NEET Biology Animal Tissue
A group of structurally similar or dissimilar cells along with intercellular material, of common embryonic origin and performing a definite function is called tissue. Cells of tissue can recognise each other.
- The term tissue was introduced in Biology by Bichct (French surgeon).
- Although Marcello Malpighi (Italian scientist) founded a separate branch of Histology for the study of tissues, the name histology was given by Meyer (1819) and it is synonymous with “microanatomy”.
The usefulness of Histology.
- To understand the formation or construction of organs.
- To investigate the correlation between structures and functions of an organ.
- To be quite familiar with the normal cells and tissues and to distinguish them from abnormal or diseased ones. It helps in the diagnosis of many diseases.
Animal Tissues NEET Notes
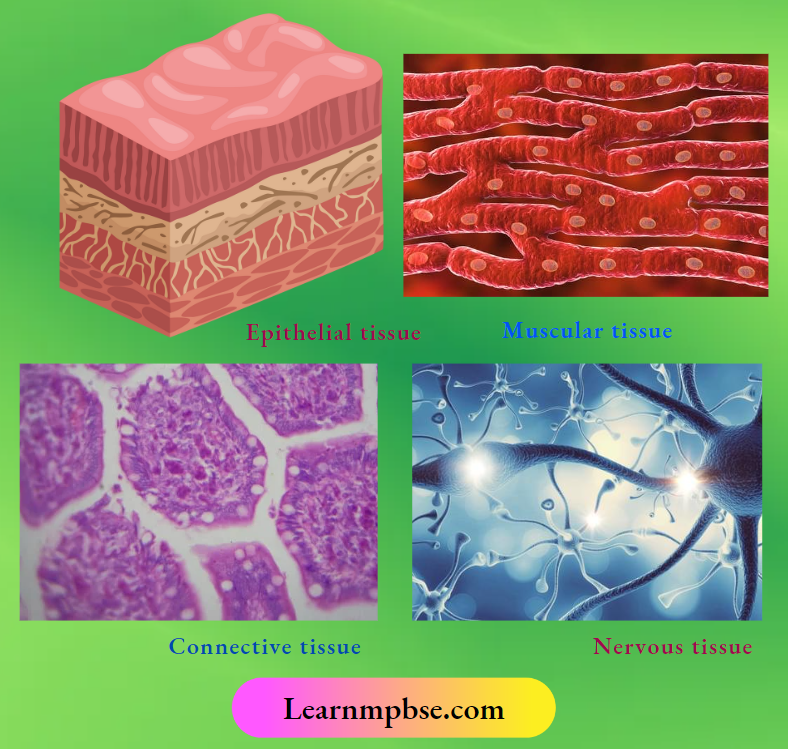
Kinds of tissues
They are of four major, primary or basic types.
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
- Epithelial tissue (covering and glandular tissue).
- Connective tissue (supporting tissue).
- Muscular tissue (contractile tissue).
- Nervous tissue
NEET Biology Epithelial Tissue
(Gr., ep. = upon; + thelia = grows). These occur as one or more layers of cells upon all external and internal exposed surfaces of the body and various organs forming a protective covering. The term epithelium was introduced by Dutch anatomist Ruysch.
- Epithelial tissue consists of variously shaped cells closely placed with very little cementing material formed of glycoprotein secreted by cells.
- Cells may be held together by modification of plasma membranes such as interdigitations, tight junctions (zonula occludens), desmosomes (macula adherens), gap junctions and terminal bars (zonula adherens).
- These cells rest on a permeable basement membrane or basal lamina composed of protein-bound mucopolysaccharides and glycoproteins. Both are secreted by epithelial cells and layers of reticular fibres of the underlying connective tissue.
Epithelial cells which line cavities may bear microvilli (simple minute protoplasmic processes) stereocilia (long cytoplasmic processes) or cilia/flagella (contractile and motile, 9+2 arrangement, arising from basal granules).
- Epithelia serve a variety of functions such as protection, formation of exoskeleton, secretion, absorption, respiration, sensation, conduction, excretion, reproduction and pigmentation.
- Cavities and ducts which communicate to the outside (alimentary canal, respiratory tract, urinogenital tract) are internally lined by epithelium containing mucus-secreting cells (=goblet cells) and along with lamina propria (underlying connective tissue) constitute mucous membrane.
- The cells lining the closed body cavities (coelom, pleural cavity, parietal cavity) secrete watery fluid and along with underlying connective tissues constitute a serous membrane.
Origin of various epithelial tissues
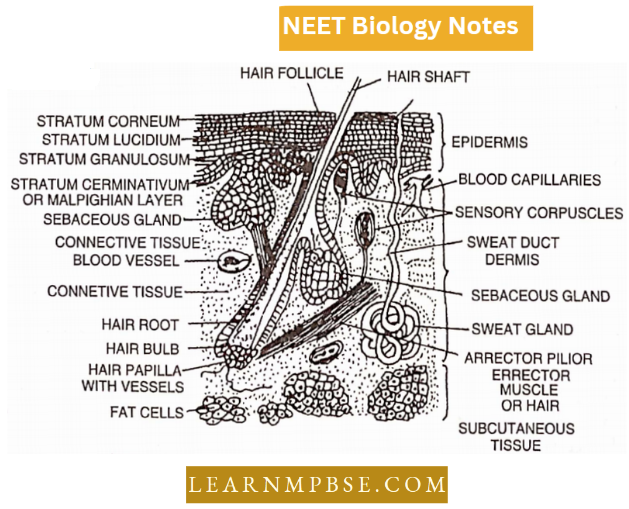
- From ectoderm. Epidermis of skin, epithelial lining of mouth, nose and anus, hair, nail, oil, mammary glands, sweat and salivary glands, taste buds, enamel of tooth, adrenal medulla etc.
- From mesoderm. Endothelium, mesothelium and mesenchymal epithelium, adrenal cortex, certain parts of urinogenital tract etc.
- From endoderni. Epithelium of the digestive tract from the pharynx downward, the epithelium of the respiratory tract from the larynx downward, the inner lining of the urinary bladder, the inner lining of the deep vagina, cells of the thyroid and parathyroid glands etc.
Classification Of Epithelial Tissue
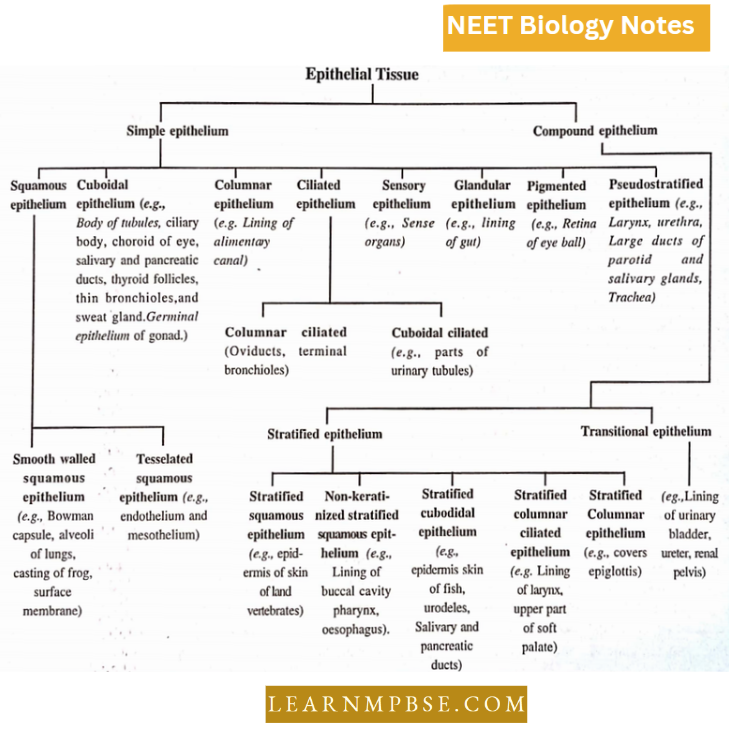
NEET Biology Glandular Tissues
- Gland. A cell or group of cells or an organ which secretes a useful secretion is called a gland (Chalice—gland cell).
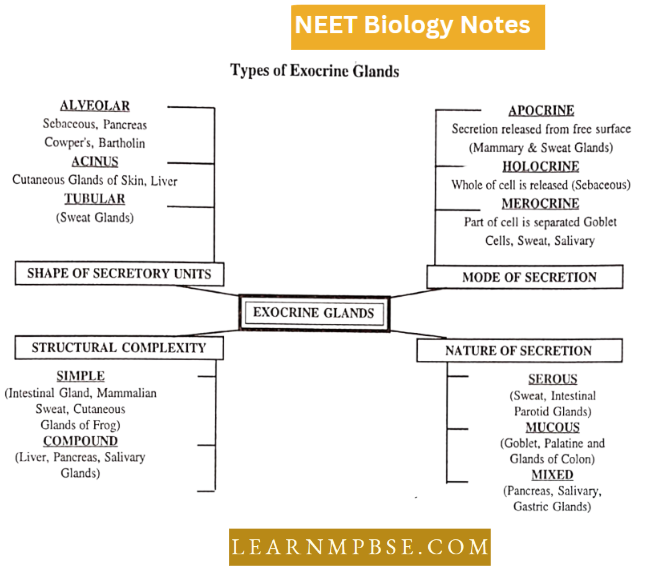
- Exocrine gland. A structure whose secretion is passed directly or by ducts to its exterior surface or other parts is called an exocrine gland.
- Endocrine gland. A ductless structure whose secretion (hormone) is passed into the bloodstream is called an endocrine gland.
- Holocrine gland. A structure whose cells undergo dissolution and are entirely extended, together with the secretory product, is called the holocrine gland For Example. sebaceous glands of mammals.
- Heterocrine gland. An exocrine gland as well as an endocrine gland is termed a heterocrine gland For Example., Pancreas.
Animal Tissues NEET Notes
Types Of Exocrine Glands
NEET Biology Muscular Tissue
All muscles originate from the mesoderm. The muscle cells (fibres) are highly specialized elongated, slender and cylindrical or spindle-shaped. They are highly contractile (contracting to 1/3 rd or 1/2 of the resting length).
- Muscle cells lose the capacity to divide, multiply and regenerate to a great extent. The study of muscle is called mycology.
- In each muscle fibre myofibrils or sarcostyle are present. Myofibrils are formed of proteins actin, myosin and tropomyosin.
The endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria present in muscle fibres are called sarcoplasmic reticulum and sarcosomes respectively.
They are of three kinds :
- Striated muscle fibres
- Smooth muscle fibres, and
- Cardiac muscle fibres.
Differences between three types of muscle fibres
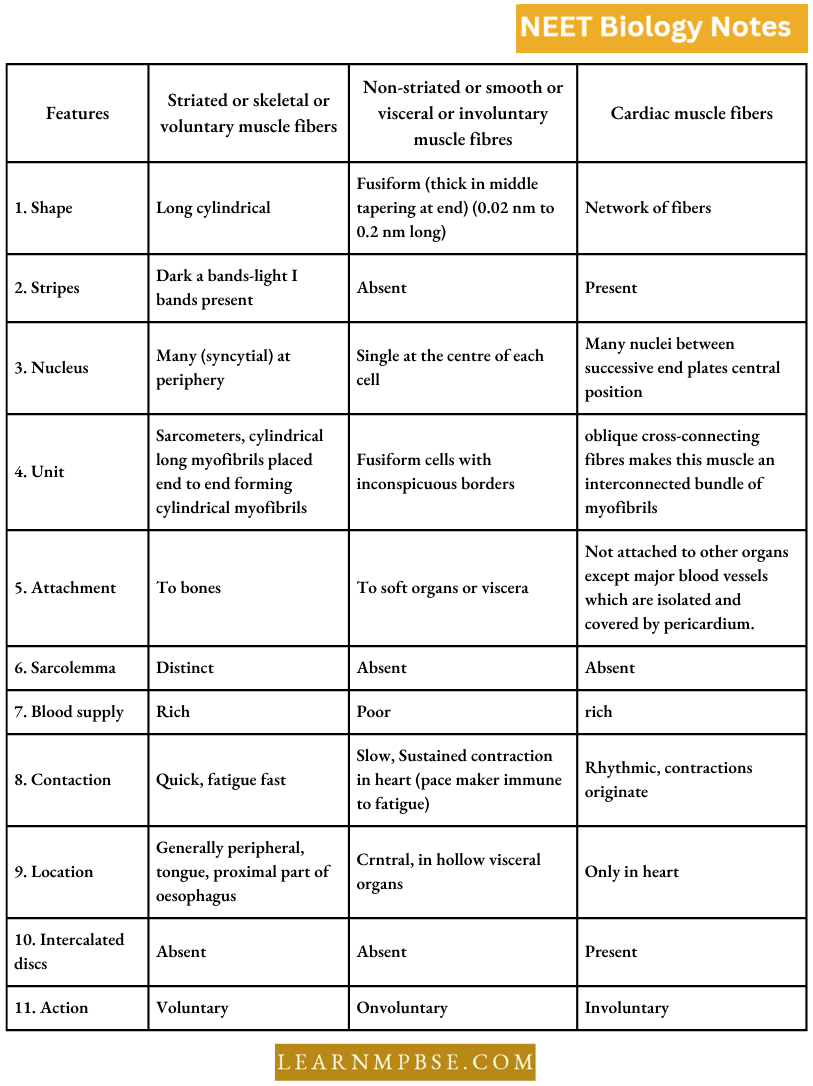
- Striated (somatic) muscles are also called phasic type of muscles because they
produce rapid, but brief movement of concerned organs. - Striated muscles are of two kinds, white (fast) fibres and red (slow) fibres.
