyams have both vernalization and photoperiodic requirements for flowering.
- Effect on Hormones. Many species with an obligate vernalization requirement such as Carrot and Hyoscyams are rosette in habit during the vegetative stage. When vernalized, these plants show flowering, and flowering is accompanied by rapid elongation.
- Such an elongation of the stem is called bolting. In such rosette plants, the vernalization requirement can be replaced by the application of gibberellic acid.
- In these plants, GA causes both bolting and flowering without the necessity of exposure to low temperatures.
Human Growth And Development NEET Chapter Summary
NEET Biology Notes On Human Growth Development Senescence
As the young plant grows, it undergoes aging and develops into mature plants in an orderly fashion. Senescence constitutes a collective, progressive, and deteriorative development process that ultimately leads to the complete loss of organization and function of plant or plant parts.
Types of senescence. Mainly senescence is of two types :
- Whole plant senescence. In the case of monocarpic species ( which flower and form fruit only once in their lifetime and then die) whole plant senescence occurs e.g.wheat, soybeans (annuals), agave, bamboo, sunflower etc.
- Organ senescence. In polycarpic species (which flower and form fruit repeatedly) senescence and death are not associated with flowering and fruiting. Organ senescence is of the following types.
- Shoot senescence. In herbaceous perennials, the whole above-ground part of the plant body may senescence and die each year. example: Gladius, Ginger, Rumex, Banana.
- Simultaneous or synchronous senescence. Leaves of temperate deciduous woody arcs may sense and fall at a certain season of the year. It is controlled by environmental factors rather than internal factors.
- Sequential senescence. It is the progressive senescence of older leaves which may occur at any time of year. Each leaf in most of the plants has a limited life span, so that the shoot grows in height, lower older leaves tend to senesce and die.
- Retardants of Sense . Kinetin, a growth regulator, retards senescence of leaves. It causes a rapid increase in the rate of RNA and protein synthesis and it also causes mobilization of metabolites.
- Growth is a quantitative phenomenon and can be measured over time.
- Quiescence is the suspension of growth due to external factors such as changes in surrounding conditions.
- Seed dormancy may be due to rudimentary, embryos, permeable seed coats, mechanically resistant seed coats, physiologically immature embryos, and due to presence of germination inhibitors.
- The common germination inhibitors are abscisic acid, phenolic acids, short-chain fatty acids, and coumarin.
- Rhizophora. Sonneratia and Heriticra growing in marshy land show a special type of germination termed vivipary, in which seed germination within the fruit, while still attached to the parent plant.
- The rate of growth is called the efficiency index.
- Auxin precursors tire the compounds which can be converted to auxins.
- Antiauxins inhibit the action of auxins
- Free auxins can be easily extracted and are active.
- Bound auxins are inactive and hard to extract. They need the use of organic solvents. A dynamic equilibrium exists between the two forms.
Human Growth And Development NEET Chapter Summary
NEET Biology Notes on Human Growth Development Quanta to Memory
- The presence of more auxin on the lower side of the stem apex causes more growth oil on that side.
- The presence of more auxin in the root has a negative effect i.e., it inhibits growth on the lower side.
- IAA (Indole Acetic Acid) is the principal naturally occurring auxin found in all plants studied so far and also in fungi.
- IAA Destruction is caused by : (i) Photo-oxidation by blue light, and (ii) Dark oxidation by IAA-oxidase.
- Auxin IAA stimulates ethylene synthesis in a plant.
- IAA also occurs in human urine, especially in persons suffering from pellagra.
- Bioiissay means the testing of a substance for its activity in living organisms under controlled conditions.
- Abscission is the shedding of leaves, fruits, or (lowers by a plant generally due to a change in the hormonal balance.
- The term Phytoalexin was introduced by Muller (1956) example. Pisatin in Pisum sativum is due to an infection of Ascochyta Ω.
- 0•025 % of maleic hydrazide prevents potato sprouting.
- Cytokinins along with auxins help in the differentiation of roots and shoots.
- 2,4 D is a synthetic auxin acting as a weedicide.
- Abscisic acid inhibits gibberellin-mediated amylase formation during the germination of cereal grains.
- ABA has been found to induce parthenocarpic development in roses.
- The use of abscisic acid promotes rooting in many stem cuttings.
- It counteracts the effects of all growth-promoting hormones (auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins) and therefore, keeps their activity under check.
- The role of IAA in humans is not known.
- In maize, the single cotyledon never leaves the germinating grain and plumule grows out of coleoptile.
- Vernalization was first studied in Europe on the winter varieties of cereals such as wheat, barley, rye, and oat.
- The chemical nature of vernalin (Cold induced stimulus) is not known.
- In growth anabolic processes dominate over the catabolic processes and therefore growth is the final product of successful metabolism.