NEET Biology Reproduction In Angiosperms Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Uniscxunlity of flowers prevents:
- Autogany and geitonogamy
- Both geitonogamy and xenogamy
- Autogamy but not geitonogamy
- geitonogamybut not xenogamy
Answer: 3. Autogamy but not geitonogamy
Question 2. The endosperm is completely consumed by the developing embryo in :
- Pea and castor
- Maize and castor
- Castor and groundnut
- Maize and Pea
Answer: 1. Pea and castor
Question 3. A plant part having two generations is :
- Embryogeny
- Unfertilized ovule
- Germinated pollen
- Seed, grain
Answer: 4. Seed, grain
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question and Answers
Question 4. The end products of sexual reproduction are :
- Fruits
- Flowers
- Inflorescence
- Fruits and seeds
Answer: 4. Fuits and seeds
Question 5. Differentiation and development of floral primordium is preceded by :
- Hormonal changes
- Structural change
- Formation of gynoecium
- Both structural and hormonal changes.
Answer: 4. both structural and hormonal changes.
Important MCQs on Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question 6. Which of the following is a mismatch?
- Long and slender stalk – Filament
- Long and bilobed – Anther
- Short and bilobed – Anther
- Microsporangia – Anther.
Answer: 2. Long and bilobed – Anther
Question7. Microsporangium develops and :
- Form pollen
- Become pollen sac
- Produce tapetum
- Lead to the formation of embryo sac.
Answer: 1. Form pollen
Question 8. In the young anther, a group of homogenous compactly arranged sporogenous tissue occupies the centre of the microsporangium. It undergoes :
- Meiotic division to form microspore tetrad
- Growth forms pollen sac
- Mitosis to form tetrad
- Meiosis to form pollen sac.
Answer: 1. Meiotic division to form microspore tetrad
Question 9. Pollen grains are spherical and measure about:
- 10-12 diameters
- 25-50 in diameter
- 50-70 in diameter
- Less than 10 mm in diameter.
Answer:2. 25-50 in diameter
Question 10. In 40 per cent of angiosperm pollen grains are arrested at:
- 2-celled stage
- 3-celled stage
- One vegetative and generative cell
- Two generative and one vegetative cell
Answer: 2. 3-celled stage
Question 11. Pick out the mismatch :
- Embryosac – Female gametophyte
- Functional megaspore – 2 celled
- Typical embryo sac at maturity – 8 nucleate, 7 celled
- Egg apparatus – 3 celled
Answer: 2. Functional megaspore – 2-celled
Important MCQs on Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question 12. Which of the following is/are biotic pollinators of plant species?
- Bees, butterflies, beetles
- Sunbird, hummingbird
- Gecko, lemur, Rodents
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 13. Continued self-pollination leads to inbreeding depression. Which of the following devices encourage cross-pollination?
- Pollen released before stigma becomes receptive
- Stigma becomes receptive before pollen release
- Different positions of anther and stigma
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 14. In plants which shed pollen at the 3-celled stage, pollen tube. carry :
- One male gamete from the beginning’
- One male gamete
- One vegetative and One generative cell
- Two vegetative and one generative cells.
Answer: 1. wo male gametes from the beginning’
Question 15. Callose covering is present over :
- Egg
- Pollen grain
- Male gamete
- Microspore mother cells.
Answer: 4. Microspore mother cells.
Question 16. The arrangement of nuclei in a normal dicot embryo sac is :
- 3 + 3 + 2
- 3 + 2 + 3
- 2 + 4 + 2
- 2 + 3 + 3.
Answer: 2. 3 + 2 + 3
Question 17. The function of the tapetum is
- Protective
- Nutritive
- Respiratory
- All of above
Answer: 2. Nutritive
Question 18. A typical dicot embryo consists of:
- Epicotyl and plumage
- Hypocotyl and radicle
- Embryonal axis and two cotyledons,
- Embryonal axis and scutellum.
