NEET Biology Five Kingdoms Of Life And Biological Classification Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Karvotaxonomy is based upon :
- The chemical nature of chromosome
- Arrangement of chromosome
- Architect of nucleus
- The pattern of bands on the chromosome.
Answer: 2. Arrangement of chromosome
Question 2. The term “new systematics” was introduced by :
- Charles Darwin
- George Bentham
- Julian Huxley
- A. B. Randal.
Answer: 3. George Bentham
Question 3. The approximate number of species known today is :
- 1.00.000
- 2,00,000 To 3,00,000
- 1.7 million
- 1.17 million.
Answer: 3. 1.7 million
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question and Answers
Question 4. Taxon refers to:
- Genus
- Family
- Order
- All these.
Answer: 4. All these.
Biological Classification MCQ For NEET Biology Question 5. Which of the following has doubtful status?
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Blue-green algae
- Polo.
Answer: 2. Viruses
Question 6. The Latin binomial for a dog is properly written as :
- Canis familiaris
- Familiaris canis
- Kanis familiaris
- Canis familiaris.
Answer: 4. Canis familiaris.
Question 7. On examining a slide, you observe, there are numerous individual cells containing chloroplasts and swimming around rapidly. You conclude that this material belongs to the kingdom:
- Plantae
- Protista
- Fungi
- Monera
Answer: 2. Protista
Question 8. Major diversity of living organisms is found in :
- Temperate forests
- Taiga forests
- Grasslands
- Tropical rain forests.
Answer: 4. Tropical rainforests.
Question 9. Classification based on several characters is :
- Natural
- Artificial
- Hierarchy
- Phylogenetic.
Answer: 1. Natural
Question 10. In a taxonomic hierarchy, the various categories are arranged in :
- Descending series
- Horizontal series
- Ascending series
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Descending series
Biological Classification MCQ For NEET Biology Question 11. The system of arrangement of organisms into groups showing relationships is :
- Identification
- Classification
- Nomenclature
- None of them.
Answer: 2. Classification
Question 12. The science that deals with the classification, identification, and nomenclature of organisms is called :
- Physiology
- Ecology
- Biology
- Systematics.
Answer: 4. Systematics.
Question 13.1 Lie father of taxonomy is:
- Charles Darwin
- John ray
- Linnaeus
- Julian Huxley.
Answer: 3. Linnaeus
Question 14. Biochemical characters of organisms form the basis of classification, called :
- Systematics
- Ecology
- Numerical taxonomy
- Chemotaxonomy.
Answer: 4. Chemotaxonomy.
Question 15. Most primitive organisms are :
- Protists
- Bacteria
- Algae
- Fungi.
Answer: 2. Bacteria
Question 16. A virion is a :
- Viral ribosome
- Viral lysosome
- Viral gene
- Virus.
Answer: 3. Viral gene
Biological Classification MCQ For NEET Biology Question 17. The suffix for the subdivision name is :
- Phylina
- Opsida
- Ideas
- Ales.
Answer: 1. Phylina
Question 18. The natural system of classification was proposed by :
- Bentham and hooker
- Hooker and Linnaeus
- Bentham and Huxley
- Darwin and Lamarck.
Answer: 1. Bentham and hooker
Question 19. The classification of plants into herbs, shrubs, and trees is:
- Artificial
- Phylogenetic
- Natural
- None of these.
Answer: 1. Artificial
Question 20. Which one of the following taxonomic categories tops the hierarchy of categories?
- Genus
- Kingdom
- Class
- Phylum.
Answer: 2. Kingdom
Question 21. A phylogenetic classification is based on :
- External features alone
- Floral characters alone
- Origin and relationship of plant or animal groups
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Origin and relationship of plant or animal groups
Question 22. Taxon refers to :
- Genus
- Family
- Order
- Taxonomic group of any rank.
Answer: 4. Taxonomic group of any rank.
Biological Classification MCQ For NEET Biology Question 23. The classification of plants and animals based on chromosome number is called :
- Cytotaxonomy
- Biochemical systematics
- Taxonomy
- Numerical taxonomy.
Answer: 4. Numerical taxonomy.
Question 24. Systematic aids in controlling epidemic diseases because:
- Identification of vectors
- Killing their causative agents
- Observing their way of life
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Identification of vectors
Question 25. Herbarium helps in the :
- Preserving the plants
- Keeping the plants
- Comparative study of plants in an area
- All the above.
