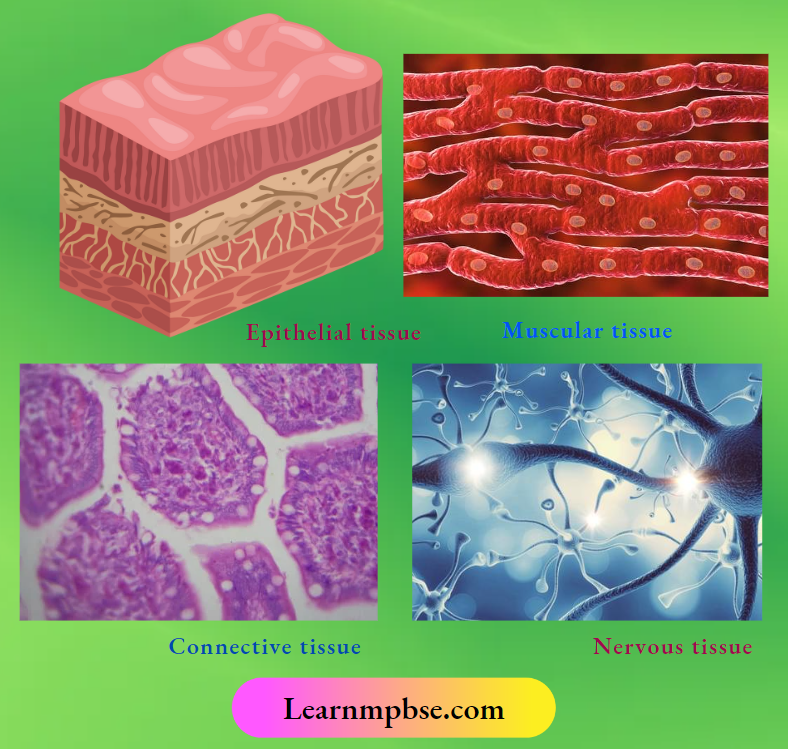
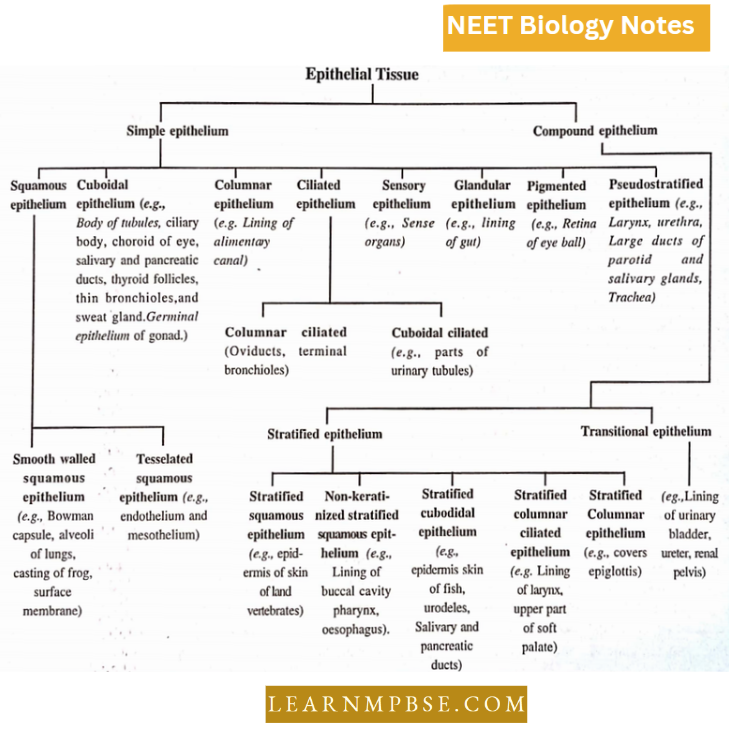
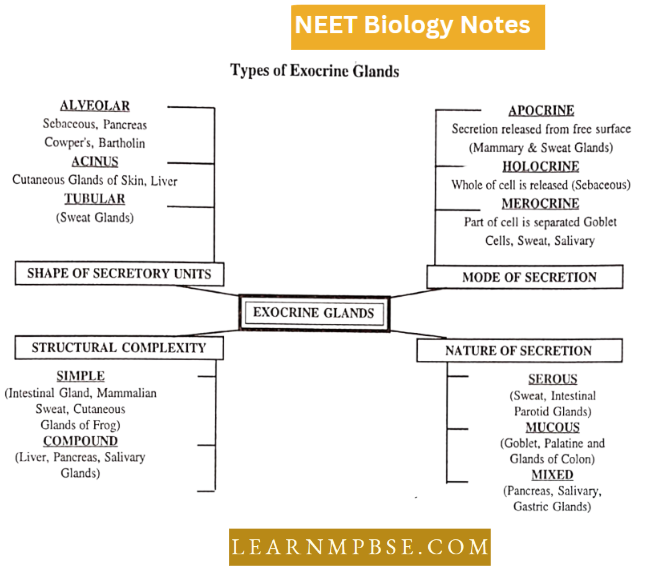
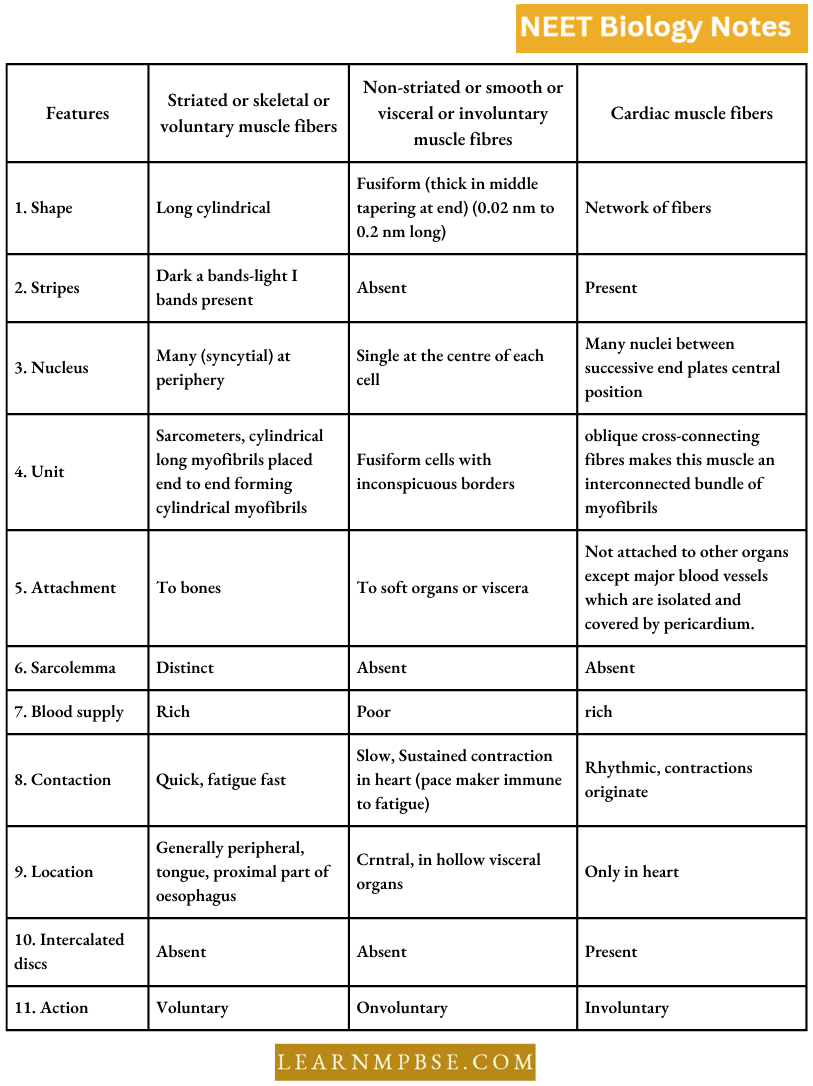
NEET Biology Ecosystem
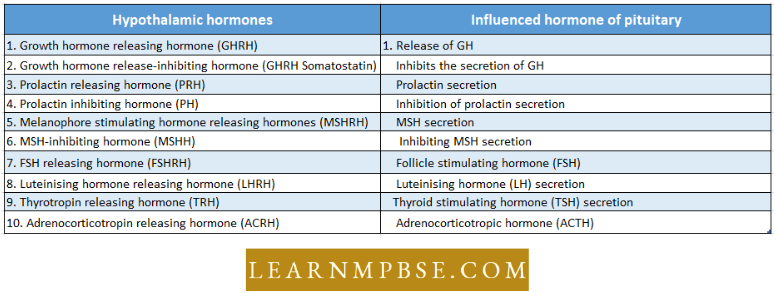
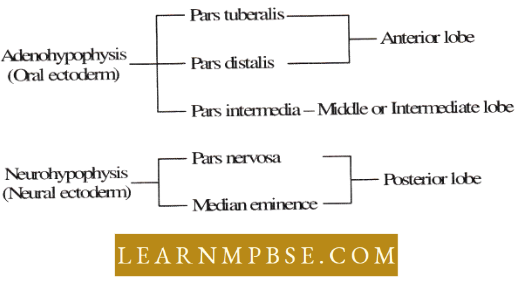
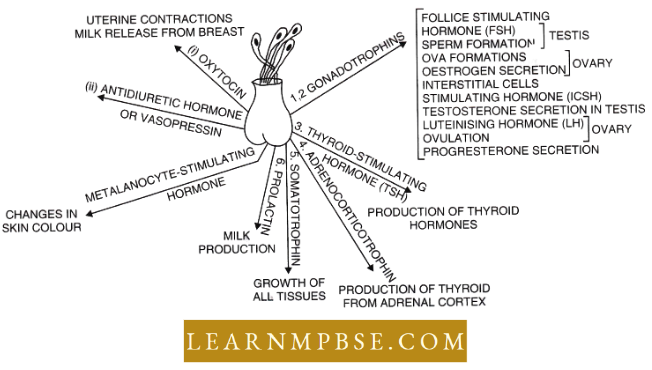
Ecosystem. The relationship between a living community (biotic) and its non-living environment (abiotic) is expressed by the term ecosystem. The term was introduced by Tansley (1937).
- Ecosystems are also called biocoenosis, geobiocoenosis, phytocoenosis, biosystem, exosome, and Holocene.
- Microecosystem. Very small-sized ecosystem.
- The Ecosystem is maintained by the flow of energy through it. This flow is unidirectional.
- Amount Of Energy Trapped. 2% of solar radiation by aquatic ecosystems.
- 1% of solar radiations by terrestrial ecosystems
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
Ecosystem NEET Notes
Bioenergetics. The flow of energy into ecosystems and its transformations in living organisms.
- Sun utilizes about 4 million tonnes of H2 per second.
- Solar energy travels in space in the form of electromagnetic waves. Only 47% of solar radiation reaches the surface of the earth.
- Biomass. The amount of living matter present in an organism is biomass.
- The amount of biomass can be calculated in terms of energy.

NEET Biology Ecosystem
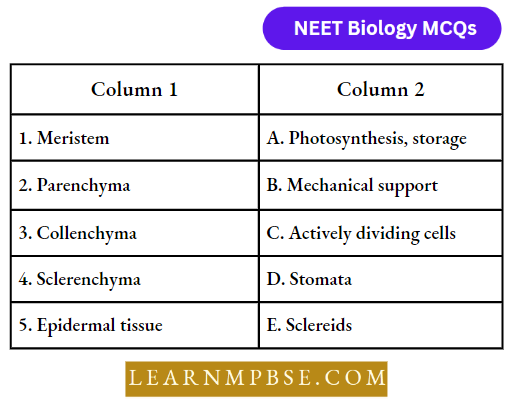
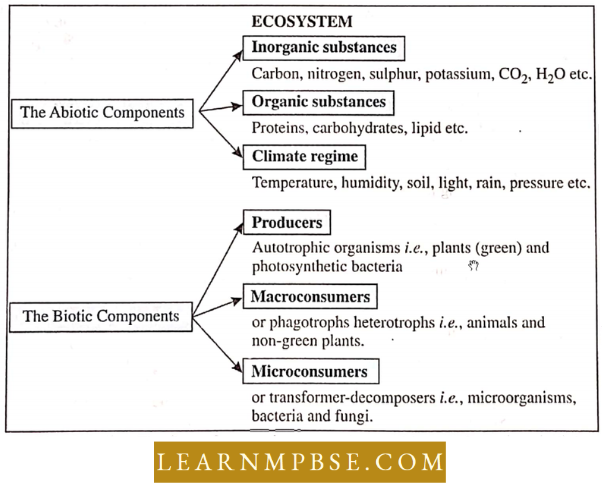
Components Of Ecosystem
Food Chains. A food chain consists of a connected group of producers, consumers, and decomposers. It starts with energy from the sun and nutrients from the soil. They pass through plants and one or several consumers to a final consumer that is not fed upon by any other.
