NEET Biology Kingdom Monera Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. An organism should be placed in the kingdom Moncra if it
- Consists of a single cell
- Has a cell wall
- Is surrounded by a capsule
- Lacks a nuclear membrane separating its genetic (material from the cytoplasm.
Answer: 4. Lacks a nuclear membrane separating its genetic (material from the cytoplasm.
Question 2. Newly started rice paddies produce poor crops until -they have established a flourishing population of cyanobacteria. This is probably because:
- Die rice needs nitrogen fixed by the cyanobacteria
- The rice cannot compete with weeds, which are poisoned by toxins produced by the cyanobacteria
- The cyanobacteria use surplus nutrients from sewage in the rice paddies
- The cyanobacteria lack proteins in their dna.
Answer: 1. Die rice needs nitrogen fixed by the cyanobacteria
Question 3. A wall-less moneran is:
- Bacteria
- Blue-green algae
- Mycoplasma
- Archaebacteria.
Answer: 3. Bacteria
Most Important MCQs on Monera Question 4. Symbiotic nitrogen fixation is found in :
- Rhizobium
- Oscillatoria
- Azotobacter
- Nitrobacter.
Answer: 1. Rhizobium
Question 5. Cyanobacteria do not possess :
- Gene recombination
- Flagella
- Plasmid
- Lamellasome.
Answer: 2. Flagella
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question and Answers
Question 6. Pili in bacteria represent :
- Extrachromosomal genetic element
- Cell membrane outgrowths of donor cells
- Small flagella
- Special bacterial cilia.
Answer: 2. Cell membrane outgrowths of donor cells
Question 7. Branched-chain lipids occur in the cell membranes of:
- Archaebacteria
- Mycoplasma
- Actinomycetes
- Streptomyces.
Answer: 1. Archaebacteria
Most Important MCQs on Monera Question 8. The decomposition of organic compounds in the presence of 02 without the development of an odoriferous substance is:
- Nitrification
- Decay
- Denitrification
- Nitrogen fixation.
Answer: 2. Decay
Question 9. The cell wall in all bacteria is composed of:
- Lipid and protein
- Murein
- Proteins only
- Cellulose and lipids.
Answer: 2. Murein
Question 10. Genophore is the name of:
- DNA of eukaryotes
- DNA of protists
- DNA of prokaryotes
- Genes of drosophila.
Answer: 3. DNA of prokaryotes
Question 11. Micro-organisms in milk are killed by heat treatment at a controlled temperature without altering the natural characteristics of milk through a process called
- Boiling
- Immunization
- Pasteurization
- Sterilization.
Answer: 3. Pasteurization
Question 12. Naked dna is that which is :
- Not covered by a nuclear envelope
- Present in cytoplasm
- Associated with histone proteins
- Not associated with histone proteins.
Answer: 4. Not associated with histone proteins.
Most Important MCQs on Monera Question 13. In the bacterium Bacillus subtilis the cells often become attached from end to end forming long filamentous chains, which are embedded in a mass of mucilage forming a scum layer on the substratum. It is called as:
- Palmella stage
- Torula stage
- Zoogloea stage
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Zoogloea stage
Question 14. Prokaryotic chromosome is :
- A naked double-stranded
- A single-stranded circular dna
- Composed of DNA or RNA
- Associated with non-histones.
Answer: 1. A naked double-stranded
Question 15. Bacteria resemble yeasts because both have property
- Degradation of food
- Binary fission
- Anaerobic respiration
- Sexual reproduction.
Answer: 2. Binary fission
Question 16. One of the following does not apply to Escherichia coli:
- Transformation
- Transduction
- Flagella
- Diploid.
Answer: 4. Diploid.
Question 17. Which of the following are intermediate between viruses and bacteria?
- Mycoplasma
- Spirilla
- Cyanobacteria
- Variola.
Answer: 1. Mycoplasma
Question 18. Bacteria are found to be primitive organisms because they:
- Are small, microscopic which are not seen with the naked eye
- It causes serious diseases in human beings, domesticated animals, and crop plants.