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 26. Systematics is useful in agriculture because it aids in :
- Evolution of new plants
- Plant protection
- Identification of plant pathogens, parasites, or pests
- A complete study of plants.
Answer: 3. Identification of plant pathogens, parasites, or pests
Question 27. The Linnaeus system of classification contains:
- 4 Classes of plants
- 8 Classes of plants
- 16 Classes of plants
- 24 Classes of plants
Answer: 4. 24 Classes of plants
Important MCQs on Biological Classification Question 28. An artificial system of classification was given by
- Linnaeus
- Darwin
- Amarok
- Wallace.
Answer: 1. Linnaeus
Question 29. Fuller Ami tippo’s system of classification is :
- An artificial system
- The phylogenetic system is natural
- Partly natural and partly phylogenetic.
Answer: 3. Partly natural and partly phylogenetic.
Question 30. Liverworts and mosses are included under :
- Pteridophytes
- Bryophyta
- Angiosperms
- Gymnospemis.
Answer: 2. Bryophyta
Question 31. In which of the following groups would you place a plant that produces seeds but lacks flowers :
- Fungi
- Pteridophytes
- Gymnospemis
- Angiosperms.
Answer: 3. Gymnospemis
Question 32. “Species Plantarum” and “Systema Naturae” were written by :
- Engler and pram
- Bentham and hooker
- Carl. Linnaeus
- Wallace.
Answer: 3. Carl. Linnaeus
Question 33. The concept of genus was first proposed by :
- Linnaeus
- Braunfels
- Bentham
- Tournefort.
Answer: 2. Braunfels
Important MCQs on Biological Classification Question 34. Central National Herbarium is situated at:
- Chennai
- Sibpur (Kolkata)
- Tarapur (Mumbai))
- Dehradun.
Answer: 2. Sibpur (Kolkata)
Question 35. The ending name of the class is :
- —Accac
- —Opsida
- — Ideas
- —Ales.
Answer: 2. —Opsida
Question 36. The taxonomic category, ‘division’ ends in :
- —Icae
- —Opsida
- —Phyla
- —Ineae.
Answer: 3. —Phyla
Question 37. Linnaeus is credited with introducing :
- The concept of inheritance of acquired characters
- The law of limiting factors.
- The binomial system of nomenclature
- Principle of independent assortment.
Answer: 3. Tltc binomial system of nomenclature
Question 38. The arrangement of taxa is called :
- Key
- Hierarchy
- Natural classification
- Taxonomy.
Answer: 2. Hierarchy
Question 39. According to the law of priority, the valid name of an organism is:
- Oldest name applied
- Oldest name modified by new workers
- Most popular name
- The name is given in Latin.
Answer: 1. Oldest name applied
Important MCQs on Biological Classification Question 40. Binomial nomenclature means writing the name of an organism in two words which designate :
- Order and family
- Family and genus
- Species and family
- Genus and species.
Answer: 4. Genus and species.
Question 41. The biological species concept was given by :
- Aristotle
- Johnruy
- Ernst Meyer
- Buffon.
Answer: 3. Ernst Meyer
Question 42. What is the ending name for the order?
- 1-Aceae
- 2-Oideae
- 3-Ideas
- 4-Ales.
Answer: 4. 4-Ales.
Question 43. Which one of the following is the famous work of nature in which Linnaeus introduced “binomial nomenclature”?
- Sexuality of plants
- Systema Naturae
- Species Plantarum
- Genera plantarum.
Answer: 2. Systema Naturae
Question 44. Plants were given (their names in Latin because:
- Latin is a simple language
- Scientists wanted to impress people with Latin words.
- Latin was the common language
- None of the above.
Answer: 4. None of the above.
Question 45. The suffix used for the tribe is :
- —Icae
- —Ineae
- —Inae
- —Ini
Answer: 4. —Ini
Question 46. Which explanation is correct for the name tamarindus indicus [L]?
- The letter [L] shows that the name is from the Latin language
- The letter [L] means that Linnaeus who gave this name to the plant
- The letter [L] has no connection with the name
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. The letter [L] means that Linnaeus who gave this name to the plant
Question 47. The botanical name of an edible banana is:
- Musa sapientum
- Musa erectus
- Mitsa textiles
- None of these.
Answer: 1. Musa sapientum
Important MCQs on Biological Classification Question 48. The highest unit of classification is :
- Kingdom
- Class
- Phylum
- Species.
