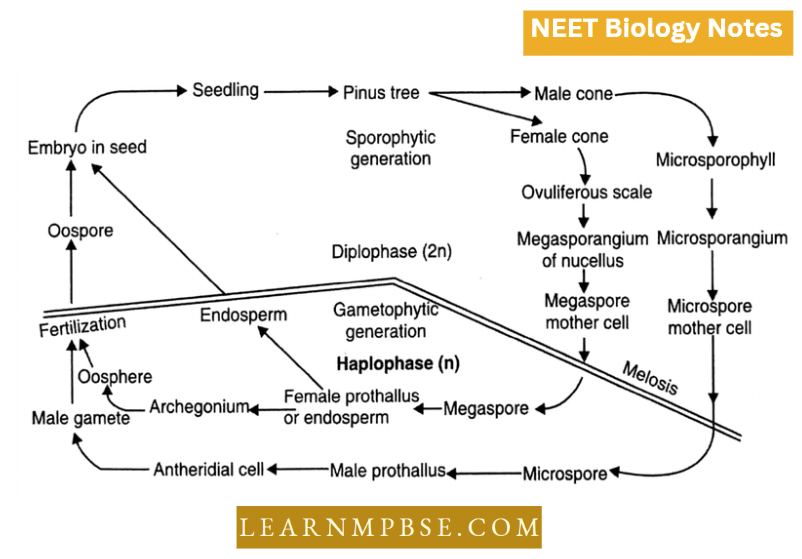
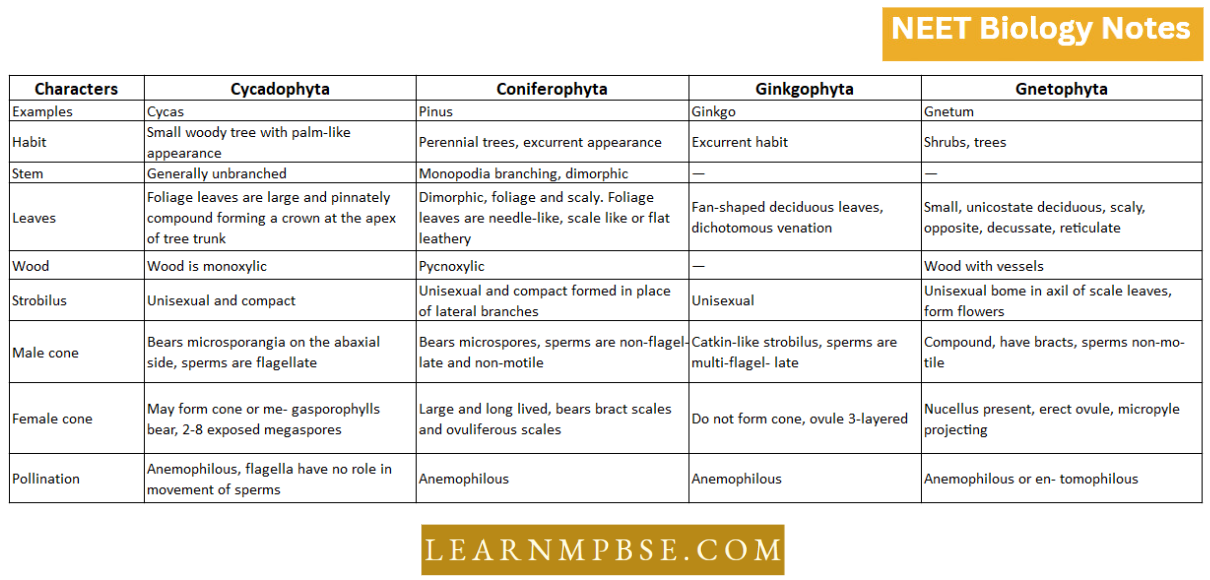
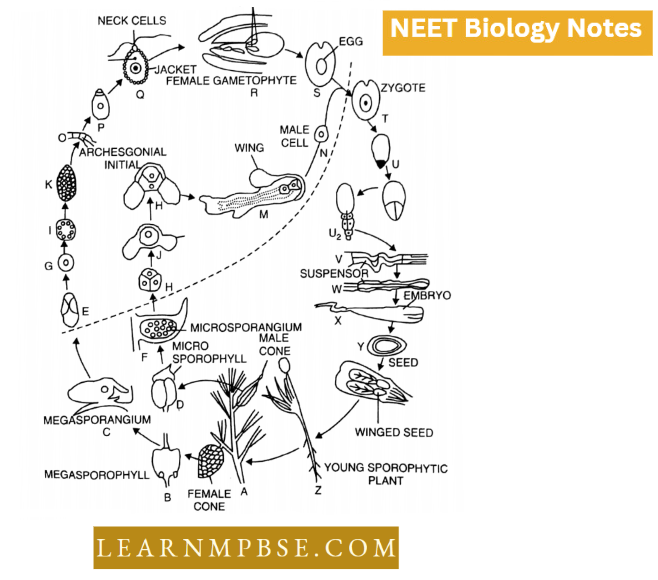
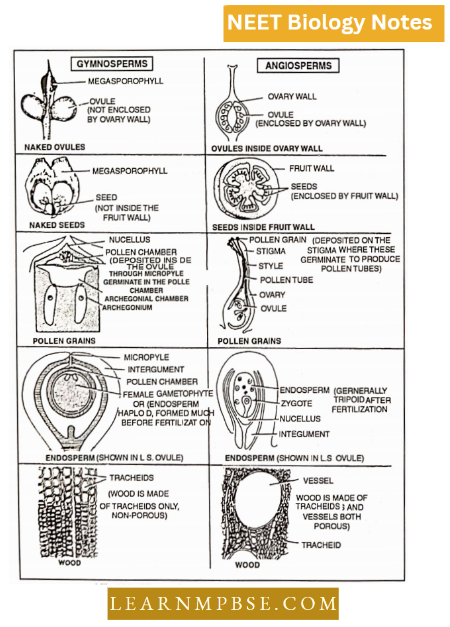
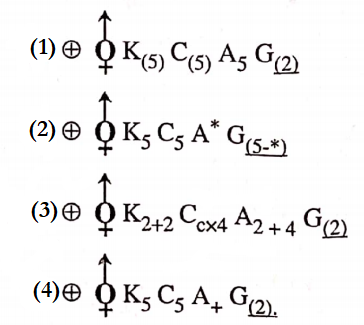
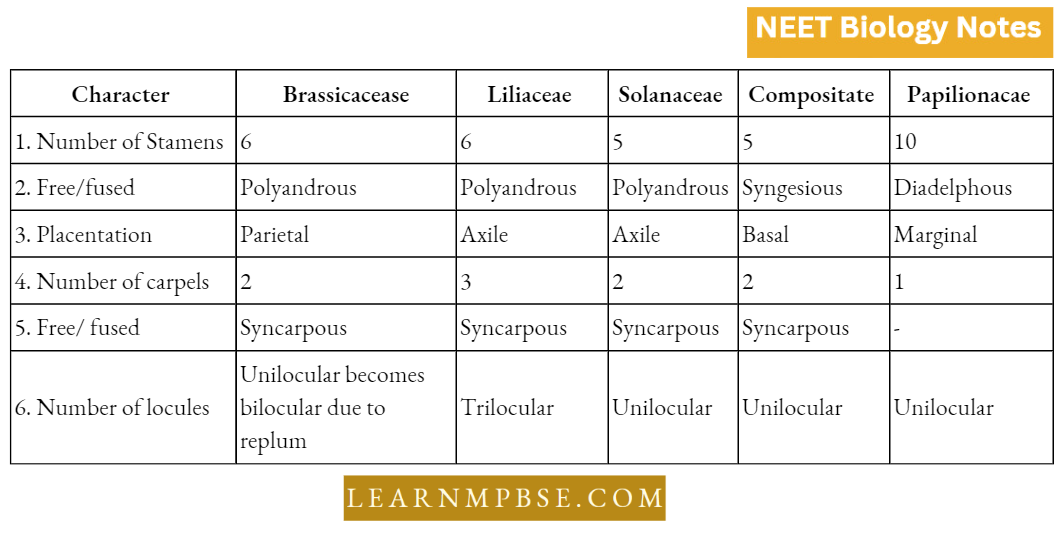
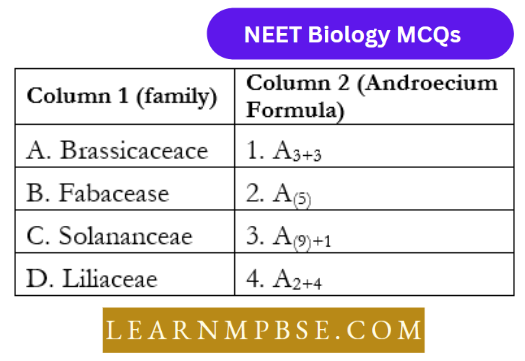
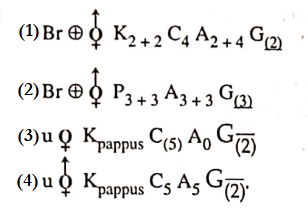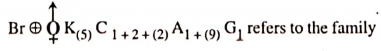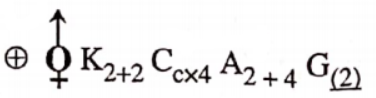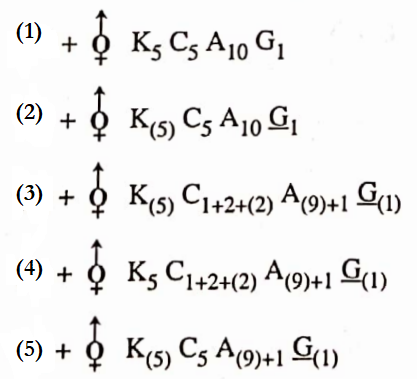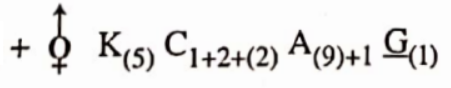NEET Biology Phylum Porifera Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Approximately what percentage of existing animal species are invertebrates?
- 20%
- 50%
- 70%
- 95%
Answer: 4. 50%
Question 2. Which of the following is not a characteristic of organisation in the kingdom Animalia?
- Storage of carbohydrates as starch
- Multicellularity
- Obtaining nutrients by ingestion
- Having eukaryotic cells without wails.
Answer: 1. Multicellularity
Question 3. Most sponges are :
- Bilaterally symmetrical
- Radially symmetrical
- Vertically symmetrical
- Asymmetrical.
Answer: 4. Asymmetrical.
Question 4. Water exits from a sponge through the :
- Osculum
- Spicule
- Choanocyte
- Amoebocyte.
Answer: 1. Osculum
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question and Answers
MCQs on PoriferaQuestion 5. Which of the following is not a function of amoebocytes in a sponge?
- Secretion of skeletal materials
- Control of pores by contraction
- Transport of food to the epidermal cells
- Participation in reproduction.
Answer: 2. Control of pores by contraction
Question 6. Which of the following is not true of reproduction in sponges?
- Asexual reproduction by gemmules
- Asexual reproduction by budding
- Internal sterilization
- Gamete production by epidermal cells.
Answer: 4. Gamete production by epidermal cells.
Question 7. Amoebocyte control of water entry
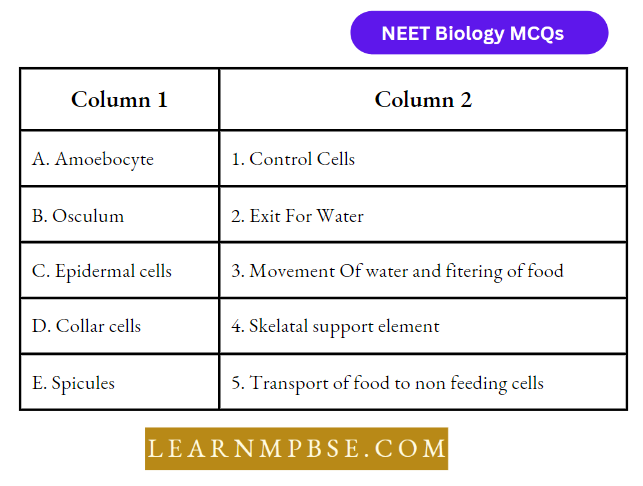
Which of the following sets is correct
- (A-1), (B-2), (C-3), (D-4) (E-5)
- (A-1) (B-3) (C-2) (D-4) (E-5)
- (A-v) (B-2) (C-1) (D-3) (E-5)
- (A-4) (B-2) (C-1) (D-3) (E-5).
Answer: 3. (A-v) (B-2) (C-1) (D-3) (E-4)
Question 8. The mode of digestion in sponges is :
- Intracellular
- Intercellular
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above.
Answer: Intercellular
Question 9. Spongocoel of leucosolenla is lined by :
- Pinacocytes
- Amoebocytes
- Choanocytes
- Scleroblasts.
Answer: 3. Choanocytes
Question 10. A common chamber for all the canals of a sponge is
- In current canal
- Paragastric
- Excurrent canal
- Radial canal.
Answer: 2. Paragastric
Question 11. Leucosolenia is :
- Sessile, colonial and marine
- Sessile, solitary and marine
- Sessile, colonial and freshwater
- Sessile, solitary and marine.
Answer: 1. Sessile, colonial and marine
Question 12. Glass rope sponge is the common name of :
- Sycon
- Hyalonema
- Euspongia
- Leucosolenia.
Answer: 2. Hyalonema
Question 13. In current canal communicates with radial canals by:
- Apopyles
- Prosopyle
- Dermal Ostia
- Gastric Ostia.
Answer: 2. Prosopyle
Question 14. Gemmules are endogenous in origin and play a vital role in:
- Perennation
- Dispersal
- Reproduction
- All of the above.
Answer: 2. Dispersal
Question 15. Mesohyal is largely secreted by :
- Collencyte
- Trophocyte
- Choanocyte
- Chromocyte.
Answer: 1. Collencyte
Question 16. In sponges, food particles are ingested by :
- Thesocytes
- Pinacocytes
- Collencyte
- Choanocytes.
Answer: 4. Choanocytes.
Question 17. Which of these cells is not found in sponges?
- Calcoblasts
- Myocytes
- Porocyte
- Cnidoblasts.
Answer: 4. Cnidoblasts.
Question 18. The power of regeneration in sponges is due to :
- Thesocytes
- Amoebocytes
- Scleroblasts
- Archaeocytes.
Answer: 4. Archaeocytes.
Question 19. Sponge differs from metazoan in :
- Cell division
- Division of labour
- Cell organization
- Sponge lacks
Answer: 3. Cell organization
Question 20. Best commercial sponges are found in :
- Cold shallow water
- Warm shallow water
- Deep seawater
- Warm shallow seawater.
Answer: 4. Warm shallow seawater.
Question 21. The skeleton of the bath sponge is made up of :
- Calcareous spicules
- Spongin fibres
- Collagen fibres
- Yellow fibres of elastic cartilage.
Answer: 2. Spongin fibres
Question 22. Sponges are not found in :
- Sea water
- Brackish water
- Cold water
- Sandy shore.