- Three soluble proteins albumin, myoglobin and myogen, some enzymes, glycogen granules and lipid droplets are found in sarcoplasm.
- Striated muscle fibres are syncytial because each fibre is formed by the fusion of several embryonic stem cells called myoblasts.
- A-band and I-band are formed of proteins actin and myosin.
- A-band (Anisotropic) contains about 100 Å thick and 1.5 μm long myosin filaments.
- I-band (Isotropic) contains 50 Å thick and 1.0 μm long actin filaments which are twice as many as myosin filaments.
- The sarcomere is the functional unit of contraction. It is the part between two adjacent Z-bands or Krause’s membrane.
- Slender transverse line the M-or-Hansen’s line is present in the middle of the H band.
- Smooth muscles may be multi-unit smooth muscles (ciliary muscles and muscles of iris, arrector pili, muscles of large blood vessels) or single units (arranged in sheets).
NEET Biology Connective Tissue
They are mesodermal in origin and form about 30% of body mass. Hertwig (1883) introduced the term mesenchyma for connective tissue.
Types Of Animal Tissues NEET Biology
Special features.
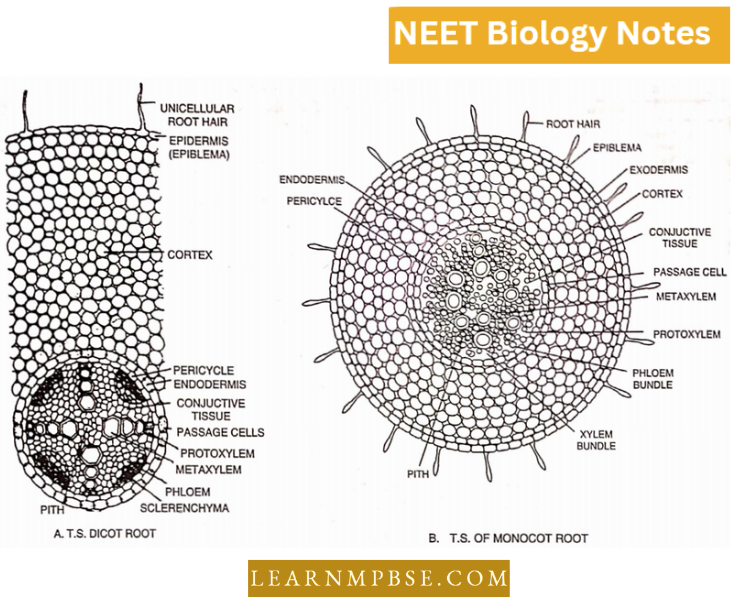
- It comprises cells, fibers, and a matrix.
- Cells consist of many sorts, and fibers are categorized into three types: collagen (white), elastin (yellow), and reticular.
- The matrix is an amorphous, gelatinous, colloidal medium.
- It occupies and fills interstitial areas surrounding organs.
- It links multiple organs.
- It provides a framework of skeletal bones, cartilages, and other components.
- It substitutes damaged tissues through processes such as scar tissue development.
- It provides immunity by the production of antibodies or by the phagocytosis of foreign entities.
- It comprises a limited number of cells and a substantial amount of cementing material.
- In comparison to epithelium, the proliferative potential of cells is significantly diminished.
- Connective tissue cells typically secrete the extracellular matrix.
Connective tissue is categorized into three types based on its structure:
1. Proper connective tissue (matrix is a resilient, gelatinous substance)
2. Skeletal Connective Tissue (Matrix infused with salts)
3. Fluid Connective Tissue, also known as Vascular Tissue The matrix is in a dynamic condition.
4. Connective Tissue
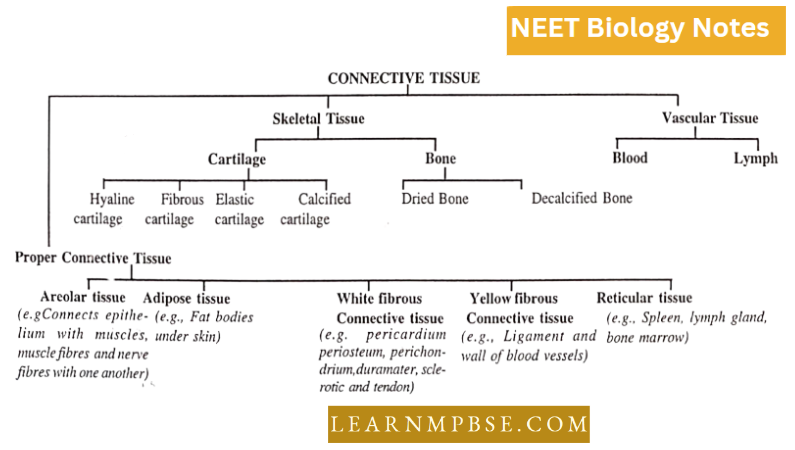
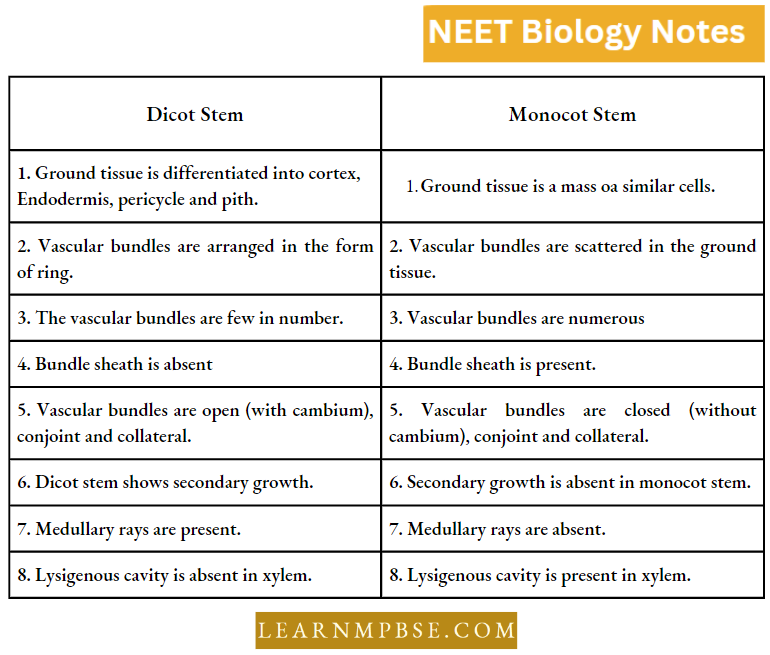
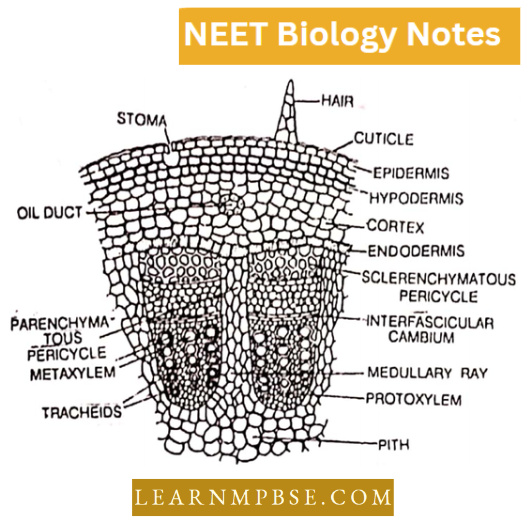
Four basic constituents of connective tissue are:
- Cellular components—fixed and wandering cells;
- Fibrous components—collagen and elastic fibres;
- Supporting matrix;
- Fluid (in fluid tissue only).
- Dust cells-Muemphugcs of connective tissues of septa of lung
- Tropocollagen—Collagen fibres.
- Reticular fibres: Delicate, freely branching and inelastic fibres of reticulin protein found interwoven, Abundant in embryos of new babies and healing and regenerative wounds.
- In the areolar tissue of adults, they are replaced by collagen but in blood-forming cells are abundant.
- Due to the presence of abundant collagen fibre, the skin dermis of large mammals yields leather after a chemical treatment called tanning.
- Subcutaneous tissue (Panniculus adiposis or blubber) hump of a camel, Thick tail of marine sheep skin.
Ground substance of cartilage, firm gel-like and transparent. Chondro niucoprolcin is formed of chondroitin sulphur and mucoprotein. It provides rigidity, elasticity and resilience.
- Functions of white fibrous tissue at the joint between skull bones: formation of immovable joints.
- Bone marrow is first affected by nuclear radiation.
- Bone marrow is a special kind of tissue called myelogenous tissue.
- Haversian canals are fine canaliculi which extend from bone marrow to the surface of the mammalian bone.
- The canals which connect Haversian canals are called Volkman’s canals.
Harversian systems are absent in the spongy bones of mammals.
- Necrosis. Area of dead tissue surrounded by a healthy area.
- The recticulo-endothelial system was given by Aschoff.
- Brown Fat. Present between neck and shoulders in hibernating mammals (bats, squirrels); produces a large amount of heat; highly vascularised; each adipocyte has many small fat globules (multilocular). centrally placed nucleus. The cytochrome oxidase of mitochondria gives the fat its brown colour. Heat is released by very rapid metabolism and is quickly distributed by ample blood circulation.
- Brown fat is found in those mammals which have an oxidation power of 20 times more than that of yellow fat because brown fat cells are loaded with a large number of
mitochondria.
In the white (yellow) fat, each adipocyte has a single large fat globule that squeezes the cytoplasm to a peripheral layer containing the nucleus.
- Gelatinous marrow: In old age marrow of cranial bones undergoes degeneration and is called gelatinous marrow.
- Ancient mummies still have their arteries intact due to elastic fibres.
- Collagen fibres are firm and most abundant fibres.
- Collagen. The most abundant protein (about 40% of total protein content) of the body.
- On boiling, the collagen protein of the white fibres changes into gelatin protein.
- Wrinkling in old age is due to collagen fibres with diminishing rigidity.
Types Of Animal Tissues NEET Biology
Tegument is the name given to the body covering in flatworms.
- The horns of a rhinoceros are formed of keratin protein.
- Keratin is also a pigment of hair giving black colour. If skin fails to synthesize it, premature greying of hair takes place.
- Bone-dissolving cells are called osteoclasts.
- Bone is the hardest tissue of the body.
The thick fibrous connective tissue layer periosteum surrounds the bones.
- Mucous tissue. It is mostly an embryonic connective tissue. It consists of a gelatinous matrix with scattered cells bearing fine branching processes. Example: Wharton’s jelly in the umbilical cord.
- Excessive stretching of ligaments is called sprain.
- As the matrix of cartilage is non-vascular, so an injured cartilage takes a long period to heal.
Astronauts pass calcium in their urine due to the faster breaking down of bones due to the absence of gravitational pull.
- Mummies: Preservation of elastic fibres of the body by chemical treatment.
- Aponeurosis: Bands of white fibrous connective tissue in which fibres are interwoven and thinner.
- Kupffer’s cells: are modified reticulocytes of the liver and act as phagocytes.
- Pigmented connective tissue is characterized by the presence of chromatophores (pigment cells) in the matrix and is found in the iris and choroid of the eye.
- Notochord: Skeletal connective tissue rod of the embryonic stage of all chordates.
- Pneumatic bones: These contain air cavities and are found in birds.
- Os-penis: A bone found in the penis of rodents.
- Os-codis: Bone in the heart of some ungulate (ruminants)
- Os-palpebrae: Bone in the eyelids of crocodiles.
Blood
An individual weighing approximately 70 kg possesses around 5 to 5.5 liters of blood. Adult individuals possess 6.8 liters of blood.
- Each red blood cell undergoes around 50,000 circulations in the body prior to hemolysis.
- The lifespan of red blood cells is 50-70 days in rabbits, 100 days in frogs, and 115-120 days in humans.
- Excess red blood cells are retained in the spleen.
- Red blood cells are lysed at a rate of 2.5 million per second, equating to approximately 1.1% of the total red blood cells every day.
- The hemoglobin count for males ranges from 14.5 to 15.5 grams per 100 milliliters of blood, whereas for females it ranges from 13.5 to 14.5 grams per 100 milliliters.