Answer: 1. Kingdom
Question 49. Which of the following includes all of the others?
- Class
- Order
- Genus
- Species.
Answer: 1. Class
Question 50. The basic unit of classification of plants and animals is:
- Genus
- Species
- Variety
- Sub-species.
Answer: 2. Species
Question 51. The common units of classification are :
- 1 Genus
- 2 Family
- 3 Species
- 4 Order
- 5 Variety
Their correct sequence starting from the smallest is:
- 3, 1, 2, 4, 5
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
- 4, 2, 3, 1, 5
- 5, 3, 1, 2. 4.
Answer: 4. 5, 3, 1, 2. 4.
Question 52. Alpha taxonomy refers to:
- Classical taxonomy
- Natural classification
- Phylogenetic classification
- Phenetic system.
Answer: 1. Classical taxonomy
Question 53. The extremists among evolutionary taxonomists are popularly known as:
- Omega taxonomists
- Phenologists
- Cladists
- Evolutionists.
Answer: 3. Cladists
Biological Classification MCQs For NEET Question 54. A group of species which resemble each other both structurally and functionally is called:
- Genus
- Order
- Suborder
- Class.
Answer: 1. Genus
Question 55. Several genera having common characters are called:
- Family
- Order
- Phylum
- Class.
Answer: 1. Family
Question 56. Point out the correct sequence of taxa :
- 1-Amily. Order. Class, genus
- Lass. Easier. Family, genus
- Class, order. Genus, family
- Order. Class, family, genus.
Answer: 2. Lass. Easier. Family, genus
Question 57. Several families having common character are called:
- Order
- Class
- Phylum
- Subclass.
Answer: 1. Order
Question 58. In the study of taxonomy, “descriptive taxonomy” refers to:
- Phonetic system
- Phylogenetic classification
- Classical taxonomy
- Natural classification.
Answer: 3. Classical taxonomy
Question 59. The material designated by the original author as the nomenclature type is a:
- Holotype
- Isotype
- Syntype
- Paratype.
Answer: 1. Holotype
Biological Classification MCQs For NEET Question 60. In which of the following taxonomies, is equal weightage given to each of thousands of characters that a taxon exhibits?
- Chemotaxonomy
- Alpha taxonomy
- Classical taxonomy
- Numerical taxonomy.
Answer: 4. Numerical taxonomy.
Question 61. Hutchinson’s primary contribution to the taxonomy is the phylogenetic studies of angiosperms. His classification of flowering plants is based on 22 principles which are comparative to Bessey’s dicta. According to him:
- Evolution does not necessarily involve all organs at the same time.
- Evolution always involves all the organs of a plant at the same time
- Monocotyledons are more primitive than dicotyledons
- Climbers are more primitive than trees.
Answer: 1. Evolution does not necessarily involve all organs at the same time.
Question 62. Which of the following taxonomic categories tops the hierarchy of categories?
- Genus
- Species
- Order
- Class.
Answer: 4. Class.
Question 63. The taxonomic category ‘family’ is between
- Phylum and order
- Order and genus
- Kingdom and class
- Genus and species.
Answer: 2. Order and genus
Question 64. Of all the taxa that exist in nature as a biologically cohesive unit is the :
- Species
- Genus
- Phylum or division kingdom.
Answer: 1. Species
Question 65. Two or more species occupying the same or overlapping areas are :
- Sympatric
- Sibling
- Subspecies
- Allopatric.
Answer: 1. Sympatric
Question 66. New systematics based on the protein and serum analysis of organisms is called :
- Biochemical taxonomy
- Cytotaxonomy
- Experimental taxonomy
- Numerical taxonomy.
Answer: 1. Biochemical taxonomy
Biological Classification MCQs For NEET Question 67. The species inhabiting different geographical areas arc:
- Taxonomic species
- Sibling species
- Allopatric
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Allopatric
Question 68. The scientists who raised the group Protista to include both plant and animal-like unicellular organisms (protozoa and slime molds) :
- L. Pasteur
- E.f. Haeckel
- J. Lister
- E. Meyer.
Answer: 2. E.f. Haeckel
Question 69. Which organisms contain usually non-vacuolated cells:
- Viruses
- Prokaryotes
- Algae
- Gymnosperms.