Answer: 3. Coldwater
Question 23. The course of the water system in the second is :
- Ostia
- In current canal
- Prosopyle
- Radial canal
- Apopyle
- Spongocoel
- Osculum
Choose The Correct Option
- 1→2→3→4→5→6→7
- 1→3→2→4→5→6→7
- 1→4→3→4→5→6→7
- 1→5→2→3→4→6→7
Answer: 1. 1→2→3→4→5→6→7
Question 24. Totipotent cells in sponges are :
- Porocyte
- Choanocyte
- Archaeocyte
- Pinacocyte;
Answer: 3. Archaeocyte
Question 25. Calcareous spicules are formed by :
- Calcoblasts
- Silicoblasts
- Spiroblasts
- Spongoblasts.
Answer: 1. Calcoblasts
Question 26. In a sponge body, the mesenchyme contains which type of cells:
- Pinacocytes
- Choanocytes
- Amoebocytes
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Amoebocytes
Question 27. Monoaxon spicule with a knob at one end is called:
- Acanthostyle
- Tylostyle
- Diastyle
- Style.
Answer: 2. Tylostyle
Question 28. One of the following cells takes part in the reproduction of sponges:
- Archaeocytes
- Thesocytes
- Myocytes
- Choanocytes.
Answer: 1. Archaeocytes
Question 29. Which one of the following is the most distinctive of the character of sponges?
- They are acellular
- They possess special cells called choanocytes
- They reproduce asexually
- They are all marine.
Answer: 2. They reproduce asexually
Question 30. Which one of the following cells maintains a current of water in a sponge?
- Trophocytes
- Porocytes
- Choanocytes
- Chromocytes.
Answer: 3. Choanocytes
Question 31. The boring sponge is :
- Spongilla
- Euplectella
- Cliona
- Euspongia.
Answer: 3. Cliona
Question 32. A chamber which is common in different types of canal systems is :
- Spongocoel
- Coelom
- Pseudocoelom
- Haernocoel
Answer: 1. Spongocoel
Question 33. Osculum is generally surrounded by :
- Spongin fibre
- Spicules
- Myocytes
- Pinacocytes.
Answer: 3. Myocytes
Question 34. The cells in which the food is stored in the form of glycogen and glycoprotein are :
- Thesocyte
- Archaeocyte
- Choanocyte
- Amoebocyte
Answer: 1. Thesocyte
Question 35. The outer epithelial layer in sponges has:
- Choanocyte
- Amoebocyte
- Porocyte
- Porocyte and pinacocyte.
Answer: 4. Porocyte and pinacocyte.
Question 36. In sponges, nutrition, excretion, and respiration depend upon the system named:
- Water vascular system
- Canal system
- Circulatory system
- Haemocoelomic system.
Answer: 2. Canal system
Question 37. Which one of the sponges is harmful in the oyster industry?
- Cliona
- Ettspongia
- Hyalonema
- Euplectella.
Answer: 1. Cliona
Question 38. Olynthus is termed as the simplest type of sponge in structure as well as in form :
- It is an adult animal belonging to the germs as suggested by Haeckel
- A species of leucopenia
- A transitory stage in the life history of the second
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. A species of leucopenia
Question 39. Which cells are found only in sponges?
- Amoeboid cells
- Choanocytes
- Pigment cells
- Gland cell.
Answer: 2. Choanocytes
Question 40. Trn most simple type of canal system of porifera, water flows through which one of the following ways?
- Ostia spongocoel – osculum + exterior
- Spongocoel – ostia + osculum + exterior
- Osculum – spongocoel + ostia -+ exterior
- Osculum – ostia – spongocoel + exterior.
Answer: 3. Osculum – spongocoel + ostia -+ exterior
Question 41. Gemmules are helpful in :
- Digestion
- Sexual reproduction
- Water current relation
- Asexual reproduction.
Answer: 4. Asexual reproduction.
Question 42. Which of the following is a freshwater sponge?
- Euplectella
- Spongilla
- Euspongia
- Sycon.
Answer: 2. Spongilla
Question 43. Larva of the sponge is known as :
- Glochidium larva
- Trochophore larva
- Zoea larva
- Amphiblastula larva.
Answer: 4. Amphiblastula larva.
Question 44. Which one of the following is not a class of phylum Porifera?
- Calcarea
- Hexactinellida
- Hydrozoa
- Demospoangiae.
Answer: 3. Hydrozoa
Question 45. Protospongia is a connecting link between :
- Protozoa and porifera
- Porifera and coelenterata
- Protozoa and annelida
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Protozoa and Porifera
Question 46. The dried piece of bath sponge is made up of :
- Cellulose fibres
- Silk fibres
- Spongin fibres
- Yellow elastic fibres.
Answer: 3. Spongin fibres
Question 47. In sponges, prostyle is a :
- Cell at the opening of the incurrent canal
- Smaller canal and connect incurrent canal with radial canal
- A cell which forms the lining of spongocoel
- Contractile element at osculum.
Answer: 2. Smaller canal and connect incurrent canal with radial canal
Question 48. Which one of the following statements is correct?
- The body of sponges consists of epithelial tissues only
- All 4 types of tissues are seen in the body of the sponge
- Only epithelial and connective tissues are present
- Structurally organized tissues are absent in the body of the sponge.
Answer: 4. Structurally organized tissues are absent in the body of a sponge.
Question 49. In an experiment, the sponge is squeezed through silk bolting cloth and allowed to stand undisturbed in an appropriate medium. It is per{ormed to prove that :
- The sponges are multicellular
- The cells are loosely arranged
- The cells are so small that they can be squeezed through cloth
- The sponges are non-living.
Answer: 2. The cells are loosely arranged
Question 50. Phylogenetically sponges have evolved from :
- Protozoans
- Flagellates
- Choanoflagellates
- Ciliates.
Answer: 3. Choanoflagellates
Question 51. The inner lining of spongocoel is formed by :
- Porocytes
- Pinacocytes
- Choanocytes
- Archeocytes.
Answer: 3. Choanocytes
Question 52. Which of the following is not diploblastic?
- Coelenterata
- Porifera
- Acnidaria
- Platyhelminthes.
Answer: 4. Platyhelminthes.
Question 53. The body of sponges is mainly composed of :
- Spongin fibres
- Mesogloea
- Spicules
- Nematoblasts
Answer: 1. Spongin fibres
Phylum Coelenterata Cnidaria Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Which of the following is a radially symmetrical animal?
- Planarian
- Rotifer
- Fluke
- Sea anemone.
Answer: 4. Sea anemone.
Question 2. A distinguishing feature of cnidarians is the presence of specialized cells that contain nematocysts. They are located on the surface of the body wall and tentacles. They are used for capturing prey. These cells are called:
- Cnidocytes
- Flame cells
- Statocysts
- Nephridiopores.
Answer: 1. Cnidocytes
Question 3. Scyphozoan medusae are most commonly called :
- Sea anemones
- Jellyfishes
- Corals
- Hydra.
Answer: 4. Hydra.
Question 4. The ciliated free-swimming larval stage of cnidarian Aurelia (jellyfish) is called:
- Blastula
- Planula
- Polyp
- Medusa.
Answer: 1. Blastula
Question 5. A hydra is the simplest form of nervous system for integrating the functions of the body. It is called as :
- Ladder system
- Nerve net system
- Ganglionic system
- Ventral solid cord system.
Answer: 2. Nerve net system
Question 6. Polymorphism is an occurrence of:
- Several organ systems in an individual
- Several patterns of adaptation in a major animal group
- Several modes of feeding in an individual.
- Several modes of phenotypes in a population.
Answer: 4. Several modes of phenotypes in a population.
Question 7. Coelenterata includes sedimentary animals, they are:
- Bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic
- Radially symmetrical, diploblastic
- Bilaterally symmetrical, diploblastic
- Radially symmetrical, triploblastic.
Answer: 2. Radially symmetrical, diploblastic
Question 8. The gastrovascular cavity is divided into compartments:
- Hydrozoa
- Scyphozoa
- Actinozoa
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Scyphozoa
Question 9. Polymorphism is exhibited by :
- Hydra
- Obelia
- Aurelia
- Coral.
Answer: 2. Obelia
Question 10. The alternation of sexual and asexual generation is known as:
- Digenesis
- Metagenesis
- Metamorphosis
- Dimorphism.
Answer: 2. Metagenesis
Question 11. Which one of the following inhabitants of freshwater bodies?
- Hydra
- Obelia
- Tubularia
- Gorgonia.
Answer: 1. Hydra
Question 12. The animal without sexual medusae is :
- Velella
- Millipore
- Hydra
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Hydra
Question 13. Testes in Hydra:
- Are less numerous than ovary
- Have a conical tip
- Are nearer the basal disc
- Develop one sperm in each.
Answer: 2. Have a conical tip
Question 14. In an association mutually beneficial to both partners, in the green hydra, some small green plants live in it giving it a green colour. They are :
- Zooxanthellae
- Zoochlorella
- Volvox
- Chlamydomonas.
Answer: 2. Zoochlorella
Question 15. Which one of the following layers contains zoochlorella?
- Gastrodermal cells
- Myoepithelial cells
- Mesogloea
- Interstitial cells.
Answer: 1. Gastrodermal cells
Question 16. Tentacles of hydra arise from :
- Aboral end
- Hypostome
- Stalk
- Body wall.
Answer: 2. Hypostome
Question 17. In hydra between the ectodermic and gastrodermis, the intermediate structureless layer is found. This is known
- Mesogloea
- Muscle endothelial
- Myoepithelial layer
- Endoderm.
Answer: 1. Mesogloea
Question 18. Spermatogonia in hydra develops from :
- Interstitial cells
- Gastrodermis
- Muscle endothelial cells
- Gland cells.
Answer: 1. Interstitial cells
Question 19. The proximal end of hydra bears an adhesive disc which secretes a sticky substance for:
- Protection
- Defence from enemies
- Sexual attraction
- Attachrnent to the substrate of hydra.
Answer: 4. Attachrnent to the substrate of hydra.
Question 20. Which of the following will happen to a hydra when it is cut transversely into 2 halves?
- Building up of lost parts
- Reunion of 2 halves
- Wound healing
- Death.
Answer: 1. Building up of lost parts
Question 21. Below the hypostome the number of tentacles is usually:
- 4-11
- 10-16
- 6-10
- 6-16.
Answer: 3. 6-10
Question 22. When an organism can be cut into two halves by one of the many longitudinal planes passing through the centre, the symmetry is said to be:
- Bilateral symmetry
- Radial symmetry
- Lateral symmetry
- Longitudinal symmetry.
Answer: 2. Radial symmetry
Question 23. The single sac-like cavity in the body of a hydra is called :
- Arachenteron
- Blastocoel
- Gastrovascular cavity
- Hypnotoxin.
Answer: 3. Gastrovascular cavity
Question 24. The poisonous fluid present in the nematocyst of hydra is:
- Toxin
- Venom
- Haematin
- Hypnotoxin.
Answer: 3. Haematin
Question 25. In hydra, the gastrodermis is composed of :
- Myoepithelial cells
- Myonutritive cells
- Sensory cells
- Cnidoblasts.
Answer: 2. Myonutritive cells
Question 26. The mesogloea of hydra contains:
- Nerve cells
- Sensory cell
- Nematoblasts
- Nocells.
Answer: 4. Nocells.
Question 27. In hydra, the nematocysts are absent on the basal disc. They are abundant in:
- Tupper part
- Tmidclle part
- Tentacles
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Tentacles
Question 28. Which animal depicts radial symmetry?
- Planaria
- Obelia
- Earthworks
- Pila.
Answer: 2. Obelia
Question 29. Stenotele nematocyst of hydra is important for :
- Catching prey
- Paralysing prey
- Tasting the food
- Tasting the water around;
Answer: 2. Paralysing prey
Question 30. Tentacles of hydra extend to the large length due to :
- Relaxation of myonemes of epitheliomuscular cells
- Relaxation of myonemes of gastrovascular cells
- The pressure generated by the body fluid
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Relaxation of myonemes of epitheliomuscular cells
Question 31. The body wall of a hydra consists of :
- Ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm
- Ectoderm, mesenchyme and endoderm
- Ectoderm and endoderm
- Epidermis, mesogloea and gastrodermis.
Answer: 4. Epidermis, mesogloea and gastrodermis
Question 32. Which one of the following is known as a persistent embryonic layer?
- Germ cells
- Cnidoblasts
- Interstitial cells
- Muscular cells.
Answer: 3. Interstitial cells
Question 33. The process of digestion of food in hydra is :
- Intercellular
- Extracellular
- Intracellular
- Both extracellular and intracellular.
Answer: 4. Both extracellular and intracellular.
Question 34. One of the following nematocysts is the most specialized for catching prey:
- Penetrant
- Large agglutinant
- Small conglutinant
- Desmoneme.
Answer: 4. Desmoneme.
Question 35. Nerve cells of hydra differ from those of higher animals in that :
- They conduct impulses in a definite direction
- They conduct impulses in all directions
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Both 1 and 2
Question 36. One of the following animals has a nervous system but no brainer:
- Cockroach
- Earthworm
- Hydra
- Sponges.
Answer: 3. Hydra
Question 37. In hydra, our contains :
- A few ova
- Single ovum
- No ova
- Lunlerous ova.
Answer: 2. Single ovum
Question 38. Mark the group, of animals that do not move :
- Bug and slug
- Coral and sponges
- Antedon and holothurian
- Coral and lepisma.
Answer: 2. Coral and sponges
Question 39. Fertilization in hydra is :
- Hxtemal
- In the body Glendale
- Both male and female individuals come close and fuse
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. In the body Lenrale
Question 40. Self-fertilization in Hydra never takes place because they are :
- Protandrous
- Protogynous
- Asexual
- Hermaphrodite.
Answer: 1. Protandrous
Question 41. Hydra reproduces by bidding during:
- Unfavourable conditions
- Favourable conditions
- Less water supply
- Summer.
Answer: 2. Favourable conditions
Question 42. Coral reefs have been a result of activity of mainly:
- Molluscs
- Echinoderms
- Coelenterates
- Hernichordates.
Answer: 3. Coelenterates
Question 43. Polymorphism is best defined as the occurrence of:
- Several types of organ systems in an individual
- Different kinds of larval forms in the life history of an animal
- Different functions performed by a single kind of organism
- Several different types of individuals in the species.
Answer: 4. Several different types of individuals in the species.
Question 44. The cells of blastula in hydra divide repeatedly and tangentially forming many cells which migrate inward from all directions and fill in the blastocoel. This process is called:
- Invagination
- Immigration
- Involution
- Ingression.
Answer: 4. Ingression.
Question 45. Which animals are exceptions to the organ system level of organisation?
- Echinoderms
- Sponges
- Coelenterates
- Both 2 and 3.
Answer: 4. Both 2 and 3.
Question 46. Hydra is negatively chemotropic because it :
- Moves away from strong light
- Prefers weak illumination
- Moves to water of low temperature
- Avoids chlorinated water.
Answer: 3. Moves to water of low temperature
Question 47. If a hydra has to propagate successfully in a pond which is going to dry up soon, what method of reproduction will take place in the animal:
- Panhenogenesis
- Budding
- Sexual
- Sporogony.
Answer: 3. Sexual
Question 48. Tentaculocyst is :
- Receptor organ in Ascaris
- A part of Scolex
- Protective covering of amoeba
- A receptor organ of aurelia.
Answer: 4. A receptor organ of aurelia.
Question 49. Metagenesis is exhibited by :
- Hydra
- Fungia
- Metridium
- Obelia.
Answer: 4. Obelia.
Question 50. Penetrants and steno-teles are the names of hydra’s nematocysts. Of these;
- Penetrants are larger
- Penetrants are smaller
- Steoteles are not found in hydra
- Both are the same.