Answer: 3. Embryonal axis and two cotyledons,
Important MCQs on Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question 19. The wall of The fruit may be flashy in :
- Guava
- Orange
- Mango
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 19. Which of the following fruits contains thousands of seeds?
- orchid fruit
- Ficus
- Orobanchae and striga
- 1 and 3.
Answer: 4. 1 and 3.
Question 20. Which of the following is the correct labelling for the figure given below :

- p/Thalamus Q/ovary R/style s/stigma
- Stigma-style ovary stigma
- Thalamus-style ovary stigma
- Thalamus Ovary stigma style.
Answer: 4. Thalamus Ovary stigma style.
Question 21. Select the mismatched pair.
- Microsporangium
- Megasporangium
- Pollen grain
- Embryo sac
Answer: 1 . Microsporangium
Question 22. The given diagram shows the microsporangium of a mature anther. Identify P, Q and R.
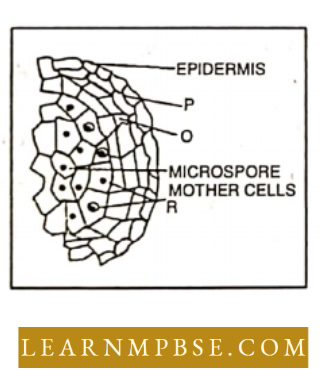
- P – Middle layer, O – Endothecium, R – Tapetum
- P – Endothecium, O – Tapetum, R – Middle layer
- P – Endothecium, O – Middle layer, R – Tapetum
- P – Tapetum, B – Middle layer, R – Endothecium.
Answer: 3. P – Endothecium, O – Middle layer, R – Tapetum
Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants MCQ For NEET Question 23. Refer to the given statements.
- The outer exine is made up of sporopollenin.
- The inner inline is pecto-cellulosic.
- Generative cells are bigger and contain abundant food reserves.
- The vegetative cell is small and floats in the cytoplasm of the generative cell
Answer: 3. Generative cells are bigger and contain abundant food reserves.
Question 24. Which of the given statements are not true regarding the structure of pollen grain
- (1) and (2)
- (2) and (3)
- (3) and (4)
- (1) and (4).
Answer: 3. (3) and (4)
Question 25. Study the following statements regarding the structure of microsporangium and select the correct answer.
(i)Microsporangium is generally surrounded by four wall layers – epidermis, endothecium, middle layers and tapetum
(ii) The outer three layers perform functions of protection and dehiscence of anthers.
(iii)Cells of tapetum undergo meiosis and produce microspore tetrads.
- Only (1) and (2) are true.
- Only (2) and (3) are true.
- Only (1) and (3) are true.
- All are true.
Answer: 1. Only (1) and (2) are true.
Question 26. Select the mismatched pair.
- Storage of pollen grains – 196 C
- Pollen allergy-carrot grass
- Chasmogamous flowers -Exposed anthers and stigmas
- Xenogamy- self-pollination
Answer: 4. Xenogamy- self-pollination
Question 27. A typical angiospermous ovule is attached to the placenta using a stalk called X. The Body of the ovule fuses with X in the region called Y. Thus Y represents the junction between the ovule and funicle. Identify X and Y.
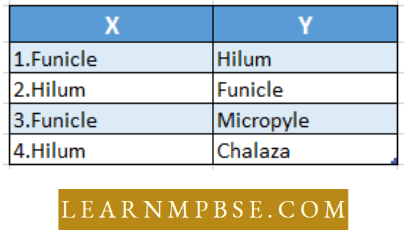
Answer: 1. Funicle Hilum
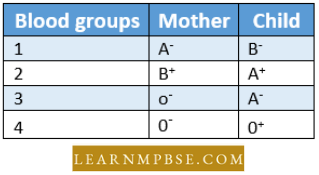
Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants MCQ For NEET Question 28. Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the codes given below.