Producers. They use the radiant energy of the sun during photosynthesis whereby CO2 is assimilated and the light energy is converted into chemical energy. Green plants are called producers transducers or converters.
Autotrophs. They are green plants that have the capacity to synthesize food in sunlight. They are also called primary producers because solar energy is locked up only in these plants.
Heterotrophs. These are those organisms that are non-green and hence can’t manufacture their own food. Hence they have to depend upon other plants and animals for their food requirement. Hence they are consumers.
Primary Consumers. These are herbivorous animals and depend upon green plants i.e. on producers for their food, for example, Cows and goats.
Secondary Consumers. These are carnivorous animals and eat the flesh of herbivorous animals, for example, dogs, and cats.
Tertiary Consumers are the carnivorous animals that eat other carnivores for example, snakes eat frogs, birds, eat fish.
Top Consumers are carnivores of an ecosystem that are not killed and eaten by other animals, for example, Lions, Vultures, bears, etc.
Microconsumer. Decomposers are termed microconsumers.
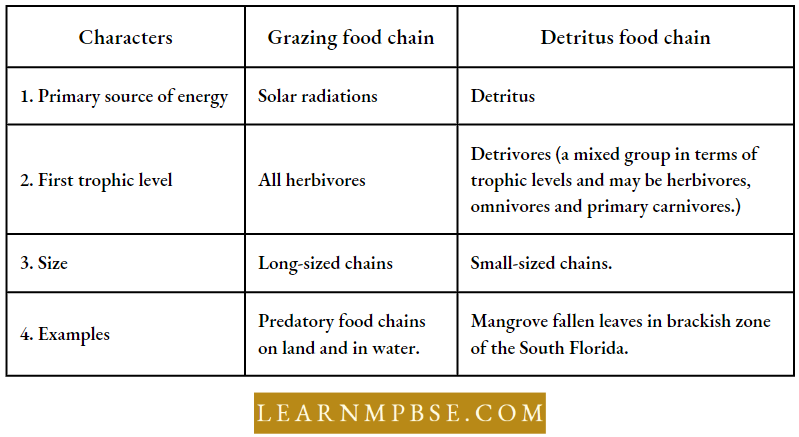
Grazing Food Chain: The grazing food chain is also known as the predator food chain.

- In grazing food chains, the size of an individual gradually increases in successive trophic levels.
- Ecosystems with grazing food chains are directly dependent on solar radiation.
- Most of the ecosystems in nature follow the grazing food chain.
Detritus Food Chain: It starts from dead organic matter into microbes and then to detritus-feeding organisms (detritivores) and their predators. A good example of a detritus food chain is given by Heald and Odum.

The chain is based on mangrove (Rhizophore wangle) leaves, which fall into shallow estuarine waters of south Florida, leaf fragments acted on by saprotrophs and colonized by algae are eaten and re-eaten by a group of small detritus consumers which in turn, provide the main food for game fish and fish (small carnivore) eaten by birds (top carnivores).
- Dead plant parts and animal remains are called detritus.
- Dried plant parts such as leaves, bark, flowers, etc., and dead remains of animals including fecal matter dropped over the soil constitute the above-ground detritus or litter fall while dead roots (root detritus) constitute the below-ground detritus.
- In the detritus food chain source of energy is detritus (dead organic matter) and not the Sun.
- The detritus food chain is composed of a long chain of detritus-eating organisms (detritivores).
- In some ecosystems such as tropical rain forests, more energy flows in the detritus food chain than the grazing food chain.
Decomposers. These include bacteria, fungi, and other organisms that break down the complex compounds present in dead producers and consumers into simpler compounds. These simple organic matters are again decomposed by bacteria into inorganic forms.
Ecosystem NEET Notes
Processes Of Decomposition
- Fragmentation of detritus.
- Leaching
- Catabolism
- Fragmentation. Due to fragmentation, the surface area of detritus particles is greatly increased.
- Leaching. Water percolating through soil removes soluble substances (for example sugars, several nutrients) from the fragmented detritus due to leaching action.
- Catabolism. The extracellular enzymes released by bacteria and fungi carry out catabolism i.e. enzymatic conversion of the decomposing detritus to simpler compounds and inorganic substances. It is important to know that all three decomposition processes operate simultaneously on the detritus.
Humification And Mineralization occur during decomposition in the soil. Humification leads to the accumulation of a dark-colored amorphous substance called humus. Humus is highly resistant to microbial action and undergoes extremely slow decomposition. It serves as a reservoir of nutrients. Mineralization results in the release of inorganic substances (for example CO2, H2O) and available nutrients (NH+4, Ca++, Mg++, K+, etc.) in the soil.
Factors Affecting The Rate Of Decomposition
- The upper layer of soil is the main site of decomposition processes in the ecosystem.
- The rate of decomposition of detritus is affected by climatic factors and the chemical quality of detritus.
- Temperature and soil moisture affect the activities of root microbes.
- The chemical quality of detritus is determined by the relative proportion of water-soluble substances, polyphenols, lignin, and nitrogen.
The amounts of energy and materials transferred from one trophic level to the next higher level become less and less and can be represented graphically as pyramids of energy and pyramids of biomass.
Abiotic Components. Abiotic components are non-living factors. It includes water, minerals, salts, humidity, light, temperature, pH, wind, topography, and background.
NEET Biology Ecosystem Food Web
Many food chains operate in a community. They are not independent but are interconnected to such an extent that disturbance in any food chain disturbs the whole community. The interrelationship among the various food chains of a community is called the food web.
When food chains are interconnected with each other forming a network of food transfer of energy flow. This network is called a food web.

The arrows in the figure indicate – the flow of energy which is always transferred but never exchanged.

Kinds Of Ecosystem
E. P. Odum classified ecosystem on the basis of photosynthesis-respiration ratio as under (P/R Ratio):
- Stabilized Ecosystem: The P/R ratio is one.
- Autotrophic Ecosystem: P/R is more than one.
- Heterotrophic Ecosystem: The P/R ratio is less than one
NEET Biology Ecosystem General Pattern Of Energy Flow
Under favorable environmental conditions, only about 1-5% of the energy of incident radiation or 2-10% of PAR is actually captured by the photosynthetic process (gross primary productivity) and the remaining portion is dissipated.
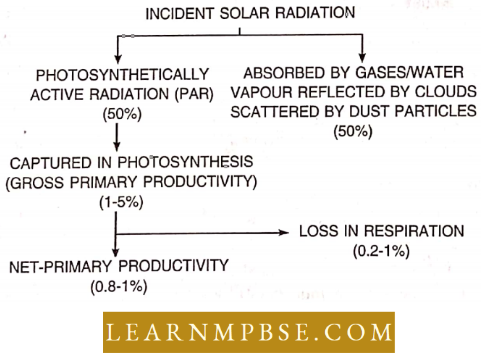
Since the simultaneously occurring respiratory processes are energy-consuming and use up part of the photosynthetic gain, the net capture of energy (net primary productivity) is reduced to only 0-8—4% of the incident total radiation or 1-6-8% of PAR. Only the energy captured in the net productivity of producers can be used by other trophic levels.
NEET Biology Ecosystem Ecological Pyramids
Ecological Pyramids can be of three types:
- Pyramid Of Number. It can be upright, inverted, or spindle-shaped.
- Upright Pyramid. Grassland, Pond ecosystem
- Spindle Pyramid. Forest ecosystem.
- Inverted Pyramid. Parasitic ecosystem
- Pyramid Of Biomass: It is upright for terrestrial habitats.
- It is inverted or spindle-shaped for aquatic habitats where the biomass of a trophic level depends upon the reproductive potential and longevity of its members.
- If the total biomass produced per unit of time is calculated, the pyramid of biomass shall always be upright.
- Maximum biomass occurs in producers. About 10-20% of the biomass is transferred from one trophic level to another.
- Upright-Pyramid. Grassland, Forest, and Parasitic ecosystems,
- Inverted Pyramid. Pond ecosystem.
- Pyramid Of Energy. Always upright, more accurate than the pyramid of biomass or the pyramid of numbers.
The energy content is expressed in kcal/ m²/ yr or kJ/ m²/yr.
Components Of Ecosystem NEET Biology
Energy Conserving Efficiency
- Grasslands: 1.15%
- Savannah: 0.9%
- Mixed Forests: 0.8%
- Modem Crops: 5%
- Sugarcane Field: 10-12%
- Community Productivity. Rate of net synthesis of organic matter by a community per unit time and area.
- Gross Primary Productivity. The total amount of food synthesized or biomass added by the organisms is called gross primary productivity.
- Net Primary Productivity. The organism loses a part of this biomass during its metabolic activities. The net or balanced dry matter accumulated in the organism, after it has consumed a part of it in metabolism or respiration, is called Net Primary Productivity. It is also called assimilative photosynthesis.
- Net primary productivity = Gross primary productivity – Biomass consumed in respiration.
- Primary Productivity. The amount of energy accumulated through photosynthesis by producers is termed primary productivity.
- Secondary Productivity. The rate of synthesis of organic matter by consumers is termed secondary productivity.
- In one year one hectare of forest shall consume 30 tonnes of CO2 and evolve 10 tonnes of O2
- The amount of carbon dioxide fixed annually through photosynthesis is 7 x 1013 kg.
NEET Biology Ecosystem NEET Biology EcosystemEcological Efficiency
It is the effectiveness with which it maintains its dynamic nature. It is expressed as the energy ratio, expressing the efficiency with which organisms exploit their food resources and convert the food into biomass.
- Such ratios are calculated by relating output to the input of energy, at various points along the pathway of energy flow.
- These ratios are multiplied by 100 to express in percentage
Photosynthetic Efficiency = Gross primary productivity/Total incident solar radiation x 100
Net Production Efficiency (NPE). The efficiency with which assimilated energy is incorporated into reproduction, growth, and storage, is called the net production efficiency. It may be shown as:
∴ NEP = Production (reproduction and growth)/Assimilation x 100
In plants, NPE is defined as the ratio of net to gross production. This varies, between 3085% depending on the habitat and growth pattern.
Gross Production Efficiency. The GPE is the product of the assimilation efficiency and net production efficiency.
∴ GPR = Assimilation efficiency x NPE = Production}/Ingestion
This represents the overall efficiency of biomass production within a trophic level.
Assimilation Efficiency. The entire food energy that is consumed is not assimilated. The assimilation efficiency is defined as the percentage expressing the proportion of ingested or consumed energy that is assimilated. It may be shown as:
∴ Assimilation Efficiency = \(\frac{\text{Assimilation}{Ingestion}}\) x 100
Herbivores assimilate about 60 to 70% of the energy in young vegetation and 80% of that in seeds.
Exploitation Efficiency. It is defined as the efficiency with which the biological production of an entire tropic level is consumed.
Components Of Ecosystem NEET Biology
∴ Exploitation efficiency = Ingestion of food/Prey production x 100,
Ecological Efficiency. The % of energy converted into biomass by a higher trophic level over the energy of food resources available at the lower trophic level is called ecological efficiency.
∴ Ecological Efficiency = Energy converted into biomass at tropic level/Energy present in biomass at lower trophic level x 100
Significance Of Ecological Efficiency:
The ratio is used to express the efficiency with which organisms exploit their food resources and convert the food into biomass. The ability of herbivores and carnivores to use the food energy ingested varies from one species to another.
NEET Biology Ecosystem Biomes
Biomes are large biogeographic areas characterized by the presence of distinct groups of climax vegetation, unique animals, and other forms of life.