Answer: 4. Both are the same.
Question 51. A fringing reef is usually located at:
- Very near the shore
- In deep sea
- In cold sea
- Far away from the shore.
Answer: 1. Very near the shore
Question 52. True corals come from the order :
- Hydroidea
- Pennatulacea
- Madreporaria
- Alcyonacea.
Answer: 3. Madreporaria
Question 53. Sea pen is a popular name for:
- Gorgonia
- Pennatula
- Fungia
- Corallium.
Answer: 2. Pennatula
Question 54. The body cavity of cockroaches is
- Hydrozoan
- Scyphozoan
- Anthozoan
- Fish.
Answer: 3. Anthozoan
Question 55. Rhopalium is a complex of :
- Two sense organs
- Three sense organs
- Four sense organs
- Five sense organs.
Answer: 3. Four sense organs
Question 56. In obelia, statocysts function as the organ for:
- Hearing
- Iight perception
- Smell
- Equilibrium.
Answer: 4. Equilibrium.
Question 57. In hydra tests are located at:
- Proximal half end of body
- The distal half end of the body
- Both the ends
- Tentacles only.
Answer: 2. Distal half end of body
Question 58. Hydra can digest all types of food except:
- Proteins
- Fats
- Sugars
- Starch.
Answer: 4. Starch.
Question 59. Aurelia belongs to:
- Hydrozoa
- Scyphozoa
- Actinozoa
- Cephalopoda.
Answer: 2. Scyphozoa
Question 60. Which of the following phyla include diploblastic animals?
- Coelenterata
- Platyhelminthes
- Aschelminthes
- Echrnodermata.
Answer: 1. Coelenterata
Phylum Platyhelminths
Question 1. Flatworms have three tissue layers and only one body cavity-the digestive cavity. They are called:
- Acoelomates
- Pseudo-acoelomates
- Pseudo-coelomates
- Coelomates.
Answer: 1. Acoelomates
Question 2. Which of the following is an ectoparasite?
- Fasciola
- Paragonimus
- Diplozoan
- Taenia
Answer: 3. Diplozoan
Question 3. A unisexual fluke is :
- Schistosoma
- Paragonimus
- Fasciola
- Opisthorchis.
Answer: 1. Schistosoma
Question 4. Locomotory and receptor organs are lacking in :
- Liver fluke
- Lung fluke
- Intestinal fluke
- Tapeworm.
Answer: 4. Tapeworm.
Question 5. Flatwornrs have:
- Ectothelial eggs
- Endothelial eggs
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Endothelial eggs
Question 6. The infective stage of taenia for man is:
- Hexacanth
- Onchosphere
- Cysticercus
- Adult worm.
Answer: 4. Adult worm.
Question 7. How many intermediate hosts does Paragonimus have?
- One
- Two
- Three
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Two
Question 8. Paragonimus lives in :
- Intestine
- Blood
- Lung
- Brain.
Answer: 3. Lung
Question 9. For protection against the infection of diphyllobothrium, do not take raw or undercooked:
- Pork
- Mutton
- Vegetables
- Fish.
Answer: 4. Fish.
Question 10. Tapeworms do not have an alimentary canal because they get good from:
- Suckers
- Mouth
- Body surface
- All of the above.
Answer: 3. Body surface
Question 11. Which of the following statements about taenia saginata is true?
- It has a double circle of hooks on the rostellum
- Its life history involves pig as an intermediate host
- It has two large hooks on the scolex
- It has no rostellar hooks.
Answer: 1. It has a double circle of hooks on the rostellum
Question 12. The study of worms which cause a parasitic infestation in man is called :
- Helminthology
- Herpetology
- Ichthyology
- Malacology.
Answer: 1. Helminthology
Question 13. Liver fluke is :
- Coelomate
- Pseudo-coelomate
- Acoelomate
- Haemo-coelomate.
Answer: 3. Acoelomate
Question 14. Taenia attaches to the intestinal wall by:
- Scolex
- Suckers
- Hooks
- Both 2 and 3.
Answer: 4. Both 2 and 3.
Question 15. Anaerobic respiration is likely to occur in :
- Ants
- Eafthworm
- Tapeworms
- Echinoderms.
Answer: 3. Tapeworms
Question 16. The correct sequence of various larvae in the liver fluke is :
- Miracidium→sporocysts →cercaria → redia→ metacercaria
- Miracidium → redia → Cercaria→metacercaria → sporocyst
- Metacercaria → cercaria → redia →sporocyst → miracidium
- Miracidium → sporocysts →redia→cercaria -→metacercaria.
Answer: 4. Miracidium →sporocysts→ redia→ cercaria→ metacercaria.
Question 17. Food is sucked into the fasciola hepatica with the help of:
- Oral sucker
- Muscular pharynx
- Ventral sucker
- Mouth.
Answer: 2. Muscular pharynx
Question 18. From the evolutionary point of view which group is considered to be the first triploblastic?
- Platyhelminthes
- Annelida
- Coelenterata
- Nemathelminthes.
Answer: 1. Platyhelminthes
Question 19. On examining the stool of a man, it was found to contain segments of tapeworms. Trace the possible source:
- Fish meat
- Beef
- Pork
- Mutton.
Answer: 3. Pork
Question 20. Which of the following is not a class of phylum Platyhelminthes?
- Turbellaria
- Hydrozoa
- Trematoda
- Cestoda.
Answer: 2. Hydrozoa
Question 21. Cysticercosis is caused by :
- Taenia
- Liver fluke
- Bladder worm
- Rhabditid.
Answer: 3. B1adder worm
Question 22. Which of the following is not a parasitic adaptation of helminths?
- Secretion of mucus and anti-enzyme
- Production of a large number of eggs
- Presence of the nervous system
- Presence of flame cells.
Answer: 3. Presence of nervous system
Question 23. Fasciola hepatica differs from taenia solium in:
- Having a better-developed digestive system
- A protective cuticle
- Mesenchyme fills up the space between ectoderm and endoderm
- Presence of nervous system.
Answer: 1. Having a better-developed digestive system
Question 24. Special mesodermal tissue fills up the space between various organs in flatworms:
- Parenchyma
- Botryoidal
- Sclerenchyma
- Mesogloea.
Answer: 1. Parenchyma
Question 25. In platyhelminthes, vitellarium is generally found in association with:
- Ovaries
- Testes
- Both the ovary and testes
- Gut.
Answer: 1. Ovaries
Question 26. In Platyhelminthes flame cells are units of :
- Excretory system
- Reproductive system
- Vascular system
- Respiratory system.
Answer: 1. Excretory system
Question 27. One of the main characteristics of taenia solium is that it:
- Sucks the predigested food from the host’s intestine by employing oral suckers
- Has no mouth, alimentary canal and anus
- Has a head, a neck and a thorax but no abdomen
- Passes eggs which are unaffected even at the boiling temperature of water.
Answer: 2. Has no mouth, alimentary canal and anus
Question 28. Cestodes have:
- A scolex with sucker and hooks
- A ribbon-like body
- Numerous proglottids
- All the above.
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 29. The primary host of taenia is.
- Pig
- Man
- Sheep
- Mollusc.
Answer: 2. Man
Question 30. The intermediate host of talent solium is :
- Pig
- Man
- Sheep
- Snail.
Answer: 1. Pig
Question 31. Which one of the following larvae does not belong to liver fluke?
- Cercaria
- Planula
- Media
- Miracidium.
Answer: 2. Planula
Question 32. Miracidium larva occurs in the life cycle of :
- Liver fluke
- Tapeworm
- Ascaris
- Malarial parasite.
Answer: 1. Liver fluke
Question 33. Taenia solium feeds with :
- Oral sucker
- Body surface
- Rostellum
- Ventral sucker.
Answer: 2. Body surface
Question 34. The tapeworm is :
- Unisexual
- Asexual
- Bisexual
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Bisexual
Question 35. The head of taenia solium is called :
- Oral sucker
- Acetabulum
- Scolex
- Rostellum
Answer: 3. Scolex
Question 36. In taenia, scolex bears at the top in the middle a prominent:
- Cup-shaped sucker
- Head
- Rostellum
- Recurved hooks.
Answer: 3. Rostellum
Question 37. The adult taenia contains :
- 500 Proglottids
- 1000 Progloltids
- 800-900 Proglottids
- Only 3 proglottids.
Answer: 3. 800-900 Proglottids
Question 38. Proglottids of cestodes have :
- Monoecious reproductive system
- Dioecious genitalia
- Well-developed alimentary canal
- Ax the above.
Answer: 1. Monoecius reproductive system
Question 39. Segments of taenia proliferate from the :
- Head
- Neck
- The special region of proliferation in the neck
- Anywhere from the body.
Answer: 3. Special region of proliferation in neck
Question 44. A proglottid is called gravid proglottid when it has :
- Both male and female reproductive units
- Only the female reproductive unit
- Only the male reproductive unit well well-developed
- Branched uterus filled with fertilized eggs.
Answer: 4. Branched uterus filled with fertilized eggs.
Question 41. Liver fluke has :
- Self-fertilization
- Cross-fertilization
- None of above
- Both of the above.
Answer: 4. Both of the above.
Question 42. The body wall in tapeworm is covered by :
- Cuticle
- Tegument
- Integument
- Mucus.
Answer: 2. Tegument
Question 43. Rhabdits are present in the epidermal cells of
- Taenia
- Fasciola
- Dugesia
- Schistosoma
Answer: 3. Dugesia
Question 44. Nen ous system of flatworms is
- Of diffuse type
- In the form of anterior ganglia and nerve cords
- Consists of the central and sympathetic nervous system
- In the form of clustered ganglia.
Answer: 2. In the form of anterior ganglia and nerve cords
Question 45. The tcstes in taenia :
- Have a single structure
- Have bulbed structure
- Consist of several follicles
- Consists of a pair of branched structures.
Answer: 3. Consist of some follicles
Question 46. The ovary in taenia is :
- Single lobed
- Bilobed
- Follicular
- A pair of glandular structures.
Answer: 2. Bilobed
Question 47. In tapeworms, fertilization is affected by one of the following manners:
- Self-fertilization
- Fusion of gametes between two parasites
- Fertilization between gametes of adjacent segments
- A combination of 1 and 3.
Answer: 4. A combination of 1 and 3.
Question 48. The life cycle of taenia is :
- Monogenetic
- Digenetic
- Polygenetic
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Digenetic
Question 49. The infective stage of taenia in pigs is :
- Onchosphere stage
- Hexacanth
- Adult stage
- None of the above.
Answer: 4. None of the above.
Question 50. Taenia saginata differs from taenia solium mainly in the absence of:
- Scolex
- Hooks upon scolex
- Suckers upon scolex
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Hooks upon scolex
Question 51. Onchosphere is an embryo which occurs in taenia characterized by the presence of:
- Six hooks, primary shell only
- Six hooks, geosphere membrane and embryophore
- Onchosphere membrane only
- Six hooks, onchosphere membrane, embryophore and primary shell only.
Answer: 4. Six hooks, onchosphere membrane, embryophore and primary shell only.
Question 52. Cysticercus is a stage in the life history of:
- Fasciola
- Ascaris
- Taenia
- Pheretima.
Answer: 3. Taenia
Question 53. Larval forni of a trematode which penetrates a gastropod mollusc is:
- Hexacanth
- Media
- Cercaria
- Miracidium.
Answer: 4. Miracidium.
Question 54. Trematodes have :
- A branched alimentary canal
- A monoecious reproductive apparatus
- Direct or indirect alimentary canal
- All the above.
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 55. Schistosoma is called
- Blood fluke
- Chinese liver t-luke
- Lung fluke
- Dog tapeworm.
Answer: 1. Blood fluke
Question 56. Dugesia is an exmple of
- Cestoda
- Turbellaria
- Digenetic Trematoda
- Mgogenetic trematoda.
Answer: 2. Turbellaria
Question 57. Taenia saginata is a parasite of
- Sheep
- Cow
- Man and cow
- Dog.
Answer: 3. Man and cow
Question 58. Fasciola hepatica is a parasite that lives in the:
- Intestine of sheep
- Liver of sheep
- Spleen of sheep
- Pancreas of sheep.
Answer: 2. Liver of sheep
Question 59. Strobilation is seen in :
- Taenia
- Fasciola
- Dugesia
- Digenia.
Answer: 1. Taenia
Question 60. The presence of spicules on the body wall is a characteristic of:
- Aurelia
- Planaria
- Taenia
- Fasciola.
Answer: 4. Fasciola.
Phylum Aschelminthes
Question 1. Which of the following are pseudocoelomates?
- Trematodes
- Nematodes
- Cestodes
- Archiannelida.
Answer: 2. Nematodes
Question 2. Round worms have three tissue layers, a digestive cavity and an additional cavity between the endoderm and mesoderm. They are called as:
- Acoelomates
- Pseudocoelomates
- Haemocoelomates
- Coelomates.
Answer: 2. Pseudocoelomates
Question 3. Dracunculus medinensis is a parasite of :
- Body fluids
- Body tissue
- Gut
- Lungs.
Answer: 2. Body tissue
Question 4. The common parasite of the human large intestine is:
- Asruris
- Trichinella
- Enterobius
- Ancylostoma.
Answer: 3. Enterobius
Question 5. The Epidermis of the nematode consists of :
- Cuticle
- Epidermis
- Muscle layer
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 6. Trichinosis is caused by :
- Trichuris
- Trichinella
- Ancylostoma
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Trichinella
Question 7. The number of cells in the various organs of the body is fixed in :
- Flatworms
- Segmental worms
- Walking worms
- Round worms.
Answer: 4. Roundworms.
Question 8. Excretory organs of hookworm are :
- Flame cells
- Green gland
- Renette glands
- Nephridia.
Answer: 3. Renette glands
Question 9. Juvenile of Ascaris undergoes moult :
- Twice
- Once
- Thrice
- Four times.
Answer: 4. Four times.
Question 10. Pinworms are found in humans:
- Alimentary canal
- Colon
- Intestine
- Lungs.
Answer: 2. Colon
Question 11. The technical name of pinworm is :
- Trichon cell
- Ancylostoma
- Oxyuris
- Microfilariae.
Answer: 3. Oxyuris
Question 12. The most dangerous parasitic roundworms of man are:
- Pinworm
- Hookworm
- Whipworm
- Guinea worm.
Answer: 2. Hook worm
Question 13. Filaria is transmitted by :
- Tsetse fly
- Sandfly
- Anopheles
- Culex.
Answer: 4. Culex.
Question 14. Which of the following groups have one or more animals which are not
- Ascaris, taenia
- Enterobius,wuchereria
- Ancylostoma, dracunculus
- Ascaris, ancyiostoma.
Answer: 1. Ascaris, taenia
Question 15. In Ascaris lumbricoides, (roundworms) the males and females can be identified externally by certain characters. This phenomenon is called
- Polymorphism
- Sexual dimorphism
- Anisogamy
- Regeneration.
Answer: 2. Sexual dimorphism
Question 16. Ascaris is a parasite found in the :
- Stomach
- Vermiform appendix
- Small intestine
- Large intestine.
Answer: 3. Small intestine
Question 17. Ln ascaris lumbricoides :
- The male is larger than the female
- The body cavity is a true coelom
- The life history involves two hosts
- None of the above.
Answer: 4. None of the above.