- The fetus weighs 23 grams per 100 milliliters of blood.
- Heme C3O32H74816 O872 N780 S8 Fe4
- In fish, amphibians, reptiles, and birds, erythrocytes are typically nucleated, oval, and biconvex.
- A lack of vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) and folic acid in the blood results in leukopenia. Amphibian red blood cells are the largest among vertebrates.
- Amphimna and Proteusarc are the largest amphibians, measuring 0.25mm. Mammals possess the smallest red blood cells among vertebrates.
The musk deer possess the smallest size among mammals, but the hill people exhibit a higher concentration of red blood cells. The concave morphology of mammalian red blood cells enhances their surface area.
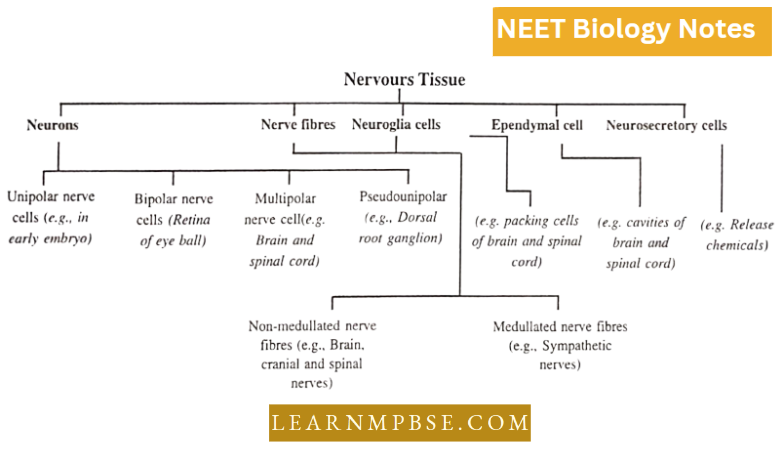
NEET Biology Nervous tissue
Special features
- It is a highly specialized tissue for generating and conducting impulses.
- The human nervous system has about 100 billion neurons.
- Nervous tissue is ectodermal in origin.
- Each neuron arises in the embryo from a single cell called a neuroblast.
- Due to a high degree of specialization, the cells (neurons) lose their ability to divide. Hence, a neuron is lost forever.
- The cells may be very long
- some neurons are up to 1 metre long.
- The neurons typically show a cyton with many branches neurites i.e., small dendrites, and a long branch—the axon.
Cytyn shows Nissl’s granules—which arc chromophilic bodies formed of rough ER having ribosomes.
The axon (axis cylinder) may be covered with a covering of white sheath (the myelin sheath). Such a nerve fibre is called nicdullaled or myelinated nerve fibre. If the sheath is absent the fibre is called Non-incdullatcd or Non- myelinated nerve fibre.
- Myelin sheath shows constrictions at regular intervals, called Nodes of Ranvier.
- The myelin sheath insulates nerve fibres and increases the speed of conduction.
- Functionally the nerve fibres are divided into two categories—afferent fibres (carrying impulses from receptor organ to CNS) and efferent fibres (carrying impulses from CNS to effector organs like muscles or glands). In other words, neurons exhibit polarity in the conduction of impulses. There is unidirectional conduction of impulse.
- The axon of one neuron lies in close contact with the dendrites of another neuron. The neurilemma of both these processes arc intact, hence there is no cytoplasmic continuity in two neurons, such a place of contact between two neurons is called the synapse. It has been discovered that the ends of axons release minute quantities of neurohumoral substances e.g. Acetylcholine in cholinergic nerve fibres and nor-adrenaline in adrenergic fibres.
- Neuron. Largest cell in the body. Its long process (axon) is its integral part. It lacks centrioles.
- Name and Functions:
- Schwann Cells-Synthesises myelin sheath
- Nodes of Ranvier
- Ionic changes and consequent depolarization take place here in myelinated nerve fibres,
- Helps in saltatory conduction.
- Myelin Sheath—acts as an electrical insulator and thus prevents depolarization.
- Dendrite-receives impulses and passes them from one nerve cell to another.
- Nissl’s granules—help in protein synthesis (they are made up of ribosomes).
Types Of Animal Tissues NEET Biology
Nervous Tissue
NEET Biology Compound Histology
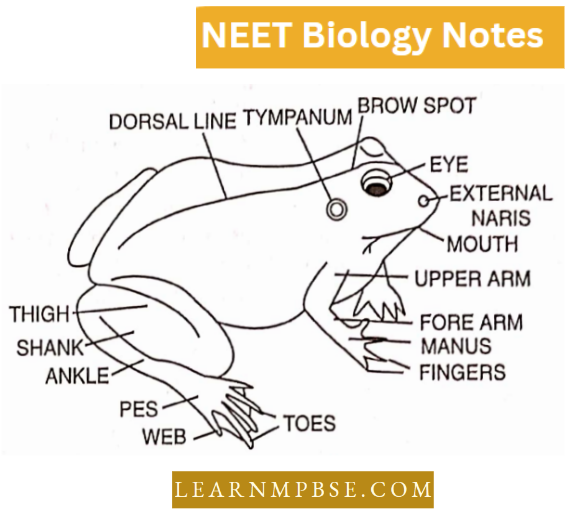
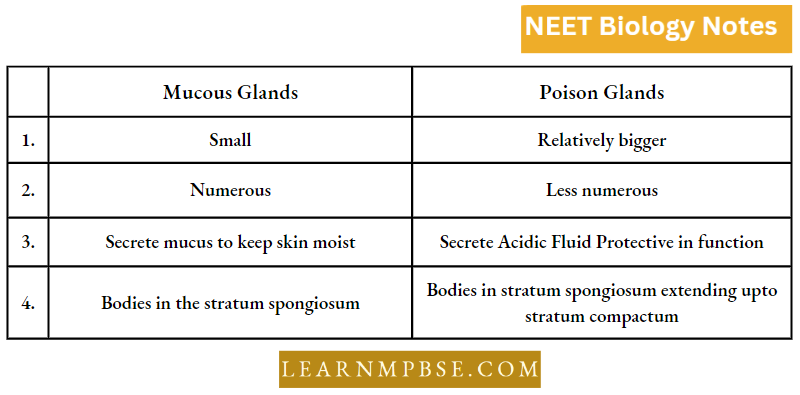
V.S. of Skin of Frog
The skin of a frog is thin, moist, smooth, loosely fitting, slimy, naked (without scales), darker on the dorsal and paler on the ventral side.
It is formed of two layers:
- Epidermis,
- Dermis
1. Epidermis. The epidermis, ectodermal in origin, is 5-6 layers in thickness. Stratum germinativum (or Stratum Malpighi) continuously produces cells which are pushed upwards and communication takes place.
- The stratum corneum is the upper layer of flattened often dead cells. Just beneath the epidermis chromatophores (pigment cells) are present, which impart colour to the skin.
- The outer, upper layer of the epidermis is the stratum corneum which consists of flat dead, keratinised cells.
2. Dennis. The dermis, mesodermal in origin and thicker than the epidermis, consists of two layers—stratum compactum and stratum spongiosum. Stratum spongiosum contains round bodies of mucus and poison glands. It also contains loose fibrous connective tissue and blood vessels.
- The underlying stratum compactum has many collagen fibres making it a dense and tough layer. The skin colour of vertebrates is almost entirely due to pigment-containing cells called chromatophores, located in the outer part of the dermis.
- Chromatophores are star-like in shape. According to their contents, they are divided into three types: Melanophores, containing melanin, Lipophores, containing red or yellow carotenoid pigments, and Guanophores with crystals of an organic substance, Guanine.
By concentrating the colour pigment granules in the centre of the cell or by spreading them throughout the cells, colour changes in skin are brought about. Chromatophores are capable of amoeboid movement and movement of a specific type of chromatophore also helps to change skin colour.
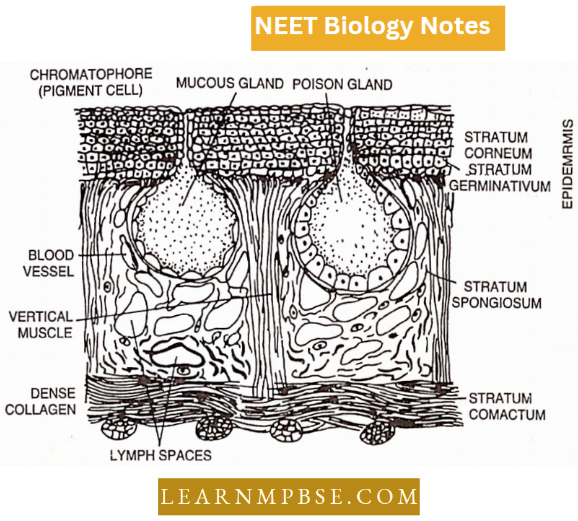
Glands in the skin of Frog :
V.S. Mammalian Skin
Epithelial Tissue Functions NEET Study Material
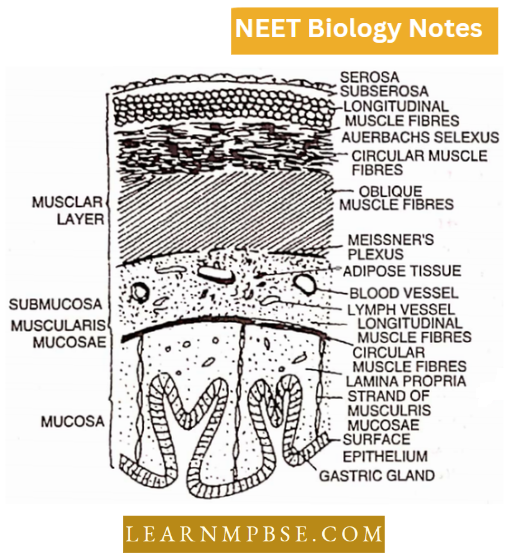
T.S. of Mammalian stomach shows the following regions (from periphery to inward) :
- The serous coat or visceral peritoneum or serosa is the outermost layer, continuous with the mesentery formed of flattened squamous epithelial cells. Inner to it lies a layer of connective tissue called sub-serosa which connects it with the muscular coat.
- Muscular coat or Tunica muscularis (Muscularis externa). It is a thicker layer formed of unstriped muscle fibres arranged in three layers, namely outer longitudinal, middle circular and inner oblique. The sympathetic mesenteric plexus or plexus of Auerbach lies between circular and longitudinal muscles.
- Sub-mucosa. It is a layer of loose connective tissue containing lymphocytes. leucocytes, mast cells, blood vessels and lymph vessels. It provides elasticity and stretching. A plexus of Meissner lies between the oblique muscles and the submucosa.
- The mucosa forms the innermost coat and is separated from the submucosa by muscularis mucosae. The middle layer is called lamina propria formed of connective tissue. Internally it is lined by simple columnar epithelial cells.
- The mucosa is folded into grooves and divided by grooves into gastric areas or gastric pits. In the columnar epithelium, three types of gastric glands are present, namely gastric or fundic, pyloric and cardiac glands.
- They are supported by a layer of connective tissue called lamina propria.
All these glands have three types of cells, i.e. chief cells or zymogen cells producing digestive enzymes, parietal or oxyntic cells producing HC1 and mucous cells producing mucus.
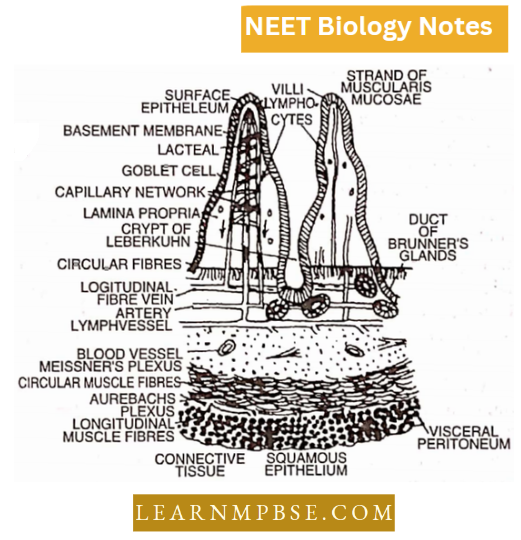
Histological differences between Stomach and Intestine
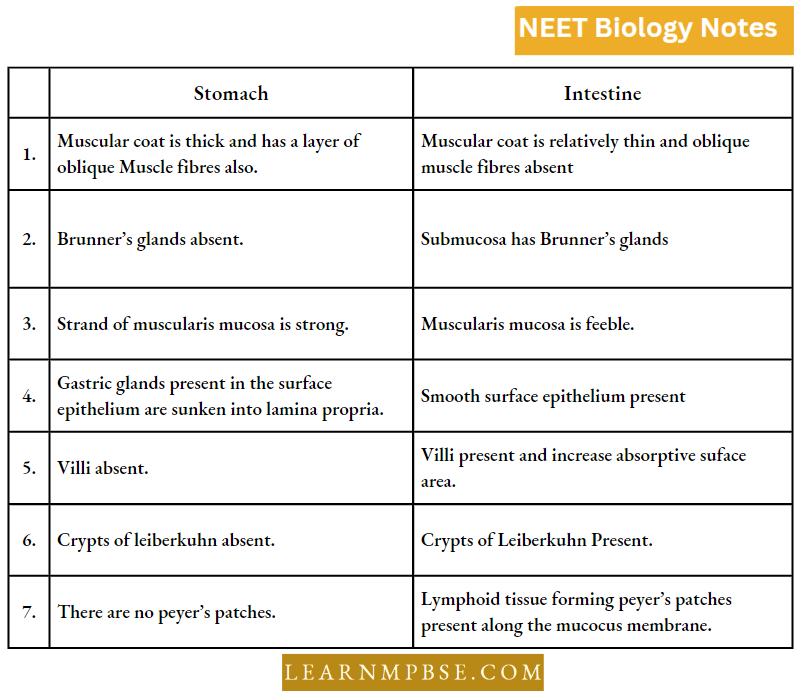
T.S. of Spleen
The spleen is a soft dark brown organ present on the left side of the abdominal cavity.