Typical Climatic Conditions In Major Forest Types In India
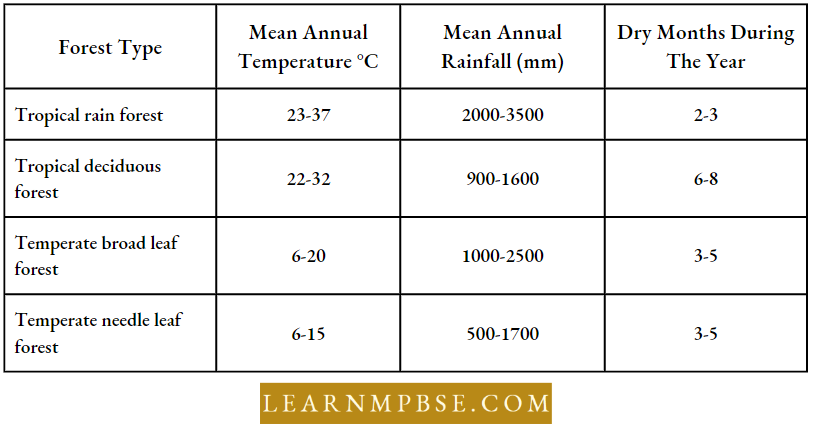
- Temperate Deciduous Forests. The areas have warm summers and moderately cool winters. Rainfall is 75-150 cm. Dominant trees are Oak, Elm, Birch, Maple Ash, Chestnut, and chickory. Beech, Poplar, and Magnolia. Conifers occur at places. Shrubs, herbs, ferns, mosses, lichens, grasses, vines, and epiphytes are abundant.
- Most trees shed their leaves during autumn or fall making the soil brown. A mixed coniferous broad-leaved forest occurs in Indian hills between 1500-3500 m. Tree height can reach 30-40 m. Fauna consists of Deer, Fox, and Beaver. Wild Cat. Racoon, Opossum, Squirrel, Rabbit, Hare, Snakes, Lizards, Salamanders. Thrushes, Owls, Sparrows, and songbirds.
- Taiga is the northern coniferous forest biome with long, severe winter and growing seasons limited largely to the few months of summer. Hardy conifers, Spruce in particular are the most representative of the flora and wolves and bears of the fauna.
- Grasslands Distribution. The temperate grasslands are present in North America (Canada and the USA), South America, Eastern Europe, Central Asia, South Africa, and Australia. These are called prairies in North America, pampas in South America, steppes in Europe and Asia, veldts in Africa, and tussocks in Australia.
- Economic Importance. The grasslands are of tremendous economic importance, for they are the prime farming (grain-growing and cattle-raising). Overfarming and loss of topsoil are serious ecological problems that threaten food production.
- Physical Conditions. The land is plain or gently rolling. The annual rainfall ranges between 25 to 75 cm and it rains intermittently. Moisture is not enough to support forest or woodland. The climate is cold in winter and hot in summer. Dry periods are long. The sunlight is bright and evaporation high.
- Life. Life is rich in the temperate grasslands.
- Flora. The short and tall grasses, legumes, and composites form the dominant vegetation. Shrubs and trees may occur as scattered individuals.
- Fauna. The animals of grasslands are grazing and burrowing mammals.
- The grazing forms include bison, elk, prong-homed antelope, zebra, bighorn sheep, and deer. The burrowing forms are represented by rodents, such as jackrabbits, prairie dogs, gophers, and ground squirrels.
- Carnivores, such as wolves, badger, coyotes, and many birds, such as lark, burrowing owl; and insects are also common. Some reptiles (lizards and snakes) also occur.
Characteristics Of Different Terrestrial Biome
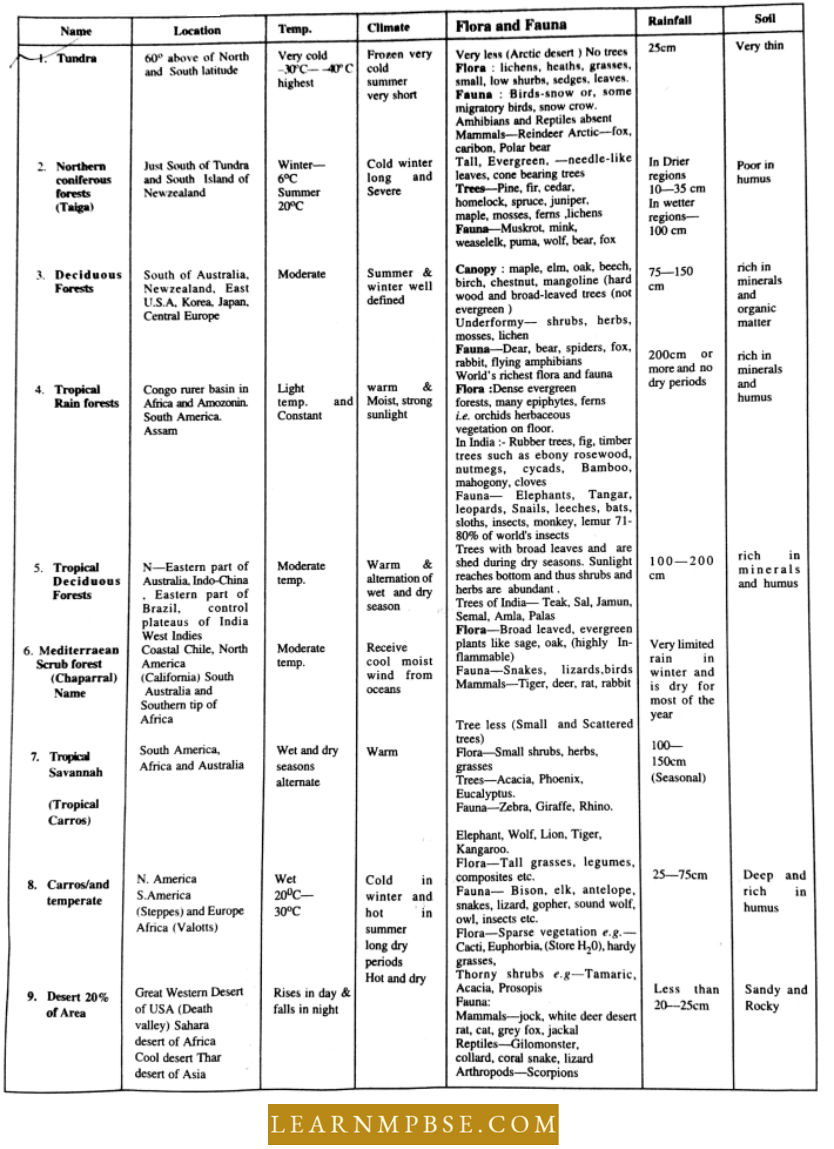
Desert: It is a dry sandy or rocky area with sparse vegetation due to the occurrence of little rain. Rainfall is low less than 120 mm or extreme deserts less than 70 mm per year because the area lies in rain shadow.
This is due to being present either far away from cloud-seeding areas, adjacent to cold ocean currents, beyond a mountain range, or without cloud intercepting mountains. Common deserts are Tibet, Gobi (Mongolia), Thar (India, Pakistan), Arabia, and Sahara, Deserts may be cold deserts or hot deserts.
Hot Deserts: Fewer plants grow in deserts. They are of different ecological categories, ephemeral annuals, rain perennials, succulents, and non-succulent perennials. Succulent include Cacti and Euphorbias. In cold deserts, Sedum, Draba, and Saxifraga occur.
Non-succulent hot desert plants are Aerua, Alhagi, Capparis, Calotropis, Cyperus, Calligonum, Eragrostis, Acacia, Tamarix, Prosopis, and Phoenix. Desert animals live in burrows during the hot periods. Common animals are ants, wasps, locusts, scorpions, spiders, lizards, snakes, desert rats, rabbits, hares, foxes, jackals, cats, etc.
Components Of Ecosystem NEET Biology
NEET Biology Ecosystem Aquatic Biomes
Oceanic, Lakes And Ponds, Marshes, Streams And Rivers.
Oceanic Biome– 2/3 of earth’s surface, 3.5%-concentration of salts, productivity is 1000 kcal/m² yr (less than the most terrestrial biomes). Temperature of ocean surface-28°C in equatorial regions and 0°C near the poles.
Divided Into (Depending Upon The Availability Of Light):
- Photic Or Euphotic Zone-upper 200 m layer of ocean.
- Apliotic Zone-200-2000 m.
- Abyssal Zone-dark zone, below 2000 m.
- Oceanic Basin Is Differentiated Into Three Parts:
- Continental– Shelf. Gradually sloping area of the seashore. Slope- 0.1° from coastline to 160 km in the sea.
- Continental Slope. A slanting area connects the continental shelf to the oceanic floor. Slope 3-6°.
- Ocean Floor. Horizontal bottom area of open sea. Normal depth-6000m to 10,000m.
Three Main Types Of Environmental Zones Of Oceanic Basin:
- Littoral Zone-sea floor of continental shelf.
- Benthonic Zone– sea floor along continental slope, aphotic and abyssal zone, further differentiated into
- The Pelagic Zone, the water of the ocean, is further differentiated into Epipelagic, Mesopelagic, Bathypelagic, and Abyssopelagic.
Marine Organisms Are Classified According To The Region Of Their Activity.
- Plankton. Passively drifted organisms in surface layers of water bodies (some workers restrict the term plankton for micro-organisms, they refer to other large-size planktons as Neuston)
- Nekton, actively swim in surface and deep waters, phagotrophic.
- Benthos. Organisms of the bottom.
The Oceanic Biome Is Divided Into Three Major Ecosystems:
- Open Sea. the area beyond the continental shelf, divisible into photic, aphotic, and abyssal zones. Otherwise has 2 parts pelagic and benthoic.
- Coastal Region. The area of the continental shelf is divisible into 3 parts-intertidal, littoral, and neritic. The intertidal region is exposed, neritic zone comprises the main water body of the area. Beaches belong to the intertidal zone. A highly productive part of the coastal region is the Coral Reef, formed by foraminiferans, calcareous algae, and calcareous skeletons of coelenterates (especially corals).
- Estuary. The name of the coastal bay is formed by the tidal mouth of the river due to the mixing of fresh and seawater, there is a wide fluctuation of salinity 0.5-3.5%. Fluctuations of temperature also occur.
Lakes And Ponds. Stationary freshwater bodies that occur on land. Ponds are small, hollow size than one hectare, depth of less than 2 in. Lakes are larger and deeper. Actually, ponds arc natural or man-made depressions which get filled with rain or runoff water. Lakes develop due to:
- As a result of glaciation,
- Natural or man-made depressions get filled with H2O.
- Develop from main stream or river (oxbow lakes).
- Oligotrophic Lakes– deep, rocky sides, little circulation of nutrients, little biota, for example, Sambhar Lake of Rajasthan.
- Eutrophic Lakes are rich in biota, quick circulation of nutrients, and shallower, for example, Dal Lake of Kashmir.
- Marshes -wetlands possessing turbid water bodies of a few cm in depth. Water received from rains and drains. Typical flora consists of amphibians and emerged hydrophytes named heliophytes. Snails, mosquitoes, larvae, insects, frogs etc occur.
- Streams And Rivers – Lotic Ecosystems – flowing fresh water which differs in physical and climatic conditions, O2 content, temperature, speed, and volume of H2O.
- Agroecology-Study of interrelationships between agricultural crops and their surrounding animate as well as inanimate environments.
Ecosystems do not occur in isolation, are in contact with adjacent ecosystems, and a part of their area overlaps (the overlapping area is called a Transition zone). Polar bear shows hibernation during winter in caves.
- Microscopic Phytoplanktons-diatoms, Chlamydomonas, chlorella, spirogyra.
- Freely Floating Plants – Lemna, Azolla, Pistia, Eichhomia.
- Suspended Macrophytes – Utricularia, Hydrilla.
- Anchored Submerged Plants – Vallisneria.
- Floating Leaned Anchored Plants – Nelumbo, Nymphaea.
- Emerged Plants – rooted at the bottom but part of them comes out of water. Sagittaria, Typha, Sciipus, Phragmites.
[All of the above varieties of plants are present in ponds and lakes]
Energy Flow In Ecosystem NEET Study Material
Aquatic Biomes Memory Points
- The word “Biocoenosis” was introduced by Carl Mobius.
- The Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro focused on the conservation of genetic resources of flora and fauna.
- The flora of Delhi is predominantly xerophytic.
- Resurrection plants – examples of drought evasion Selaginella lepidophylla.
- Fecundity refers to the potential ability of an organism to generate reproductive units, including eggs, sperm, or asexual structures.
- Association. A collection of species within a trophic level use a shared resource base in a comparable manner, such as nectar-feeding birds or grazing and browsing mammals.
- Herbivores are sometimes referred to as Key Industry Animals. (Elton, 1927) due to their ability to transform plant materials into animal matter.