Question 18. In male ascaris the posterior end is :
- Straight
- Upturned
- Blunt and straight
- Curved with pineal setae protruding out.
Answer: 4. Curved with pineal setae protruding out.
Question 19. Lips of Oscars are :
- Horny
- Bony
- Cartilaginous
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Horny
Question 20. Which of the following systems are not well-defined in nematodes?
- Respiratory and digestive
- Circulatory and respiratory
- Excretory and nervous
- Reproductive and excretory.
Answer: 2. Circulatory and respiratory
Question 21. Helminthes parasite without any intermediate host in its life cycle is:
- Liver fluke
- Tapeworm.
- Filarial worm
- Roundworm.
Answer: 4. Roundworm.
Question 22. The cuticle in Ascaris is secreted by :
- Muscular layer
- Epidermis
- Syncytial epidermis
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Syncytial epidermis
Question 23. The lateral lines of the epidermis in Ascaris contain :
- Excretory canal
- Nerves
- Oviducts
- Spermatic ducts.
Answer: 1. Excretory canal
Question 24. The transmission of scans takes place through:
- Air
- Housefly
- Contaminated food and water
- Female anopheles.
Answer: 3. Contaminated food and water
Question 25. In Ascaris, the respiration is:
- Anaerobic
- Anaerobic
- Cutaneous
- All the above.
Answer: 2. Anaerobic
Question 26. Cuticle of ascaris is an adaptation for :
- Growth
- Parasitism
- Reproduction
- Locomotion.
Answer: 2. Parasitism
Question 27. The matrix layer of the cuticle of ascarls is :
- Spongy in consistency
- Formed of keratin
- Collagen fibres
- Formed of basement membrane.
Answer: 1. Spongy in consistency
Question 28. Musculature it ascaris is formed of :
- Circular muscles
- Circular and longitudinal muscles
- A single layer of spindle-shaped cells
- Oblique and tangential circular muscles.
Answer: 3. Single layer of spindle-shaped cells
Question 29. Locomotion in Ascaris is brought about by:
- Circular muscles
- Oblique muscles
- Alternate contraction of dorsolateral and ventrolateral muscles
- Circular and oblique muscles to counteract
Answer: 3. Alternate contraction of dorsolateral and ventrolateral muscles
Question 30. The toxins produced by Ascaris interfere in:
- Carbohydrate metabolism
- Protein metabolism
- Basal metabolic rate
- Fat metabolism.
Answer: 2. Protein metabolism
Question 31. In Ascaris, excretory organs are:
- Excretory cell
- Kidney
- Nephridia
- Flame cells.
Answer: 1. Excretory cell
Question 32. Rectum of Ascaris :
- Consists of tall columnar cells
- Consists of internal cuticle
- In males opens into the cloaca
- All the above.
Answer: 2. Consists of internal cuticle
Question 33. The total number of apertures in male and female Ascaris are
- Two and three
- Three and four
- Two each
- Two and four.
Answer: 4. Two and four.
Question 34. Sperm in Ascaris is :
- Monoflagellate
- Biflagellate
- Amoeboid
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Amoeboid
Question 35. Female ascsris lay eggs daily at the rate of about:
- 10
- 10,000
- 1,00,000
- 2,00,000.
Answer: 4. 2,00,000.
Question 36. In states, fertilization occurs in :
- Water
- Intestine of man
- Proximal part of the uterus
- Vagina.
Answer: 3. Proximal part of uterus
Question 37. A coiled embryo within the egg shell is formed in:
- 24 Hours
- 5 To 8 days
- 10 -14 Days
- 2 To 3 days.
Answer: 3. 10 -14 Days
Question 38. The innermost layer of shells of eggs is formed of :
- Esterified glycosides
- Proteins
- Carbolrydrates
- Phospholipids.
Answer: 1. Esterified glycosides
Question 39. First stage of the ascaris larva is :
- Juvenile
- Rhabdite larva
- Rhabditoid larva
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Rhabditoid larva
Question 40. Final moulting gin ascaris takes place in :
- Outside the body of a man
- Intestine of man
- Lungs of man
- The trachea of man.
Answer: 2. Intestine of man
Question 41. Rhabditoid larva infects man by :
- Boring the sole of feet
- With water
- With air
- With contaminated food.
Answer: 4. With contaminated food.
Question 42. The infective stage of Ascaris is :
- 1st stage larva
- 2nd stage larva
- 3rd stage larva
- Egg itself.
Answer: 2. 2nd stage larva
Question 43. In the life cycle of Ascaris 3rd moulting occurs in:
- Intestine
- Lung
- Heart
- Liver.
Answer: 3. Heart
Question 44. Sites of first, second and third moulting of Ascaris larva are :
- Stomach, intestine and liver
- Soil, lungs and lungs
- Intestine, lungs and liver
- Lungs, intestine and liver.
Answer: 2. Soil, lungs and lungs
Question 45. Ascariasis is syntonised by :
- Abdominal discomforts
- Headache
- High fever
- All the above.
Answer: 1. Abdominal discomforts
Question 46. The larva of Ascaris circulates in the body of a man:
- Intestine-liver-trachea-lungs-intestine
- Intestine-heart-lungs-trachea-intestine
- Intestine-liver-heart-lungs-intestine
- Intestine-lungs-liver-trachea-intestine
Answer: 3. Intestine-liver-heart-lungs-intestine
Question 47. Infection of which parasite often gives rise to cough
- Tapeworm
- Pinworm
- Guinea worm
- Roundworm.
Answer: 4. Roundworm.
Question 48. In,a.sihelminthes the space between the body wall and visceral organs is called:
- Pseudocoel
- Schizocoel
- Hameocoal
- Roundworm
Answer: 1. Pseudocoel
Question 49. All roundworms differ from all flatworms in having :
- Longitudinal nerve cord
- Segrnerited body
- Metamorphosis in their life cycle
- Presence of pseudocoelom.
Answer: 4. Presence of pseudocoelom.
Question 50. Special modifications of ascaris in its parasitic mode of life is:
- Segmented body
- Resistant cuticle
- Tubular body
- Presence of toothed lips
Answer: 2. Resistant cuticle
Phylum Annelids
Question 1. Segmentation is found in :
- Annelida
- Arthropoda
- Vertebrata
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 2. Trochophore larva occurs in :
- Anneiida
- Mollusca
- Brachiopoda
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 3. The zoological name of the paddle worm is :
- Phererimr
- Arenicola
- Chaetopterus
- Polynoe
Answer: 3. Polynoe
Question 4. Branchiae are respiratory organs in
- Nereis
- Aphrodite
- Polynoe
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 5. Parapodia are locomolory organs in :
- Oligochaeta
- Polychaeta
- Diplopoda
- Chiropoda.
Answer: 2. Polychaeta
Question 6. Segmentation in annelids is :
- Hornonornous
- Heteronomous
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
Question 7. Aphrodite is popularly called as
- Scale worm
- Faloloworm
- Lugworm
- Sea mouse.
Answer: 4. Sea mouse
Question 8. Locomotion in leeches is brought about by :
- Parapodia
- (Ts) setae
- Suckers
- Body muscles and suckers.
Answer: 4. Body muscles and suckers.
Question 9. The excretory material of leech is mainly :
- Ammonia
- Urea
- Uric acid
- Amino acids.
Answer: 1. Ammonia
Question 10. Leech is :
- Unisexual
- Bisexual
- Dioecious
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Bisexual
Question 11. In earthworm brain is located in :
- Prostorniurn
- Peristomium
- Third segment
- Second segment
Answer: 3. Third segment
Question 12. In earthworms, coelomic fluid oozes out through the :
- Nephridiopores
- Nephrostome
- Dorsai acres
- Spermathecal pores.
Answer: 3. Dorsai acres
Question 13. Which of the following does not apply to earthworms?
- In indirect development
- Protandry
- Extracellular digestion
- Closed circulatory system.
Answer: 1. In indirect development
Question 14. Blood of nereids contains haemoglobin in
- Plasma
- Amoeboid corpuscles
- Red blood corpuscles
- Both 1 and 2.
Answer: 1. Plasma
Question 15. A coelomic cavity in earthworms is
- Schizocoelic
- Enterocoelic
- Haemocoelic
- Pseudocoeiic.
Answer: 1. Schizocoelic
Question 16. The colour of the earthworm is given by :
- Porphyrin
- Chromatophores
- Vitamins
- Lacrnoglohin.
Answer: 1. Porphyrin
Question 17. The function of dorsal pores in earthworms is:
- Respiration
- Elimination of waste,
- Exudation of body fluids
- Excretion
Answer: 3. Exudation of body fluids
Question 18. In earthworm’s body is devoid of the:
- Cuticle
- Setae
- Appendages
- Epidermis.
Answer: 3. Appendages
Question 19. Septa without aperture lies between :
- 11/12; 12/13 And 13/14 segrnents
- 12/13; 13/14 And 14/15 segments
- 10/11; 14/12 and 12/13 segments
- 9/10; 10/11 And 11/12 segments.
Answer: 4. 9/10; 10/11 And 11/12 segments.
Question 20. In earthworms, chromophil cells are found in :
- Pharyngeal gland
- Respiratory cell
- Sensory cell
- Vascular system.
Answer: 1. Pharyngeal gland
Question 21. The major role of typhiosole in the intestine of earthworms is :
- To control the flow of blood
- To increase the absorptive surface
- To produce digestive enzyme
- To kill bacteria.
Answer: 2. To increase absorptive surface
Question 22. The presence of coelom and metamerism are important characters in :
- Helminthes
- Arthropods
- Annelids
- Coeienterates.
Answer: 3. Annelids
Question 23. The cuticle of annelids is ;
- Non-chitinous and albuminoid
- Chitinous
- Chitinous and albuminoid
- Non-chitinous.
Answer: 4. Non-chitinous.
Question 24. Earthworm is composed of 120 segments and prostomium refers to
- First segment
- 2nd segment
- Not a segment
- Fart of the reproductive system.
Answer: 3. Not a segment
Question 25. Setae are present in all segments except:
- First and last segment
- The first segment and the clitellum
- Cliteltum, first and anal segments
- Clitellum and last segrnent.
Answer: 3. Cliteltum, first and anal segments
Question 26. Clitellum in earthworms includes :
- First three segments
- 14,15 And 16 segments
- Last three segments
- 19, 20 And 21 segments.
Answer: 2. 14,15 And 16 segments
Question 27. In earthworms, the clitellar region helps in the process of:
- Copulation
- Conformation
- Digestion
- Locomotion.
Answer: 2. Conformation
Question 28. Where would you find calcareous glands in heretical?
- Oesophagus
- Stomach
- Rectum
- Typhlosole.
Answer: 2. Stomach
Question 29. During locomotion of earthworms:
- Longitudinal muscles contract first
- Circular muscles contract first
- Both muscles contract simultaneously
- Both muscles relax simultaneously.
Answer: 2. Circular muscles contract first
Question 30. The animals that drifted passively by water currents are known as :
- Pelagic
- Planktons
- Freshwater form
- Benthos.
Answer: 2. Planktons
Question 31. Which of these is secreted by pharyngeal mass?
- Albumen
- Mucin
- Mucin arid proteases
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Mucin arid proteases
Question 32. The flow of blood in a dorsal blood vessel of heretical is :
- From in front backwards
- From behind forward
- In both directions
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. From behind forward
Question 33. l-lateral hearts in heretical are situated in the following segments :
- 12th and 13th
- 10th and 11th
- 7th and 9th
- Both 1st and 3rd.
Answer: 3. 7th and 9th
Question 34. Blood glands in earthworms are situated in 4, 5 and 6 segments. These are associated with:
- Excretion
- Digestion
- Secretion
- Formation of blood corpuscles.
Answer: 4. Formation of blood corpuscles.
Question 35. Lateral oesophageal hearts in heretical are situated in the following segments :
- 12 And 13
- 10 And 11
- 9 And 14
- 7 And 9th.
Answer: 1. 12 And 13
Question 36. The blood of earthworms is :
- Colourless
- Pinkish
- Bluish
- Red.
Answer: 4. Red.
Question 37. Which of these vessels distribute the blood in the first thirteen segments :
- Dorsal
- Oesophageal
- Subneural
- Lateral.
Answer: 1. Dorsal
Question 38. The blood from the seminal vesicle of earthworm is collected by :
- Lateral oesophageal
- Ventral blood vessel
- Ventro tegumentary vessel
- Subneural vessel
Answer: 1. Lateral oesophageal
Question 39. The excretory organs in earthworms are :
- Nephridia
- Malpighiantubules
- Flame cells
- Coelomc ducts.
Answer: 1. Nephridia
Question 40. Pharyngeal nephridia of earthworms are situated in segments :
- 4,5 And 6
- 5,6,7
- 3, 4 And 5
- 6, 7, 8.
Answer: 1. 4,5 And 6
Question 41. In earthworms, mesonephric excretion takes place by:
- Integumentary nephridia
- Septal nephridia
- Septal and pharyngeal nephridia
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Integumentary nephridia
Question 42. The pharyngeal nephridia in earthworms do not open :
- Externally
- Terminally
- Internally
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Externally
Question 43. The origin of nephridium is :
- Germinal
- Ectodermal
- Mesodermal
- Endodermal.
Answer: 2. Ectodermal
Question 44. In heretical in which segments septal nephridia are found?
- In all the segments
- From the 15th to the last segment
- In the first 15 segments
- From last to last segment.
Answer: 2. From the 15th to the last segment
Question 45. Where nephrostome is present in heretical?
- Septal nephridia
- Integumentary nephridia
- Pharyngeal nephridia
- All the above.
Answer: 1. Septal nephridia
Question 46. In earthworms, chloragogen cells perform :
- Glycogen synthesis
- Synthesis of urea
- Removal of silicates
- Elimination of surplus ca+ ions.
Answer: 2. Synthesis of urea
Question 47. How many eyes are found in heretical :
- None
- One
- Two
- Many.
Answer: 1. None
Question 48. Enteronephric nephridia throws out the excretory material:
- Through alimentary canal
- Through cloacal aperture
- Directly outside
- Through circulatory system
Answer: 1. Through alimentary canal
Question 49. In earthworms the ovary is situated in the :
- 11th segment
- 10Th segment
- 13th segment
- 14th segment.
Answer: 4. 14th segment.
Question 50. In earthworms, the testes are enclosed in the following segments :
- 3th and 10th
- 8Th and 9th
- 11Th and 10th
- 12th and 10th.
Answer: 2. 8th and 9th
Question 51. In which segment female genital aperture is found heretical?
- 14th
- 19th
- 18th
- 17th.
Answer: 4. 17th.
Question 52. In earthworms, the spermathecae are used for
- Development of ovum
- Development of sperms
- Storing of spermatozoa
- Storing oval
Answer: 3. Development of Sperms
Question 53. In earthworm the
- Oviduct
- Spermatheca
- Clitellum
- Cocoon.
Answer: 4. Trochophore
Question 54. The annelids larva if present is :
- Tadpole
- Planula
- Trochophore
- Ephyra.
Answer: 3. Trochophore
Question 55. The Polychaeta have all but one of the following characteristics :
- Exclusively marine
- Segmentation infinite
- Distinct head
- Setae are numerous throughout the body.
Answer: 1. Exclusively marine
Question 56. The term deuterostomes excludes :
- Vertebrata
- Echinoderamta
- Cephalochordata
- Annelida.
Answer: 4. Vertebrata
Question 57. Which statement is not correct for septal nephridia of heretical?