- Produce endospores which are very resistant to adverse conditions
- Possess incipient nucleus and show amitotic division.
Answer: 4. Possess incipient nucleus and show amitotic division.
Question 19. Ih bacteria the most resistant stage is:
- Capsuled vegetative cell
- Newly divided cell
- Endospore stage
- Torula stage.
Answer: 3. Endospore stage
Most Important MCQs on Monera Question 20. Some diseases caused by bacteria are:
- Measles, mumps, malaria
- Tetanus, typhoid, tuberculosis
- Smallpox, sleeping sickness
- Poliomyelitis, psittacosis
Answer: 2. Tetanus, typhoid, tuberculosis
Question 21. bacterium which is commonly present in the intestine of man and animal is :
- Vibrio comma
- Escherichia.
- Script
- Pseudomonas citri.
Answer: 2. Escherichia.
Question 22. The chemotherapeutic substance derived from a living organism that has an inhibitory effect on parasitic organisms is known as:
- Exotoxin
- Antibody
- Bactericide
- Antibiotic.
Answer: 4. Antibiotic.
Question 23. Bacteria are plant-like because they have :
- Rigid cell wall
- Ability to reproduce
- Both the above
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Rigid cell wall
Kingdom Monera NEET MCQ Question 24. In transduction :
- Bacteriophage transfers dna from donor to recipient cell
- Extracellular dna enters the recipient cell
- The donor cell survives
- The donor and recipient cells survive.
Answer: 1. Bacteriophage transfers dna from donor to recipient cell
Question 25. Gram+ve bacteria have :
- Thick and homogeneous cell walls
- As much as 70% of peptide molecules
- Either no lipids or less than 10% lipids
- All the above.
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 26. Honey, jams, jelly, and chutney are free of bacteria, because:
- Bacterial cells are plasmolysed in these substrates
- These substrates are poisonous
- These substrates have a foul smell
- These substrates have complex substances which cannot be utilized by bacteria for their nutrition.
Answer: 1. Bacterial cells are plasmolysed in these substrates
Question 27. Cyanobacteria is a :
- Category of bacteria
- Is the new name of all bacteria
- New name of Myxophyceae or Cyanophyceae or blue-green algae
- None of them.
Answer: 3. New name of Myxophyceae or cyanophyceae or blue-green algae
Question 28. Both bacteria and cyanobacteria are :
- Prokaryotic
- Eukaryotic
- Eukaryotic as well as prokaryotic
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Prokaryotic
Kingdom Monera NEET MCQ Question 29. If a bacterial cell is dividing every minute and takes one hour to fill a cup. It will require how much time to fill half of the cup.
- 30 Minutes
- 60 Minutes
- 59 Minutes
- 61 Minutes
Answer: 3. 59 Minutes
Question 30. The formation of vinegar from alcohol is caused by
- Bacillus subtilis
- Clostridium
- Acetobacter aceti
- Otobacter.
Answer: 4. Otobacter.
Question 31. The formation of vinegar from alcohol is caused by
- Bacilius subtitles
- Clostridium
- Acetobacter aceti
- Azotobacter.
Answer: 3. Acetobacter aceti
Question 32. Photosynthetic bacteria have:
- Pigment system 1 (only one pigment system)
- Pigment system 2
- Both
- Some other types.
Answer: 1. Pigment system 1 (only one pigment system)
Question 33. Which of the following causes nitrification?
- Bacillus ramosus
- Nitrosomonas
- Nitrobacter
- Both 2 and 3.
Answer: 4. Both 2 and 3.
Question 34. Bacteria having a tuft of flagella at both ends tire called :
- Peritrichate
- Bitrate
- Amphitrichate
- Lophotrichate.
Answer: 4. Lophotrichate.
Kingdom Monera NEET MCQ Question 35. What turns the wine sour?