- Chaparral vegetation comprises resilient, dense, broad-leaved evergreen plants, such as sage and oak, that exhibit fire resistance.
- Illumination is severely deficient in the tundra, with winter temperatures ranging from -30°C to -40°C. Summer lasts around 60 days at a temperature of 10°C.
NEET Biology Ecosystem Vegetation Of India
In India, there are two most common types of plant formations.
Forests. Indian forests are classified into four major types based on temperature such as tropical, mountain subtropical, temperate, and alpine.
- Tropical forests. They are of two types moist and dry. Moist tropical forests. On the basis of the degree of wetness, they may be
- Tropical Wet Evergreen Forests. Annual rainfall is over 250 cm. as in the West Coast, Assam, Bengal, and Andaman islands. The dominant trees arc Dipterocarpus, Hopea, Artocarpus, Emblica, Man gif era, Iscora, and some climbers (Lianas) and epiphytes.
- Tropical Moist Semi-Evergreen Forests. They are found in North Assam, Bengal, parts of Orissa receiving heavy rainfall. Trees shed their leaves for a brief period. They include trees such as Terminalia; and Shorca.
- Tropical Moist Deciduous Forests. They are common in moist areas of Kerala, Karnataka, South Madhya Pradesh, Northern Uttar Pradesh, and Bihar. Bengal and North Orissa. They include teak and Sal trees.
- Dry Tropical Deciduous Forests. Trees remain leafless for several weeks in the dry season. Trees are moderate in size with sparse canopy. Thorny shrubs, grasses, and some bamboos are also present in some regions. In the north, such forests are found in Punjab, U.P. Bihar, and Orissa in regions that are neither wet nor too dry.
- Temperate Forests. They occur above 5,300 ft altitude, chiefly in the mountains of the Himalayas and Nilgiri. In the Himalayas, Oaks and conifers are abundant.
- Alpine Vegetation. They are extensive throughout the Himalayas above 11,000 ft. The tree’s height becomes lesser with increasing altitude. Alpine vegetation is characterized by Rhododendrons. It includes small plants like Sedum, Primula, Saxifraga, and lichens.
- Grasslands. In India, natural grasslands are not found. Most Indian grasslands are being maintained in their present serai stage due to biotic interference.
NEET Biology Ecosystem Biosphere
Biosphere. The inhabited part of the earth and its atmosphere form the biosphere. It extends to about 22.5 km in thickness from the ocean bottom to the mountain tops.
- Maximum Density Of Organisms is found in coral reefs and tropical rain forests.
- Pedosphere. Consists of soil.
- The lithosphere is the dry crust of the earth (rocks and soil) 20 km in thickness.
- Hydrosphere. Oceans and sea (70% of the total earth’s surface).
- The atmosphere consists of 78% N2, 20.9% 02, 0.94% Ar, and 0.03% CO2.
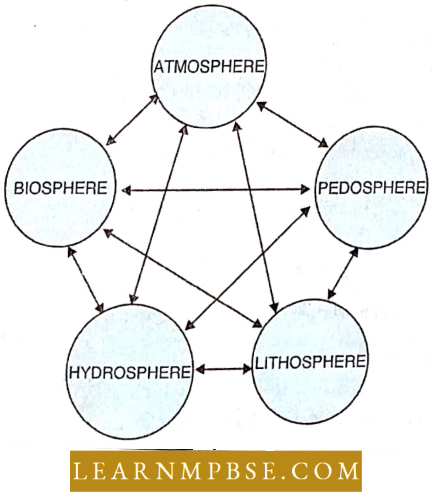
The atmosphere is differentiated into the troposphere, stratosphere, ozonosphere, and ionosphere.
NEET Biology Ecosystem Ecological Succession
Biotic Succession. A biologically controlled modification in the composition of a community of a particular area is called biotic succession or ecological succession. Biotic succession is also known as the successive development of different communities in a particular area till a climax community is formed.
It was first studied by King (1685). The term succession was coined by Hult(1885). Clements defined it as a natural process by which the same locality becomes successively colonized by different groups of plants. Odum further described it.
Energy Flow In Ecosystem NEET Study Material
Kinds Of Succession
- Primary Succession (Prisere). In any of the basic environments, primary succession starts from the primitive substratum, where there was no previously any sort of living matter. The first group of plants established there are known as pioneers, primary community, or primary colonizers and the last group is of climax community formed of tall trees.
- The time taken for the development of forest climax or sand-dune or barren land is about 1000 yrs. Time taken is about 50-100 yrs in the case of grassland and more than 200 yrs for a forest
- Autotrophic Succession. This type of succession is dominated by autotrophs which represent the first serial stage. lt occurs on a substratum having excess mineral matter but little organic matter.
- Heterotrophic Succession. It occurs on a substratum having an excess of organic matter. This type of succession is always dominated by detrivores i.e., fungi and bacteria.
- Induced Succession. It occurs due to extensive external interference. Here the initial community has high productivity which gradually decreases. The agriculture can be deemed as an example of induced succession.
- Here a steady state is maintained for an ultimate good harvest. Elimination of weeds can be deemed as a step towards retrogression as it inhibits the arrival of a stable state.
- Autogenic Succession. When the plants themselves gradually modify the environment to the extent that the habitat itself becomes unfavorable for the existing vegetation, a new type of succession starts. The old communities disappear and new ones come up for whom the environment is more suitable. This has been described as autogenic succession.
- Allogenic Succession. The habitat may change due to external thrust i.e. of the environment. The succession taking place on account of this is called as allogenic.
- Retrogressive Succession. Due to environmental thrust and human interference the climax vegetation may retrograde into shrubland or savannah. This is referred to as retrogressive succession.
- Deflated Succession. When the succession doesn’t proceed through its normal course and sidetracks the advancement line, it is called as deflated succession. If the normal stages are 1 → 2 → 3 → 4 and the succession occurs as 1 → 2 → 3A → 3B → 4 is deflated.
- Cyclic Succession. It occurs within the normal discourse of succession. If at a certain stage, the normal succession line is substituted by repetition of a previous stage due to external thrust, the succession is called cyclic for example 1 → 2 ⇔ 3 → 4.
Causes Of Succession
- Initiation.
- Physiographic factors include erosion, deposition, submergence, and emergence.
- Climatic Factors produce secondary, barren areas including wind, water, snow, hail, re, and draught.
- Biotic Factors produce secondary barren areas including animals, mankind, and microorganisms.
- Continuation. Once started succession continues
- Stabilization
Process Of Succession: The various stages are
- Nudation
- Migration
- Ecesis
- Aggregation
- Competition
- Co-action
- Reaction and
- Stabilization.
Secondary Succession Subsere. It occurs when an early community has been damaged leaving a few organisms and considerable organic matter.
- Ecological Succession in dry habitats, bare rock, sandy soil, and aquatic habitats are respectively called Xerosere, lithosere, psammosere, and hydrosere.
- In hydrosere (or hydrarch), pioneers in an ecological succession are submerged hydrophytes.
- In lithosere, the pioneers in an ecological succession are crustose (Saxicaulous lichens, Graphis, Rhijocaibon).
- The dominant species are different for each succession stage in the series.
- The last succession in a series is called the climatic climax or climax.
Energy Flow In Ecosystem NEET Study Material
NEET Biology Ecosystem Different Stages In Hydrosere With Component Plants
Phytoplankton Stage: (blue-green and green algae pioneer, Diatoms, bacteria.)
Rooted submerged Stage: Hydrilla, Vallisnaria Utricularia, Potamogeton Elodea, Najas, Ceratophyllum, certain got volume crunch as choro ano Nitalla
Floating Stage: Nelumbo, Nymphala, Zolle hemna, Trapa
Reed Swamp Stage: (Typha, Sagittaria Phragmites, Sagittaria, Siripus (Amphibious stage)
Sedge Meadow Stage: (Cyperus, Juncus, Eleocharis, Carix)
Wood Land Stage: (Salix, Populus, Alnus) (Climax community) Forest stage (Temperate mixed tropical rain and tropical deciduous)
NEET Biology Ecosystem Different Stages In Xerosere With Component Plants

NEET Biology Ecosystem Differences Between Terrestrial And Aquatic Succession
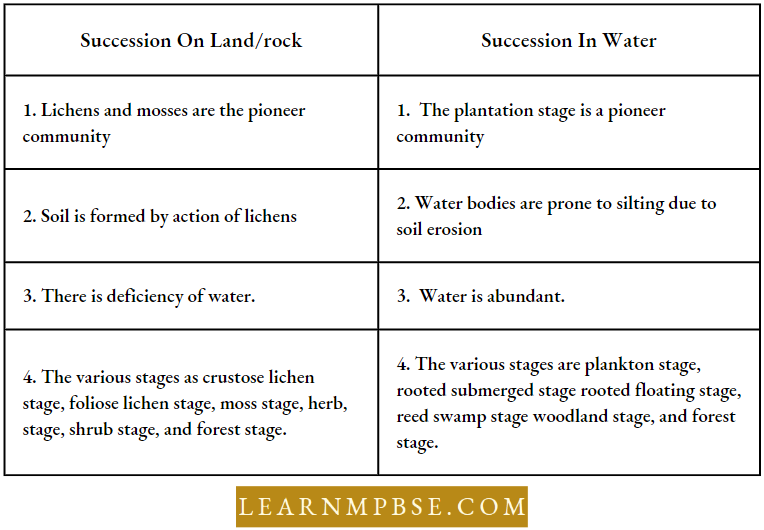
NEET Biology Ecosystem Differences Between The Seral And Climax Community During Succession
Dominance of a species:
Any one or more species is present in a majority during succession in every stage, and that species is the dominant species in the community. For instance, a location may be classified according to the species that predominate the region, such as a teak forest or pine forest.
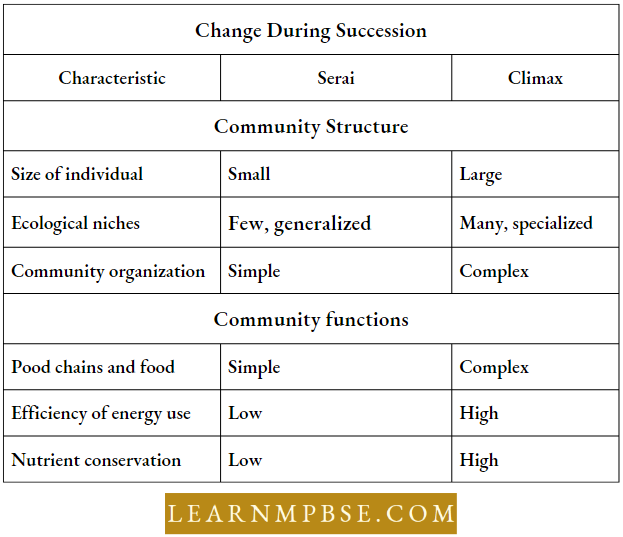
The dominant species significantly influences the community and the surrounding environment. At any stage, it is not requisite for a single species to dominate; multiple species may coexist in dominance. For example, in the rainforests of tropical regions, 10 to 12 species dominate.
NEET Biology Ecosystem Biogeochemical Cycle
The circular paths of the chemical elements between organisms and the environment are known as biochemical cycles.
Cycles of material are classified into gaseous and sedimentary cycles,
- For Gaseous cycles, the reservoir of materials is the atmosphere or water. The four major elements in living organisms: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, are predominantly gaseous;
- In the Sedimentary cycle involving minerals, like phosphorus, sulfur, and calcium, the reservoir is the lithosphere.
Energy Flow In Ecosystem NEET Study Material
Oxygen Cycle: The oxides can be reduced both chemically as well as biologically to produce oxygen. Microbial oxidation can also occur. O2 content of the atmosphere has remained constant for the last several million years.
Most of the O2 lost is replenished by photosynthesis.
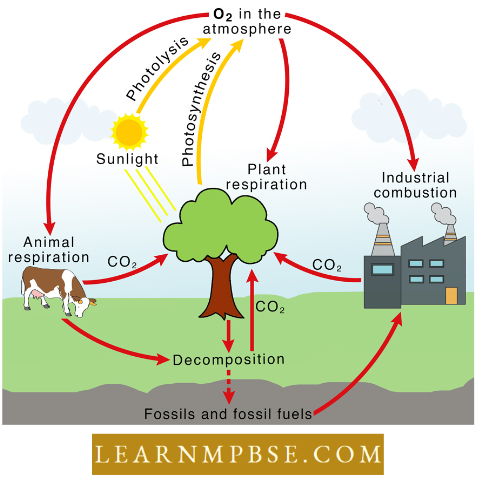
Greenhouse gases tire (CO2 CH4, dust, HO2, NO2, SO2) are transparent to incoming solar radiations but are strong absorbers of long wave or infrared radiations emitted by the earth’s surface.