- These occur in all segments except the first fourteen
- They are enteronephric
- They have a complicated nephrostome
- They are exonephric.
Answer: 4. They are exonephric.
Question 58. Which has not been correctly classified
- Oli go chaeta-heretical
- Archiannelida-glossophobia
- Hirudinea-pontobdella
- Polychaeta-series
Answer: 2. Archiannelida-glossophobia
Question 59. Copulation occurs between two earthworms :
- Generally at night during the rainy season
- Generally at day time during the rainy season
- At night during the winter season
- At night during the summer season.
Answer: 1. Generally at night during the rainy season
Question 60. The difference between septal and pharyngeal nephridia in earthworms relates to:
- Straight lobe
- Vesicle
- Funnel
- Mode of action.
Answer: 3. Funnel
Question 61. The neurons in earthworms are :
- Motor
- Sensory
- Adjustor
- Motor, sensory and adjustor.
Answer: 4. Motor, sensory and adjustor.
Question 62. Septal nephridia are :
- Largest in size
- Double the size of integumentary nephridia
- Both 1 and 2
- Smallest in size.
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
Question 63. The total number of pores in the body wall of heretical, which are concerned with reproduction is :
- 7
- 11
- 13
- 14.
Answer: 3. 13
Question 64. Which is correct about earthworms?
- It has a brain but no head
- It has locomotory organs
- It secretes cocoon around unfertilized egg
- It can crawl on a smooth surface easily.
Answer: 2. It has locomotory organs
Question 65. Earthworms are:
- Harmful to man
- Useful to man
- Both useful and harmful to man
- Found only near banks of river.
Answer: 1. Harmful to man
Question 66. Hirudin, an enzyme in the saliva of leech
- Coagulation of blood
- Excretion
- Sucking the blood
- Digestion of blood.
Answer: 3. Sucking the blood
Question 67. In which area there is a hydrostatic support system?
- Insects
- Earthworm
- Snail
- Jelly lish.
Answer: 2. Earthworm
Phylum-Arthropoda
Question 1. Which of the following is not an arthropod characteristic?
- Jointed appendages
- Unsegmented body
- Periodic moulting
- Artiithted exoskeleton.
Answer: 2. Unsegmented body
Question 2. Which of the following arthropods are not manipulated?
- Insects
- Crab
- Stumps
- Spider.
Answer: 4. Spider.
Question 3. Lobster, crayfish and cancer &re
- Myriapods
- Crustaceans
- Arachnids
- Insects.
Answer: 2. Crustaceans
Question 4. Which of the following is not a characteristic of insects?
- Three body divisions
- Three pairs of jointed legs
- Two pairs of antennae
- Excretion by malpighian tubule.
Answer: 3. Two pairs of antennae
Question 5. Which of the following arthropods is a chelicerate?
- Horseshoe crab
- Lobster
- Millipede
- Grasshopper.
Answer: 1. Horse-shoe crab
Question 6. Which of the following animals does not have a hydrostatic support system?
- Insects
- Earthworm
- Snail
- Jellyfish.
Answer: 1. Insects
Question 7. Mouthparts of butterflies are :
- Siphoninc
- Chewing
- Chewing lapping
- Sponging.
Answer: 1. Siphoninc
Question 8. Wriggler is the larva of :
- Housefly
- Butterfly
- Moth
- Mosquito.
Answer: 3. Moth
Question 9. Which of the following is a social insect?
- Butterfly
- Moth
- Wasp
- Locust.
Answer: 3. Wasp
Question 10. The body cavity of an arthropod is :
- Coelorn
- Haemocoel
- Spongocoel
- Pseudocoel.
Answer: 2. Haemocoel
Question 11. Drones in honeybee are :
- Fertile males
- Fertile females
- Sterile males
- Sterile females.
Answer: 1. Lertile males
Question 12. The arthropod with a sting at the hind end is :
- Scorpion
- Periplaneta
- Mantis
- Spider.
Answer: 1. Scorpion
Question 13. Millipede belongs to the class :
- Chilopoda
- Diplopoda
- Arachnida
- Gastropoda
Answer: 2. Diplopoda
MCQs on Porifera Question 14. Which of the following has raptorial proleg?
- Locust
- Praying mantis
- Wasp
- Bed bug.
Answer: 2. Praying mantis
Question 15. Excretory organs of crustaceans are :
- Nephridia
- Malpighian tubules
- Green glands
- Flame cells.
Answer: 3. Green glands
Question 16. Cockroach is :
- Ammonotelic
- Uricotelic
- Ureotelic
- Aminotelic.
Answer: 2. Uricotelic
Question 17. Which of the underlying causes plague :
- Salmonella Typhimurium
- Tric hine llaspiralis
- Yersinia pestis
- Leishmania donovani.
Answer: 3. Yersinia pestis
Question 18. In silkworm silk is a product of :
- Salivary glands of the larva
- Cuticle of adult
- Cuticle of larva
- Salivary glands of the adult.
Answer: 1. Salivary glands of the larva
Question 19. Earthworms and cockroaches have one thing in common:
- Ventral nerve bord
- Closed blood vascular system
- Nephridia
- Trachea.
Answer: 1. Ventral nerve bord
Question 20. In insects compound eyes are composed of :
- Ocelli
- Ommatidia
- Fye spots
- Haematochrome.
Answer: 2. Ommatidia
Phylum Porifera Recommended MCQs NEET Questions Question 21. Scorpion respires with the help of :
- Gills
- Book lungs
- Trachea
- Malpighian tubules.
Answer: 2. Book lungs
Question 22. Drones in the colony of honey bees are produced by:
- Parthenogenesis
- Parthenocarpy
- Zygote
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Parthenogenesis
Question 23. The male cricket produces a chirping sound with the help of its:
- Vocal cords
- Pharynx
- Legs
- Wings.
Answer: 3. Legs
Question 24. Locusts are closely related to :
- Moth
- Beetles
- Butterflies
- Grasshopper.
Answer: 4. Grasshopper.
Question 25. The larvae of sacculina are known as :
- Tornaria
- Nauplius
- Trochophore
- Veliger.
Answer: 2. Nauplius
Question 26. Which of these is an insect?
- Tick
- Mite
- Spider
- Lepisma.
Answer: 4. Lepisma.
Question 27. The number of segments in centipede is about :
- 300
- S0
- 10-30
- 10-25.
Answer: 4. 10-25.
Phylum Porifera Recommended MCQs NEET Questions Question 28. One of the following traits which is not found in arthropods :
- Jointed feet
- Segmented body
- Movable jaws
- Closed circulation.
Answer: 4. Closed circulation.
Question 29. Theropods include animals with jointed legs, they have a body cavity called :
- Coelorn
- Haemocoel
- Gastrovascular cavity
- Pseudocoel.
Answer: 2. Haemocoel
Question 30. The crustacean biramous appendages have a basal part is known as :
- Exopodite
- Epipodite
- Protopodite
- Endopodite.
Answer: 3. Protopodite
Question 31. Mites are closely related to :
- Scorpions
- Cyclops
- Aphids
- Beetles.
Answer: 1. Scorpions
Question 32. The first antennal segment is known as :
- Frons
- Pedicel
- Scape
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Scape
Question 33. Antennae are absent in :
- Dragon fly
- Spider
- Prawn
- Peripatus.
Answer: 2. Spider
Question 34. Which of the following two parts in a cockroach are fundamentally similar in structure :
- Mandible and antenna
- Wings and anal cerci
- Anal style and labrum
- Maxilla and labium.
Answer: 4. Maxilla and labium.
Phylum Porifera MCQ Questions With Answers Question 35. In Periplaneta, the number of spiracles is :
- Six pairs
- Eight pairs
- Ten pairs
- Twelve pairs.
Answer: 3. Ten pairs
Question 36. It feriplaneta the sclerites which surround the genital aperture are termed :
- Conophores
- Genitals
- Gonapophyses
- Sterna.
Answer: 3. Gonapophyses
Question 37. In cockroaches the exoskeleton is made of :
- Calcium carbonate
- Calcium phosphate
- Chitinous cuticle
- Calcium sulphate.
Answer: 3. Chitinous cuticle
Question 38. A dorsal plate of the cockroach is :
- Pleuron
- Plastron
- Tergum
- Stemum.
Answer: 3. Tergum
Question 39. Glossa and paraglossa are collectively termed as:
- Lingua
- Ligula
- Labium
- Labrum.
Answer: 2. Ligula
Phylum Porifera MCQ Questions With Answers Question 40. Anal cerci are present :
- Only in male Ascaris
- Only in rare cockroaches
- Only in female cockroaches
- In both male and female cockroaches.
Answer: 4. In both male and female cockroaches.
Question 41. The flagellum of the antenna of a cockroach is :
- 11 jointed
- 13 Segmented
- Unjointed
- Many jointed.
Answer: 4. Many jointed.
Question 42. In cockroach antennae function as :
- Thigmoreceptors, sensitive to touch
- To help in catching insects
- Locomotory structures
- Feeding structures.
Answer: 1. Thigmoreceptors, sensitive to touch
Question 43. The chitinous endoskeleton in the head of the cockroach is known as :
- Apodeme
- Tentorium
- Crematorium
- Notatum.
Answer: 2. Tentorium
Question 44. Wings of. cockroaches are attached to anterolateral corners of terga of :
- Mesothorax
- Metathorax
- Prothorax
- Mesothorax and metathorax.
Answer: 4. Mesothorax and metathorax.
Question 45. Which one of the following characters of the forewing of the cockroach is wrong :
- Leathery
- Without veins
- Opaque
- Protective.
Answer: 2. Without veins
Question 46. Clypeus is a part of :
- Head
- Wing
- Abdomen
- Leg.
Answer: 4. Leg.
Phylum Porifera Animal Kingdom NEET Practice Question 47. For an insect feeding on body fluids, blood of the prey, the mouth parts should be of :
- Sucking type
- Sponging type
- Piercing and sucking type
- Biting type.
Answer: 3. Piercing and sucking type
Question 48. From the feeding habits, cockroaches could be classified as:
- Herbivore
- Carnivore
- Frugivore
- Omnivore.
Answer: 4. Omnivore.
Question 49. The mouth parts of cockroach are :
- Piercing type
- Sponging type
- Siphoning type
- Cutting and biting type.
Answer: 4. Cutting and biting type.
Question 50. Hepatic caecal in cockroaches is derived from :
- Ileum
- Midgut
- Oesophagus
- Crop.
Answer: 2. Midgut
Question 51. Which part of the digestive system secretes the peritrophic membrane around the food in cockroaches?
- Crop
- Gizzard
- Hepatic caeca
- Stomodaeal valve.
Answer: 4. Stomodaeal valve.
Question 52. What will happen if a peritrophic membrane is not formed in cockroaches?
- Digestion of food will stop
- Absorption of food will stop
- Midgut will be injured
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Midgut will be injured
Question 53. In cockroach, the term regurgitation is associated with :
- Swallowing
- Ingestion
- Egestion
- Absorption.
Answer: 4. Absorption.
Phylum Porifera Animal Kingdom NEET Practice Question 54. The body cavity of a cockroach is :
- Coelom
- Haemocoel
- Coelenteron
- Pseudocoel.
Answer: 2. Haemocoel
Question 55. The blood of cockroaches is white due to :
- Absence of haemoglobin
- The circulatory system is open
- There are no salts in the blood
- There is more water in the blood.
Answer: 1. Absence of haemoglobin
Question 56. The tubular heart of a cockroach is composed of :
- 7 Chambers
- 9 Chambers
- 13 Chambers
- 14 Chambers.
Answer: 3. 13 Chambers
Question 57. What is the name of the Blood cells in Periplaneta americana?
- Erythrocytes
- Leucocytes
- Haemocytes
- Amoebocytes.
Answer: 3. Haemocytes
Question 58. The respiratory passage in cockroaches during inspiration is:
- Spiracle and trachea
- Longitudinal respiratory tube
- Air chamber
- Stigmata.
Answer: 1. Spiracle and trachea
Question 59. Oxygen is transported in cockroaches by :
- Blood
- Lymph
- Trachea
- Spiracle.
Answer: 3. Trachea
Question 60. Tracheae are supported by chitinous rings :
- Inside the epithelium
- Outside the epithelium
- In between two epithelial layers
- Both inside and around the epithelial.
Answer: 1. Inside the epithelium
Question 61. The nervous system of an insect consists of :
- Sympathetic
- Autonomous
- Central, peripheral and sympathetic
- Simple nerve cells.
Answer: 3. Central, peripheral and sympathetic
Question 62. Statolith is a sense organ that helps in :
- Tactile stimulus
- Viscous
- Equilibrium
- Chemical stimulus.
Answer: 3. Equilibrium
Question 63. Green glands are :
- Respiratory organs of arachnids
- Respiratory organs of insects
- Excretory organs of many crustaceans
- Digestive glands of myriapods.
Answer: 3. Excretory organs of many crustaceans
Question 64. The total number of ganglia present in the ventral nerve cord of a cockroach is:
- 6
- 9
- 10
- 13.
Answer: 2.
Phylum Porifera Animal Kingdom NEET Practice Question 65. Ingluvial ganglion in cockroaches is present on the surface of.
- Crop
- Gizzard,
- Brain
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Crop
Question 66. During the night, the isolation of ommatidia is incomplete and all act as a single body. What type of image would be formed:
- Single
- Blind
- Blurred
- Superimposed.
Answer: 4. Superimposed.
Question 67. Which one of these is formed by corneagen cells of an ommatidium?
- Cone cell
- Crystalline cone
- Corneal lens
- Rhabdome.
Answer: 3. Corneal lens
Question 68. The main excretory product of cockroaches is :
- Urea
- Ammonia
- Uric acid
- Urine.
Answer: 3. Uric acid
Question 69. The main excretory organs of insects are :
- Kidneys
- Nephridia
- Malpighian tubules
- Far bodies.
Answer: 3. Malpighian tubules
MCQs on Porifera Question 70. The malpighian tubules open at the junction of :
- Gizzard and gur
- Mid gut and ileum
- Ileum and colon
- Colon and rectum.
Answer: 2. Mid gut and ileum
Question 71. Malpighian tubules pour the nitrogenous waste into the gut for the reabsorption of :
- Useful salts
- Glucose
- Water
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Water
Question 72. A pair of rod-like structures situated on the sides of the oesophagus just behind the brain. Secrete a growth hormone, which is the one?
- Corpora allata
- Corpora cardiaca
- Corpus srratum
- Corpus callosum.
Answer: 2. Corpora cardiaca
Question 73. Brain hormone secreted by the intercerebral gland cells is responsible for the activation of:
- Corpora cardiaca
- Cerebral ganglia
- Prothoracic gland
- Salivary gland.
Answer: 3. Prothoracic gland
Question 74. The function ofthe collateral gland in cockroaches is to
- Store spends
- Secrete the egg case
- Keep vagina moist
- Store eggs.
Answer: 2. Secrete the egg case
Question 75. The function of the spermatheca in Periplaneta is
- To help in copulation
- To store eggs
- To secrete musky fluid
- To store sperm.
Answer: 4. To store sperms.
Question 76. Testes of cockroach lie in which segment:
- 3Rd and 4rh
- 4Th and 5rh
- 6Th and 7th
- 7Th and 8th.
Answer: 2. 4Th and 5rh
Question 77. Mushroom-shaped gland name is given to :
- Phallic gland
- Conglobate gland
- Utricular gland
- Collateral glance.
