Mental Health And Community Health For NEET Mental Health Growth Of Human Populations
Modern humans appeared around 50,000 years ago from the archaic Homo sapiens that existed between 1,00,000 and 2,00,000 years ago.
Population is defined as a group of organisms of the same species or other species within which individuals may change genetic information occupying a particular space.
Demography deals with the statistical study of the population.
- The population has characteristics which are a function of the whole group and not of the individuals; these are population density, birth rate, death rate, age distribution, biotic potential, rate of dispersion and growth form.
- In the beginning, the human population was sparsely distributed over the earth. Its growth was very slow in the beginning.
- About ten thousand years ago, the growth of the human population increased. Since then it is grown rapidly.
- Today in the world the population is not evenly distributed.
- Nearly 70 per cent of the world population lives in less developed countries
- In 1700 the human population was about 0.6 billion, it touched the one billion mark around 1850. It reached 6.1 billion by 2000.
- This dramatic increase is called a population explosion.
Maximum Carrying Capacity is the maximum size which can be supported in the environment. It has the first two components life-supporting capacity and waste assimilative capacity.
- The increased levels of environmental degradation arise from population explosion and population densities within different parts of the world.
- Population growth is determined by biotic potential and environmental resistance. The human population shows a T-shaped growth curve in the absence of environmental resistance. Enhanced longevity has also contributed towards the population explosion.
Mental Health And Community Health NEET Notes
Malthus, An Economist, Proposed A Theory Of Human Population Growth that states when unchecked population grows geometrically, whereas, the means of sustenance grows only arithmetically and this would cause imbalance. There are positive checks such as floods, wars, volcanic eruptions, earthquakes etc. which maintain population.
Fertility-Related Statistics. Fertility can be measured by a number of the following factors:
Birth Rate. The birth rate is the simplest indicator of fertility and is defined as “the number of live births per 1000 estimated mid-year population, in a given year. It is calculated by the formula
= \(\frac{\text { Number of live births during the year }}{\text { Estimated mid }- \text { year population }} \times 1000\)
The birth rate is an unsatisfactory measure of fertility because the total population is not exposed to childbearing. Therefore it does not give a true idea of the fertility of a population.
Rate Of Change In Population Size
- In the ‘S’ shaped growth curve, the rate of change in population size \(\left[\frac{d \mathrm{~N}}{d t}\right]=r \mathrm{~N}\left[\frac{\mathrm{K}-\mathrm{N}}{\mathrm{K}}\right]\)
- In ‘J’ shaped growth curve, Rate of change in population size \(\left[\frac{d \mathrm{~N}}{d t}\right]=r \mathrm{~N}\) where \(\left[\frac{\mathrm{K}-\mathrm{N}}{\mathrm{K}}\right] \text { or }\left[1-\frac{\mathrm{N}}{\mathrm{K}}\right]\) = Environment resistance, r = Biotic potential, population size.
General Fertility Rate (GFR). It is the ‘number of live births per 1000 women in the reproductive age group (15-44 or 49 years) in a given year’.
GFR = \(\frac{\text { Number of live births in an area during the year }}{\text { Mid year female population of age } 15-44} \times 1000\)
The general fertility rate is a better measure of fertility than the crude birth rate because the denominator is restricted to the number of women of childbearing age, rather than the whole population. The major weakness of this rate is that not all women in the denominator are exposed to the risk of childbirth.
Total Fertility Rate (TFR) is the average number of children that would be bom to a woman during her lifetime assuming the age-specific birth rates at a given time. The total fertility rate is lower in developed countries as compared to underdeveloped countries. It is controlled by economics and human aspirations.
Doubling Time. The time required for a population to double itself is called doubling time.
Dobuiling Time = \(\left(\frac{70}{\text { Growth rate (in %age) }}\right)\)
With a 2% growth rate in India, the doubling time will be 70/2 = 35 years
The doubling time for the world population = 35 -10 years
Crude Birth And Crude Death Rates are the number of live births and deaths respectively per thousand people, on July 7 i.e. middle of the year.
Demographic transition. If birth and death rates are equal, it results in a zero population growth rate, it is termed demographic transition. It may occur in all countries as they become developed but it may take many decades in underdeveloped countries.
Immigration is the movement of individuals into a place or country.
Emigration refers to the movement of individuals out of a place or a country.
Population Explosion. If the growth of the population is continued either due to an increased birth rate or decreased death rate, it is called a population explosion. This is a great hazard to the development and prosperity of a nation.