Carbon Cycle: The three main sources of carbon in the non-living world are:
- CO2 of air as well as dissolved in water
- Carbonates of rocks in the earth’s crust
- Coal and petroleum of fossil fuels.
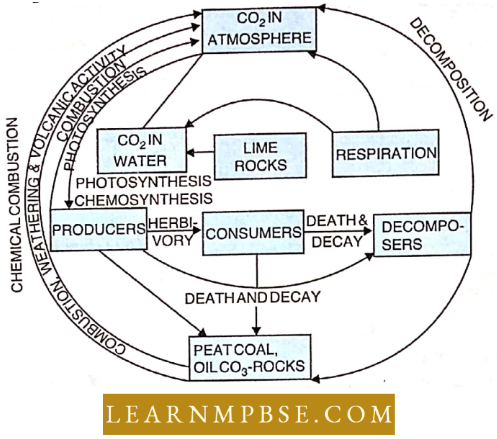
Most CO2 enters the living world through photosynthesis.
- The amount of carbon fixed by photosynthesis is 7 x 1013 kg per year.
- One hectare of healthy forest produces about 10 tonnes of O2 and absorbs 30 tonnes of CO2 every year.
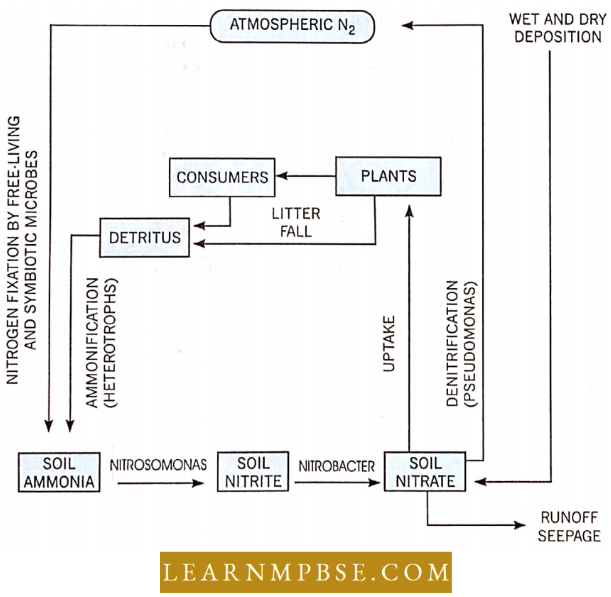
Nitrogen Cycle: N2 forms 4/5 part of the atmosphere; picked up as inorganic compounds by plants and some prokaryotes (NO–3 and NH4) and converted into organic N2.
N2 Fixation Is Of Three Types
1. Atmospheric-electrochemical and photochemical reactions (35 mg/ m²/ yr).
2. Biological by free-living bacteria (Azotobacter, Clostridium), symbiotic bacteria (Rhizobium), and cyanobacteria (Anabaena, Nostoc) [140-700 mg/m²/yr].
Proteins (Nitrogenous Compounds)
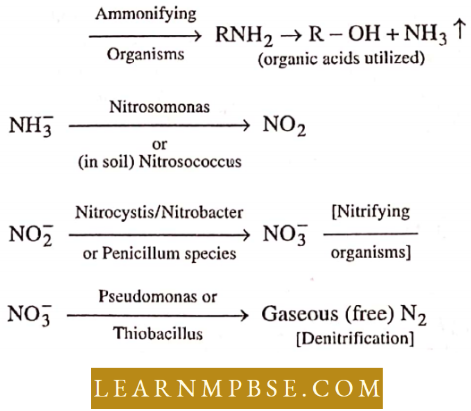
Ammonifying bacteria are Bacillus vulgaris and Bacillus remosa.
Dead bodies of plants and animals also contain nitrogenous compounds, for example, Bacillus, actinomycetes, and fungi.
3. Industrial – Haber’s process
Water Cycle: 60-90% of the body weight of an organism is made up of water.
- The water or hydrological cycle is actually made up of two overlapping cycles: Larger ‘global’ and smaller ‘local’
- Precipitation is of three main types. Rain, Snow, and Hail.
- The total world precipitation amounts to 4.46 x 1020 G per year. (1G = 1020 gm).
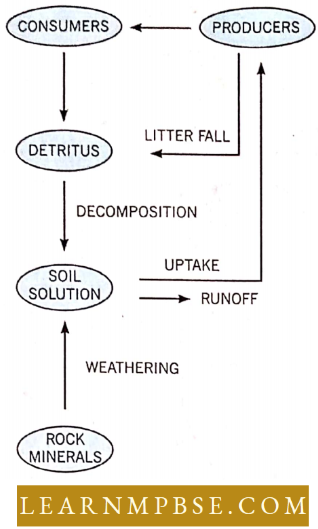
- Biogeochemical Cycle. The cycling of materials between living and non-living components of the biosphere is called the biogeochemical cycle.
Phosphorus Cycle: The atmospheric or gaseous cycle for phosphorus is absent. Guano (excreta of marine birds) is a good source of phosphorus.
Sulfur Cycle: In the sulfur cycle, the gaseous phase is reduced. In nature, sulfur occurs in the elemental form (as metal sulfides and sulfates) and some amount as SO2 gas.
- Sulfur is available to plants as sulfate
- Sulfur is available to plants as sulfate. (SO42-) ions which are produced by the oxidation of exposed acid eroded rock surfaces. Most of this oxidation is biological and is carried out by specialized bacteria which derive energy from the process.
- In plants, absorbed SO42- ions are incorporated into the thiol (-SH) groups of amino acids and proteins. In this form, the sulfur passes through the various trophic levels being released from living organisms only as a constituent of feces.
- Decomposing bacteria break down the protein of dead organisms, reducing the -SH groups to H2S (hydrogen sulfide). It is the presence of this gas that sometimes gives the characteristic odor of rotten eggs to decomposing matter. The H2S produced may be oxidized to SO42- by certain bacteria but this is only possible under aerobic conditions.
- Specialized photosynthetic bacteria living in sulfur springs use H2S instead of H2O as a raw material in the manufacture of carbohydrates and this sulfur returns to earth’s sediments.
Calcium, Magnesium, And Other Minerals: They are also cycled like other materials. These elements are slowly released from the rocks by the action of water and wind. These are either blown into the air as dust or are absorbed by plants through their roots.
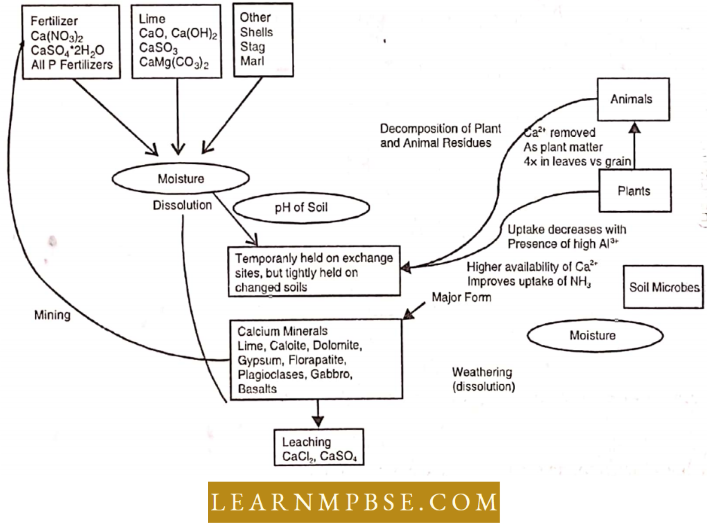
Some organisms, such as mollusks and corals, deposit a substantial quantity of calcium in their shells and skeletons that are not available for quick cycling.
- The vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels is called stratification
- Components of the ecosystem are seen to function as a unit with the following consideration
Energy Flow In Ecosystem NEET Study Material
Productivity
- Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)
- Net Primary Productivity (GDP)
- Secondary Productivity
Primary Productivity Depends Upon:
- Plant species Environmental factors
- Availability of nutrients
- Photosynthetic capacity
Decomposition. Steps: Fragmentation, Leaching, Catabolism, Humification, Mineralization (Temperature, Soil moisture, Oxygen and detritus composition regulate decomposition,
Energy Flow: Producers → Primary → Secondary
- Detritus Food Chain (DFC)
- Grazing Food Chain (GFC)
Food Web. The natural interaction of food chains makes the food web.
- The number of trophic levels is restricted as the transfer of energy follows 10 percent law Ecological pyramids
- The pyramid of energy is always upright
- The pyramid of number and biomass is generally upright
- The pyramid of biomass in the sea is generally inverted
- The pyramid of biomass of a small standing crop of phytoplankton supports a large standing crop of zooplankton thus it is inverted.
NEET Biology Ecosystem Ecosystem Synopsis
The deep sea constitutes an incomplete ecosystem due to the absence of producers. Koala bears are monophagous and will perish in the absence of eucalyptus leaves.
- The pH of oceans exhibits minimal variation.
- Snails and earthworms are absent in acidic soils.
- Euglena and other flagellates are prevalent in acidic aquatic environments.
- Organisms with calcareous shells inhabit environments with neutral or alkaline pH levels.
- Snails inhabit soils abundant in calcium.
- Animals counteract seawater salinity via salt-secreting glands.
- Terrestrial animals are unaffected by alterations in pH levels. Nonetheless, it dictates the distribution of terrestrial flora and edaphic creatures.
- Sloths are exclusively arboreal in their environment.
- Some creatures function as both producers and consumers, such as insectivorous plants like Nepenthes (pitcher plant) and Drosera (Sundew plant).
- Omnivores such as humans and bears occupy multiple trophic levels.
Ecological equivalents. Animals occupying similar ecological niches (similar food) in different geographical areas for example both owls and cats feed upon shrews and rats in woodland areas and near human habitations respectively.
- There is the highest species diversity in the Tropical rainforest ecosystem.
- Gujarat has the largest number of salt lakes in India.
- Brine is water that has a high concentration of salt.
- Herbs other than grass are called forb.
- The number of biomes on a mountain range decreases with the increase in the latitude of the mountain.
- Brackish lakes are always oligotrophic for example Sambhar Lake of Rajasthan.
- Detritus trophic level – The last trophic level is constituted by decomposers.
- Detritivores are decomposers as well as scavengers.
The detritus food chain is the shortest. Dystrophic lakes are rich in bogs (undecomposed organic matter), poor in CaCO2 and other inorganic matter, and poor in oxygen for example marshy lakes.
- With increasing dependence on animal diets, the human population will need more farm produce.
- Britain receives 2500 cal/cm²/yr of solar radiation while the amount at Varanasi in India is 75000 cal/ cm²/yr.
- The fish ‘Hilsa’ is found in both fresh and marine waters.
- Gauses hypothesis or Principle of competitive exclusion.
- No two species can occupy the same ecological niche. In case it happens, only one survives while the other is excluded.
- Tropical region occurs between 23°N and 23°S.
- Secchi disc is used in measuring turbidity.
Plagiosere. It is a deflected sere where plant succession deviates from its natural course due to human activity and other forms of external intervention.
- The climax of plagiosere is known as plagioclimax or disclimax.
- The daily tidal cycle recurs after every 12.4 hours.
- Characteristic vegetation beyond the timberline is Elfin scrub and Alpine meadows.
- The water cycle is made up of two overlapping cycles — larger global and smaller local.
- Matter occupies a space. It can be seen, smelled, tasted, and touched while energy does not occupy space and it can be felt through specific receptors for example heat, sound, light.
- Earth is a closed system as far as materials are concerned.
- Beijerinck (1888) isolated Bacillus radicicola and showed its ability to produce root nodules.
- Winogradsky (1891) discovered nitrogen fixation.
- Sea birds excrete uric acid, which is deposited to form guano in littoral islands. It is rich in uric acid and phosphorus and used as fertilizer.
Ozone-depleting gases are on NO2 (6%) chloroform carbons (25%) halocarbon/halons, and CO2 (57%)
Ecological Pyramids NEET Exam Preparation
Differences Between Grazing And Detritus Food Chains
Differences Between Wet Deposition And Dry Deposition

The Ecosystem Receives Nutrients By
- Wet deposition
- Dry deposition
NEET Biology Ecosystem Multiple Choice Questions And Answers
Question 1. The term ecosystem was coined by:
- Sukachey
- Vernadsky
- Haeckel
- Tansley.