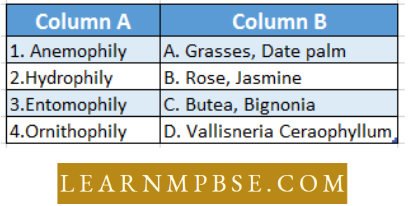
1→A 2 →D 3 →B 4→C
1 →A 2 →D 3→ C 4 →B
1→ B 2 →C 3→ A 4 →D
1 →B 2 →A 3 →1 4→ D
Answer: 1. 1→A 2 →D 3 →B 4→C
Question 29. Given below are the events that are observed in an artificial hybridization programme. Arrange them in the correct sequential order.
- Re-bagging
- Selection of parents;
- Bagging;
- Dusting the pollen on the stigma;
- Emasculation;
- Collection of pollen from the male parent.
1. 2 → 3→ 5→ 6→ 4 → 1
2. 2→ 5 →3→ 6 →4 →1
3. 5 →2 →3 →6 →1 →4
4. 2 →3 →6 →4 →5 →1
Answer: 2. 2 →3 →5 →6 →4 →1
Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants MCQ For NEET Question 30. Identify the different parts of a typical dicot embryo labelled as A. 11 and C and select the correct option.
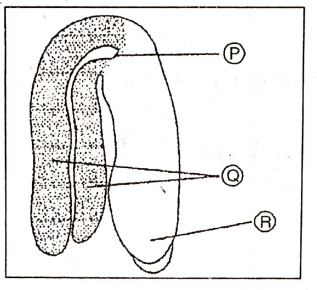
- Plumule Cotyledons Radicle
- Radicle Cotyledons Plumule
- Cotyledons Plumule Radicle
- Cotyledons Radicle Plumule.
Answer: 1 . Plumule Cotyledons Radicle
Question 31. A typical example of cross-pollination is :
- Wheat (Triticum)
- Rice (Oryza saliva)
- CLCotton (Gossypium)
- Zea mays.
Answer: 4. Zea mays.
Question32. Continued self-pollination generation after generation, results in :
- better progeny
- pure line formation
- formation of new varieties
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. pure line formation
Question 33. Stigma is always sticky and rough in :
- Anemophilous flower
- Hydrophilous flowers.
- Entomophilous flowers
- All the above types of flowers.
Answer: 3. Entomophilous flowers
Question 34. The chief pollinators of our agro-horticultural crops are :
- Butterflies
- Moths
- Beetles
- Bees
Answer: 4. Bees
Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants MCQ For NEET Question 35. The phenomenon of opening of flower buds is called :
- Gcjmetogenesis
- Sporogenesis
- Anthesis
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Anthesis
Question 36. In wheat and sugarcane, pollination takes place by :
- Wind
- Water
- Insects
- Animals.
Answer: 1. Wind
Question 37. If water causes pollinatior^-it is called :
- Anemophily
- Hydrophily
- Chiropterophily
- Zoophily.
Answer: 2. Hydrophily
Question 38. Insect-pollinated flowers possess:
- Smooth and dry pollen
- A larger amount of pollen
- Coloured corolla
- Rough pollen.
Answer: 3. Coloured corolla
Question 39. Protandry is a condition in which :
- Anthers mature after stigma
- Anthers and stigmas mature at the same time
- Anthers mature earlier than the stigma
- Pollens of the same flower pollinate stigmas.
Answer:3.Anthers mature earlier than the stigma
Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plant Question 40.Cleistogamous flowers arc ;
- Open male flowers
- Open bisexual flowers
- Male flowers which never open
- Bisexual flowers which never open.
Answer: 4. bisexual flowers which never open.
Question 41. In Ficus the pollination is affected by :
- Air
- Water
- Birds
- Wasps.
Answer: 4. Wasps.
Question 42.Palynpld’gy deals with the study of:
- Pollen grains
- Chromosomes
- DNA
- Genes.