- It is highly vascular and covered by a visceral layer of peritoneum. A fibrous capsule formed of fibrous connective tissue surrounds it from all sides.
- From the capsule arise cylindrical or flattened projections into the substance of the spleen called trabeculae.
In the spaces surrounding the trabeculae, two lymphatic tissues are distinguished called red and white pulp.
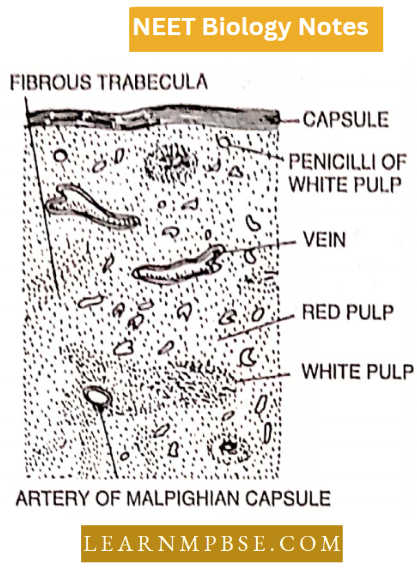
The red pulp consists of erythrocytes, blood capillaries and blood sinuses; while the white pulp consists of reticular fibres. The amount of red pulp is more than the white pulp.
The spleen removes die-disintegrated RBCs from the blood that pass into it and also acts as a storehouse of blood cells, even producing RBCs during the embryonic stage. The plasma cells of the spleen produce antibodies.
T.S. of Kidney
- An excretory organ covered by a fibrous sheath called a capsule shows the outer granular cortex region and inner striated medulla region in a vertical section. Three main types of tissues are found in the kidney i.e., blood capillaries, connective tissue and Kidney tubules or nephrons.
- Each kidney is made up of many tiny microscopic filters called nephrons or uriniferous tubules. Each nephron consists of a small cup-shaped structure called Bowman’s capsule lined by squamous epithelium, which along with a network of capillaries, and glomerulus, forms a malpighian body lying in the cortex.
- A tiny winding tubule lined by cuboidal epithelium with ciliated cells at places comes from each capsule differentiated into the proximal convoluted part, Loop of Henle and the distal convoluted part which opens into collecting tubules.
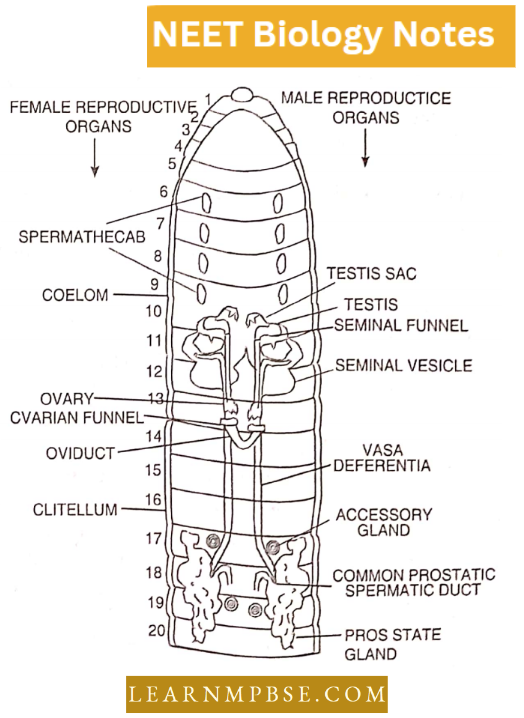
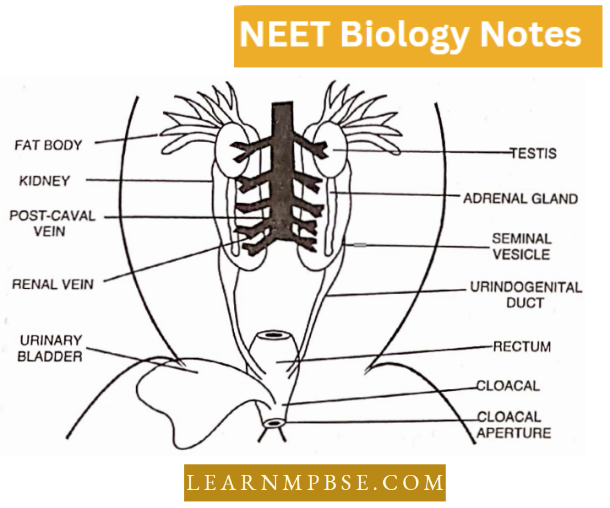
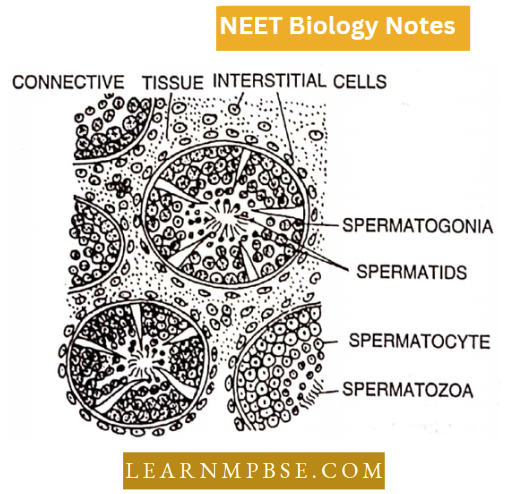
T.S. of Testis
A male gonad is composed of a large number of seminiferous tubules surrounded by connective tissue in which occur numerous cells called Interstitial cells or Leydig’s cells.
- The testis is covered by a layer of dense connective tissue called tunica albuginea. The seminiferous tubules are coiled structures lined by a layer of germinal epithelial cells.
- In between the germinal cells, certain large cells called Sertoli (nurse) cells are present. The germinal epithelial cells give rise to sperms.
They are in various stages of development like spermatogonia, primary spermatocytes, secondary spermatocytes and spermatids by a process known as spermatogenesis.
Epithelial Tissue Functions NEET Study Material
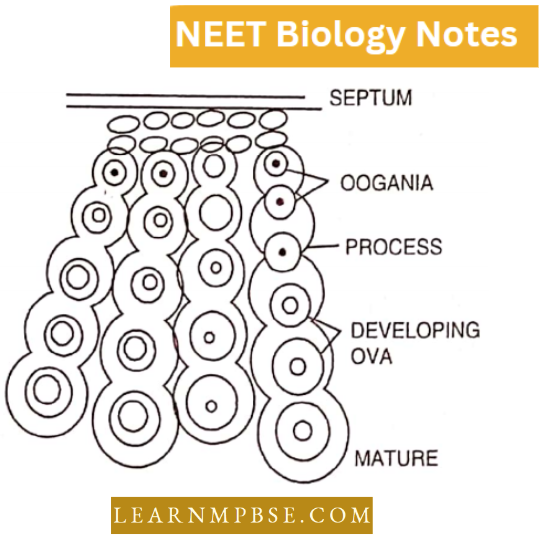
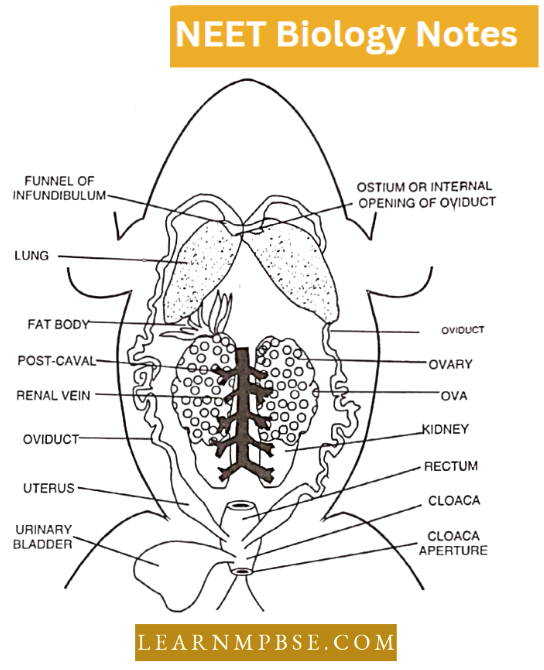
T.S. of Ovary
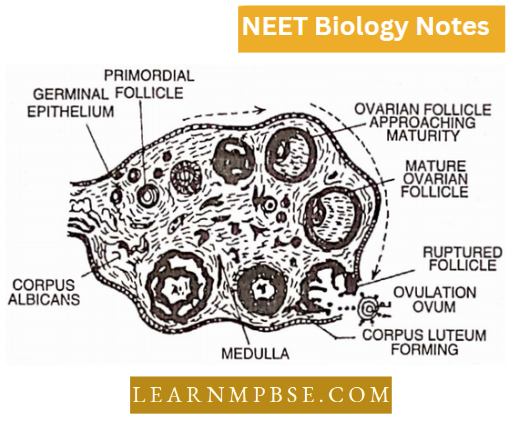
Its central part is called the stroma. It contains blood capillaries and nerve fibres. The outer part is called the cortex. A large number of Graafian follicles are embedded in the cortical layer.
- Each follicle is sac-shaped and contains a female germ cell. It develops from the germinal epithelial layer.
- In a sexually mature female the follicles are all at different stages of development and of different sizes giving rise to one ovum by the process known as oogenesis.
In the connective tissue is present corpus luteum formed at the site of ruptured Graafian follicle, which secretes a hormone called progesterone.
Histology of liver
The largest gland in the body is a dark red, spongy structure that is located under the dome of the diaphragm. It partially covers the stomach and duodenum, which is what maintains it in its proper position. The complete liver is enveloped by a fold of peritoneum.
- Inner to its connective tissue layer is a structure known as Glisson’s capsule. The liver is composed of numerous hepatic lobules in a histological sense.
- The liver cells, known as hepatocytes, are polyhedral and are arranged in cords or rows, which are in direct contact with blood capillaries and blood spaces or sinusoids.
- The Kupffer cells are phagocytic. The endothelium of the sinusoid is incomplete, and they are anchored to the wall. In the center of each hepatic lobule, there is an intra-tubular vein, and at its angles, there are portal canals.
The latter is enclosed in a capsule of loose connective tissue forming a perivascular fibrous capsule which is continuous with Glisson’s capsule. Each portal canal encloses branches of the hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein, lymph vessels and bile ducts.
- Henson’s line (H-zone). Light line or zone of dark band (A-band).
- Z-line (Membrane of Krause). The dark line is present in the centre of the I-band.
- Intercalated discs. The modified plasma membrane presents transversely as thick striation in cardiac muscle fibres and acts as a booster of a wave during cardiac muscle contraction.
- Schwann’s Sheath (Neurilemma). The thin tubular sheath around the neuraxis.
- Myelin or Medullarysheath. The thick sheath of white fatty tissue around the neuraxis is called myelin sheath and is broken at places to form Nodes of Ranvier.
Macrophages (Histiocyte or clasmocytes) These are phagocytic cells which feed upon bacteria, extracellular material and remains of the cell organelles.
- Mesenchymal cells. These cells retain the development potentialities of embryonic mesenchyme cells in the connective tissue of adults.
- Lymphocytes. These are the agranular leucocytes having a round nucleus and little cytoplasm. Their function is the protection of the body against diseases by ingesting the germs.
- Haemopoiesis. The formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow.
- Lymphopoiesis. The formation of lymphocytes.
- Ligament. Tough, somewhat elastic, yellow fibrous bands which connect bone with bone.
- Tendon. A cord-like structure consisting of parallel white fibres ensheathed by connective tissue which connects muscles with bone.
- Pseudounipolar neurons are found in the dorsal root ganglion of spinal nerves.