Answer: 4. Tansley.
Question 2. Biotic components of an ecosystem include:
- Producers
- Consumers
- Decomposers
- All the above.
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 3. Which is the most stable ecosystem?
- Mountain
- Desert
- Forest
- Ocean.
Answer: 4. Ocean.
Question 4. In a biotic community, primary consumers are:
- Omnivores
- Carnivores
- Detritivores
- Herbivores.
Answer: 4. Herbivores.
Question 5. If we completely remove the decomposers from an ecosystem, the ecosystem functioning will be adversely affected because:
- Mineral movement will be blocked
- Herbivores will not receive solar energy
- Energy flow will be blocked
- The rate of decomposition of another component will be very high.
Answer: 1. Mineral movement will be blocked
Question 6. The food chain will end with:
- Carnivores
- Herbivores
- Decomposers
- Secondary carnivores.
Answer: 4. Secondary carnivores.
Question 7. Which of the following is a way flow rather than a two-way or cyclic flow?
- Carbon
- Nitrogen
- Potassium
- Free energy.
Answer: 4. Free energy.
Ecological Pyramids NEET Exam Preparation
Question 8. The importance of the ecosystem lies in:
- Flow of energy
- Cycling of materials
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Question 9. The driving force for an ecosystem is:
- Biomass
- Producers
- Food
- Solar Energy.
Answer: 4. Solar Energy.
Question 10. About how much of solar energy that falls on the leaves of a plant is converted to chemical energy by photosynthesis?
- 1%
- 10%
- 30%
- 50%.
Answer: 1. 1%
Question 11. Energy and nutrients enter a community by way of:
- Producers
- Consumers
- Scavengers
- Detritivores.
Answer: 1. Producers
Question 12. A consumer whose carbon atoms have already passed through three species is a:
- Scavenger
- Tertiary Producers
- Tertiary Consumers
- Secondary Consumers.
Answer: 3. Tertiary Consumers
Question 13. The average annual precipitation in a desert biome is:
- 15-25 cm
- 25-30 cm
- 50-75 cm
- 75-100 cm.
Answer: 1. 15-25 cm
Question 14. A sequence of species through which the organic molecules in a community pass is called:
- Pyramid of energy
- Food chain
- Food web
- Nutrient cycle.
Answer: 2. Food chain
Question 15. Savannahs are:
- Tropical rain forest
- Desert scrubs
- Grassland with scattered trees
- Dense forests.
Answer: 3. Grassland with scattered trees
Ecological Pyramids NEET Exam Preparation
Question 16. Most food chains are composed of:
- 1 or 2 species
- 3 or 4 species
- 9 or 10 species
- More than 16 species.
Answer: 2. 3 or 4 species
Question 17. A micro-climate is controlled mostly by factors associated with:
- The flatness of the terrain
- Vegetation
- Latitude
- Longitude.
Answer: 3. Latitude
Question 18. In which of the following habitats does the diurnal temperature of soil surface vary most?
- Desert
- Grassland
- Shrubland
- Forest.
Answer: 1. Desert
Question 19. A biome with high temperature, high rainfall no seasonal change, and soil rich in minerals and humus is:
- Shrub land
- Coral reef
- Tropical rain forest
- Temperate evergreen forest.
Answer: 3. Tropical rainforest
Question 20. A plant eaten by herbivorous animals which in turn is eaten by a carnivorous animal, it forms a:
- Food chain
- Food web
- Food pyramid
- Biotic potential.
Answer: 1. Food chain
Question 21. A pond is a:
- Biome
- Agro-ecosystem
- Natural ecosystem
- Community.
Answer: 3. Natural ecosystem
Question 22. Which of the following communities would have trees?
- Taiga
- Littoral zone
- Shrub land
- Tundra.
Answer: 1. Taiga
Question 23. Which of the following has a vegetation structure with only one level?
- Tropical rain forest
- Taiga
- Grassland
- Shrub land.
Answer: 3. Grassland
Question 24. What type of pyramids are commonly referred to in ecological studies?
- Lateral
- Compound
- Upright
- Inverted.
Answer: 3. Upright
Question 25. Which type of system does the earth along with its atmosphere constitute?
- Open
- Closed system
- Cut off system
- Biogeochemical system.
Answer: 2. Closed system
Question 26. Enrichment of habitat (say pond) with nutrients is called:
- BOD
- Biological magnification
- Eutrophication
- Autopurification.
Answer: 3. Eutrophication
Question 27. Wolves and lions may be said to occupy the same trophic level because:
- They both eat primary consumers
- They both utilize their food with about 10% efficiency
- They both live in a pond
- Both are large mammals.
Answer: 1. They both eat primary consumers
Question 28. About how much of the chemical energy within the producer’s tissue becomes chemical energy within herbivore tissue.
- 1%
- 10%
- 30%
- 50%.
Answer: 2. 10%
Question 29. The most diverse oceanic communities are in the:
- Abyssal zone
- Littoral zone
- Neritic zone
- Oceanic zone.
Answer: 2. Littoral zone
Nutrient Cycling In Ecosystems NEET
Question 30. Which of the following aquatic ecosystems has very little primary productivity?
- River
- Estuary
- Lake
- Marsh.
Answer: 1. River
Question 31. Which of the following statements is true about ecological relationships?
- Competition with members of other species is more severe than that with one’s own species
- Competition with members of other species is less severe than with one’s own species
- Competition with members of other species is as severe as that with one’s own species
- Competition does not exist between members of different species.
Answer: 2. Competition with members of other species is less severe than with one’s own species
Question 32. The above represents:

- Food chain
- Food web
- A population
- Ecosystem.
Answer: 2. Food web
Question 33. Light compensation zone refers to the zone:
- Where all light energy is used efficiently
- Where light is available
- Beyond which light does not penetrate
- Where light is maximum.
Answer: 3. Beyond which light does not penetrate
Question 34. Aquatic ecosystem covers how much of the earth’s surface?
- 87%
- 23%
- 72%
- 49%.
Answer: 3. 72%
Question 35. A biome with high temperature, and high rainfall is:
- Shrub land
- Coral reef
- Semi-desert scrub
- Tropical rain forest.
Answer: 4. Tropical rainforest.
Question 36. The importance of the ecosystem lies in:
- Cycling of materials
- Flow of materials
- Both of the above
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Both of the above
Question 37. What are biotic components?
- The living components
- The non-living components
- Both living and non-living
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. The living components
Question 38. The flora and fauna in lakes and ponds are;
- Lentic biota
- Lotic biota
- Abiotic
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Lentic biota
Question 39. The source of energy in an ecosystem is:
- The heat from the soil
- Heat reflected by leaves
- Burning of sugar
- Sunlight is received by leaves.
Answer: 4. Sunlight received by leaves.
Nutrient Cycling In Ecosystems NEET
Question 40. The energy storage at the consumer level is called:
- Gross primary productivity
- Secondary productivity
- Net primary productivity
- Net productivity.
Answer: 2. Secondary productivity
Question 41. The hardest competition for food, light, and space is seen in:
- Closely related species growing in the same niche
- Closely related species growing in different habitats
- Distantly related species growing in the same niche
- Distantly related species growing in different habitats.
Answer: 1. Closely related species growing in the same niche
Question 42. Given below is an imaginary pyramid of numbers. What could be one of the possibilities about certain organisms at some of the different levels?
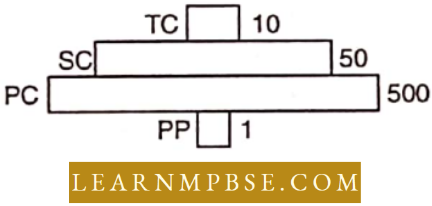
- Level PC is “insects” and level SC is “small insectivorous birds”
- Level PP is “phytoplanktons” in sea and “Whale” on top-level TC
- Level one PP is “pipal trees” and the level SC is “sheep”
- Level PC is “rats” and level SC is “cats”.
Answer: 1. Level PC is “insects” and level SC is “small insectivorous birds”
Question 43. Which of the following relations is correct regarding the GPP and NPP of an ecosystem?
- NPP = GPP – Animal consumption
- NPP = GPP + Plant respiration
- NPP = GPP – Plant respiration
- NPP = GPP + Animal consumption.
Answer: 3. NPP = GPP – Plant respiration
Question 44. An ecosystem resists change because it is in a state of:
- Imbalance
- Shortage of components
- Homeostasis
- Deficiency of light
Answer: 3. Homeostasis
Question 45. The ecosystem has two components:
- Plants and animals
- Weeds and trees
- Biotic and abiotic
- Frogs and men.
Answer: 3. Biotic and abiotic
Question 46. The number of producers within a specified area would be maximum in:
- Pond ecosystem
- Grassland
- Desert
- Forest ecosystem.
Answer: 1. Pond ecosystem
Question 47. In an ecosystem, a big fish eats small fishes which eat water fleas supported by phytoplanktons. The water fleas in this ecosystem are:
- Producers
- Primary consumers
- Secondary consumer
- Top consumers.
Answer: 2. Primary consumers
Question 48. Which one of the following represents the largest population in an ecosystem?
- Consumers
- Top consumers
- Decomposers
- Producers.
Answer: 4. Producers.
Question 49. With regard to the ecological food chain, man is a:
- Consumer
- Producer
- Producer and consumer
- Producer and decomposer.
Answer: 1. Consumer
Nutrient Cycling In Ecosystems NEET
Question 50. The first link in a food chain is always a green plant because:
- It has the capacity to synthesize organic food
- Plants are fixed to a place
- Plants are present everywhere
- There are more herbivorous animals than carnivorous animals.
Answer: 1. It has the capacity to synthesize organic food
Question 51. A food chain is represented by :
- Producers
- Decomposers in succession
- Primary consumers
- Producers—consumers—decomposers.
Answer: 4. Producers—consumers—decomposers.
Question 52. Organisms linked in a food chain represent:
- Food web
- Trophic levels
- Ecosystem
- Community.
Answer: 2. Trophic levels
Question 53. Free-floating organisms are termed:
- Planktons
- Benthos
- Nekton
- All algae.
Answer: 1. Planktons
Question 54. The bottom-dwelling organisms are:
- Nektons
- Phytoplankton
- Benthos
- Zooplanktons.
Answer: 3. Benthos
Question 55. The first trophic level is represented by :
- Herbivores
- Carnivores
- Insectivores
- Autotrophs.
Answer: 4. Autotrophs
Question 56. In a grassland, top consumers are:
- Herbivores
- Carnivores
- Bacteria
- Tall pine tree.
Answer: 2. Carnivores
Question 57. The food chain in which micro-organisms absorb and break the energy-rich compounds synthesized by the producers is
- Predator food chain
- Parasitic food chain
- Detritus food chain
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Detritus food chain
Question 58. Lichens do not normally grow in cities :
- Because of the absence of the right type of algae and fungi
- Because of the lack of moisture
- Because of air pollution
- Because natural habitat is missing.
Answer: 3. Because of air pollution
Question 59. Primary productivity of the ecosystem refers to:
- Increase in primary consumers
- Net production of primary producers
- CO2 fixation of organic carbon
- Increase in mortality of primary producers.
Answer: 3. CO2 fixation of organic carbon
Question 60. The individuals in the uppermost ring of the pyramid represent the one with:
- Maximum number
- Maximum biomass
- The ultimate consumer in the chain
- Minimum biomass.
Answer: 3. The ultimate consumer in the chain
Ecosystem NEET Notes
Question 61. The pyramid of a number of individuals per unit area in a grassland ecosystem will be:
- Linear
- Upright
- Irregular
- Inverted.
Answer: 2. Upright
Question 62. The ecological niche is:
- Place of dwelling
- Place of origin
- Competitive ability
- Function with habitat.
Answer: 4. Function with habitat.
Question 63. Which of the following food chains is correct?
- Fallen leaves-bacteria-insect larvae
- Phytoplankton -zooplankton-fish
- Grasses-fox-rabbit
- Grasses-chameleon -insect-bird.
Answer: 2. Phytoplankton -zooplankton-fish
Question 64. ‘Greenhouse effect’ is:
- Growing maximum green plants in home gardens
- Reduction of the green part of sunlight reaching the earth
- Growing vegetables in green-coloured houses
- Retention of heat radiation from the earth by CO2
Answer: 4. Retention of heat radiation from the earth by CO2
Question 65. For recycling of materials which one is necessary?