Answer: 1. Pollen grain
Question 43.When an anther dehisces towards the centre of the flower/it is called :
- Montrose
- Extras
- Inserted
- Exerted.
Answer: 1. Introse
Question 44. The lever mechanism is found in the pollination of:
- Ipomoea
- Euphorbia
- Salvia
- Vallisneria.
Answer: 3. Salvia
Question 45. When male and female parts of a flower mature at different times, it is termed:
- Dichogamy
- Heterostyly
- Herkogamy
- Monoclinic.
Answer: 1. Dichogamy
Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plant Question 46. Pollination by bats is known as :
- Anemophily
- Hydrophily
- Chiropterophily
- Ornithophily.
Answer: 3. Chiropterophily
Question 47. Cross-pollination is advantageous because it results in information of:
- Weaker progen
- Better progeny
- Female offspring
- Male offspring.
Answer: 2. Better progeny
Question 48. To avoid self-pollination, the pollen grains of some flowers have no fertilizing effect on the stigma of the same flower. This condition is :
- Self sterility
- Herkogamy
- Dicliny
- Dichogamy.
Answer: 1. Self sterility
Question 49. If the pollen of a flower falls on the stigma of another flower belonging to the same plant, it is :
- Genetically self-pollinated
- Ecologically cross-pollinated
- Both and
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Ecologically cross-pollinated
Question 50. Malacophily is pollination by
- Insects
- Snails
- Ants
- Elephant.
Answer:2. Snails
Question 51. Which one of the following parts of the pistil receives the pollen during pollination?
- Stigma
- Ovule
- Micropyle
- Nucellus.
Answer:1. Stigma
Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plant Question 52. The following plant has pollination above ground but its fruit develops underground.
- Sweet potato
- Solarium tuberosum
- Onion.
- Arachis hypogea.
Answer:4. Arachis hypogea.
Question 53. Pollinia are sac-like structures in which :
- Anther lobes are present
- Anthers lose their individuality
- Pollen grains get fused in a mass.
- yellow substance is secreted.
Answer:3. Pollen grains get fused in a mas
Question 54.Allog. um, though the biotic agency is called :
- Entomophily
- Ancmophily
- Hydrophily
- Both 1 and 2.
Answer:1 .Entomophily
Question 55. Chiropterophilous flowers possess :
- coloured petals
- Abundant nectar
- Hydrophily
- Less pollen.
Answer:2. Abundant nectar
Question 56. pollination of pinus is:
- Entomophilous
- Anemophilous
- Hydrophily
- Malacophily.
Answer:2. Anemophilous
Question 57. In Salvia, pollination takes place by :
- Animals
- Insects
- Air
- Water.
Answer:2. Insects
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants NEET Question 58. The entry of the pollen tube into the embryo sac through the integuments is termed as :
- Porogamv
- Chalazogamy
- Monogamy
- Both 1 and 2.
Answer:3. Mesogamy
Question 59.512 microspores will be formed following meiosis How many spores?
- 16
- 64
- 128
- 256.
Answer:3. 128
Question 60. An example of triploid tissue is :
- Onion leaf
- Onion root
- Maize endosperm
- Fern prothallus.
Answer:3. Maize endosperm
Question 61. Triploid plants can be obtained from the culture of :
- Pollen
- Endosperm
- Megaspore
- Ovule.
Answer:2. Endosperm
Question 62.After fertilization synergids and antipodal cells form :
- Embryo
- spore
- Endosperm
- None of the above.
Answer:4. None of the above.
Question 63. Pollen grain in angiosperm develops from :
- Endothecium
- Tapetum
- Sporogenous tissue
- Middle layer.
Answer:3. Sporogenous tissue
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants NEET Question 64.The nucellus of the ovule is :
- Haploid
- Diploid
- Triploid
- Polyploid.
Answer:2. Diploid
Question 65. In the case of angiosperms, the embryo sac represents :
- Female gametophyte
- Sporophyte
- Male gametophyte
- All the above.