- Light exposure
- Aerobic bacteria
- Anaerobic bacteria
- High temperature.
Answer: 2. Aerobic bacteria
Question 36. Streptomycin is produced by :
- Streptomyces grievous
- Streptomyces soleus
- Streptomyces fragile
- Streptomyces venezuellae.
Answer: 1. Streptomyces grievous
Question 37. Botulism, a type of food poisoning, is caused by:
- Rhizobium
- Vibrio
- Streptococcus
- Clostridium botulinum.
Answer: 4. Clostridium botulinium.
Question 38. Fever typhoid is caused by the bacteria :
- Xanthomonas typhous
- Salmonella typhi
- Bacillus diplococcus
- Bacillus dysenteriae.
Answer: 2. Salmonella typhi
Question 39. Griffith performed experiments on which bacteria and concluded the occurrence of transformation in bacteria
- Bacillus pneumonieae
- Salmonella pneumonieae
- Diplococcus pneumonieae
- Xanthomonas pneumonieae.
Answer: 3. Diplococcus pneumonia
Question 40. Bacteria have flagella around the periphery of the cell. This condition is known as:
- Peritrichate
- Monotrichate
- Lophotrichate
- Amphitrichate.
Answer: 1. Peritrichate
Question 41. The estimated length of dna molecule in Escherichia coli is :
- 1000 Pm
- 100 Pm
- 100 A
- 1000 A.
Answer: 3. 100 A
Biological Classification MCQ For NEET Question 42. Form of sexual reproduction where genetic material is carried from one strain of bacteria to another by bacteriophage:
- Transformation
- Transduction
- Mesomixis
- Conjugation.
Answer: 2. Transduction
Question 43. The structure formed by the bacterial genome is called:
- Nucleus
- Nucleoid
- Nucleoli
- Nucleolus.
Answer: 2. Nucleoid
Question 44. Bacteria having a tuft of anger at our CML are called :
- Monotridious
- Amphitnehous
- Cephalotrichoues
- Peritrichous
Answer: 3. Cephalotrichoues
Question 45. Staplix kvivcus causes :
- Food jvisoniug
- Citrus canker
- Denitrification
- Vinegar fonnation.
Answer: 1. Food jvisoniug
Question 46. Photoautotrophic bacteria contain the pigment:
- Chlorophyll
- Bacteriochlorophyll
- To carotene
- No pigment.
Answer: 2. Bacteriochlorophyll
Biological Classification MCQ For NEET Question 47. E.coli lives in the human intestine and causes:
- Urinary tract infection
- Diarrhea
- Meningitis
- None of the above.
Answer: 4. None of the above.
Question 48. In e. Coli when the flagella rotates in a clockwise and anticlockwise direction, the movements are:
- Jumping and hooping
- Running and tumbling
- Tumbling and hooping
- Hooping and running.
Answer: 2. Running and tumbling
Question 49. A bacterial cell undergoes binary fission every twenty minutes. Starting with a single bacterium how many bacteria will be produced at the end of 3 hours?
- 128
- 256
- 512
- 1024.
Answer: 3. 512
Question 50. Which of the following is a free-living anaerobic nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
- Azotobacter
- Nitrobacter
- Rhizobium
- Clostridium.
Answer: 4. Clostridium.
Question 51. E. Coli bacterium possesses a single large circular dna as its genetic material. This strand codes for :
- 1000-2000 Different proteins
- 2000-3000 Different proteins
- 3000 To 4000 different proteins
- More than 4000 different proteins.
Answer: 2. 2000-3000 Different proteins
Question 52. Bacteria that get their energy from fermentation and for whom oxygen is lethal are called:
- Obligate anaerobes
- Obligate aerobes
- Facultative aerobes
- Facultative anaerobes.
Answer: 1. Obligate anaerobes
Biological Classification MCQ For NEET Question 53. The bacteria (treponema pallidum) that cause the v.d. Syphilis are :
- Pseudomonas
- Purple non-syphilis
- Rickettsia
- Spirochaetes.