Ependyma is a single-layered epithelium that lines the central canal and ventricles of the spinal cord and brain respectively.
- Fibro-cartilage is found in pubic symphysis and intervertebral discs.
- Mast cells are present in the areolar tissue.
- Transitional epithelium lines the urinary bladder.
- Platelets are found in the mammalian blood.
- The endothelium is a layer of flat tesselated epithelial cells forming the lining of blood vessels.
- Volkman’s canals are present in the mammalian long bones.
- The perichondrium is an outer covering of cartilage formed of white fibrous connective tissue.
- Synaptic knobs. The ends of terminal arborization of the axon may be swollen to form synaptic knobs.
- Bone Marrow. Adipose tissue along with blood capillaries present in the marrow cavity of bone is called bone marrow and is a haemopoietic tissue.
Epithelial Tissue Functions NEET Study Material
Tunica adventin. A layer of loose yellow fibrous connective tissue present as sheets forming the outer coat of blood vessels is termed tunica adventin.
- Glisson’s capsule. It is the outer covering of the liver formed of connective tissue.
- Corpus luteum. Yellowish, glandular body formed in an empty Graafian follicle after the release of an egg and functions as a temporary endocrine gland during pregnancy.
- Sertoli cells. In the germinal epithelial layer of seminiferous tubules are present large pyramidal cells called Sertoli cells which nourish developing sperms.
- Kupffer cells. Large star-like phagocytic cells present in the lining of sinusoids of the liver and ingest worn-out thrombocytes.
- Glomerulus. A bunch of blood capillaries present in the cup-like cavity of Bowman’s capsule Is called glomerulus.
Malpighian corpuscle. Bowman’s capsule and glomerulus present at one end of the uriniferous tubule is called the malpighian corpuscle.
- Rugae are longitudinal folds of gastric mucosa visible in an empty stomach and allow expansion of the stomach.
- Kinocilia. Motile cilia (about 12- 15).tm long) arise from basal granules and are present on the cells lining the respiratory and genital tract. They undergo rhythmic contraction.
- Stereodlia. Non-motile elongated having a broad base and tapering tip and do not arise from basal granule. They form the lining of epididymis and vasa deferentia in the human body.
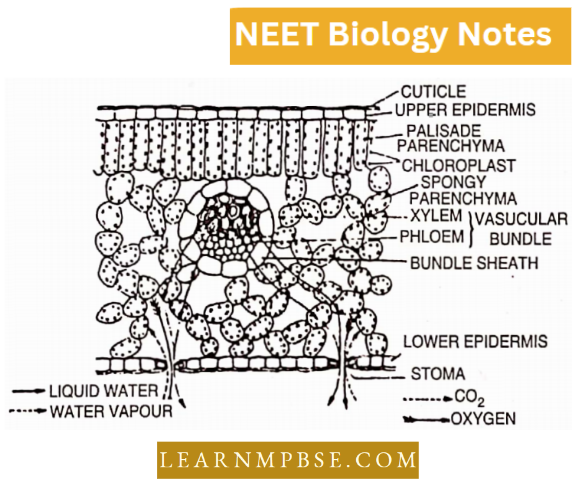
- Microvilli are very fine protoplasmic evaginations, visible with an electron microscope from the free surface of absorptive cells of the intestinal mucosa.
- Villi are finger-like projections of the intestinal mucosa and increase the absorptive surface area.
NEET Biology Animal Tissues Quanta To Memory
- The lining of neuronal is ciliated and known as ependyma.
- Scheneiderian membrane = Olfactory epithelium.
- In primates, lipochrome pigment gives a yellow colour to fat.
- Extremities of long bones have hyaline cartilage which acts as shock absorbers.
- Phosphogens are energy-rich compounds phosphocreatine which under rest conditions have 14-16 times more energy than ATP.
Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT). Christian. Medical College, Vellore, is India’s first BMT centre. The first BMT was done here in 1991 to treat thalassemia, a hereditary blood disorder.
- Osteoclasts. These are derived from osteoblasts and osteocytes, rich in acid phosphatase, and contain slightly basophilic cytoplasm. Osteoclasts destroy the bone.
- O. Hertwig introduced the term mesenchyme for the connective tissue.
- Cells vary in diameter from 7.5 m (RBC of man) to 85 mm. (ostrich egg).
- Bernard (1859) demonstrated the formation of glycogen by the liver.
- Nerve fibres are covered by special cells called Schwann cells.
- Chylomicrons: Minute fat globules which occur in blood after a meal rich in fat.
- Hacmoconia: Minute bits of disintegrated blood cells.
- Least regeneration power: nervous tissue
- Hacmoglobi nanometer: Instrument for recording the haemoglobin content of the blood.
- Haemocytometer: Instrument for counting erythrocytes,
- Chondroclasts: Cartilage-destroying cells.
- Marcello Mnlpighii: Father of microscopic anatomy.
- Jean Fresnel: Introduced the term Physiology.
Blood clotting in a test tube can be prevented by adding a little sodium oxalate or sodium nitrate.
Certain neutrophils in female mammals possess small spherical lobes attached to their nuclei by a stalk. This lobe is called a drumstick.
- The cells obtained by a smear from the oral mucous membrane of a normal female have been found to possess a small mass of deeply staining chromatin lying against the nuclear membrane. It is called Hnrr body (Barr-name of scientist). The Drumstick of Barr’s body represents an inactivated X-chromosome and is called sex chromatin.
- Elic Mctchnikoff. discovered phagocytosis in 1882, got the 1908 Nobel Prize for medicine and physiology, A Russian physiologist,
- Immature RBCs are called reticulocytes.
- Poikilocytosis: Multiplicity in distortion of the shape of RBCs due to a decrease in both the number and size of RBCs. It leads to microcytic anaemia.
- Normovolemia: Normal blood volume, while decreased blood volume is called hypovolemia and increased blood volume is called hypervolemia.
- Platelets. It occurs only in the mammalian blood.
The normal cholesterol level of human blood is 50-180 mg per 100 ml. of blood. High levels of cholesterol may lead to heart attack.
- Fibroblasts produce fibrous connective tissue. Volkman’s canals are canals through which blood vessels connect the periosteal vessels to the vessels of the Haversian canals.
- Ca+2 -ions are essential during blood coagulation for the activation of thrombin.
Epithelial Tissue Functions NEET Study Material
NEET Biology Animal Tissues Questions From Competitive Examinations
Question 1. Kupffer’s cells are:
- Hormone secreting
- Fat cells
- Mast cells
- Phagocytic.
Answer: 4. Phagocytic.
Question 2. Sebaceous glands secrete:
- Sweat
- Wax
- Water
- Mucus.
Answer: 2. Wax
Question 3. Mammalian skin is without:
- Sweat glands
- Sebaceous glands
- Mucous glands
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Mucous glands
Question 4. Used-up erythrocytes are broken down into:
- Liver
- Spleen
- Pancreas
- Thyroid.
Answer: 2. Spleen
Question 5. Bring out the matching pair:
- Saliva-Friction
- Sebum-Shock absorber
- Sweat-Thermoregulation
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Sweat-Thermoregulation
Connective Tissue Types And Functions NEET
Question 6. Match the types of animal tissues listed under column 1 with the location given under column 2; Choose the answer which gives the correct combination of the alphabets of the two columns.
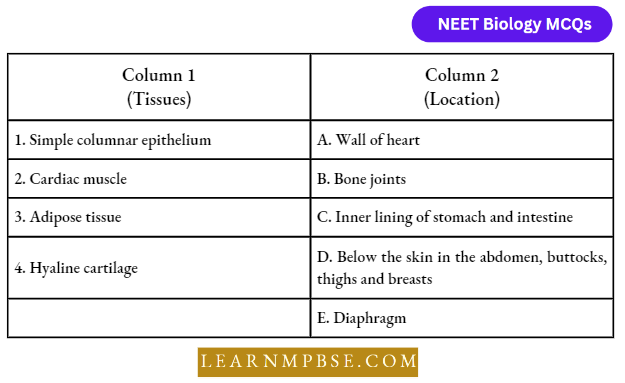
- 1-C, 2-A, 3-E, 4-D
- 1-A, 2-C, 3-D, 4-E
- 1-C, 2-E, 3-B, 4-D
- 1-C, 2-A, 3-D, 4-B
Answer: 4. 1-C, 2-A, 3-D, 4-B
Question 7. Match the term listed under column-1 with the structures when they occur given under column-2; Choose the answer which gives the correct combination of the alphabets of the two columns.
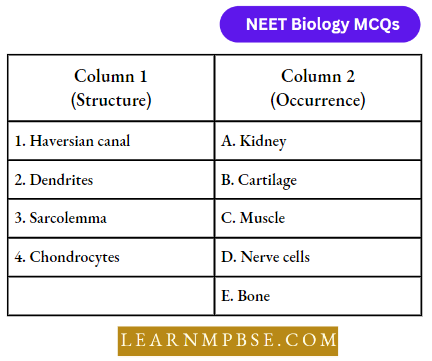
- 1-D, 2-E, 3-B, 4-C
- 1-E, 2-D, 3-C, 4-B
- 1-A, 2-C, 3-D, 4-E
- 1-B, 2-C, 3-D, 4-E.
Answer: 2. 1-E, 2-D, 3-C, 4-B
Question 8. Which cells do not form layers and remain structurally separate:
- Epithelial cells
- Muscle cells
- Nerve cells
- Gland cells.
Answer: 3. Nerve cells
Question 9. During an injury, the Nasal septum gets damaged and for its recovery which cartilage is preferred:
- Elastic cartilage
- Hyaline cartilage
- Calcified cartilage
- Fibrous cartilage age.
Answer: 2. Hyaline cartilage
Question 10. Term Tissue was given by:
- Bichat
- Milliken
- Maxwell
- Diroe.
Answer: 1. Bichat
Question 11. Tendons and ligaments are specialized types of:
- Nervous tissue
- Muscular tissue
- Epithelial tissue
- Fibrous connective tissue.
Answer: 4. Fibrous connective tissue.
Question 12. Adult R.B.C. is produced by:
- Thymus
- Yellow bone marrow
- Red bone marrow
- Heart.
Answer: 3. Red bone marrow
Connective Tissue Types And Functions NEET
Question 13. Stratum corneum is absent in:
- Fish
- Frog
- Birds
- Reptiles.
Answer: 1. Fish
Question 14. Match the correct pair:
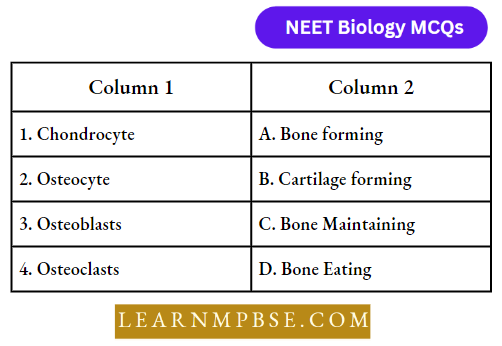
- D-B-A-C
- B-A-C-D
- B-D-C-A
- B-C-A-D
Answer: 4. B-C-A-D
Question 15. Epithelial cells arise from:
- Endoderm
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 16. The outer covering of non-myelinated neurons in the brain is:
- Neurilemma
- Axolemma
- Sacrolemma
- Oolema.
Answer: 1. Neurilemma
Question 17. Collagen is:
- Libros protein
- Fat
- Epithelial tissue
- Tight junction.
Answer: 1. Librous protein
Question 18. In mammals, melanocytes give protection from:
- Visible light
- Infrared rays
- X-rays
- Uv rays.
Answer: 4. Uv rays.
Question 19. In a neuron, Schwann cells occur in association with:
- Axon
- Soma
- Dendrite
- Axon hillock.
Answer: 1. Axon
Connective Tissue Types And Functions NEET
Question 20. Which one acts as a shock absorber when the tibia and femur come together:
- Ligament
- Cartilage
- Tendon
- Disc.
Answer: 2. Cartilage
Question 21. The lining layer of fallopian tubes, bronchi and bronchioles consists of:
- Squamous epithelium
- Ciliated epithelium
- Columnar epithelium
- Cubical epithelium.
Answer: 2. Ciliated epithelium
Question 22. Which is not the property of yellow fibres:
- Contain elastin
- Fewer in number
- Straight and branched
- Provide toughness and strength.
Answer: 4. Provide toughness and strength.
Question 23. Which one has abundant white fibres:
- Tendon
- Ligament
- Cartilage
- Bone.
Answer: 1. Tendon
Question 24. Volkman’s canals occur in:
- Cartilage
- Liver
- Bone
- Internal ear.
Answer: 3. Bone
Question 25. Epithelial cells of the intestine involved in food absorption have on their surface:
- Pinocytic vesicles
- Phagocytic vesicles
- Zymogen granules
- Microvilli.
Answer: 4. Microvilli.
Question 26. Abnormal fall in the total count of WBCs in the human blood is called:
- Anaemia
- Polycythemia
- Leucopenia
- Leukaemia.