Answer: 2. Prokaryotes
Question 70. Bacteriophages are :
- Algae
- Fungi
- Viruses
- Lichens.
Answer: 3. Viruses
Question 71. Viruses are made up of:
- Proteins and DNA or RNA
- Proteins, DNA, and RNA
- Proteins, DNA, RNA, and lipids
- Carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids.
Answer: 1. Proteins and DNA or RNA
MCQ on five kingdom classification Question 72. R.h. Whittaker proposed the :
- Two-kingdom system of classification
- Three-kingdom system of classification
- Four-kingdom system of classification
- Five-kingdom system of classification.
Answer: 4. Five-kingdom system of classification.
Question 73. The prokaryotes are included in the kingdom :
- Monera
- Product
- Plantae
- Fungi.
Answer: 1. Monera
Question 74. To determine the correct place of an organism in a previously established, plan of classification is called :
- Classification
- Taxonomy
- Identification
- Systematics.
Answer: 3. Identification
Question 75. Neotype is:
- Nomenclatural type when the original material is missing
- New species discovered by a scientist
- Nomenclatural type from original material
- One of two or more specimens cited by the author.
Answer: 1. Nomenclatural type when the original material is missing
MCQ on five kingdom classification Question 76. The typological concept of species was given by :
- Aristotle and Plato.
- J.ray
- Hutchinson
- Mendel.
Answer: 1. Aristotle and Plato.
Question 77. A convenient way for easy identification of an organism of applying diagnostic characters is called :
- Systematics
- Classification
- Key
- None of these.
Answer: 3. Key
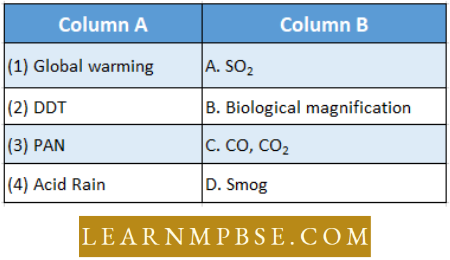
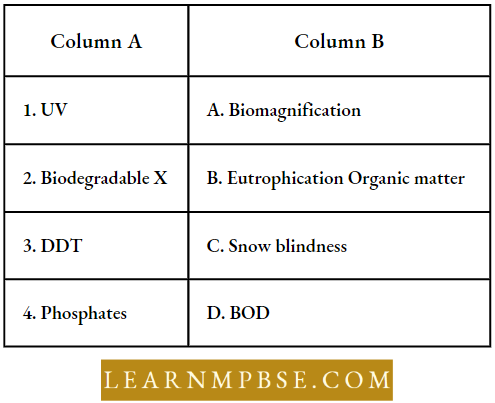
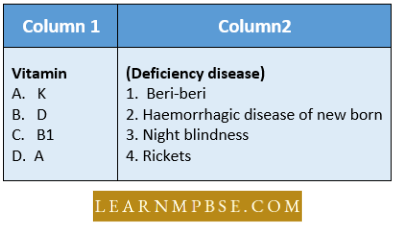
Question 78. Associate the terms in column 1 with those in column 2.
- 1-D,2-B,3-E,4-A
- 1-D,2-E,3-B,4-C
- 1-D,2-B,3-A,4-C
- 1-D,2-A,3-E,4-B
Answer: 1. 1-D,2-B,3-E,4-A
Question 79. Lectotypc is :
- Specimen selected from original material for nomenclature. il type when there is no holotype
- Duplicate of holotype
- Specimen cited by the author without making one holotype
- Specimen described along with holotype.
Answer: 2. Duplicate of holotype
MCQ on five kingdom classification Question 80. A species characterized by only morphological traits is :
- Sibling species
- Morphospecies
- Biospecies.
- Taxonomic species.
Answer: 4. Taxonomic species.
Question 81. Which organisms are generally classified as protists :
- Algae, fungi, bacteria, and bryophytes
- Protozoa, bacteria, algae and bryophytes
- Protozoa, some algae and fungi
- Fungi, slime molds, and tracheophytes.
Answer: 1. Protozoa, bacteria, algae and bryophytes
Question 82. Who suggested the five-kingdom classification of organisms?
- Copeland
- R.h. Whittaker
- Hutchinson
- Bentham and hooker.
Answer: 2. R.h. Whittaker
Question 83. Isotype is a duplicate of:
- Syntype
- Holotype
- Neotype
- Lectotype.