Answer: 4. Rickettsia
Question 54. Which of the following jives in the gut of termites and helps them digest cellulose:
- Plasmodium
- Trypanosoma
- Trichonympha
- Trichosomes.
Answer: 3. Trichonympha
Question 55. An example of a chemoautotrophic bacterium is:
- Lactobacillus
- Nitrosomonas
- E. Coli
- Rhizobium.
Answer: 2. Nitrosomonas
Question 56. Bag included amongst :
- Fungi
- Prokaryotes
- Bryophytes
- Protista.
Answer: 2. Prokaryotes
Biological Classification MCQ For NEET Question 57. Some bacteria produce resting spores during unfavorable conditions. They are:
- Exports
- Endosporcs
- Aplanosporcs
- Chlamydospores.
Answer: 2. Endosporcs
Question 58. The similarity between bacterium and cyanobacterium is:
- Presence of flagella
- Presence of 80 s ribosome
- Presence of nucleoid
- Presence of phycobilisomes.
Answer: 3. Presence of nucleoid
Question 59. Conjugation in bacteria was discovered by :
- Jacob and Wollman
- Zinder and Lederberg
- Lederberg and Tatum
- Beadle and Tatum.
Answer: 3. Zinder and lederberg
Question 60. Archaebacteria found in salty pans and salt marshes are
- Methanogens
- Thermoacidophiles
- Ruminant symbiosis
- Halophiles.
Answer: 4. Halophiles.
Most Important MCQs on Monera Question 61. Prokaryotic cells have a volume range of :
- 0.2 to 10 pm3
- 100-1000 Pm3
- 1000-10000 Pm3
- 0.01 to 0.1 pm3.
Answer: 1. 0.2 to 10 pm3
Question 62. Prokaryotic flagella possess :
- A helically arranged protein molecule
- Protein membrane-enclosed fiber
- Unit membrane-enclosed fiber
- Microtubular (9+2) membrane.
Answer: 1. Protein membrane-enclosed fiber
Question 63. Organisms used in alcohol fermentation are:
- Penicillium
- Pseudomonas
- Aspergillus
- Saccharomyces.
Answer: 4. Saccharomyces.
Question 64. Tailed bacteriophages are :
- Motile on the surface of bacteria
- Non- motile
- Actively motile in water
- Motile on the surface of plant leaves.
Answer: 1. Motile on the surface of bacteria
Question 65. A large number of organic food molecules can be prepared by:
- Chemolithotrophs
- Pseudomonas
- Azotobacter
- Mycoplasma.
Answer: 1. Chemolithotrophs
Most Important MCQs on Monera Question 66. Bacteria were first observed by :
- W.h Stanley
- Louis Pasteur
- A.v. Leeuwenhoek
- Robert koch.
Answer: 3. A.v. Leeuwenhoek
Question 67. “Little leaf” of brinjal is caused by :
- Bacteria
- Mycoplasma
- Fungi
- Venus
Answer: 2. Mycoplasma
Question 68. Crown gall is caused by
- Mycobacterium
- Bacteria
- Clostridium
- Erwinia
Answer: 2. Bacteria
Question 69. Which of the following is an antibiotic?
- Chloramphenicol
- Ethwphous
- Phosphon-d
- Amo 11.1s
Answer: 1. Chloramphenicol
Question 70. Which of the following mg is a bacterial disease?
- Measles
- Tuberculosis
- Rabies
- Smallpox.
Answer: 2. Tuberculosis
Most Important MCQs on Monera Question 71. An aerobic nitrogen-fixing soil bacterium is :
- Rhizobium
- Clostridium
- Azotobactcr
- Rhodospirillum.
Answer: 3. Azotobactcr
Question 72. Hormogonia help in the reproduction of:
- Cladophora
- Bacteria
- Archaebacteria
- Cyanobacteria.
Answer: 4. Cyanobacteria.