Answer: 3. Leucopenia
Connective Tissue Types And Functions NEET
Question 27. Leucopenia is the condition where:
- Leucocyte decrease below 5000 per cubic mm of blood
- Bone marrow is destroyed
- The total number of lymphocytes decreases from 2% to 0.5%
- Leucocytes increase by about 6000.
Answer: 1. Leucocyte decrease below 5000 per cubic mm of blood
Question 28. Choose the odd pair out in the following:
- Areolar connective tissue-collagen
- Epithelium-keratin
- Neuron-melanin
- Muscle fibre-actin.
Answer: 3. Neuron-melanin
Question 29. Which of the following tissues originates exclusively from the ectoderm of the embryo?
- Muscular tissue
- Epithelial tissue
- Nervous tissue
- Connective tissue.
Answer: 3. Nervous tissue
Question 30. Which of the following structures are derivatives of the endoderm?
- Alimentary canal and respiratory structures
- Muscles and blood
- Excretory and reproductive structures
- Skin and nerve cord.
Answer: 1. Alimentary canal and respiratory structures
Question 31. Match the items in column 1 with column 2 and choose the correct answer given below:
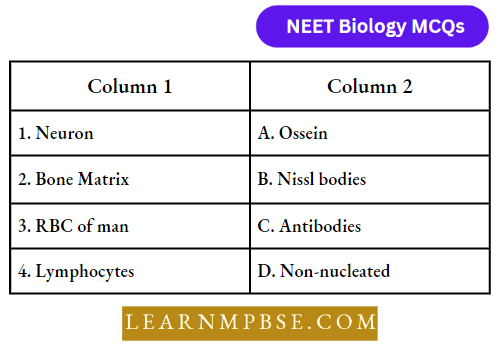
- 1-D, 2-B, 3-C, 4-A
- l-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
- 1-D, 2-B, 3-A, 4-C
- 1-B, 2-A, 3-D, 4-C.
Answer: 4. 1-B, 2-A, 3-D, 4-C.
Question 32. Which of the following statements is wrong?
- Leucocytes disintegrate in the spleen and liver.
- RBC, WBC and blood platelets are produced by bone marrow.
- Neutrophils bring about the destruction and detoxification of toxins of protein origin.
- The important function of lymphocytes is to produce antibodies.
- (l) and (2) only
- (l) and (4) only
- (1) and (2) only
- (2) and (3) only.
Answer: 3. (1) and (2) only
Question 33. The progenitors that are formed in bone marrow and differentiate elsewhere are:
- Pre-nk cell
- Pre-erythroblast
- Pre-t cell
- Myeloblast.
Answer: 3. Pre-t cell
Muscular Tissue Structure NEET Exam
Question 34. The hump of a camel is made up of which of the following tissues?
- Areolar tissue
- Adipose tissue
- Epithelial tissue
- Muscular tissue.
Answer: 2. Adipose tissue
Question 35. The erythrocyte maturing factor is:
- Folic acid
- Cyanocobalamin
- Vitamin B2
- Vitamin c.
Answer: 1. Folic acid
Question 36. Fat is present in which part of a neuron:
- Cyton
- Node of Ranvier
- Dendron
- Axon.
Answer: 4. Axon.
Question 37. Heparin is synthesised in:
- Liver
- Kidney
- Saliva
- Pancreas.
Answer: 1. Liver
Question 38. Thousand of year-old mummies are still in their condition as they were before due to the non-destruction of:
- Yellow elastin fibres
- White elastin fibres
- Collagen fibres
- Veins.
Answer: 1. Yellow elastin fibres
Question 39. Nerve cells do not divide because they do not have:
- Nucleus
- Centrosome
- Golgi body
- Mitochondria.
Answer: 2. Centrosome
Question 40. Which of the following is phagocytic?
- Monocyte
- R.B.C
- Eosinophil
- Basophil.
Answer: 1. Monocyte
Question 41. Areolar connective tissue joins:
- Integument with muscles
- Bones with muscles
- Bones with bones
- Fat body with muscles.
Answer: 1. Integument with muscles
Muscular Tissue Structure NEET Exam
Question 42. Mast cells secrete:
- Myoglobin
- Histamine
- Haemoglobin
- Hippurin.
Answer: 2. Histamine
Question 43. People living at sea level have around 5 million RBC per cubic millimetre of their blood whereas those living at an altitude of 5400 metres have around 8 million. This is because at high altitudes:
- Atmospheric O2 level is less and hence more RBCs are needed to absorb the required amount of O2 to survive
- There is more UV radiation which enhances RBC production
- People eat more nutritive food, therefore more RBCs are formed
- People get pollution-free air to breathe and more oxygen is available.
Answer: 1. Atmospheric O2 level is less and hence more RBCs are needed to absorb the required amount of O2 to survive
Question 44. Bowman’s glands are found in:
- Cortical nephrons only
- Juxtamedullary nephrons
- Olfactory epithelium
- External auditory canal.
Answer: 3. Olfactory epithelium
Question 45. The type of epithelial cells which line the inner surface of the fallopian tube, bronchioles and small bronchi are known as:
- Squamous epithelium
- Columnar epithelium
- Ciliated epithelium
- Cubical epithelium.
Answer: 3. Ciliated epithelium
Question 46. Match the following simple epithelial tissues in column 1 with their occurrence in column 2 and choose the correct combination from the options given.

- 1-A, 2-B, 3-D, 4-C, 5-E
- 1-E, 2-D, 3-B, 4-A, 5-C
- 1-D, 2-E, 3-A, 4-B, 5-C
- 1-D, 2-C, 3-A, 4-B, 5-E
- 1-B, 2-C, 3-A, 4-E, 5-B.
Answer: 5. 1-B, 2-C, 3-A, 4-E, 5-B.
Question 47. In which one of the following preparations are you likely to come across cell junctions most frequently?
- Thrombocytes
- Tendon
- Hyaline cartilage
- Ciliated epithelium.
Answer: 4. Ciliated epithelium.
Question 48. Which one of the following pairs of structures distinguishes a nerve cell from other types of cells?
- Vacuoles and fibres
- Flagellum and medullary sheath
- Nucleus and mitochondria
- Perikaryon and dendrites.
Answer: 4. Perikaryon and dendrites.
Question 49. A drop of each of the following is placed separately on four slides. Which of them will not coagulate?
- Blood serum
- Blood plasma
- Whole blood from the pulmonary vein
- Sample from the thoracic duct of the lymphatic system.
Answer: 1. Blood serum
Animal Tissues NEET Notes
Question 50. What is the correct sequence of thickness of muscle layers in the stomach of human beings?
- Circular → oblique → longitudinal
- Oblique → longitudinal → circular
- Longitudinal → circular → oblique
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Longitudinal → circular → oblique
Question 51. The dendrite carries impulses:
- Across the body
- Towards the cyton
- Away from the cyton
- From one neuron to another.
Answer: 2. Towards the cyton
Question 52. Adipocytes are mainly found in:
- Bonos
- Nerves
- Cartilages
- Connective tissues.
Answer: 4. Connective tissues.
Question 53. The main difference between white and yellow fibre is of:
- Protein
- Colour of fibres
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these.
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Question 54. In a myelinated neuron, two adjacent myelin sheaths are separated by gaps called:
- Nodes of Ranvier
- Synaptic cleft
- Schwann cells
- Synaptic know
- Neural plate
Answer: 1. Nodes of Ranvier
Question 55. Histamine and heparin are secreted by
- Monocytes
- Neutrophils
- Eosinophils
- Lymphocytes
- Basophils
Answer: 5. Basophils
Question 56. Which type of white blood cells are concerned with the release of histamine and the natural anticoagulant heparin?
- Basophils
- Monocyte
- Neutrophils
- Eosinophils.
Answer: 1. Basophils
Question 57. The most active phagocytic white blood cells are:
- Neutrophils and monocytes
- Neutrophils and eosinophils
- Eosinophils and lymphocytes
- Lymphocytes and macrophages
Answer: 1. Neutrophils and monocytes
Question 58. The haemoglobin of a human foetus:
- Has only two protein subunits instead of four
- Has a lower affinity for oxygen than that of an adult
- Its affinity for oxygen is the same as that of an adult
- Has a higher affinity for oxygen than that of an adult.
Answer: 4. Has a higher affinity for oxygen than that of an adult.
Question 59. The ciliated columnar epithelial cells in humans are known to occur in:
- Eustachian tube and stomach lining
- Bronchioles and fallopian tubes
- Bile duct and oesophagus
- Fallopian tubes and urethra.
Answer: 2. Bronchioles and fallopian tubes
Animal Tissues NEET Notes
Question 60. Compared to those of humans the erythrocytes in frogs are:
- Nucleated and with haemoglobin
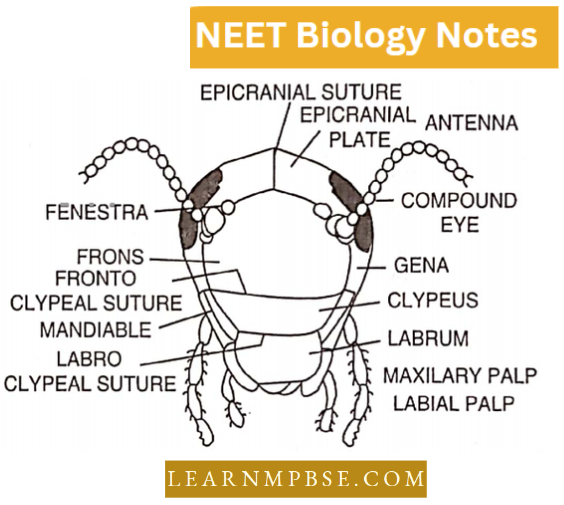
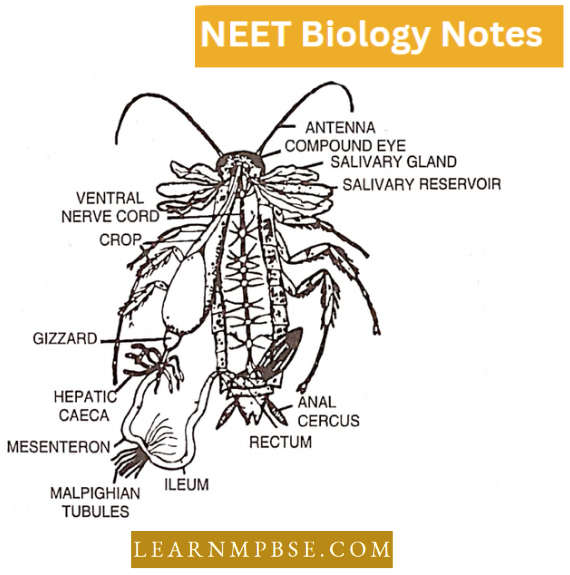
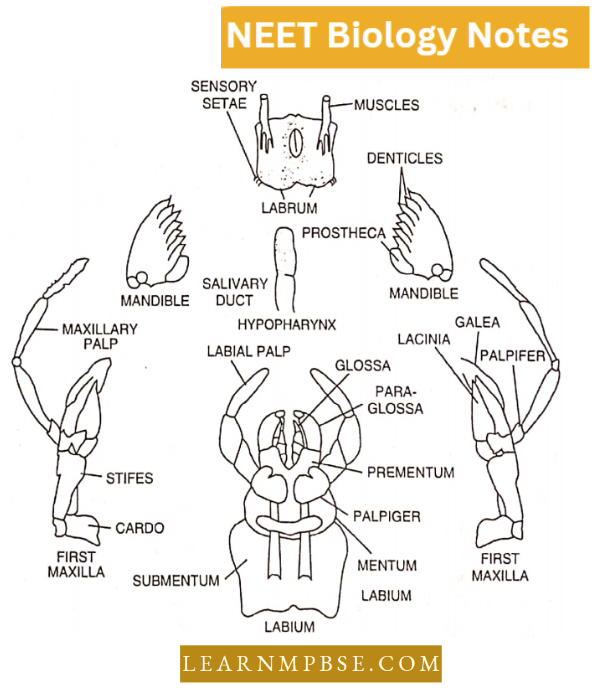
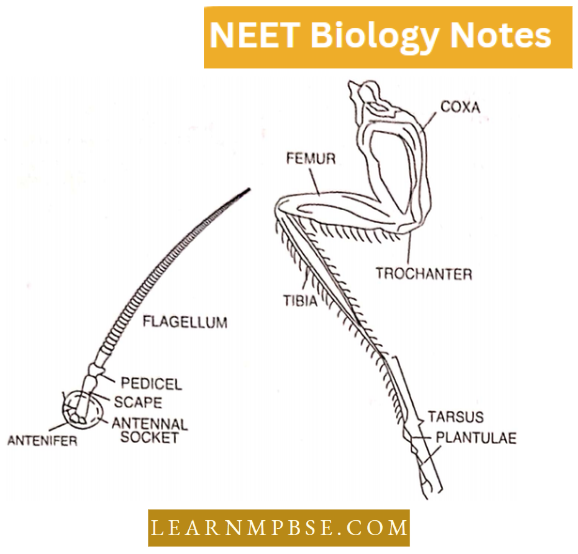
- Very much smaller and fewer
- Nucleated and without haemoglobin
- Without a nucleus but with haemoglobin.