- Producers
- Consumer
- Man
- Decomposers.
Answer: 4. Decomposers
Question 66. Energy flow in an ecosystem is:
- Multidirectional
- Bidirectional
- Unidirectional
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Unidirectional
Question 67. The pyramid of energy in a terrestrial ecosystem may be:
- Inverted
- Upright
- Upright and inverted
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Upright
Ecosystem NEET Notes
Question 68. Green plants are:
- Complete food chain
- First trophic level
- Second trophic level
- Third trophic level.
Answer: 2. First trophic level
Question 69. Solar energy can be trapped to the maximum capacity by:
- Planting trees
- Crops
- Grasses
- Xerophytic plants.
Answer: 3. Grasses
Question 70. The equilibrium of species is disturbed by
- Overgrazing
- Selective grazing
- Fanning
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Overgrazing
Question 71. A food chain starts with:
- Decay
- Photosynthesis
- Respiration
- Nitrogen fixation.
Answer: 2. Photosynthesis
Question 72. Biological equilibrium is an equilibrium among the:
- Producers
- Producers and consumers
- Decomposers
- Producers, consumers, and decomposers.
Answer: 4. Producers, consumers, and decomposers.
Question 73. When the number of organisms at successive levels are plotted, they assume the shape of a pyramid. This is called:
- Pyramid of Numbers
- Pyramid of Energy
- Pyramid of Biomass
- None of these.
Answer: 1. Pyramid of Numbers
Question 74. The salt concentration in the open sea is about:
- 35 per cent
- 3.5 per cent
- 85 per cent
- 0.8 per cent.
Answer: 2. 3.5 per cent
Question 75. The upper vertical zone up to the depth of 200 meters is known as:
- Photic zone
- Aphotic zone
- Abyssal zone
- None of these.
Answer: 1. Photic zone
Question 76. In a food chain, the largest number is of:
- Decomposers
- Consumers
- Predators
- Producers.
Answer: 4. Producers.
Question 77. The ecosystem is a self-sustaining unit because it consists of:
- Plants and animals only
- Physical environment only
- Microbes only
- All the above.
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 78. A component of the physical environment of an ecosystem is:
- Sunlight
- Decomposers
- Water
- Temperature.
Answer: 1. Sunlight
Question 79. In a food chain animals constitute the:
- First trophic level
- Second trophic level
- Intermediate trophic level
- Ultimate trophic level.
Answer: 3. Intermediate trophic level
Ecosystem NEET Notes
Question 80. Second-order consumers are:
- All heterotrophs
- Animals feeding on plants
- Animals preying on herbivorous animals
- Larger animals.
Answer: 3. Animals preying on herbivorous animals
Question 81. Active swimmers are:
- Phytoplankton
- Nektons
- Benthos
- Zooplankton.
Answer: 2. Nektons
Question 82. A food web is constituted by:
- Various interlinked food chains in a community
- Relationship between organisms and their environment
- Relationship between plants and animals
- Relationship between plants, animals and microbes.
Answer: 1. Various interlinked food chains in a community
Question 83. Vegetation found around the Mediterranean coast is called:
- Savannah
- Prairie
- Chaparral
- Melee.
Answer: 3. Chaparral
Question 84. An ecosystem is a complex interacting system of:
- Individuals
- Population
- Communities and their physical environment
- Communities and their soil condition.
Answer: 3. Communities and their physical environment
Question 85. Which of the following is truly a biome?
- Wheat crop field
- Pond ecosystem
- Greenfield
- Deciduous forest.
Answer: 4. Deciduous forest.
Question 86. The ecological niche of an organism is its:
- Way of life
- Habitat
- Habitat as well as climate
- Defended territory.
Answer: 1. Way of life
Question 87. Which of the following forests is more diverse?
- Coniferous evergreen
- Deciduous evergreen
- Tropical rain forest
- Sub-tropical rain forest.
Answer: 3. Tropical rainforest
Question 88. The solar energy is trapped to the maximum by:
- Wheat
- Rice
- Sugarcane
- Grams.
Answer: 1. Wheat
Question 89. Agroecosystem is a:
- Natural ecosystem
- Man-made ecosystem
- Balanced ecosystem
- Peripheral ecosystem.
Answer: 2. Man-made ecosystem
Question 90. Mangrove vegetation is found in:
- Dehradun valley
- Kulu valley
- Western ghats
- Sunderbans.
Answer: 4. Sunderbans.
Question 91. In a grassland ecosystem, the pyramid of energy is as:
- Inverted
- Upright
- Inverted or upright
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Upright
Question 92. Which of the following is one-way flow rather than two directions or cyclic?
- Nitrogen
- Potassium
- Free energy
- Both (2) and (3).
Answer: 4. Both (2) and (3).
Question 93. The photic zone is spread up to a depth of:
- 10 m
- 10-100m
- 100-300 m
- 200 m.
Answer: 4. 200 m.
Question 94. Chaparral occurs in the Mediterranean area and rainfall occurs during:
- Throughout the year
- Summer
- Winter
- Spring.
Answer: 3. Winter
Components Of Ecosystem NEET Biology
Question 95. The most diverse oceanic communities are in the:
- Abyssal zone
- Littoral zone
- Neritic zone
- Oceanic zone.
Answer: 2. Littoral zone
Question 96. Daily tidal cycle recurs after:
- 8 hrs
- 12.4 hrs
- 10.4 hrs
- 12 hrs
Answer: 2. 12.4 hrs
Question 97. The pyramid of numbers is based on
- Unit per area
- Food per individual
- Individuals with trophic levels
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Individuals in trophic levels
Question 98. Bach couple should produce only two children which will help in
- Checking pollution
- Stabilizing the ecosystem
- Fertility of soil
- Improving food web.
Answer: 2. Stabilising the ecosystem
Question 99. The trophic level of Woji in a forest ecosystem is:
- T3
- T4
- T2
- T1
Answer: 2. T4
Question 100. About how much of the net primary productivity of a terrestrial ecosystem is eaten and digested by herbivores?
- 10%
- 1%
- 30%
- 50%.
Answer: 1. 10%
Question 101. About how much of the net primary productivity of an aquatic ecosystem is eaten and digested by herbivores?
- 1%
- 10%
- 40%
- 90%.
Answer: 4. 90%
Question 102. Life without air is:
- Free from oxidative damage
- Impossible
- Anaerobic
- Reduction in life spam
Answer: 3. Anaerobic
Question 103. Tropical dense forest is due to:
- High temp, and excess rain
- Low temp, and excess rain
- High temp, and less rain
- Wild animals like tigers, lions, bears.
Answer: 1. High temp, and excess rain
Question 104. The pyramid of energy is always:
- Inverted
- Upright
- Both upright and inverted
- Inverted in the forest ecosystem.
Answer: 2. Upright
Question 105. A kite eats mice, mice live on grains, Hence the kite is a:
- Primary producer
- Secondary consumer
- Primary consumer
- Secondary producer.
Answer: 2. Secondary consumer
Question 106. The composition of soil air is affected by:
- Pore size
- Soil organisms
- Type of roots
- All of these.
Answer: 4. All of these
Components Of Ecosystem NEET Biology
Question 107. Plants growing in alpine zone are short due to:
- Low temperature
- High wind velocity
- High light intensity
- None of these.
Answer: 2. High wind velocity
Question 108. Plants growing in the seashore are generally resistant to:
- Lodging
- Erosion
- Salt spray
- Injuries.
Answer: 3. Salt spray
Question 109. An anatomical feature that exclusively develops to counter the high velocity of wind:
- Reaction wood formation
- Absence of secondary growth
- Absence of leaves
- Absence of more branches.
Answer: 1. Reaction wood formation
Question 110. The classification of plant groups on the basis of temperature differentiating four zones such as mega therms was proposed by:
- Clements
- Raunkiaer
- Odum
- Warming.
Answer: 2. Raunkiaer
Question 111. Flowering is induced if germinating seeds are exposed
- Low temperature
- High temperature
- Temperature below freezing
- Temperature above 45°C.
Answer: 1. Low temperature
Question 112. The percentage of light from total solar input utilized by plants:
- About 1 %
- 3-5%
- 7-8%
- 14%.
Answer: 1. About 1 %
Question 113. Albido value refers to:
- Turbidity of solar radiations
- Percentage of solar absorption
- Percentage of reflected light by a surface
- Amount of light absorbed by forests.
Answer: 3. Percentage of reflected light by a surface
Question 114. According to Geiger, the percentage of light reflected by the clouds is
- 9%
- 10%
- 48%
- 33%.
Answer: 4. 33%.
Question 115. The albedo value of a forest is around:
- 1-2%
- 3-5%
- 5-10%
- 20-30%.
Answer: 3. 5-10%
Question 116. The aquatic thermal strata where no temperature gradients are observed is called as:
- Hypolimnion
- Metalimnion
- Epilimnion
- Thermocline.
Answer: 1. Hypolimnion
Components Of Ecosystem NEET Biology
Question 117. The alpine forests are classed under the plant group called:
- Mesotherms
- Hekistotherms
- Microtherms
- Megatherms.
Answer: 2. Hekistotherms
Question 118. The optimum temperature for seedling growth in the upper Gangetic plains is around:
- 10°-15°C
- 5°-10°C
- 0°-25°C
- 30°—40°C.
Answer: 3. 0°-25°C
Question 119. When a plant of ho^ climate is transferred to colder regions, it gets an injury called:
- Chilling
- Thermal death
- Desiccation
- Freezing.
Answer: 1. Chilling
Question 120. In the western Himalayas, the Betula trees usually occur in:
- Tropical zone
- Sub-tropical zone
- Alpine zone
- Temperate zone.
Answer: 3. Alpine zone
Question 121. Annual carbon fixation by photosynthesis is:
- 7 x 1013
- 7×1010
- 7 x 1012
- 7 x 1020
Answer: 1. 7 x 1013
Question 122. Annual world precipitation is:
- 7 x 1010 g
- 7 x 1010 g
- 4.46 x 1010 g
- 4.46 x 1020 g.
Answer: 4. 4.46 x 1020 g.
Question 123. Maximum oxygen comes from:
- Phytoplankton
- Grasslands
- Forests
- Herbs and shrubs.
Answer: 1. Phytoplankton
Question 124. The main nitrogen reservoir in the biosphere is:
- Atmosphere
- Ocean
- Organisms
- Rocks.
Answer: 1. Atmosphere
Energy Flow In Ecosystem NEET Study Material
Question 125. Which one of the following pairs is a sedimentary type of biogeochemical cycle?
- Phosphorus and CO2
- Oxygen and Nitrogen
- Phosphorus and Nitrogen
- Phosphorus and Sulphur.
Answer: 4. Phosphorus and Sulphur
Question 126. The largest reservoir of phosphorus in the biosphere is the
- Atmosphere
- Ocean
- Organisms
- Rocks.
Answer: 4. Rocks
Question 127. Which one of the following pairs is a sedimentary type of biogeochemical cycle?
- Phosphorus and CO2
- Oxygen and Nitrogen
- Phosphorus and Nitrogen
- Phosphorus and Sulphur.
Answer: 4. Phosphorus and Sulphur
Question 128. Sedge is:
- Polygonum
- Potamogeton
- Carex
- Typha.
Answer: 3. Carex
Question 129. The perennial grass stage is represented by:
- Aristida
- Heteropogon
- Poa
- Tortula.
Answer: 2. Heteropogon
Question 130. The series of changes on the previously barren area is:
- Sere
- Climax community
- Primary succession
- Secondary succession.
Answer: 3. Primary succession
Question 131. Crustose lichen is:
- Rhizocarpon
- Pannelia
- Dermatocarpon
- Cladonia.
Answer: 3. Dermatocarpon
Energy Flow In Ecosystem NEET Study Material
Question 132. Secondary succession will not be completed if the bare area is invaded by:
- Sphagnum
- Lantana
- Eichhomia
- All the above.
Answer: 4. All the above
Question 133. Plant succession occurring in a sandy area is:
- Psammosere
- Halosere
- Xerosere
- Hydrosere.
Answer: 1. Psammosere
Question 134. A plant growing on rock is:
- Psammophyte
- Eremophyte
- Lithophyte
- Chersophyte.
Answer: 3. Lithophyte
NEET Biology Ecosystem Questions From Competitive Examinations
Question 1. Green plants constitute:
- First trophic level
- Second trophic level
- Third trophic level
- Fourth trophic level.