Question 73. Which one of the following belongs to none?
- Amoeba
- Escherichia
- Gelidium
- Spirogyra.
Answer: 2. Escherichia
Question 74. Streptomyces ramosus is the source of the antibiotic :
- Chloromycetin
- Erythromycin
- Aureomycin
- Terramycin.
Answer: 4. Terramycin.
Question 75. The cells of cyanobacteria and bacteria exhibit similarity in having:
- Nuclei
- Centrosome
- Plastids
- Dna.
Answer: 4. Dna.
Question 76. Bacteria without flagella are known as :
- Monotrichous
- Lophotrichous
- Peritrichous
- Atrichous.
Answer: 4. Atrichous.
Question 77. Chromoplasm is part of protoplast in :
- Actinomycetes
- Myxobacteria
- Cyanobacteria
- Eubacteria.
Answer: 3. Cyanobacteria
Question 78. Which of the following is not a bacterial action?
- sewage disposal
- Ripening of cheese
- nitrogen fixation
- Precipitation.
Answer: 4. Precipitation.
Kingdom Monera NEET MCQ Question 79. The vinegar is prepared from sugary molasses by the activities of:
- Fa; diplococcus
- FB; acetobacter acetic
- Staphylococcus
- B. Subtilis.
Answer: 2. Fb; acetobacter acetic
Question 80. Genophore is made up of:
- Rna arid histones
- Histones and non-histones
- A single-stranded dna
- A double-stranded dna.
Answer: 4. A double-stranded dna.
Question 81. In rice fields, the soil fertility can be improved by :
- Rhizobium
- Sod. Chloride
- Gypsum
- Blue-green algae.
Answer: 4. Blue-green algae.
Question 82. Which it billowing is with denitrification
- Uhiobinm
- Srudomnuns
- Otohacler
- Khodospirillum.
Answer: 2. Srudomnuns
Question 83. Which of the following cells is a prokaryote
- Bacterium
- Virus
- Both 1 and 2
- Green algae.
Answer: 1. Bacterium
Question 84. Peptidoglycan forms many layers in the wall of:
- Gram-ve bacteria
- Gram neutral bacteria
- Gram -i-ve bacteria
- All of them.
Answer: 3. Gram -i-ve bacteria
Question 85. Which era is dubbed the age of prokaryotic microbes?
- Palaeozoic
- Proterozoic
- Precambrian
- Archaeozoic.
Answer: 4. Archaeozoic.
Question 86. Sexual reproduction is absent in:
- Ulothrix
- Volvox
- Spirogyra
- Nostoc.
Answer: 4. Nostoc.
Kingdom Monera NEET MCQ Question 87. Salmonellosis is the process of:
- Food poisoning by bacteria
- Reproduction by bacteria
- Manifestation of typhoid
- Decomposition by bacteria.
Answer: 1. Food poisoning by bacteria
Question 88. Meningitis a disease that is responsible for membrane damage of the brain is caused by :
- Neisseria
- A fungus
- Bacillus
- Bordetella.
Answer: 1. Neisseria
Question 89. Which of the following bacterium converts the sucrose into dextrin
- Spirillum solutions
- Leuconostoc mesenteroids
- Bacillus megatherium
- Both 1 and 2.
Answer: 2. Leuconostoc mesenteries
Question 90. When bacteria are rod-like and cubical packet of 8 cocci, are called as:
- Bacilli and sarcina
- Spirilla and cocci
- Sarcina and vibrio
- Spirilla and sarcina.
Answer: 1. Bacilli and sarcina
Question 91. Whose cell wall dissolves by antibiotic action :
- Bacteria
- L-form bacteria
- Mycoplasma
- Actinomycetes.
Answer: 2. L-form bacteria
Kingdom Monera NEET MCQ Question 92. Special taste is developed in the tea leaves by fermentative action of:
- Mycococcus candisans
- Megatherium micrococcus
- Bacillus megatherium
- Clostridium acetobutylicum.