Answer: 2. Holotype
Question 84. The biological species concept was formulated by :
- Meyer
- Heywood
- Stebbins
- R. Koch.
Answer: 1. Meyer
Question 85. In the statement, isotype is a duplicate specimen of x from the same collection of the same date and same locality. ‘X’ stands for:
- Isotype
- Holotype
- Paratype
- Neotype.
Answer: 2. Holotype
Question 86. Two morphologically similar populations which cannot interbreed among themselves are called:
- Sympatric species
- Allopatric species
- Sibling species
- Morphospecies.
Answer: 3. Sibling species
Question 87. Two related species having very distinct non-overlapping geographical areas are :
- Sympatric species
- Allopatric species
- Taxonomic species
- Biological species.
Answer: 2. Allopatric species
Biological Classification MCQ with answers Question 88. To which kingdom of Whittaker, producers belong :
- Protista and Plantae both
- Protista only
- Monera, protista and plantae
- The five kingdoms.
Answer: 3. Monera, Protista, and Plantae
Question 89. Which of the following is not included in any of the five kingdoms of Whittaker:
- Viruses
- Viroids and prions
- Bacteriophages
- All of these.
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 90. Which one of the following is a protist with a flexible lifestyle?
- Chlamydomonas
- Euglena
- Paramecium
- Entamoeba.
Answer: 2. Euglena
Question 91. Which one of the following shows plant-like and animal-like characters
- Amoeba
- Frog
- Slime moulds
- Mushroom.
Answer: 3. Slime moulds
Question 92. Yeasts lack:
- Chlorophyll
- Nucleus
- Cell wall
- Cytoplasm.
Answer: 1. Chlorophyll
Biological Classification MCQ with answers Question 93. Species are:
- Population of individuals with similar genotypic and phenotypic traits.
- Population of one type
- Population of interbreeding individuals
- Group of individuals occurring in a geographical area.
Answer: 3. Population of interbreeding individuals
Question 94. Members of biological species are potentially able to :
- Compete
- Interbreed
- Inirogross
- Express all the same genes,
Answer: 2. Interbreed
Question 95. Which is the correct arrangement of taxa based on the number of the individuals (lowest to the highest) that each taxon has:
- Species, genus, phylum, kingdom
- Kingdom, phylum, species, genus
- Kingdom, genus, phylum, species
- Genus, species, phylum, kingdom.
Answer: 1. Species, genus, phylum, the kingdom
Question 96. Taxonomic keys are constructed to identify a species. Which key is most popular:
- Indented keys
- Bracketed keys
- Taxonomic keys
- None of these.
Answer: 2. Bracketed keys
Question 97. Carl Linnaeus is referred to as :
- Father of genetics
- Father of phylogenetic classification
- Father of biological taxonomy
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Father of biological taxonomy
Question 98. Two plants a and b differ in correlated morphological characters and should be treated as:
- Two varieties
- Two taxonomic species
- Two subspecies
- Members of the same species.
Answer: 2. Two taxonomic species
Biological Classification MCQ with answers Question 99. Out of 5 kingdoms in which kingdom of Whittaker living organisms are grouped:
- 3rd, 4th and 5th kingdom
- 2nd kingdom
- 3rd and 4th kingdom
- All kingdoms.
Answer: 4. All kingdoms.
Question 100. At present scientific names have been given to :
- 10 Million species
- 3.9 million species
- 1.7 million species
- One million species.
Answer: 3. 1.7 million species
Question 101. 102.3.5 billion years ago :
- Life appeared
- Eukaryotes appeared
- Moon appeared
- Plants appeared.
Answer: 1. Life appeared
Question 102. A collection of populations within which interbreeding may occur is called :
- Genus
- Family
- Species
- Phylum.
Answer: 3. Species
Question 103. Which one of the following is a composite dual organism?
- Fungi
- Metazoa
- Algae
- Lichens.
Answer: 4. Lichens.
Question 104. Ocnwcnluvh discovered:
- Nucleus
- Cell wall
- Bacteria
- Virus.
Answer: 3. Bacteria
Question 107. Two-kingdom system classification was given by
- Linnaeus
- John ray
- Copeland
- Whittaker.
Answer: 1. Linnaeus
Biological Classification MCQ with answers Question 108. Multicellular producers belong to kingdoms:
- Plantae
- Protista
- Plantae and mycota
- Protista and plantae.