Answer: 1. First trophic level
Question 2. Tip of an ecological pyramid is occupied by:
- Producers
- Herbivores
- Carnivores
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Carnivores
Question 3. Zooplanktonic forms are:
- Primary producers
- Carnivores
- Primary consumers
- Secondary consumers.
Answer: 3. Primary consumers
Question 4. Which of the following occurs in the abiotic component of the ecosystem?
- Flow of energy
- Cycling of materials
- Consumers
- Flow of energy and cycling of materials.
Answer: 2. Cycling of materials
Question 5. A treeless biome is:
- Tundra
- Grassland
- Desert
- All the above.
Answer: 4. All the above
Question 6. A man-made micro-ecosystem is:
- Plants grown in a pond
- Crop field
- Tank formed naturally in your courtyard
- Lake in a forest.
Answer: 2. Crop field
Energy Flow In Ecosystem NEET Study Material
Question 7. Which one has always a steeper vertical gradient?
- Pyramid of mass
- Pyramid of energy
- Pyramid of numbers
- Pyramid of energy in aquatic ecosystem.
Answer: 2. Pyramid of energy
Question 8. Which one is exclusive of xerophytic adaptation?
- Absence of stomata
- Long tap root system
- Stipular leaves
- Spines.
Answer: 4. Spines.
Question 9. Which one has evergreen vegetation and drought-adapted animals?
- Chaparral
- Savannah
- Tundra
- Deciduous forest.
Answer: 1. Chaparral
Question 10. Which part of the world has a high density of organisms?
- Grasslands
- Savannahs
- Deciduous forests
- Tropical rain forests.
Answer: 4. Tropical rainforests
Question 11. Viviparity and pneumatophores are features of:
- Hydrophytes
- Halophytes
- Mesophytes
- Xerophytes.
Answer: 2. Halophytes
Question 12. The flora and fauna in lakes or ponds are:
- Lefitic biota
- Lotic biota
- Abiotic biota
- Field layer.
Answer: 1. Lefitic biota
Components Of Ecosystem NEET Biology
Question 13. Trophic levels are formed by:
- Only plants
- Only animals
- Only carnivores
- Organisms linked in food chains.
Answer: 4. Organisms linked in food chains.
Question 14. An ecosystem has which of the following two components?
- Frogs and men
- Weeds and trees
- Biotic and abiotic
- Plants and animals.
Answer: 3. Biotic and abiotic
Question 15. The atmospheric/humidity is measured by
- Potometer
- Photometer
- Hygrometer
- Auxanometer.
Answer: 3. Hygrometer
Question 16. The concept of ecological pyramids was developed by
- Elton
- Darwin
- Odum
- Reiter.
Answer: 1. Elton
Question 17. Feeding on herbivorous insects is:
- Primary consumer
- Secondary consumer
- Tertiary consumer
- Top carnivore.
Answer: 2. Secondary consumer
Question 18. Maximum biomass of autotrophs in oceans is made of:
- Benthic brown algae, coastal red algae, and daphnids
- Benthic diatoms and marine viruses
- Seagrasses and slime molds
- Free-floating microalgae, cyanobacteria, and nanoplankton.
Answer: 4. Free-floating microalgae, cyanobacteria, and nanoplankton.
Question 19. Terai forest is:
- Tropical
- Coniferous
- Deciduous
- Temperate deciduous.
Answer: 1. Tropical
Components Of Ecosystem NEET Biology
Question 20. Savannah is found commonly in :
- U.S.A.
- U.S.S.R.
- Australia
- India.
Answer: 3. Australia
Question 21. A recently discovered ecosystem is:
- Crater
- Tundra
- Floating Iceberg
- Vent.
Answer: 1. Crater
Question 22. Controlling factors in the ecosystem is:
- Soil moisture
- Food
- Trepidation
- Temperature.
Answer: 3. Trepidation
Question 23. The transition zone between the two vegetational types is:
- Ecotone
- Ecotype
- Ecocline
- Ecosystem.
Answer: 1. Ecotone
Question 24. Plant decomposers are:
- Monera and fungi
- Fungi and plants
- Protista and Animalia
- Animalia and Monga.
Answer: 1. Monera and fungi
Question 25. The ecosystem consists of:
- Producers
- Consumers
- Decomposers
- All of these.
Answer: 4. All of these.
Question 26. Desert can be converted into green land by planting:
- Oxylophytes
- Psammophytes
- Halophytes
- Tropical trees.
Answer: 2. Psammophytes
Question 27. In the food chain, the lion is a:
- Primary consumer
- Secondary producer
- Tertiary consumer
- Secondary consumer.
Answer: 3. Tertiary consumer
Question 28. Which ecosystem shows maximum genetic diversity?
- Tropical rain forests
- Temperate forests
- Coniferous forests
- Subtropical forests.
Answer: 1. Tropical rainforests
Question 29. Which of the following is correctly matched?
- Butterfly camouflage
- Garden lizard mimicry
- House lizard autotomy
- None of these.
Answer: 3. House lizard autotomy
Nutrient Cycling In Ecosystems NEET
Question 30. Organisms found at the bottom of the sea are:
- Planktons
- Benthos
- Nektons
- Phytons.
Answer: 2. Benthos
Question 31. X is eating curd/yogurt. For this food intake in a food chain, he should be considered as occupying:
- First trophic level
- Second trophic level
- Third trophic level
- Fourth trophic level.
Answer: 3. Third trophic level
Question 32. These belong to the category of primary consumers:
- Eagle and snake
- Insects and cattle
- Snake and Frog
- Water insects.
Answer: 2. Insects and cattle
Question 33. If the high-altitude birds become rare or extinct, the plants that may disappear along with them are:
- Pine
- Oak
- Orchids
- Rhododendrons.
Answer: 2. Oak
Question 34. An ecosystem that can be easily damaged but can recover after some time if the damaging effect stops will have the following:
- Low stability and low resilience
- High stability and high resilience
- Low stability and high resilience
- High stability and low resilience.
Answer: 3. Low stability and high resilience
Question 35. Which of the following is expected to have the highest value (gm/m²/year) in a grassland ecosystem?
- Gross production (GP)
- Net production (NP)
- Secondary production
- Tertiary production.
Answer: 1. Gross production (GP)
Question 36. If by radiation all nitrogenase enzymes are inactivated, then there will be no:
- Conversion from nitrate to nitrite in the legumes
- Conversion from ammonium to nitrate in soil
- Fixation of nitrogen in the legumes
- Fixation of atmospheric nitrogen.
Answer: 4. Fixation of atmospheric nitrogen.
Question 37. The Great Barrier Reef along the east coast of Australia can be categorized as:
- Population
- Community
- Ecosystem
- Biome.
Answer: 4. Biome.
Question 38. Which one of the following pairs is mismatched?
- Savannah – acacia trees
- Prairie – epiphytes
- Tundra – permafrost
- Coniferous forest – evergreen trees.
Answer: 2. Prairie – epiphytes
Question 39. Which one of the following is the correct matching of the plant, its habitat, and the forest type where it normally occurs?
- Prosopis, tree, scrub
- Saccharum, grass, forest
- Shorea robusta, herb, tropical rainforest
- Acacia catechu, tree, coniferous forest.
Answer: 2. Saccharum, grass, forest
Question 40. Given below is one of the types of ecological pyramids. This type represents:

- Pyramid of numbers in a grassland
- Pyramid of biomass in a fallow land
- Pyramid of biomass in a lake
- Energy pyramid in a spring.
Answer: 3. Pyramid of biomass in a lake
Question 41. Energy transferred from one trophic level to another is:
- 5%
- 10%
- 15%
- 20%.
Answer: 2. 10%
Question 42. Maximum absorption of rainfall water is done by:
- Tropical deciduous forest
- Tropical evergreen forest
- Tropical savannah
- Scrub forest.
Answer: 2. Tropical evergreen forest
Question 43. The pyramid of energy is always upright for any ecosystem. This situation indicates the fact that
- Producers have the lowest energy conversion efficiency
- Carnivores have a better energy conversion efficiency
- Energy conversion efficiency is the same in all trophic levels
- Herbivores have a better energy conversion efficiency than carnivores.
Answer: 4. Herbivores have a better energy conversion efficiency than carnivores.
Question 44. Which of the following is called as a detritivore?
- An animal feeding on decaying organic matter
- An animal feeding on a plant
- A plant feeding on an animal
- An animal feeding on another animal.
Answer: 1. An animal feeding on decaying organic matter
Question 45. Which one of the following is not used for the construction of ecological pyramids?
- Dry weight
- Fresh weight
- Rate of energy flow
- Number of individuals.
Answer: 2. Fresh weight
Nutrient Cycling In Ecosystems NEET
Question 46. In the given formula, what does “a” represent?
Formula: Assimilatory efficiency = \(\frac{\text{Use of energy in food}{“a”}}\) x 100.
- Energy obtained through primary producer
- Biomass at own level
- Biomass at lower trophic level
- Energy is obtained through food.
Answer: 4. Energy obtained through food.
Question 47. Increased asthmatic attacks in certain seasons are related to:
- Eating fruits preserved in tin containers
- Inhalation of seasonal pollen
- Low temperature
- Hot and humid environment.
Answer: 2. Inhalation of seasonal pollen
Question 48. Which one of the following ecosystem types has the highest annual net primary productivity?
- Tropical deciduous forest
- Temperate evergreen forest
- Temperate deciduous forest
- Tropical rain forest.
Answer: 4. Tropical rainforest.
Question 49. Identify which one of the following is an example of an incomplete ecosystem.
- Cave
- Grassland
- River
- Wetland.
Answer: 1. Cave
Question 50. Consider the following statements concerning food chains.
- Removal of 80% of tigers from an area resulted in greatly increased growth of vegetation
- Removal of most of the carnivores resulted in an increased population of deer
- The length of food chains is generally limited to 3-4 trophic levels due to energy loss
- The length of food chains may vary from 2 to 8 trophic levels.
Answer: 3. The length of food chains is generally limited to 3-4 trophic levels due to energy loss
Question 51. Large Woody Vines are more commonly found in:
- Temperate forests
- Mangroves
- Tropical rainforests
- Alpine forests.
Answer: 3. Tropical rainforests
Question 52. Which one of the following statements for the pyramid of energy is incorrect, whereas the remaining three are correct?
- Its base is broad
- It shows the energy content of different trophic-level organisms
- It is inverted in shape
- It is upright in shape.
Answer: 3. It is inverted in shape
Question 53. The mass of living matter at a trophic level in an area at any time is called:
- Standing crop
- Detritus
- Humus
- Standing state.
Answer: 4. Standing state.
Question 54. Of the total incident solar radiation, the proportion of PAR is:
- About 70%
- About 60%
- Less than 50%
- More than 50%.
Answer: 4. More than 50%.
Question 55. Identify the possible link, “A” in the following food chain:
Plan—insect—frog—‘ ‘A” —Eagle
- Wolf
- Cobra
- Parrot
- Rabbit.
Answer: 2. Wolf
Question 56. The upright pyramid of numbers is absent in:
- Forest
- Lake
- Grassland
- Rabbit.
Answer: 2. Lake
Question 57. An inverted pyramid of numbers and an inverted pyram of biomass are respectively seen in
- Grassland and tree ecosystem
- Sea and tree ecosystem
- Tree and sea ecosystem
- Sea and grassland ecosystem.
- Tree and grassland ecosystem.
Answer: 3. Sea and grassland ecosystem
Question 58. Which of the following is a pioneer in xerarch success?
- Phytoplanktons
- Lichens
- Bryophytes
- Rooted hydrophytes
- Sedges
Answer: 2. Lichens
Question 59. The natural reservoir of phosphorus is
- Animal bones
- Rock
- Fossils
- Sea water.
Answer: 2. Rock
Question 60. Which one of the following processes during decomposition is correctly described?
- Humification leads to the accumulation of a dark coloured substance humus which undergoes microbial action at a very fast rate.
- Catabolism-Last step decomposition under fully anaerobic condition
- Leaching-Water soluble inorganic nutrients rise to the top layers of soil
- Fragmentation- carried out by organisms such as earthworms.
Answer: 4. Fragmentation- carried out by organisms such as earthworms.
Question 61. Secondary productivity is the rate of formation of new organic matter by:
- Parasite
- Consumer
- Decomposer
- Producer.
Answer: 2. Consumer