Answer: 1. Mycococcus candisans
Question 93. An episome in bacteria is:
- Nutritional factor
- Sex factor
- Cofactor
- None of these.
Answer: 2. Sex factor
Question 94. Aureomycin and chloramphenicol are obtained from :
- Strcptomyces aureofaciens and s. Ramosus
- S. Venezuelae and s.rimosus
- S. Aureofaciens and s.fradiae
- S. Aureofaciens and s. Venezuela.
Answer: 4. S. Aureofaciens and s. Venezuela.
Question 95. Chloramphenicol ami erythromycin (broad speetmm antibiotics Produced by:
- Rhizobium cnieillmm
- Strcptomyccs
- Niirobnetct.
Answer: 3. Niirobnetct.
Question 96. Spiroplasms arc also walks nipple layered unit membrane-covered orgasms like mycoplasma but they differ from them in being :
- Non-infections
- Satisfying Koeh’s postulates
- Motile and helical filamentous
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Motile and helical filamentous
Question 97. Term spiroplastna was suggested by:
- Pavis and Worley
- Worley
- Davis
- Ehrenberg.
Answer: 1. Pavis and Worley
Question 98. Rhizosphere bacteria are present around the;
- Leaf surface
- Floral surface
- Root surface
- Shoot surface.
Answer: 3. Shoot surface.
Question 99. A mixture of bacteria, viruses, and mycoplasma is drained through a filter with 450 pore size which of these would not pass through:
- Virus
- Mycoplasma
- Bacteria
- All of these.
Answer: 3. Bacteria
Question 100. A chain of spherical bacteria is called streptococci. When spherical cocci are found in grape-like irregular aggregates, they are called :
- Sarcinae
- Staphylococci
- Palisade
- Streptobacilli.
Answer: 2. Staphylococci
Biological Classification MCQ For NEET Question 101. A cubical packet of 8 cocci is called:
- Staphylococcus
- Vibrio
- Gaffkva
- Sarcina.
Answer: 4. Sarcina.
Question 102. Monerans are plants because they have :
- Ability to synthesize vitamins
- Rigid cell wall
- Both and
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Both and
Question 103. “Bacillus thuringiensis is used to control:
- Bacterial pathogens
- Fungal pathogens
- Nematodes
- Insect pests.
Answer: 4. Insect pests.
Question 104. Penicillin kills bacteria by :
- Suppression of cell wall synthesis
- Lysis of protoplasm
- Interfering with RNA synthesis
- Inhibiting dna synthesis.
Answer: 1. Suppression of cell wall synthesis
Question 105. Which of the following antibiotics is more a research tool rather than used for clinical purposes :
- Penicillin
- Terramycin
- Actinomycin-d
- None of these.
Answer: 3. Actinomycin-d
Biological Classification MCQ For NEET Question 106. Doxycycline treatment cures :
- Aids caused by virus
- Polio caused by virus
- Measles caused by virus
- Male sterility caused by mycoplasma.
Answer: 4. Male sterility caused by mycoplasma.
Question 107. Wall is not pirseni in :
- Mycoplasma
- Aciiiiomycclcs
- Vituses
- L.-Loim baelcria.
Answer: 1. Mycoplasma
Question 108. Penicillin and vancomycin do not ail late mycoplasma because :
- Prokaryotic and unicellular
- Eukaryotic and unicellular
- There is no nucleus
- There is no cell wall.
Answer: 4. There is no cell wall.
Question 109. Llypersaline and hyperthermal aquatic environments are inhabited mostly by :
- Eubacteria
- Micro fungi
- Cyanobacteria
- Archacbactcria.
Answer: 4. Archacbactcria.
Question 110. Peritrichous bacteria have :
- Flagella all over the body
- Tuft of flagella at one end
- Tuft of flagella at both ends
- Single flagellum at one end.