Answer:1. Female gametophyte
Question 66. The other wall consists of four wall layers where :
- The tapetum lies just inner to endothecium
- Middle layers lie between endothecium and tapetum
- Endothecium lies inner to middle layers
- The tapetum lies next to the epidermis.
Answer:2. Middle layers lie between endothecium and tapetum
Question 67. Emasculation is achieved by :
- Removal of anthers
- Removal of stigma
- Removal, of gynoecium
- Removal of calyx and corolla.
Answer:1. Removal of anthers
Question 68. A (lower pan whose primary MLC is protection, is the :
- Stamen
- Ovary
- Sepal
- Embryo sac.
Answer:3. Sepal
Question 69. In a fully developed male gametophyte, the number of nuclei is:
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four.
Answer:3. Three
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants NEET Question 70. The mature anther wall comprises an epidermis followed by a layer of radially elongated cells with fibrous bands of callose called endothecium whose function is :
- Nutrition
- Protection
- Mechanical
- Dehiscence.
Answer:4. Dehiscence.
Question 71. The innermost layer of the anther is the tapetum whose function is
- Dehiscence
- Mechanical
- Nutrition
- Protection.
Answer:3. Nutrition
Question 72. Ovule represents :
- Hierpsporangium
- Megasporangium
- Gametophyte
- Embryo.
Answer:2. Megasporangium
Question 73. The female plant is diploid and the male plant is tetraploid. Find out the correct match.

Answer: 1. 3n 4n 2n n 2n 4n
Question 74. Mature ovules are classified based on the funiculus. If the micropyle comes to lie close to the funiculus the ovule is termed as :
- Orthotropous
- Anatropous
- Amphitropous
- Campylotropous.
Answer:2. Anatropous
Question75. In a bisexual flower when the gynoecium matures earlier than another, it is called:
- Protandry
- Protbgyny
- Herkogyny
- None of the above.
Answer:2 .Protbgyny
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants NEET Question 76. Plants which flower only once in life are termed as:
- Polycarpic
- Monocarpic
- Pericarpic
- Leucas.
Answer:2. Monocarpic
Question 77. Translators are found in :
- Calotropis flower
- Hibiscus
- Vinca flower
- Leucas.
Answer:1. Calotropis flower
Question 78. When the micropyle, chalaza and hilum he in a straight line, the ovule is said to be :
- Anatropous
- Orthotropous
- Amphitropous
- Campylotropous.
Answer:2. Orthotropous
Question 79. Double fertilization was first described by :
- Hofmeister
- Nawaschin
- Strasburger
- Leeuwenhoek.
Answer: 2. Nawaschin
Question 80. The secondary nucleus after fusing with one of the male gametes develops into :
- Embryo
- Seed
- Endosperm
- Fruit.
Answer: 3. Endosperm
Question 81. The fusion of the male gamete with the secondary nucleus of the embryo sac is the process of:
- Fertilization
- Double fertilization
- Parthenocarpy
- Parthenogenesis.
Answer: 2. Double fertilization
Question 82. The fertilization occurs in the :
- Ovary
- Ovule
- Embryo sac
- Nucellus.
Answer: 3. Embryo sac
Important MCQs on Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question 83. In the diagram given above, parts labelled as *P\ ‘Q\ ‘R’,‘S’, ‘T\ ‘U’ are respectively identified as
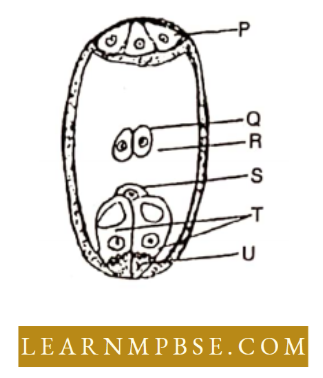
- synergids, polar nuclei, central cell, antipodal cell, filiform apparatus and egg.
- polar nuclei egg, antipodal cell, central cell, filiform apparatus and synergids.