Answer: 3. Utricular gland
Question 78. How many times between hatching and its complete development the young cockroach undergoes ecdysis:
- Not less than 7
- Not less than 8
- Not less than 9
- Not less than 10.
Answer: 1. Not less than 7
MCQs on Porifera Question 79. The spermatophore of the cockroach has 3 layered walls. The middle layer is secreted by:
- Seminal vesicles
- Long tubules
- Ejaculatory duct
- Phallic gland.
Answer: 3. Ejaculatory duct
Question 80. In female cockroaches the 7th, 8th and 9th sterna enclose a cavity known as :
- Egg chamber
- Brood pouch
- Oothecal chamber
- Salivary chamber.
Answer: 2. Brood pouch
Question 81. The thoracic region of insects is divided into :
- Anterior thorax and posterior thorax
- Tergum and sternum
- Prothorax, mesothorax and metathorax
- Prosoma, mesosoma and metasoma
Answer: 1. Anterior thorax and posterior thorax
Question 82. Egg case of cockroach is known as :
- Embryophore
- Ootheca
- Gonophore
- Female gamete
Answer: 2. Ootheca
Question 83. How many eggs do you find in the egg case of a cockroach?
- Eight
- Six
- Twelve
- Sixteen
Answer: 4. Sixteen
Question 84. Gradual metamorphosis occurs in :
- Crow
- Cat
- Amoeba
- Cockroach
Answer: 4. Cockroach
Question 85. The young of some insects resemble the adult in general structure but lack the wings and the mature reproductive organs, such a young one is called :
- Nymph
- Grub
- Caterpillar
- Maggot
Answer: 1. Nymph
Question 86. Which species lay eggs in the soil?
- Anopheles
- Aedes
- Culex
- Both culex and anopheles
Answer: 2. Aedes
Phylum Porifera Recommended MCQs NEET Questions Question 87. Which disease is transmitted through culex :
- Elephantiasis
- Yellow fever
- Diphtheria
- Malaria
Answer: 1. Elephantiasis
Question 88. Why male mosquitoes is unable to pierce the skin of man?
- Reduced mandibles
- Mandibles absent
- Antennae shott
- None of them.
Answer: 2. Mandibles absent
Question 89. Anopheles lays eggs on:
- Kitchen garbage
- Dead bodies of animals
- Still water
- Cow and horse dung
Answer: 3. Still water
Question 90. Mouth parts of mosquitoes are :
- Biting type
- Sucking type
- Piercing and sucking type
- Chewing type.
Answer: 3. Piercing and sucking type
Question 91. Yellow fever is transmitted through :
- Male anopheles mosquito
- Aedes mosquito
- Female anopheles
- Culex.
Answer: 2. Aedes mosquito
Question 92. What is the name of the full-grown larva of Musca domestica?
- Puparium
- Maggot
- Caterpillar
- Cocoon
Answer: 2. Maggot
Question 93. The mouth parts of houseflies are of :
- Cutting and chewing
- Piercing and sucking
- Sponging
- Siphoning
Answer: 3. Sponging
Question 94. Number of eggs a housefly lays is :
- 8-16
- 25-50
- 51-100
- 500-600.
Answer: 4. 500-600.
Question 95. 2nd instar larva of the housefly has :
- Two abdominal and one thoracic spiracle
- One abdominal and one thoracic spiracle
- Abdominal and two thoracic spiracles
- Two abdominal and two thoracic spiracles
Answer: 2. One abdominal and one thoracic spiracle
Phylum Porifera Recommended MCQs NEET Questions Question 96. The maggot breathes through :
- Trachea
- Integument
- External gill
- Rectum
Answer: 1. Trachea
Question 97. Which set of insects is useful to man?
- Silk moth, honey bee and dragonfly
- Lac insect, silk moth and honey bee
- Rice weevil, silk moth and honey bee
- Honey bees, lac insects and locust
Answer: 2. Lac insect, silk moth and hone3r bee
Question 98. Which of these insects helps in pollination in plants?
- Musca dotneslictt
- Apis torsade
- Bombyx more
- Drosphila welano gaster
Answer: 2. Apis torsade
Question 99. Which one of these insects is a voracious feeder and worst destroyer of standing crops and orchards?
- Schistosoma
- Mantis
- Dragonfly
- Tineapellionella
Answer: 1. Schistocera
Question 100. Write of these cause main damage to sugarcane crops?
- Locust
- Termites
- Perilla
- Aphids
Answer: 3. Pyrilla
Question 102. In part of the body, honey bee keeps the nectar for some time.
- Crop
- Mouth
- Gizzard
- Pollen basket
Answer: 1. Crop
Phylum Porifera Recommended MCQs NEET Questions Question 103. What is the function of vector insects?
- Spread disease acting as agents
- Destroy crops
- Act as scavengers
- Useful insects.
Answer: 1. Spread disease acting as agents
Question 104. Which one of these produces drones in honey bee colonies?
- Unfertilized eggs
- Fertilizecl eggs
- Larvae fed on royal jelly
- Fasting larvae.
Answer: 1. Unfertilized eggs
Question 105. Locomotory organs in the maggot of house fly are:
- Mandibular hooks
- Bristles
- Spiniferous pads
- Mandibular hooks and spiniferous pads
Answer: 4. Mandibular hooks and spiniferous pads
Question 106. The ants make their path in a definite direction in a perfect manner of cures it is due to :
- Vision
- Smell
- Sight
- Intelligence
Answer: 2. Smell
Question 107. Spider makes the web with the help of fluid which comes out from the:
- Mouth
- Leg
- Abdominal glands
- Salivary glands.
Answer: 3. Abdominal glands
Phylum Porifera MCQ Questions With Answers Question 108. Which of the following terms includes all of the others?
- Larva
- Maggot
- Caterpillar
- Grub.
Answer: 1. Larva
Question 109. Which of the following is an insect?
- Spiny headed worm
- Shipworm
- Sandworm
- Screwworm.
Answer: 4. Screwworm.
Question 110. Systematic insecticides :
- Are absorbed by plants and then by insects
- Enter the insects through the cuticle
- Enter insect through the spiracle
- Are of short-duration effects.
Answer: 1. Are absorbed by plants and then by insects
Question 111. Which of these insects work as scavengers?
- Apis
- Ants
- Wasp
- Locust.
Answer: 2. Ants
Question 112. Nectar sucking apparatus is formed of :
- Galeae and glossae
- Galeae only
- Glossae only
- Galeae, glossae and labial palps.
Answer: 4. Galeae, glossae and labial palps.
Question 113. The most specialized leg for the collection of pollen is :
- Proleg
- Mesothoracic leg
- Metaleg
- None of these.
Answer: 1. Proleg
Question 114. Chemically queen substance is :
- 9 Oxodec-2 enoic acid
- 3 Oxodec-9 enoic acid
- 2 Oxodec-3 enoic acid
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. 9 Oxodec-2 enoic acid
Question 115. Embryonic development of honey bees is :
- Heterometabolous
- Hemimetabolous
- Holometabolous
- Holometabolous.
Answer: 4. Holometabolous.
Question 116. From which one of these formic acids is obtained?
- Honey bee
- Red and
- Gryllus
- Cimax.
Answer: 2. Red and
Question 117. From where does the spider prepare the web?
- Mouth
- Legs
- Spinnerets
- Salivary glands.
Answer: 3. Spinnerets
Question 118. Which stage of silkworm produces silk?
- Esg
- Caterpillar
- Cocoon
- Adult.
Answer: 3. Laccfer lacca
Question 119. Which of these insects secrete shellac?
- Bomby
- Laccfer lacca
- Apis
- Aepisma.
Answer: 2. Laccfer lacca
Question 120. The silk gland of the larva is the modification of :
- Labial gland
- Wall of the pharynx
- Mandibular gland
- All the above.
Answer: 1. Labial gland
Phylum Porifera MCQ Questions With Answers Question 121. Where from you get Catherine :
- Apis
- Blister beetle
- Lepisma
- Culex.
Answer: 2. Blister beetle
Question 122. Which of these is a very useful scavenger?
- Dung beetle
- Bombyx
- Wasp
- Dragon fly.
Answer: 1. Dung beetle
Question 123. Which one of these spoils cotton before harvest :
- Apis
- Lepisma
- Boll weevil
- Dung beetle.
Answer: 3. Boll weevil
Question 124. Who decoded the language of honey bee :
- Charles Darwin
- William Harvey
- Karl von Frisch
- Carolus Linnaeus.
Answer: 3. Karl von frisch
Question 125. Which one of these surrounds the fine threads of silk emerging out from the exit tube :
- Sericin
- Collagen
- Mucin
- Myosin.
Answer: 1. Sericin
Question 126. Rostrum of lac insect is :
- Two jointed
- Three jointed
- Four jointed
- Unjointed.
Answer: 1. Two jointed
Question 127. Lac is :
- Resinous substance
- Alkaloid
- Mucoid substance
- Juice is acidic.
Answer: 1. Resinous substance
Question 128. Which of the following groups of animals can be included in the same group?
- Planaria, tubularia, plumularia and radiolarians
- Starfish, jellyfish, cuttlefish and dogfish
- Millipede, crab, scorpion, cockroach and tick
- Leech, locust, leucosolenia and lobster.
Answer: 3. Millipede, crab, scorpion, cockroach and tick
Question 129. In the life history of the culex mosquito :
- A larva floats passively on the surface of the water
- Each egg contains air spaces
- Respiratory trumpets in pupa are long and narrow
- Respiratory siphons in the area are very short.
Answer: 3. Respiratory trumpets in pupa are long and narrow
Phylum Porifera MCQ Questions With Answers Question 130. The food canal in the proboscis of housefly is formed of :
- Labrum, epipharynx and hypopharynx
- Labial groove and hypopharynx
- Right and left mandibles
- Labella and pseudoffachea.
Answer: 2. Labial groove and hypopharynx
Question 131. The larva of anopheles differs from the larva of culex in the :
- Absence of spiracles
- Presence of piercing and sucking mouth parts
- Absence of pecten
- Absence of respiratory siphon.
Answer: 4. Absence of respiratory siphon.
Question 132. A housefly feeds upon sugar by :
- Lapping up sugar crystals
- Chewing sugar crystals and ingesting
- Dissolving sugar in saliva and sucking it
- Sucking sugar grain through pseudo trabeculae.
Answer: 3. Dissolving sugar in saliva and sucking it
Phylum Porifera Animal Kingdom NEET Practice Question 133. The period between two moults in insects is termed:
- Incubation
- Insrar
- Stadium
- Ecdysis.
Answer: 3. Stadium
Question 134. Which one is a colonial insect?
- Housefly
- Termite
- Bed bug
- Mosquito.
Answer: 2. Termite
Question 135. All of the following are blood-sucking except ;
- Leech
- Bed bug
- Musca
- Chigger.
Answer: 3. Musca
Question 136. Which one out of the following is a connecting link between annelids and arthropods?
- Planoblast
- Planaria
- Peripatus
- Pila.
Answer: 3. Peripatus
Question 137. An open type of circulatory system with no well-defined arteries and veins is characteristic of :
- Coelenteraa
- Sponges
- Arthropoda
- Mollusca
Answer: 3. Arthropoda
Question 138. Common house fly (Musca nebula) lays its eggs on:
- Open meats and sweets
- Hanging ropes
- Stagnant water
- Cow/horse dung
Answer: 4. Cow/horse dung
Phylum Mollusca
Question 1. In a mollusc nitrogenous wastes are removed from the body by tubular structures that connect the coelom with the mantle cavity. These structures are the:
- Radula
- Opercula
- Kidneys
- Ctenidia.
Answer: 3. Kidneys
Question 2. In all molluscs except bivalves, there is a tongue-like toothed structure, that is used to scrap off the food from the surface of rocks and convey it towards the digestive cavity. This structure is called :
- Meta-nePhridium
- Radulae
- Palp
- Ctenidium
Answer: 2. Radulae
Question 3. Which of the following characteristics is not found in gastroPods?
- Shell of two valves
- Asymmetrical due to torsion
- Presence of ctenidia
- Mostly marine.
Answer: 1. Shell of two valves
Question 4. A harmiul mollusc is :
- Chiton
- Teredo
- Pinctada
- Unio.
Answer: 2. Teredo
MCQs on Porifera Question 5. Shell is internal and reduced in :
- Pila
- Helix
- Teredo
- Limax.
Answer: 4. Limax.
Question 6. Superior quality pearls are formed by :
- Pinctada
- Unio
- Octopus
- Pecten.
Answer: 1. Pinctada
Question 7. Arms are webbed at the base in :
- Loligo
- SePia
- Octopus
- All the above
Answer: 3. Octopus
Question 8. CephaloPods are :
- Herbivorous
- Carnivorous
- Omnivorous
- Scavengers
Answer: 2. Carnivorous
Question 9. Most cephalopods when alarmed react by :
- Releasing a dark-coloured ink from an ink-producing gland
- Force water out of the ventral tubular funnel
- Both A+B
- Lie passively and do not react
Answer: 3. Both A+B
Question 10. The foot is missing in :
- Pelecypoda
- Aplacophora
- Monoplacophora
- Polyplacophora
Answer: 2. Aplacophora
Phylum Porifera Recommended MCQs NEET Questions Question 11. The blood vascular system of pila is :
- Open
- Closed
- Reduced
- Lacking
Answer: 1. Open
Question 12. The body cavity in the apple snail is :
- Coelom
- Pseudocoelom
- Haemocoel
- Absent
Answer: 3. Haemocoel
Question 13. Discriminate the Iayer that secretes pear lina molluscan shell:
- Brownish layer
- Prismatic layer
- Periostracum
- Nacre.
Answer: 4. Nacre.
Question 14. Commercial Pearl is formed by :
- Unio
- Lamellidens
- Ostrea
- Pecten.
Answer: 3. Ostrea
Question 15. Identify the larva which is characteristic of gastropods and scaphoPoda:
- Trochophore
- Tornaria
- Bipinnaria
- Muller’s Larva’
Answer: 1. TrochoPhore
Question 16. In molluscs the shell formation is affected by arms and not by the mantle:
- Sepia
- Dentalium
- Argonatae
- Nautilus.
Answer: 3. Argonatae
Question 17. The colour change in cephalopods is due to the presence of :
- External shell
- Internal secretions
- Ink sac
- ChromatoPhores
Answer: 4. ChromatoPhores
Question 18. Molluscan characters do not include one of the following :
- Soft body
- Mantle folds
- Coelom reduced
- Ventral ganglionated nerve cord
Answer: 4. Ventral ganglionated nerve cord
Question 19. Which one is not a class of Mollusca:
- Decapoda
- Scaphopoda
- Gastropoda
- PelecyPoda
Answer: 1. Decapoda
Phylum Porifera MCQ Questions With Answers Question 20. Select the class with the wrong example :
- Aplacophora Example Chaetoderma
- Polyplacophora Example Chiton
- CephaloPoda Example Dentalium
- Gastropoda Example Achatina.
Answer: 2. Polyplacophora Example Chiton
Question 21. Gastropods are characterised by one of the characters :
- Ventral muscular and massive foot
- Vertebrate like eYes
- Head degenerated
- Radula absent.
Answer: 3. Head degenerated
Question 22. Which one of the following is not a cephalopod?
- Octopus
- Sea Squirt
- Sea Squid
- Nautilus
Answer: 2. Sea Squirt
Question 23. Which one of the following is an amphibious mollusc?