Answer: 1. Flagella all over the body
Question 111. A bacterial cell contains :
- Mesosomes, Golgi bodies, and nucleoid
- Mesosomes and Golgi bodies
- Mesosomes and nucleoid
- Golgi bodies and nucleoids.
Answer: 3. Mesosomes and nucleoid
Biological Classification MCQ For NEET Question 112. To develop flavor and taste in tobacco, leaves are processed with bacterium:
- Mycococcus candisans
- Megatherium micrococcus
- Aerobacter
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Megathenium micrococcus
Question 113. Magnesium ribonuclease is present in :
- Gram (+) ve bacteria
- Gram (-) ve bacteria
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Gram (+) ve bacteria
Question 114. The bacterial decomposition of nitrogenous organic compounds in the absence of abundant oxygen usually results in the formation of substances of offensive odor, chiefly sulfur compounds. Such anaerobic decomposition is called :
- Nitrification
- Denitrification
- Putrefaction
- N2 fixation.
Answer: 3. Putrefaction
Question 115. Bacteria were called ‘tiny animalcules’ by Leeuwenhoek who discovered them from tartar scrapped from teeth. Who coined the term bacteria:
- Ehrenberg
- Nageli
- Pasteur
- Koch.
Answer: 1. Ehrenberg
Question 116. Name the bacterium that gets its energy from fermentation and if oxygen is given, it dies:
- Obligate aerobe
- Facultative anaerobe
- Obligate anaerobe
- Aerobe.
Answer: 3. Obligate anaerobe
Question 117. During gram’s staining :
- Gram (+) ve bacteria take crystal violet stain
- All bacteria take crystal violet stain
- Only gram (-) ve bacteria take crystal violet stain
- Gram (-) ve bacteria lose this stain after alcohol treatment.
Answer: 4. Gram (-) ve bacteria lose this stain after alcohol treatment.
Question 118. Compared to gram(-) bacteria. Gram (+) vc bacteria:
- Are more resistant to antibiotics
- Have more complex cell walls
- Have less muicopcptidc
- Retain crystal violet dye even after alcohol treatment.
Answer: 4. Have more complex cell walls
Question 119. Cyanobacteria living inside (the protozoans are called:
- Cyanellc
- Blue-green algae
- Mvxophyceac
- Euglenoids.
Answer: 1. Cyanellc
Question 120. The true diploid condition in bacteria is not obtained due to the reasons:
- Only a part of a chromosome is transferred to the female cell
- Introduced dna merely adds to the original dna of the female cell
- Introduced dna replaces a part of the original dna of the female cell
- All of the above.
Answer: 1. Only a part of a chromosome is transferred to the female cell
Most Important MCQs on Monera Question 121. Water bloom occurs mainly due to the presence of:
- Cyanobacteria
- Insects
- Bacteria
- Red algae.
Answer: 1. Cyanobacteria
Question 122. Which one of the following is a false statement regarding plasmids:
- Plasmids are extrachromosomal materials found in bacterial cells
- Most plasmids can be transmitted from cell to cell by infection without bringing about the death of host cells
- Plasmids can be integrated into the host chromosomes
- Plasmids are integrated but inert parts of the genetic element.
Answer: 2. Most plasmids can be transmitted from cell to cell by infection without bringing about the death of host cells
Question 123. Which of the following is a bacterial disease?
- Club rot disease of cotton
- Angular leaf spot disease of cotton
- Leaf spot disease of turmeric
- Wilt disease of tomato.
Answer: 2. Angular leaf spot disease of cotton
Question 124. Which of the following causes crown gall in plants :
- Erwinia carotovora
- Pseudomonas solanacearum
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- Xanthomonas malvacearum.