- egg, synergids, central cell, filiform apparatus, antipodal cell and polar nuclei
- central cell, polar nuclei, filiform apparatus, antipodal cell, synergids and egg.
Answer: 1. synergids, polar nuclei, central cell, antipodal cell, filiform apparatus and egg.
Question 84. If an endosperm cell of an angiosperm contains 24 chromosomes, the number of chromosomes in each cell of the root will be :
- 8
- 4
- 16
- 24.
Answer: 4. 16
Question 85.In ovule meiosis occurs in :
- Megaspore
- Megaspore mother cell
- Endosperm
- Integument
Answer: 2. Megaspore mother cell
Question 86.The female gametophyte of a typical dicot at the time of
fertilization is :
- 8-celled
- 7-celled
- 6-celled ‘
- 4-celled.
Answer: 2. 7-celled
Question 87. Development of embryo sac from any cell of nucellus is called :
- Apogamy
- Apospory
- Parthenogenesis
- Sporogenesis.
Answer: 2. Apospory
Important MCQs on Reproduction in Flowering Plants Question 88. The method of fertilization (in an angiosperm) in which the pollen tube enters the ovule by way of micropyle is known as:
- Chalazogamy
- Porogamy
- Microgamy
- Syngamy.
Answer: 2. Porogamy
Question 89. Simple fruit develops from :
- The single ovary which is simple
- The single ovary which is a compound
- The single ovary which may be simple or compound
- None of the above.
Answer: 3 . The single ovary which may be simple or compound
Question 90. Parthenocarpic fruit is :
- Fruit with immature seeds
- Fruit, with mature seed
- Developed without fertilization
- Only seeds and no fruits.
Answer: 3. Developed without fertilization
Question 91. After fertilization, the ovary is converted into :
- Embryo
- Endosperm
- Seed
- Fruit.
Answer: 4. Fruit.
Question 92. Perisperm in angiosperm seed is derived from :
- Nucellus
- Endosperm
- Integuments
- Antipodal cells.
Answer: 1. Nucellus
Question 93. The entry of the pollen tube into the embryo sacs through the chalaza is called :
- Porogamy
- Monogamy
- Chalazogamy
- C either A or B.
Answer: 3. Chalazogamy
Question 94.Ovule is ategenic in :
- Helianthus
- Pea
- Santalum
- Brassica.
Answer: 3. Santalum
Question 95. Vivipary is of common occurrence in
- Halophytes
- xerophytes
- Hydrophytes
- Psaminophytes.
Answer: 1. Halophytes
Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants MCQ For NEET Question 96. Polyembryony commonly occurs in < 0
- Turmeric
- Tomato.
- Potato
- Citrus.
Answer: 4. Citrus.
Question 97. The main embryo develops from the structure formed as a result of fusion of:
- Two polar nuclei of embryo sac
- Egg cell and male gamete
- Synergid and male gamete
- Male gamete and antipodals.
Answer: 2. Egg cell and male gamete
Question 98. The function of an obturator for any ovular structure is to :
- Nourish ovule
- Nourish pollen grains
- Guide pollen tube towards micropyle
- Keep the ovule alive.
Answer: 3. Guide pollen tube towards micropyle
Question 99. The term xenia denotes the effect of the following:
- Pollen on endosperm
- Pollen on egg
- Pollen on nucellus
- Pollen on the seed coat.
Answer: 1. Pollen on endosperm
Question 100. Polygonum type of embryo sac is:
- 8-nucleate, 7-celled
- 8-nucleate, 8-celled
- 7-nucleate, 7-celled
- 4-nucleate, 3-celled.
Answer: 1. 8-nucleate, 7-celled
Question 101. Which of the following statements is true for the pollen tube :
- It shows the growth of intent
- It is composed of three non-cellular zones
- It shows thigmotactic movement
- It shows cytoplasmic streaming.