- Pecten
- Teredo
- Nautilus
- Pila.
Answer: 4. Pila.
Question 24. Tusk shell is a :
- Tooth of an elephant
- Mollusc
- Apple Snail
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Mollusc
Question 25. The respiratory pigment of most molluscs is :
- Vanadium
- Haemoenyrhrin
- Haemocyanin
- Haemoglobin.
Answer: 3. Haemocyanin
Question 26. Rasping organ of mollusc is :
- Radula
- Ctenidium
- Buccal mass
- Osphradium.
Answer: 1. Radula
Question 27. Slug belongs to class :
- Cephalopoda
- Gastropoda
- Pelecypoda
- Scaphopoda.
Answer: 2. Gastropoda
Phylum Porifera MCQ Questions With Answers Question 28. Gastropods are characterized by :
- Absence of shell
- Absence of head and tentacles
- Large foot and head with eyes and tentacles
- Absence of body mass.
Answer: 3. Large foot and head with eyes and tentacles
Question 29. Sepia belongs to the class :
- Gastropoda
- Bivalvia
- Cephalopoda
- Pelecypoda.
Answer: 3. Cephalopoda
Question 30. The foot is modified into an oral arm in the:
- Pelecypoda
- Gastropoda
- Cephalopoda
- Scaphopoda.
Answer: 3. Cephalopoda
Question 31. Pearls are formed of :
- Calcium carbonate
- Calcium sulphate
- Magnesium trisilicate
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Calcium carbonate
Question 32. Which of the following is an invertebrate structure?
- Bowman’s capsule
- Cowper’s gland
- Volkman’s canal
- Aristotle lantern.
Answer: 4. Aristotle lantern.
Question 33. Which one of the following is the oldest living fossil?
- Limulus
- Nautilus
- Architeuthis
- Neopilina.
Answer: 2. Nautilus
Question 34. Cleavage in molluscs is usually :
- Radial
- Spiral
- Biradial
- Bilateral.
Answer: 2. Spiral
Question 35. Leaf-like chemoreceptors in apple snails is :
- Odontophore
- Ctenidium
- Radula
- Osphradium.
Answer: 4. Osphradium.
Question 36. Pearl is secreted by :
- Edge of mantle
- The inner lining of the mantle
- The outer lining of the mantle
- Organ of Bojanus.
Answer: 3. Outer lining of mantle
Phylum Porifera Animal Kingdom NEET Practice Question 37. One of the following genera has the wrong common name:
- Dentalium-Tusk shell
- Loligo-Sea squirrel
- Octopus-Devil fish
- Pila-Apple snail.
Answer: 2. Loligo-Sea squirrel
Question 38. To which class does oyster belong?
- Cephalopoda
- Gastropoda
- Pelecypoda
- None of these.
Answer: 3. Pelecypoda
Phylum-Echinodermata
Question 1. Which of the following is a deuterostome?
- Starfish
- Sea anemone
- Ant
- Octopus.
Answer: 1. Starfish
Question 2. Which of the following is not characteristic of echinoderms?
- Water vascular system
- Trochophore larva
- Tube feet
- Interior skeleton with projecting spines
Answer: 2. Trochophore larva
Question 3. Which of the following has a melon-shaped body:
- Sea star
- Sea cucumber
- Sea urchin
- Brittle star.
Answer: 1. Sea star
Question 4. Cloacal respiration occurs in :
- Clypester
- Antedon
- Sea cucumber
- Echinus.
Answer: 2. Antedon
Question 5. The skeletal ossicles of starfish arise from :
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Endoderm
- None of the above.
Answer: 4. None of the above.
Question 6. The ambulacral system contains :
- Blood
- Coelomic fluid
- Mucus
- Water.
Answer: 2. Coelomic fluid
Question 7. The echinoderms are related to chordates by their similarity in the development of :
- Gut
- Nervous system
- Heart
- Coelom.
Answer: 4. Coelom.
Question 8. The locomotory organs of echinoderms are called :
- Parapodia
- Pseudopodia
- Tube feet
- Setae.
Answer: 3. Tube feet
Question 9. Coelom of echinoderms is :
- Enterocoelous in origin
- Filled with coelomic fluid
- Provided with coelomocytes
- All the above.
Answer: 4. A1l the above.
MCQs on Porifera Question 10. Echinoderms :
- Lack of an alimentary canal
- Have a straight or coiled alimentary canal
- Have a poorly developed alimentary canal
- Have an alimentary canal.
Answer: 3. Have a poorly developed alimentary canal
Question 11. Adapted for hematophagous habit starfish belongs to the :
- Moilusca
- Hemichordata
- Cephalochordata
- Echinodermata.
Answer: 1. Moilusca
Question 12. All echinoderms are :
- Freshwater animals
- Terrestrial
- Arboreal
- Marine.
Answer: 4. Marine.
Question 13. Sea star is :
- Omnivorous
- Sanguivorous
- Herbivorous
- Carnivorous.
Answer: 4. Carnivorous.
Question 14. Respiration in stadish occurs by :
- Gills
- Lungs
- Water vacuoles
- Dermal branchiae.
Answer: 2. Lungs
Question 15. Echinoderm has calcareous and non-living :
- Exoskeleton
- Endoskeleton
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Endoskeleton
MCQs on Porifera Question 16. A sieve plate in the vascular system is called :
- Ossicle
- Polian vesicle
- Podium
- Madreporite.
Answer: 4. Madreporite.
Question 17. Brown gland or axial gland is the other name heart in:
- Molluscs
- Echinoderms
- Insects
- Crustaceans.
Answer: 4. Crustaceans.
Question 18. The larva of starfish is called:
- Bipinnaria
- Trochophore
- Ephyra
- Tadpole.
Answer: 1. Bipinnaria
Question 19. The ability ofthe starfish to break off its arm is:
- Autonasty
- Autogamy
- Autotomy
- Autoplasty
Answer: 3. Autotomy
Question 20. Development in echinoderms is :
- Direct
- Indirect
- Completed in the intermediate host
- Retrogressive.
Answer: 2. Indirect
Question 21. Brittle Star is the name of :
- Asterias nebula
- Astropecten
- Ophiothrir
- Cucumaria-
Answer: 1. Asterias nebula
Question 22. Which one of the following is a sea cucumber?
- Thyone
- Synapta
- Cucumaria
- All the above.
Answer: 2. Synapta
Question 23. Sense organs in echinoderms are:
- Poorly developed
- We are developed
- Overdeveloped
- Absent.
Answer: 4. Absent.
Question 24. The group of echinoderms without spines, pedicellariae and suckers on tube feet are:
- Sea cucumber
- Sea star
- Sea lily
- Brittle star.
Answer: 2. Sea star
Question 25. Basket star belongs to the class :
- Ophiuroidea
- Echinoidea
- Asteria
- Crinoidea.
Answer: 1. Ophiuroidea
Phylum Porifera Recommended MCQs NEET Questions Question 26. Select the one with the wrong class :
- Sea star-Asteroidea
- Sea urchin-Echinoidea
- Holothuriodea-sea cake
- Ophiuroidea-brittle star.
Answer: 3. Holothuriodea-sea cake
Question 27. The water vascular system performs all but one function :
- Locomotion
- Sensation
- Excretion
- Food capturing and respiration.
Answer: 2. Sensation
Question 28. Which one of the following is not a part of the vascular system?
- Tube feet
- Polian vesicle
- Teidmanns body
- Axial sinus.
Answer: 4. Axial sinus.
Question 29. Antedon belongs to the class :
- Asteroidea
- Phiuroidea
- Crinoidea
- Echinoidea.
Answer: 3. Echinoidea.
Question 30. Aristotle’s lantern occurs in :
- Sea urchin
- Asterias
- Ophiothuria
- Sea anemone.
Answer: 1. Sea urchin
Phylum-Hemichordata
Question 1. Acorn worms belong to the phylum:
- Chordata
- Hemichordata
- Unrochordata
- Cephalochordata.
Answer: 2. Hemichordata
Question 2. Larva of hemichordate is:
- Tornaria
- Glochidium
- Bipinnaria
- Nauplius.
Answer: 1. Tornaria
Question 3. A non-contractile heart occurs in :
- Earthworm
- Sew star
- Acorn worms
- Apple snail
Answer: 3. Acorn worms
Question 4. The hollow nerve cord that occurs in the acorn worms is the:
- Proboscis
- Collar
- Trunk
- Entire body.
Answer: 2. Collar
Question 5. The circulatory system of palatoglossus is :
- Open
- Closed
- Absent
- Highly specialized.
Answer: 1. Open
Phylum Porifera Recommended MCQs NEET Questions Question 6. Respiration in palatoglossus is;
- Cutaneous
- Branchial
- Tracheal
- Pulmonary.
Answer: 2. Branchial
Question 7. Hemichordates are :
- Acoelomate
- Pseudocoelomate
- Coelomates
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Coelomates
Question 8. Gill slits in hemichordates are :
- Lateral in position
- Dorsal in position
- Ventral in position
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Lateral in position
Question 9. Tornaria larva of palatoglossus first discovered by j.muller resembles with:
- Tadpole larva
- Glochidium larva
- Axolotl larva
- Bipinnaria larva.
Answer: 4. Bipinnaria larva.
Question 10. The body of Balanoglossus is divisible into :
- Head, thorax and abdomen
- Head, trunk and tail
- Proboscis, collar and tail
- Proboscis, collar and trunk.
Answer: 4. Proboscis, collar and trunk.
Question 11. Epidermis of hemichordate is formed of :
- A single layer of cells
- Two layers of cells
- Many layers of cells
- Three lawyers of fat cells.
Answer: 1. Single layer of cells
Phylum Porifera MCQ Questions With Answers Question 12. The excretory organ of palatoglossus is :
- Body wall
- Glomeruli
- Kidneys
- Gills.
Answer: 2. Glomeruli
Question For competitive examinations
Question 1. The larva of bomby mori is
- Nymph
- Cocoon
- Trochophore
- Caterpillar.
Answer: 4. Caterpitlat.
Question 2. In hydra waste material of food digestion and nitrogenous waste material removed from :
- Mouth and mouth
- Body wetland body wall
- Mouth and body wall
- Mouth and tentacles.
Answer: 3. Mourh and body wall
Question 3. In which of the following haemocyanin pigment is found :
- Mollusca
- Echinodermata
- Insecta
- Lowerchordata.
Answer: 1. Mollusca
Question 4. Which of the following is present in molluscs but absent in echinoderms?
- Malpighian tubules
- Kidney
- Flarire cells
- None of above
Answer: 2. Kidney
Question 5. Which one of the following pair is a matching pair of an animal and a certain phenomenon it exhibits?
- Taenia – polymorphism
- Pheretima – sexual dimorphism
- Musca – complete metamorphosis
- Chametean – mimicry.
Answer: 3. Taenia – polymorphism
Question 6. A moulting hormone in insects is secreted by which gland?
- Corpora aliata
- Pineal gland
- Hypothalamus
- Prothoracic gland.
Answer: 4. Prothoracic gland.
Phylum Porifera MCQ Questions With Answers Question 7. The excretory system of prawn is called :
- Malpighian tubule
- Nephridia
- Solenocytei
- Green gland
Answer: 4. Green gland
Question 8. Hard shell, muscular body, ommatidiophores and foot are descripition abotrt :
- Prawn
- Limulus
- Pila
- Tortoise.
Answer: 3. Pila
Question 9. Sycon belongs to a group of animals, which are best described as :
- Multicellular having tissue organization, but no body cavity
- Multicellular with a gastrovascular system.
- Multicellular without any tissue organization
- Unicellular or acellular
Answer: 3. Multicellular without any tissue organization
Question 10. During the life cycle, fasciola hepatica infects its intermediate host and primary host at the following larval stages respectively:
- Miracidium and metacercaria
- Media and miracidium
- Cercaria and media
- Metacercaria and cercaria.
Answer: 1. Miracidium and metacercaria
Phylum Porifera Animal Kingdom NEET Practice Question 11. Ommatidia serve the purpose of photoreception in :
- Cockroach
- Frog
- Human
- Sunflower.
Answer: 1. Cockroach
Question 12. Which one of the phylum is devoid of coelom?
- Platyhelminthes
- Echinodermara.
- Arthropoda
- Annelida
Answer: 1. Platyhelminthes
Question 13. Body cavity not lined by mesoderm and directly connected to archenteron occurs in :
- Platyhelminthes
- Nematodes
- Earthworm
- Echinoderm.
Answer: 2. Nematodes
Question 14. Which one is correctly matched?
- Jellyfish and starfish-radial symmetry
- Hydra and shark-bilateral symmetry
- Tapeworm and octopus-radial symmetry
- Amoeba and sea urchin-asymmetry.
Answer: 1. Jellyfish and starfish-radial symmetry
Question 15. From the point of view of taxonomy, which of the following groups are correct :
- Dentalium, octopus
- Ascaris, cockroach, grasshopper.
- Spongilla, teredo, leucoselenia
- Starfish, petronryzon, solen
Answer: 1. Dentalium, octopus
Question 16. The young of cockroach is called :
- Fingerling
- Maggor
- Caterpillar
- Nymph.
Answer: 4. Nymph.
Question 17. Which one feature is common to leeches, cockroaches and scorpion ?
- Nephridia
- Ventral nerve cord
- Cephalization
- Antennae.
Answer: 2. Venrral nerve cord
Question 18. The contractile vacuole is absent in :
- Sporozoa
- Sarcodina
- Zooflagellata
- Slimemoulds.
Answer: 1. Sporozoa
Question 19. In nemathelminthes, the coelom not lined by the peritoneum is :
- Acoelom
- Pseudocoelom
- Enterocoelom
- Haemocoel.
Answer: 2. Pseudocoelom
Question 20. In arthropods, the head and thorax are often fused to form a cephalothorax, but in which one of the following classes, is the body divided into head, thorax and abdomen?
- Crustacea
- Arachnida and crustacea
- Insecta
- Myriapoda.
Answer: 3. Insecta
Question 21. The animals with bilateral symmetry in the young stage, and radial pentamerous symmetry in the adult stage belongs to phylum :
- Cnidaria
- Echinodermata
- Annelida
- Mollusca-
Answer: 2. Echinodermata
Phylum Porifera Animal Kingdom NEET Practice Question 22. The largest invertebrate animal is :
- Whale
- Giant squid
- Shrew
- Python.
Answer: 2. Giant squid
Question 23. Which one of the following genera of insects prefers to breed in clean water and their larvae lie parallel to the surface of the water?
- Culex
- Aedes
- Anopheles
- Phlebomotus
Answer: 3. Anopheles
Question 24. The spider web is formed by a fluid secreted by its :
- Abdominal gland
- Salivary gland
- Cephalothorax
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Abdominal gland
Question 25. Which one is not correctly matched?
- Annelida-enterocoeomate
- Arthropoda-schizo-coelomate
- Platyhelminthes-acoelomate
- Nemathelminthes-pseudocoelomate
Answer: 1. Annelida-enteroscopyomate
Question 26. Coelomate animal where blastopore develops into the anus is:
- Blastostomate
- Protostomate
- Deuterostomes
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Deuterostomate
Question 27. Nektons are :
- Floating plants
- Swimming organisms
- Suspended plants
- Animals associated with plants.