Answer: 1. Nucleated and with haemoglobin
Question 61. What external changes are visible after the last moult of a cockroach nymph?
- Anal cerci develop
- Both forewings and hindwings develop
- Labium develops
- Mandibles become harder
Answer: 2. Both forewings and hind wings develop
Question 62. Rearrange the following zones as seen in the root in the vertical section and choose the correct option.
- Root hair zone
- Zone of meristems
- Rootcap zone
- Zone of maturation
- Zone of elongation.
- 3, 2, 5, 1, 4
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
- 4, 5, 1, 3, 2
- 5, 4, 3, 2, 1.
Answer: 1. 3, 2, 5, 1, 4
Question 63. In an inflorescence where flowers are borne laterally in an acropetal succession, the position of the youngest floral bud shall be:
- Proximal
- Distal
- Intercalary
- Anywhere.
Answer: 2. Distal
Question 64. The mature seeds of plants such as gram and peas possess no endosperm, because:
- These plants are not angiosperms
- There is no double fertilization in them
- Endosperm is not located in them
- Endosperm gets used up by the developing embryo during seed development.
Answer: 4. Endosperm gets used up by the developing embryo during seed development.
Question 65. Roots developed from parts of the plant other than radicle are called:
- Taproots
- Fibrous roots
- Adventitious roots
- Nodular roots.
Answer: 3. Adventitious roots
Question 66. Venation is a term used to describe the pattern of arrangement of:
- Floral organs
- Flower in inflorescence
- Veins and veinlets in a lamina
- All of them.
Answer: 3. Veins and veinlets in a lamina
Question 67. Endosperm, a product of double fertilization in angiosperms is absent in the seeds of:
- Gram
- Orchids
- Maize
- Castor.
Answer: 2. Orchids
Question 68. Many pulses of daily use belong to one of the families below:
- Solanaceae
- Fabaceae
- Liliaceae
- Poaceae.
Answer: 2. Fabaceae
Types Of Animal Tissues NEET Biology
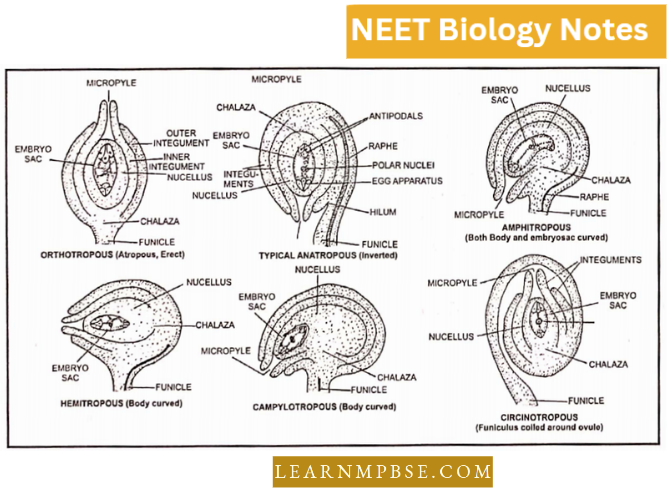
Question 69. The placenta is attached to the developing seed near the:
- Testa
- Hilum
- Micropyle
- Chalaza.
Answer: 4. Chalaza.
Question 70. Which of the following plants is used to extract the blue dye?
- Trifulium
- Indigofera
- Lupin
- Cassia.
Answer 2. Indigofera
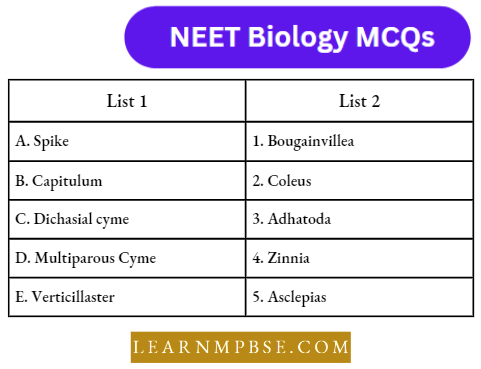
Question 71. Match the following and choose the correct option:
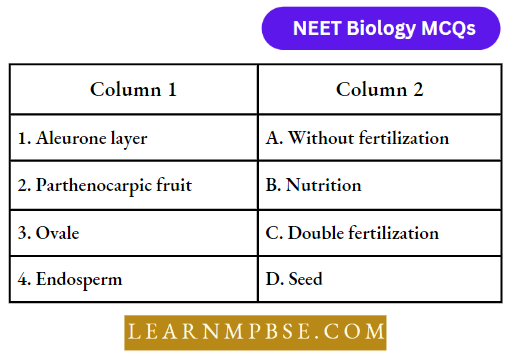
- 1-(A), 2-(B), 3-(C), 4-(D)
- 1-(B), 2-(A), 3-(D), 4-(C)
- 1-(D), 2-(B), 3-(A), 4-(C)
- 1-(B), 2-(D), 3-(A), 4-(C).
Answer: 2. 1-(B), 2-(A), 3-(D), 4-(C)
Question 72. A transverse section of stem is stained first with safranin and then with fast green following the usual schedule of double staining for the preparation of a permanent slide. What would be the colour of the stained xylem and phloem?
- Red and green
- Green and red
- Orange and yellow
- Purple and orange.
Answer: 1. Red and green
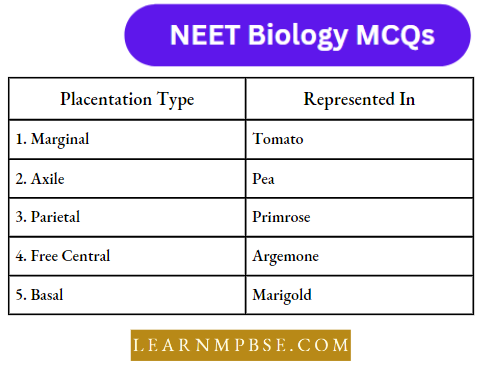
Question 73. Match the following and choose the correct option from below:
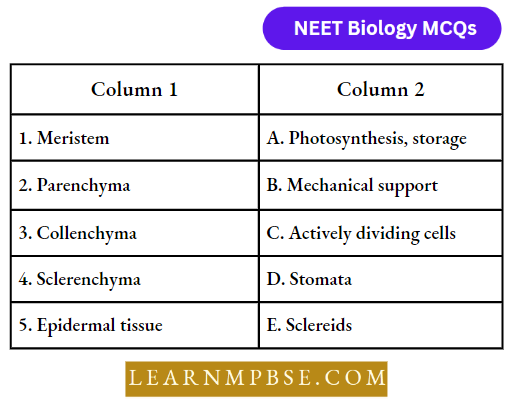
- 1-A, 2-C, 3-E 4-B, 5-D
- 1-C, 2-A, 3-B 4-E, 5-D
- 1-B, 2-D, 3-E 4-A, 5-C
- 1-E, 2-D, 3-C 4-B, 5-A.
Answer: 2. 1-C, 2-A, 3-B 4-E, 5-D
Question 74. Match the following and choose the correct option from below:
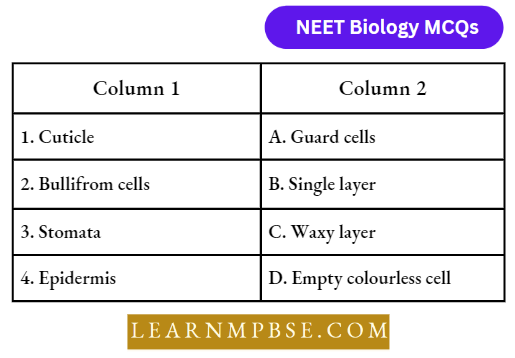
- 1-C, 2-D, 3-A, 4-B,
- 1-A, 2-B, 3-C, 4-D,
- 1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A,
- 1-C, 2-B, 3-A, 4-D.
Answer: 1. 1-C, 2-D, 3-A, 4-B,
Question 75. Identify the tissue system from among the following:
- Parenchyma
- Xylem
- Epidermis
- Phloem.
Answer: 1. Parenchyma
Types Of Animal Tissues NEET Biology
Question 76. Cells of this tissue are living and show angular wall thickening. They also provide mechanical support. The tissue is:
- Xylem
- Sclerenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Epidermis
Answer: 3. Collenchyma
Question 77. Epiblema of roots is equivalent to:
- Pericycle
- Endodermis
- Epidermis
- Stele.
Answer: 3. Epidermis
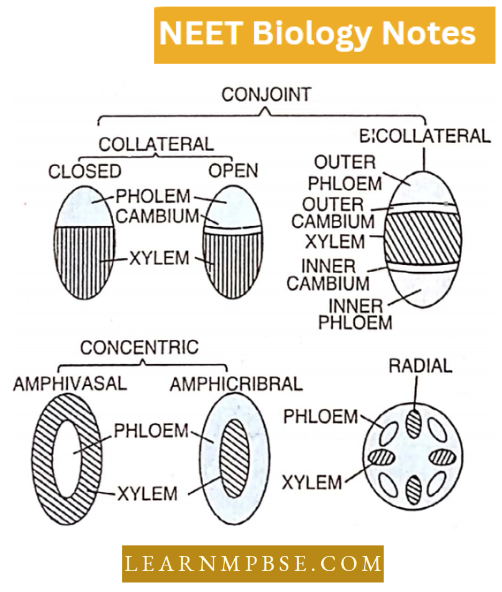
Question 78. A conjoint and open vascular bundle will be observed in the transverse section of:
- Monocot root
- Monocot stem
- Dicot root
- Dicot stems.
Answer: 4. Dicot stem.
Question 79. Interfascicular cambium and cork cambium are formed due to:
- Cell division
- Cell differentiation
- Cell dedifferentiation
- Differentiation.
Answer: 1. Cell division
Question 80. Phellogen and phellem respectively denote:
- Cork and cork cambium
- Cork cambium and cork
- Secondary eofiex and cork
- Cork and secondary cortex.
Answer: 2. Cork cambium and cork
Question 81. In which of the following pairs of parts of a flowering plant is the epidermis absent?
- Root tip and shoot tip
- Shoot bud and floral bud
- Ovule and seed
- Petiole and pedicel.
Answer: 1. Root tip and shoot tip
Question 82. How many shoot apical meristems are likely to be present in a twig of a plant possessing 4 branches and 26 leaves?
- 26
- 1
- 5
- 30
- 4.
Answer: 3. 5
Question 83. A piece of wood having no vessels (trachea) must belong to:
- Teak
- Mango
- Pine
- Palm.
Answer: 3. Pine
Epithelial Tissue Functions NEET Study Material
Question 84. A plant tissue, when stained, showed the presence of hemicellulose and pectin in the cell wall of its cells. The tissue represents.
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
- Xylem
- Meristem.
Answer: 1. Collenchyma
Question 85. Fibres are likely to be absent in:
- Secondary phloem
- Secondary xylem
- Primary phloem
- Leaves
Answer: 4. Leaves
Question 86. When we peel the skin of a potato tuber, we remove:
- Periderm
- Epidermis
- Cuticle
- Sapwood.
Answer: 1. Periderm
Question 87. A vessel-less piece of stem possessing prominent sieve tubes would belong to the:
- Pinus
- Eucalyptus
- Crass
- Trochodendron
Answer: 4. Trochodendron
Question 88. Which one of the following cell types always divides by anticlinal cell division?
- Fusiform initial cells
- Root cap
- Protoderm
- Phellogen
Answer: 4. Phellogen
Question 89. What is the fate of the primary xylem in a dicot root showing extensive secondary growth?
- It is retained in the centre of the axis
- It gets crushed
- May or may not get crushed
- It gets surrounded by primary phloem.
Answer: 1. It is retained in the centre of the axis
Question 90. Which one of the following types of cells is involved in making the inner walls of large blood vessels?
- Columnar epithelium
- Ciliated
- Squamous epithelium
- Stratified epithelium.
Answer: 3. Squamous epithelium
Question 91. To which one of the following categories does adipose tissue belong?
- Epithelial
- Connective
- Neural
- Muscular.
Answer: 2. Connective
Question 92. Which one of the following is not a connective tissue?
- Bone
- Ligament
- Blood
- Muscles.
Answer: 4. Muscles.
Question 93. The clitellum is a distinct part of the body of an earthworm, it is found in?
- Segments 13 – 14 – 15
- Segments 14 -15 – 16
- Segments 15 – 16 – 11
- Segments 72 – 13 – 14.