Answer: 1. It shows the growth of intent
Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants MCQ For NEET Question 102. Lire seed coat develops from the
- Sepals
- Ovary wall
- Ovule wall
- Endosperm.
Answer: 3. Ovule
Question 103. Which of the following is required for germination of
seeds?
- Certain temperature conditions
- Oxygen
- Water
- All the above.
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 104. The fusion of egg with male gamete is called :
- Syngamy
- Apogamy
- Autogamy
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Syngamy
Question 105. In angiosperms, the oospore on development produces :
- Endosperm
- Protonema
- Embryo
- Seed.
Answer: 3. Embryo
Question 106. A female gametophyte would be found in the :
- Ovule
- Stigma
- Endosperm
- Seed.
Answer: 1. Ovule
Question 107. Pollen grain gets nutrition fronts
- Endothecium
- Tape turn
- Sporogenous sac
- Middle layer.
Answer: 2 . Tape turn
Question 108 .The nucellus of the ovule is :
- Haploid
- Diploid
- Triploid
- Polyploid.
Answer: 2 .Diploid
Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants MCQ For NEET Question109 .The diagram given below shows ovules megasporogenesis and megagametogenesis in an angiosperm named Polygonum.
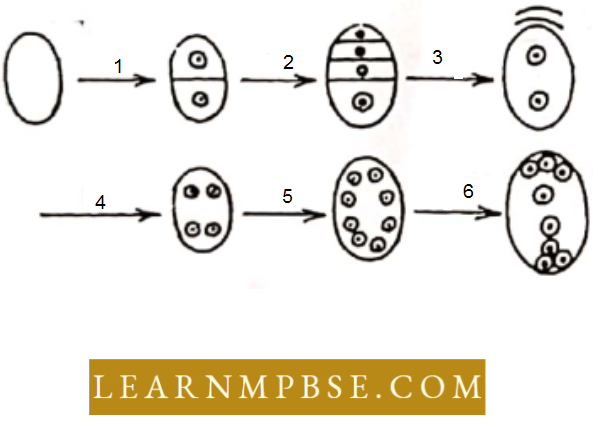
Reduction division takes place at which step?
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Steps 2 and 3
- Steps 3 and 4
Answer: 1. Step 1
Question 110. In the case of angiosperms, pollen grain produces :
- Female gametophyte
- Sporophyte
- Male gametophyte
- All the above.
Answer: 3. Male gametophyte
Question 111.Sexual reproduction in which morphologically and physiologically similar gametes fuse is termed as :
- Plasrnogamy
- Anisogamy
- Isogamy
- Oogamy.
Answer: 3. Isogamy
Question 112. A normal plant suddenly started reproducing parthenogenetically. ‘The number of chromosomes of the second generation as compared to the parent plant will be :
- Double
- Half
- One fourth
- same.
Answer: 4. same.
Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants MCQ For NEET Question 113. If cotyledons remain below soil during germination, it is:
- Rhypogeal germination
- vivipary
- Epigeal germination
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Rhypogeal germination
Question 114. Seeds are dispersed by :
- Water
- Living organism
- Wind
- All the above.
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 115. Micropyle of ovule allows entry of:
- Pollen tube
- water
- Wind
- All the above.
Answer: 1. Pollen tube
Question 116. When seeds develop without meiosis and syngamy, the phenomenon is :
- Parthenogenesis
- Parthenocarpy
- Agamospermy
- Apogamy.
Answer: 4. Apogamy.
Question 117. The inner integument of the majority of the dicot seed is :
- Hypocotyl
- Scutellum
- Funicle
- Tegmen
Answer: 4. Tegmen
Question 118. Epigeal seed germination is found in :
- Wheat
- Castor
- Pea
- Maize.
Answer: 2. Castor
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants NEET Question 119. Which of the following statements is correct?