Answer: 1. Plantae
Question 109. Absorptive (saprozoic) mode of nutrition is found in the kingdom:
- Plantae
- Fungi
- Animalia
- All of these.
Answer: 2. Fungi
Question 110. Term Protista was given by
- Haeckel
- Daughtery
- Aristotle
- Copeland.
Answer: 1. Haeckel
Question 111. Species change over a period to form new species. These changes are :
- Jerky
- Slow over generations
- Slow and gradual over generations
- Sudden.
Answer: 3. Slow and gradual over generations
Question 112. Graphic representation indicating the evolutionary relationship of organisms is:
- Dendrogram
- Hierarchy
- Cladogram
- A-taxonomy.
Answer: 3. Cladogram
Question 113. In Whittaker’s classification, which kingdom is the main producer:
- Plantae
- Protista
- Mycota
- Monera.
Answer: 1. Plantae
Question 114. The first person who used structural likeness as the basis of classification and made systematics a scientific discipline
- C. Linnaeus
- Lamarck
- Theophrastus
- John ray.
Answer: 1. C. Linnaeus
Question 115. The five kingdoms of Whittaker arranged evolutionarily are:
- Monera — protista — animalia — plantae—mycota
- Monera — protista — plantae — fungi — animalia
- Monera — mycota — protista — plantae — animalia
- Monera — protista — fungi — animalia plantae
Answer: 2. Monera — Protista — Plantae — fungi — Animalia
Question 116. In which year, Whittaker proposed his five-kingdom system of classification:
- 1972
- 1989
- 01969
- 1959.
Answer: 3. 1969
Important MCQs on Biological Classification Question 117. Which of the following share the attributes of a plant and an animal:
- Yeast
- Euglena
- Polo
- Bacteria
Answer: 2. Euglena
Question 118. Decomposers belong to the kingdom:
- Protista and fungi
- Monera, protista and fungi
- Monera and Protista
- Protista, fungi and animalia
Answer: 2. Monera, Protista, and fungi
Question 119. Term ‘species’ and phylum were coined by :
- Species by ray and phylum by Linnaeus
- Species by John Ray and phylum by Cuvier.
- Species by cuvier and phylum by ray
- Species by Meyer and phylum by Linnaeus.
Answer: 2. Species by John Ray and phylum by Cuvier.
Question 120. The most famous botanical garden in the world is:
- Llyod Botanical Garden Darjeeling
- Ncvv york botanical garden USA
- Royal Botanical Garden, Kew, England
- Royal Botanic Garden Sydney Australia.
Answer: 3. Royal Botanical Garden, Kew, England
Important MCQs on Biological Classification Question 121. In taxonomic classification, the correct sequence is :
- Class — family — tribe — order—genus— species
- Class — order — family, tribe — genus — species
- Tribe — order — family — genus — species
- Class — tribe — order — family — genus
Answer: 2. Class — order — family, tribe — genus — species
Question 122. Genera Planetary was written by:
- Engler
- Hutchinson
- Bentham and hooker
- Bessey. (B.h.u. 1991)
Answer: 3. Bentham and hooker
Question 123. The basic unit of classification is :
- Species
- Genus
- Kingdom
- Phylum.
Answer: 1. Species
Question 124. A person who studies the origin, evolution, and variations in plants and also about the classification of plants is referred to as:
- A – taxonomist
- Herbal taxonomist
- Classical taxonomist
- P- taxonomist.
Answer: 3. Classical taxonomist
Question 125. The system of classification of angiosperm which is based on a maximum number of phenotypic attributes or several characters is referred to as:
- Artificial system
- Natural system
- Phylogenetic system
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Natural system
Question 126. Linnaeus’s system of classification of flowering plants is based on:
- Ecology
- Embryology
- Cytology
- Morphology.
Answer: 4. Morphology.
Question 127. Phytospecies is taxonomically
- A group of evolutionarily related population
- A population with common characteristics as an evolutionary base of variations
- A fundamental unit in the phylogenetic history of an organism
- A basic category to which most taxonomic information is attached.
Answer: 1. A group of evolutionarily related population
Question 128. The first act in taxonomy is;
- Description
- Identification
- Naming
- Classification.
Answer: 2. Identification
Question 129. A taxon is a :
- Group of related families
- Group of related species
- Type of living organisms
- Taxonomic group of any ranking.
Answer: 4. Taxonomic group of any ranking.