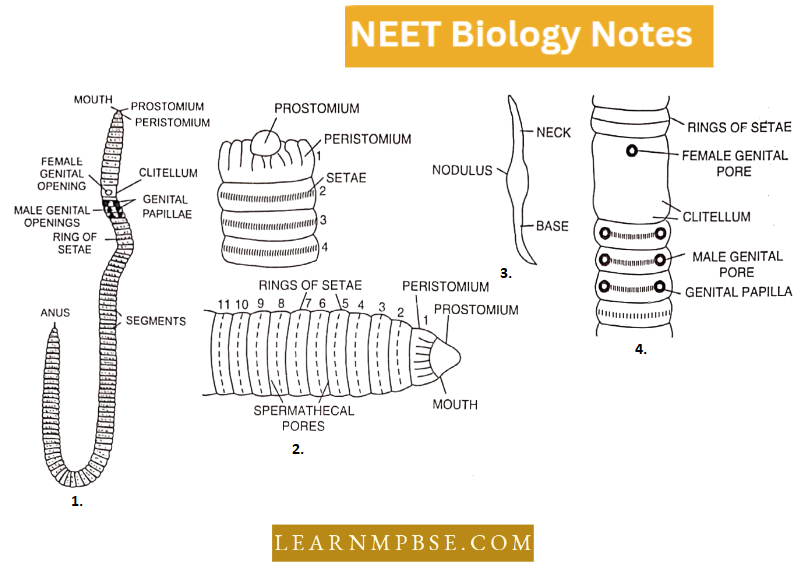
Answer: 2. Segments 14 -15 – 16
Question 94. Setae help in locomotion in the earthworm but are not uniformly present in all the segments. Select among the following that represents setae.
- Peristomium
- Anal segment
- Clitellar segment
- 20th – 22nd segment
Answer: 4. 20th – 22nd segment
Epithelial Tissue Functions NEET Study Material
Question 95. Which one of the following statements is true for cockroaches?
- The number of ovarioles in each ovary is ten
- The larval stage is called the caterpillar
- Anal styles are absent in females
- They are ammonotelic
Answer: 3. Anal styles are absent in females
Question 96. Match the following and choose the correct option:
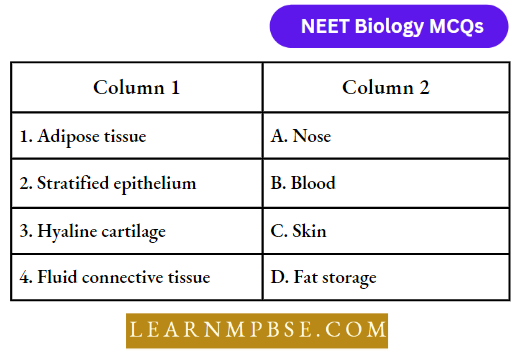
- 1-A, 2-B, 3-C, 4-D
- 1-D,, 2-C, 3-A, 4-B
- 1-C, 2-A, 3-D, 4-B
- 1-B, 2-A, 3-D, 4-C.
Answer: 2. 1-D,, 2-C, 3-A, 4-B
Question 97. Match the following and choose the correct answer:
- 1-B, 2-C, 3-D, 4-A
- 1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A
- 1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-A
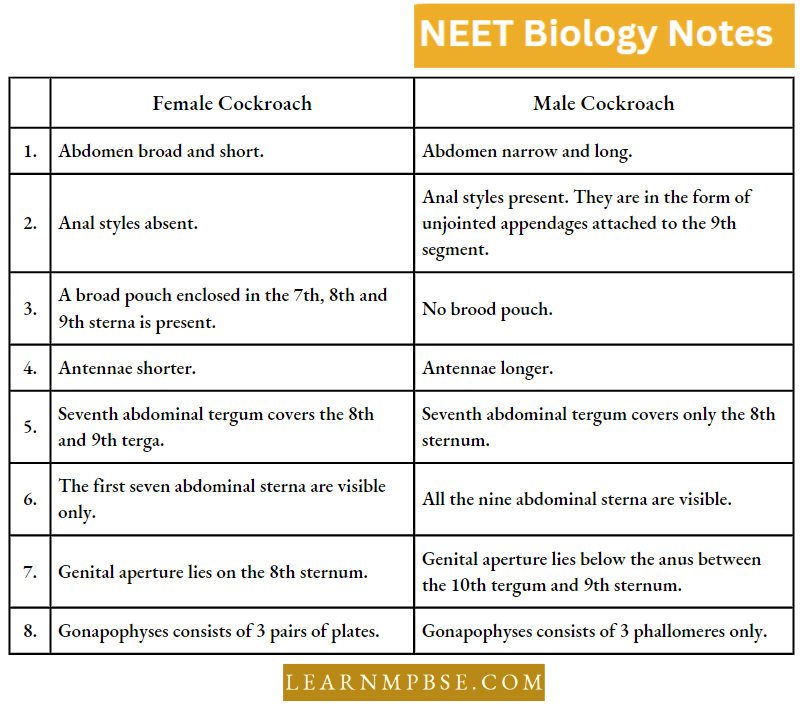
- 1-B, 2-D, 3-C, 4-A.
Answer: 1. 1-B, 2-C, 3-D, 4-A
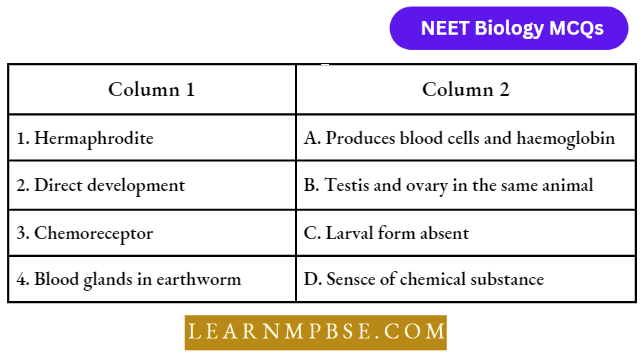
Question 98. Match the following concerning Cockroach and choose the correct option:
- 1-C, 2-D, 3-B, 4-A
- 1-D, 2-C, 3-B, 4-A
- 1-D, 2-B, 3-C, 4-A
- 1-B, 2-D, 3-C, 4-A.
Answer: 2. 1-D, 2-C, 3-B, 4-A
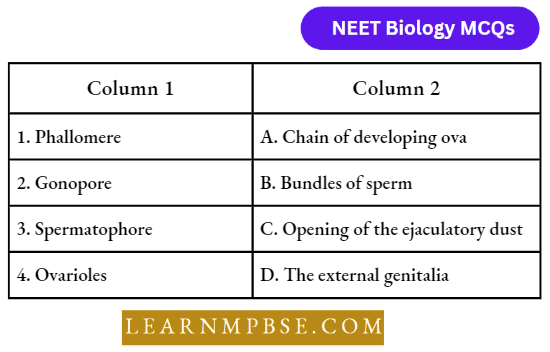
Question 99. Match the following and choose the correct answer:
- 1-C, 2-A, 3-B, 4-D
- 1-B, 2-A, 3-D, 4-C
- 1-C, 2-D, 3-B, 4-A
- 1-C, 2-A, 3-D, 4-B.
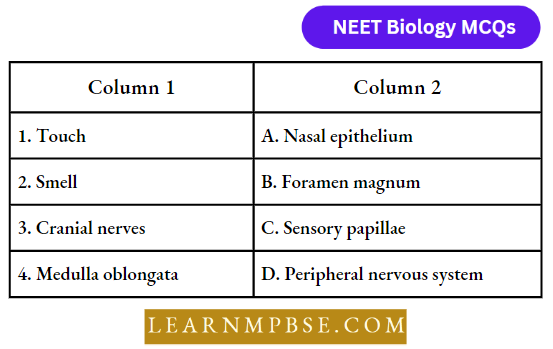
Answer: 4. 1-C, 2-A, 3-D, 4-B.
Question 100. The swollen root of the Radish is made of two parts:
- Stem and epicotyl
- Primary root and hypocotyl
- Primary root and epicotyl
- Secondary root and primary root.
Answer: 2. Primary root and hypocotyl
Question 101. Adventitious storage roots are found in:
- Canot and radish
- Potato and asparagus
- Asparagus and sweet potato
- Dahlia and sugarbeet.
Answer: 3. Asparagus and sweet potato
Connective Tissue Types And Functions NEET
Question 102. Vegetative propagation in ginger takes place by:
- Sucker
- Buds
- Rhizome
- Stem.
Answer: 3. Rhizome
Question 103. In groundnut. the root is:
- Nodulated
- Napiform
- Epiphytic
- Photosynthetic.
Answer: 1. Nodulated
Question 104. The underground storage structure in Gladiolus is:
- Corm
- Bulb
- Rhizome
- Stem tuber.
Answer: 1. Corm
Question 105. Extra-axillary bud is present in:
- Duranta
- Dentaria
- Zizyphus
- Cucurbita.
Answer: 4. Cucurbita.
Question 106. Buds typically are found:
- At the tips of branches and roots
- At the tips of branches and the bases of leaves
- Along roots and at the bases of leaves
- Only based on leaves.
Answer: 2. At the tips of branches and the bases of leaves
Question 107. Banana possesses:
- Unbranched stem
- Pseudobulb
- Pseudostem
- Largest bud.
Answer: 3. Pseudostem
Question 108. Branched rootstock rhizome occurs in:
- Saccharum
- Canna
- Tunneric
- Banana.
Answer: 4. Banana.
Question 109. The primary function of the stern is:
- To bear and hold out the leaves
- To anchor the plant in the soil
- To absorb water and mineral salts from the soil
- To help the vegetative reproduction.
Answer: 1. To bear and hold out the leaves
Question 110. In autumn. leaf fall occurs because:
- Leaves do not remain green
- Leaves become very heavy
- An abscission layer formed at the base of the petiole
- Of low temperature.
Answer: 3. Of an abscission layer formed at the base of the petiole
Question 111. The stipules are modified into tendrils in:
- Smilax
- Cucurbita
- Gloriosa
- Clematis.
Answer: 1. Smilax
Question 112. The Medulla part of the adrenal gland is made of:
- Ectoderm
- Endoderm
- Mesoderm
- Both ectoderm and mesoderm.
Answer: 1. Ectoderm
Question 113. Match the types of the animal tissues under colour 1 with the parts or organs in which they occur, given under column 2; choose the answer which gives the correct combination of the alphabets of the two columns:
- (1) = E, (2) = D, (3) = A, (4) = C
- (1) = E, (2) = A, (3) = D, (4) = B
- (1) = B, (2) = D, (3) = A, (4) = C
- (1) = B, (2) = A, (3) = D, (4) = C
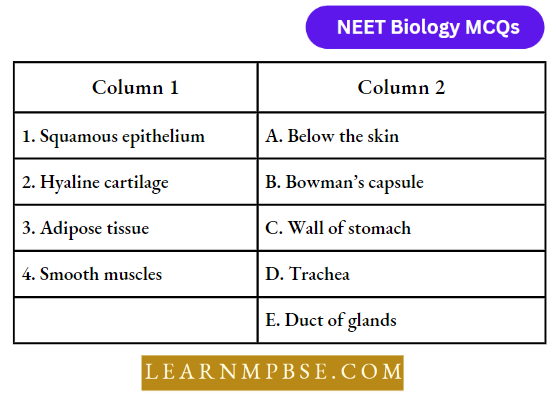
Answer: 3. (1) = B, (2) = D, (3) = A, (4) = C
Question 114. Cardiac muscles are of the type:
- Myofibrils are large and distinct
- Striped, skeletal muscles
- Elongated, spindle shape with tapering ends
- Long, cylindrical and branched to form a network.
Answer: 4. Long, cylindrical and branched to form a network.
Question 115. Tracheal rings are made of which type of cartilage:
- Elastic cartilage
- Hyaline cartilage
- Fibrous cartilage
- Calcified cartilage.
Answer: 2. Hyaline cartilage
Question 116. During muscular contraction:
- ATP is formed
- GTP is broken down
- ATP is broken down
- None of the above
Answer: 3. ATP is broken down
Question 117. Patella is associated with:
- Knee
- Neck
- Wrist
- Elbow.
Answer: 1. Knee
Question 118. Ligaments and tendons are correct for:
- Muscular tissue
- Connective tissue
- Epithelial tissue
- Skeletal tissue
Answer: 2. Connective tissue
Question 119. Where would you find mast cells:
- Yellow fibrous tissue
- White librous tisstre
- Areolar tissue
- Adipose tissue.
Answer: 3. Areolar tissue
Question 120. In the embryonic stage R.B.C. der, rips in:
- Liver and pancreas
- Spleen and kidney
- Liver and spleen
- Liver and kidney.
Answer: 3. Liver and spleen
Question 121. Squamous epithelial cells are found in:
- Bone
- Stronach
- Blood vessels
- Testis.
Answer: 3. Blood vessels