- In angiosperms, the main plant body is gametophytic and
sporophytic generation is reduced - In angiosperms, the main plant body is sporophytic and gametophytic
generation is altogether absent - In angiosperms the main plant body is sporophytic and the male and
female gametophytes are represented by pollen and embryo sacs respectively - In angiosperms, the ovules and anthers are gametophytic whereas all other parts are sporophytic.
Answer: 3. In angiosperms the main plant body is sporophytic and the male and female gametophytes are represented by pollen and embryo sacs respectively
Question 120. Monosporic, 8 nucleate embryo sac is called :
- Allium type
- Oenothera type
- Polygonum type
- Peperomia type.
Answer: 3. Polygonum type
Question 121. An example of triploid tissue is :
- Fern prothallus
- Cycas ovule
- Lily endosperm
- Moss capsule.
Answer : 3 . Lily endosperm
Question 122.If soaked pea seeds are kept in four separate flasks, the best
germination will be in the flask having :
- Oxygen
- Carbon dioxide
- Nitrogen
- Water.
Answer: 1. Oxygen
Question123.Which of the following plants are likely to have a wider range of distribution?
- Those distributed by seeds
- Those distributed by spores
- Those distributed vegetatively
- Those distributed by fruits.
Answer: 1. Those distributed by seeds
Question 124. In albuminous seeds, the food is stored mostly in :
- Cotyledons
- Endosperm
- Testa
- Plumule.
Answer: 2. Endosperm
Question125.For the formation of 50 zygotes in a tobacco plant, the minimal number of meiosis involved would be:
- 59
- 63
- 99
- 109.
Answer: 2. 63
Question 126.In angiosperms normally after fertilization:
- The zygote divides earlier than the primary endosperm nucleus
- The primary endosperm nucleus divides earlier than the zygote
- TO both the zygote and primary endosperm nuclei divulge simultaneously
- Both the /vote and primary endosperm nuclei undergo a resting period.
Answer: 2. The primary endosperm nucleus divides earlier than the zygote
Question1 27. Match the two columns and select the correct answer
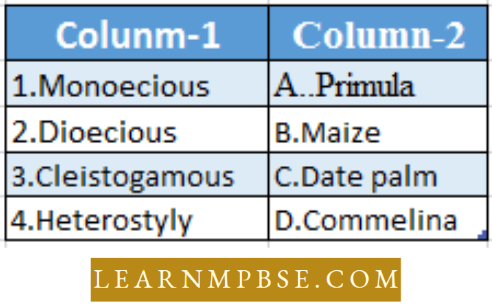
P Q R S
- 3 2 4 1
- 2 3 4 1
- 2 3 1 4
- 1 2 3 4
Answer: 2. 2 3 4 1
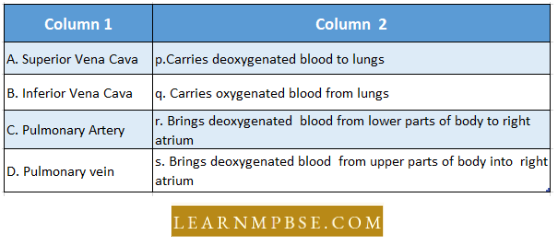
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants NEET Question 128. Match column-1 with column-2 and select the correct option from the codes given below.
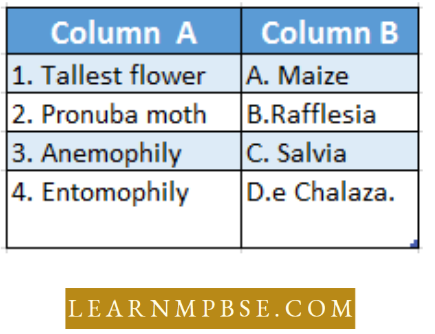
- 1→ B 2 →D →3→ A 4→ 3
- 1 →B 2→ D 3 →C 4 →A
- 1 →C 2→ B 3 →A 4 →D
- 1 →D 2 →C 3→ B 4 →A
Answer: 1. 1→ B 2 →D →3→ A 4→ 3