Answer: 3. Pseudomonas solanacearum
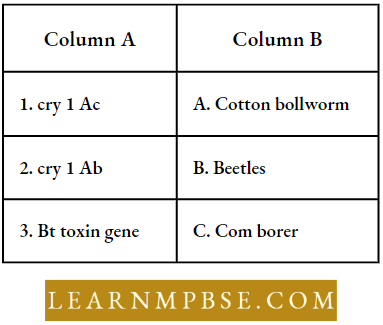
Question 125. Match the terms in column I with those in column d:
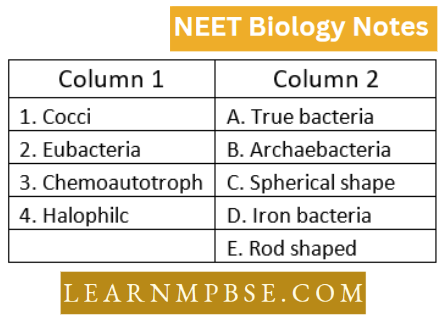
- 1-C,2-B,3-A,4-D
- 1-C,2-A,3-B,4-D
- 1-C,2-D,3-A,4-B
- 1-C,2-A,3-D,4-B
Answer: 4. 1-C,2-A,3-D,4-B
Question 126. Which of the following pairs is/arc correctly matched:
- E.coli— circular dna
- Tobacco mosaic virus—single-stranded RNA
- Rcovirus—double-stranded RNA
Select the correct answer using the codes given below Codes:
- A alone
- A, b and c
- A and c
- B and c.
Answer: 2. A, b and c
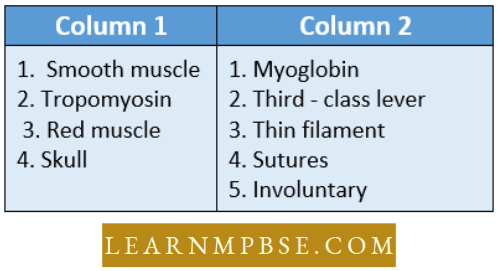
Most Important MCQs on Monera Question 127. Match list 1 wish list 2 and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists-
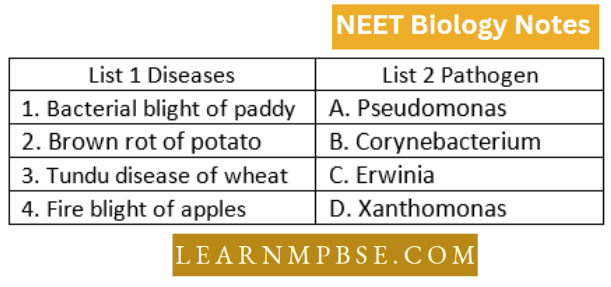
- 1-A,2-B,3-C,4-D
- 1-D,2-A,3-B,4-C
- 1-C,2-B,3-A,4-D
- 1-B,2-C,3-D,4-A
Answer: 2. 1-D,2-A,3-B,4-C
Question 128. Wine turns sour because of :
- By fermentation of sugar by lactobacillus
- By fermentation of sugar by Aspergillus
- By fermentation of sugar by saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Is a two-step process, first involving fermentation of sugar by yeast and second involving fermentation of ethyl alcohol by acetic acid bacteria.
Answer: 4. Is a two-step process, first involving fermentation of sugar by yeast and second involving fermentation of ethyl alcohol by acetic acid bacteria.
Question 129. Clear areas of agar plates containing phage particles as well as bacteria are called:
- Bacteriophage
- Transparencies
- Plaques
- Holes.
Answer: 3. Plaques
Question 130. Bacteria do not have a major role in the production of the following
- Coffee
- B-complex
- Cheese
- Bread.
Answer: 4. Bread.
Question 131. Episome or f factor is the extrachromosomal genetic material of bacteria, useful in:
- Control of essential characters
- Genetic recombination
- Formation of endospores
- Nitrogen fixation.
Answer: 2. Genetic recombination
Question 132. A scientist wants to try to grow a culture of an animal virus. Which of the following would most likely be a suitable cultural medium?
- Boiled and cooled water with minerals and vitamins added.
- Sterile jelly made with malt and agar.
- An infertile egg.
- Living chick embryos.
Answer: 4. A living chick embryo.