Answer: 2. Swimming organisms
Question 28. From the following statements select the wrong one:
- Millipedes have two pairs of appendages in each segment of the body
- Prawn has two pairs of antennae
- Animals belonging to phylum Porifera are exclusively marine
- Nematocysts are characteristic of the phylum Cnidaria.
Answer: 3. Animals belonging to phylum Porifera are exclusively marine
Question 29. In contrast to annelids, the platyhelminths show:
- Radial symmetry
- Presence of pseudocoel
- Bilateral symmetry
- Absence of body cavity.
Answer: 4. Absence of body cavity.
Question 30. Hydra shows positive as well as negative responses in dim, and strong lights it shows :
- Negative response to strong and positive to dim lights
- Positive response to strong and negative to dim lights
- A negative response to both
- Positive response to both
Answer: 1. Negative response to strong and positive to dim lights
Question 31. The digestive system is not found in :
- Earthworm
- Cockroach
- Taenia
- Ascaris.
Answer: 3. Taenia
Question 32. Female Ascaris is identified based on:
- The presence of two spicules at the posterior end
- Presence of preanal and postanal papillae
- Straight posterior end
- A common cloacal aperture.
Answer: 3. Straight posterior end
Question 33. The stage of plasmodium when mosquitoes get infection:
- Exoerythrocytic stage
- Pre-erythrocytes cycle
- Sexual stage or gametogamy
- None of these.
Answer: 3. Sexual stage or gametogamy
Question 34. Classification of phylum proffer is primarily based on:
- Branching
- Symmetry
- Spicules
- Canal system.
Answer: 3. Spicules
Question 35. The phylum ‘Echinodermata’ was established by :
- Von Seibold
- Lamarck
- Jacob Klein
- Leuckart.
Answer: 3. Jacob Klein
Question 36. Which of the following has corect grouping ?
- Taenia solium, roundworm, flatworm-platyhel- minthes
- Cuttlefish, silverfish, sea urchin-coelenterate
- Centipede, millipede, silverfish sharthropoda
- None of these.
Answer: 4. None of these.
Question 37. Males are haploid in :
- Ascaris
- Honeybee
- Silkworm
- Hydra.
Answer: 2. Honeybee
Question 38. Molluscans possess :
- Enterocoel
- Pseudocoel
- Schizocoel
- No coelom.
Answer: 3. Schizocoel
Question 39. The coelenteron of hydra is :
- Gastrovascular cavity
- 181 Perivisceral cavity
- Pseudocoelomic cavity
- Coelomic cavity.
Answer: 1. Gastrovascular cavity
Question 40. Gynaecophoric canal is present in some animals of :
- Turbellaria
- Trematoda
- Cestoda
- Nematoda.
Answer: 2. Trematoda
Question 41. In Ascaris, eggs are fertilized in the :
- Seminal vesicle
- Lower parts of uteri
- Oviducts
- Vagina.
Answer: 2. Lower parts of uteri
Question 42. Flow of blood in dorsal vessel of earthworm is:
- Forwards
- Backwards
- Backwards in half of it and forwards in another half
- None of these.
Answer: 1. Forwards
Question 43. The male cockroach has :
- Longwing
- Anal style
- Anal cerci
- Both 2 and 3.
Answer: 4. Both 2 and 3.
Phylum Porifera Animal Kingdom NEET Practice Question 44. Honey is :
- Neutral
- Acidic
- Alkaline
- Basic after some days
Answer: 1. Neutral
Question 45. Which of the following is determinantal to pearl industry?
- Euspongia
- Oyster
- Chalina
- Cliona.
Answer: 4. Cliona.
Question 46. Antedon is a member of the class :
- Asteroidea
- Ophiuroidea
- Crinoidea
- Echinoidea.
Answer: 3. Crinoidea
Question 47. Which one of the following features is common in silverfish, scorpion, dragonfly and prawn?
- Three pairs of legs and a segmented body
- Chitinous cuticle and two pairs of antennae
- Jointed appendages and chitinous exoskeleton
- Cephalothorax and tracheae.
Answer: 3. Jointed appendages and chitinous exoskeleton
Question 47. Spiracles found in cockroaches are :
- 2 Pairs in the thorax and 10 pairs in the abdomen
- 2 Pairs in the thorax and 6 pairs in the abdomen
- 2 Pairs in the thorax and 8 pairs in the abdomen
- 2 Pairs in the thorax and 4 pairs in the abdomen.
Answer: 3. 2 Pairs in the thorax and 8 pairs in the abdomen
Question 48. The blood of earthworms is :
- Red in colour, due to dissolved haemoglobin in plasma
- Red in colour, due to dissolved haemoglobin in corpuscles
- Blue in colour, due to dissolved haemocyanin in plasma
- Blue in colour, due to dissolved haemocyanin in corpuscles.
Answer: 1. Red, due to dissolved haemoglobin in plasma
Question 49. Which of the following is a freshwater sponge?
- Euplectella
- Spongilla
- Euspongia
- Sycon.
Answer: 2. Spongilla
Question 50. Hepatic caeca in cockroaches are derived from:
- Crop
- Midgut
- Gzzad
- Ileum.
Answer: 2. Midgut
Question 51. Neoteny refers to
- Development of gonads
- Pre-adult animal
- Metamorphosis
- Retention of larval or embryonic trait in the adult body.
Answer: 4. Retention of a larval or embryonic trait in the adult body.
Question 52. In earthworm, the dorsal wall of the intestine from the 26th segment to the 95th segment forms a median internal fold called
- Trochophore
- Typhlosole
- Clitellum
- Trachea.
Answer: 2. Typhlosole
Question 53. The diagram represents the reproductive organ of a male cockroach. Choose the correct combination of labelling.
- A- 8th sternum, b-anal cercus, c – 10th tergun, d- anal style
- A – 10th tergum, b – anal cercus, c – anal style, d – 8th sternum
- A – anal style, b – anal cercus, c – 10th tergum, d – 8th sternum
- A- anal cercus, b – 8th sternum, c – 10th tergum. D . Analstyle.
Answer: 1.A- 8th sternum, b-anal cercus, c – 10th tergun, d- anal style
Question 54. Which one of the following groups of structures/organs have similar functions?
- Typhlosole in earthworms, intestinal villi in rats and contractile vacuole in amoeba
- Nephridia in earthworms, malpighian tubules in cockroaches and urinary tubules in rats.
- Antennae of cockroach, tympanum of frog and clitellum of earthworm
- Incisors of rats, gizzard(proventriculus) of cockroaches and tube feet of starfish.
Answer: 2. Nephridia in earthworms, malpighian tubules in cockroaches and urinary tubules in rats.
Question 55. The nasofrontal nerves in cockroaches originated from :
- Suboesophageal ganglia
- Supraoesophageal ganglia
- Antennary nerves
- Frontal ganglia
Answer: 2. Supraoesophageal ganglia
Question 56. Metameric segmentation is the characteristic of :
- Annelida and Arthropoda
- Mollusca and chordata
- Platyhelminthes and arthropoda
- Echinodermataandannelida.
Answer: 1. Annelida and Arthropoda
Question 57. Earthworms are :
- Uricotelic under conditions of water scarcity
- Ammonotelic when plenty of water is available
- Uricotelic when plenty of water is available
- Ureotelic when plenty of water is available.
Answer: 2. Ammonotelic when plenty of water is available
Question 58. Two common characteristics found in crabs are :
- Green gland and tracheae
- Book lungs and antennae
- Compound eyes and anal cerci
- Jointed legs and chitinous exoskeleton
Answer: 4. Jointed legs and chitinous exoskeleton
Question 59. Biradial symmetry and lack of cnidoblasts are the characteristics of:
- Aureiia and paramctiunt
- Hydra and starfish
- Stylish and sea anemone
- Ctenoplana and beroe
Answer: 2. Hydra and starfish
Question 60. Which one of the following is a matching set of a phylum and its three examples?
- Mollusca- loligo, teredo, octopus
- Porifera- spongilla, euplectella, pennatula
- Cnidaria-b onellio, physalia, aurelia
- Platyhelminthes-planaria, Schistosoma, Enterobius
Answer: 1. Mollusca- loligo, teredo, octopus
Phylum Porifera MCQ Questions With Answers Question 61. Psetrdocoelom occur in
- Lascaris
- Taenia solium
- Fasciolu hepatica
- Planaria
Answer: 1. Lascaris
Question 62. What is true about nereis, scorpions, cockroaches and silver fish?
- They all possess a dorsal heart
- None of them is aquatic
- They all belong to the same phylum
- They all have joined paired appendages.
Answer: 1. They all possess a dorsal heart
Question 63. Which one of the following is a matching feature and the animal possessing it?
- Ventral solid – leech nervous system
- Pharyngeal gill slits – chamaeleon absent in embryo
- Ventral heart – scorpion
- Post-anal tail – octopus.
Answer: 1. Ventral solid – leech nervous system
Question 64. Which one of the following pairs is
- Apis inda – honey
- Kenia ACL – lac
- Bomhy mori – silk
- Pila – pearl
Answer: 4. Pila – pearl
Question 65. The radial symmetry is observed in :
- Plaryhelminrhes
- Coelerrterates
- Aschelminthes
- Annelids.
Answer: 2. Coelerrterates
Question 66. In understanding different types of symmetry, the term used as principal axis means :
- A flat area that runs through any axis
- An imaginary straight line joining two opposite points at the ends
- An imaginary straight line joining the midpoint at one end and the midpoint at the opposite end
- An animal has its body parts affected in such a manner to exhibit symmetry.
Answer: 2. An imaginary straight line joining two opposite points at the ends
Question 67. In hydra, nematocysts are found only in :
- Epidermis
- Gastrodermis
- Mesoderm is
- Endoderinis.
Answer: 1. Epidermis
Question 68. The jellyfish is classified under the phylum :
- Porifera
- Cnidaria
- Mollusca
- Echinodermara.
Answer: 2. Cnidaria
Question 69. Which of the following possesses a hard exoskeleton formed by calcium carbonate?
- Physalia
- Aurelicr
- Corallium
- Halisremma.
Answer: 3. Corallium
Phylum Porifera Animal Kingdom NEET Practice Question 70. Which of the following is not found in vertebrates?
- Body scales
- Cniodblasts
- Gill opening
- Bilateral symmetry
Answer: 2. Cniodblasts
Question 71. The infection of Enterobius in an
- Flying
- Piercing
- Inoculation
- Contamination.
Answer: 4. Contamination.
Question 72. Trophocytes, mycetocytes, oenocytes and urate cells are found in the body of cockroach. Which statement is true?
- Trophocyfes contain reserve blood
- Mycetocytes contain symbiotic bacteria
- Oenocytes secrete war and rate cells contain uric acid
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 73. Cockroach have a stomodaeal valve between :
- Ileum and colon
- Crop and gizzard
- Mesenteron and ileurn
- Gizzad and mesenteron.
Answer: 4. Gizzad and mesenteron.
Question 74. Caterpillar and maggot are :
- Pupa
- Larvae
- Adults
- Nymphs.
Answer: 2. Pupa
Question 75. Which group of animals being to the same pirylurn
- Earthworms, pinworms, tapeworms
- Prawn, scorpion, locusta
- Sponge, sea anemone, starfish
- Malarial parasite, amoeba, mosquito
Answer: 4. Malarial parasite, amoeba, mosquito
Question 76. Mesogloea is seen between :
- Ectoderm and endoderm
- Ectoderm and mesoderm
- Mesoderm and endoderm
- Just below mesoderm.
Answer: 1. Ectoderm and endoderm
Question 78. Green giand is the excetory organ of:
- Prawn
- Butterlly
- Snail
- Earthworrn.
Answer: 1. Prawn
Question 79. The parasite completes its life cycle in a single host is :
- Fasciola hepatica
- Pktsmadiwn vivax
- Taenia solium
- Ascaris lum bricoides.
Answer: 4. Ascaris lum bricoides.
Question 80. In which triploblastic animal coelom is absent?
- Platyhelminthes
- Aschelminares
- Annelids
- Arthropoda.
Answer: 1. Platyhelminthes
Question 81. A waxy substance produced by honey bees to repair combs are called :
- Propolis
- Honeydew
- Nectar
- Sporopollenin
Answer: 1. Propolis
Question 82. Which one of the following groups of three animals each is correctly matched with their one characteristic morphological feature?
- Animal morphological feature
- Cockroach, locust, metameric segmentation taenia
- Liver fluke, bilateral symmetry sea anemone, sea cucumber
- Centipede, prawn, jointed appendages sea urchin
- Scorpion, spider, ventral solid central
- Cockroach nervous system.
Answer: 4. Cockroach nervous system.
Question 83. Which one of the following phyla is correctly matched with its two general characteristics?
- Chordat notochord at some stage and separate anal and urinary, openings to the outside
- Mollusca – normally oviparous and developement through a trochophore or veliger larva
- Arthropoda – body divided into head, thorax and abdomen and respiration by trachea
- Echinodermata – pentamerous radial symmetry and mostly internal fertilisation.
Answer: 2. Mollusca – normally oviparous and developement through a trochophore or veliger larva
Question 84. Ascaris is characterized by :
- Presence of true coelom and metamerism (metamerisation)
- The presence of neither true coelom nor metamerism
- The absence of true coelom but the presence of metamerism
- Absence of true coelom but the absence of metamerism
Answer: 2. Presence of neither true coelom nor metamerism
Question 85. Which of the following is not a characteristic of the phylum annelida?
- Segmentation
- Pseudocoelom
- Ventral nerve cord
- Closed circulatory system.
Answer: 2. Pseudocoelom
Question 86. Which of the following are correctly matched concerning their taxonomic classification?
- Centipede, millipede, spider, scorpion-Insecta
- Housefly, butterfly, silverfish-Insecta
- Spiny anteater, sea urchin, sea cucumber- Echinodermata
- Flying fish, cuttlefish, silverfish – pisces
Answer: 2. Housefly, butterfly, tsetse fly, silverfish-Insecta
Question 87. Which of the following is the true description of an animal concerned?
- Cockroach – 10 pairs of spiracles (2 pairs on thorax and 8 pairs on abdomen)
- Earthworm – the alimentary canal consists of a sequence of pharynx, oesophagus, and stomach. Gizzard and intestine
- Frog – body divisible into three regions, head, neck and trunk
- Rat – left kidney is slightly higher in position than the right one
Answer: 1. Cockroach – l0 pairs of spiracles (2 pairs of on thorax and 8 pairs on the abdomen)
Question 88. The number of abdominal segments in male and female cockroaches is :
- 10, 10
- 10, 10
- 10, 11
- 8, 10.
Answer: 1. 10, 10
Question 89. In earthworms, the characteristics internal median fold of the dorsal wall of the intestine called typhlosole are present in:
- 5 To 9 segments
- 9 To 14 segments
- 26 To 95 segments
- 15 To the last segment
Answer: 3. 26 To 95 segments
Question 90. In which of these following phyla, while the adults show radial symmetry, the larva shows bilateral symmetry?
- Annelids
- Arthropods
- Molluscs
- Echinoderms
- Porifera.
Answer: 4. Porifera.
Question 91. Muga silk worm feeds on :
- Shorea
- Terminalia
- Machilus
- Morus
Answer: 3. Machilus
Question 92. Which of the following phylum possesses spicules
- Annelids
- Mollusca
- Porifera
- Platyhelminthes
Answer: 3. Porifera
Question 93. One of the representatives of phylum Arthropoda is :
- Silverfish
- Pufferfish
- Flying fish
- Cuttlefish
Answer: 1. Silverfish