Mental Health And Community Health NEET Notes
Reasons For Population Explosion
- Management of Natural Disasters: Mitigation of floods, earthquakes, cyclones, and cold weather has lowered mortality rates, thereby leading to population growth.
- Management of Epidemics: Control over plague, smallpox, diphtheria, cholera, diarrhea, and whooping cough has also reduced the death rate.
- Augmented Food Production: The Green Revolution pertains to the enhancement of crops such as wheat and rice. The White Revolution for dairy and the Blue Revolution for aquaculture have augmented the quantity and accessibility of food for a broader segment of the population.
- Modes of Transportation: The enhancement of rapid transportation services has facilitated the delivery of food to remote locations during emergencies. During a flood, food packets are delivered via helicopter or other rapid transportation methods.
- Deficiency in Education: Individuals lack education and awareness on the detrimental effects of overpopulation.
- Decrease in Infant Mortality Rate and Increase in Life Expectancy. Improvements in medical facilities have reduced the newborn mortality rate and raised the life expectancy of the population.
Annual Average Growth Rate:
It is a measure of the human population. It is calculated as follows:
Annual average growth rate in percent = \(\left[\frac{P_2-P_1}{P_1 \times N}\right] \times 100\)
Where P1 = Population size in the previous census
P2 = Population size in the present census.
N = Number of years between two censuses.
Dependency Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Person in dependent ages }}{\text { Persons in economically providing ages }}\)
Replacement Level (RL). It is the number of children a couple must produce to replace clientele, The actual RL, is always higher than 2.0 because children may the even better than the reproductive ape, In developed countries RL, is achieved at 2. 1 whereas in developing countries it is around 2.7 due to higher mortality rate and short life expectancy.
Three Components Of Environment
- Productive System. Such as croplands, and orchards which provide food and fibres.
- Protective System. It buffers the air and water cycle and extremes in temperature example, forests and ocean.
- Waste Assimilative System. This part assimilates wastes produced by human activities, for example, waterways, and wetlands.
Maximum Carrying Capacity. It is defined as the “Feeding capacity of an environment of an ecosystem for a population of a species under a provided set of conditions.” It is also defined as the “Level beyond which no major increase can occur.” This limit is a constant and represented by K.
Maximum Carrying Capacity Depends Upon Following Components Of Environment:
- Productive system and
- Protective system.
The use of advances in science and technology for the productive system of the environment has increased the carrying capacity.
Sustainable Development encourages a process of change in which the exploitation of resources, the direction of investments, the orientation of technological development and institutional changes are all in harmony. Such development enhances both present and future potential to meet human needs and aspirations.
The concept of sustainable development, thus, aims at a framework to integrate developmental strategies and environmental policies at local, national and global levels. Development should not endanger the natural systems that support life.
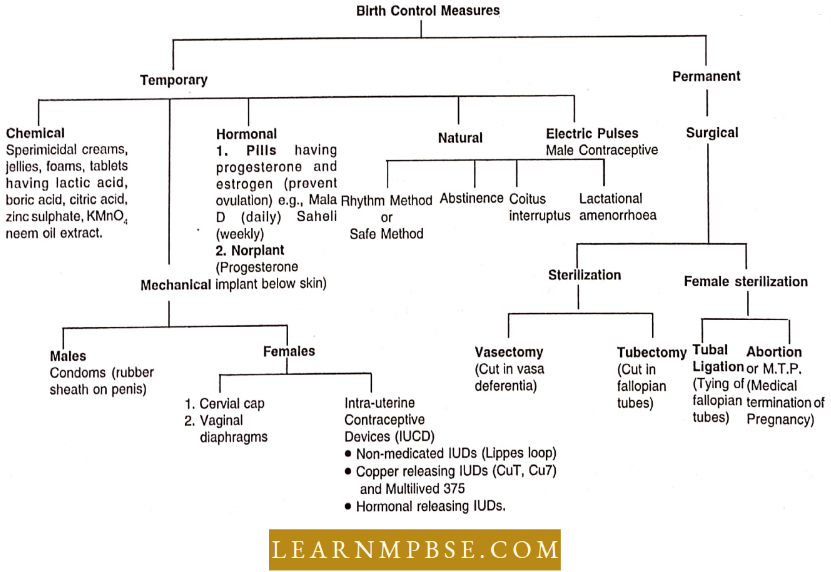
Birth Control Measures
Mental Health and Community Health For NEET Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis Aim. It is a technique to determine:
- Sex of the developing baby;
- Genetically controlled congenital diseases;
- Metabolic disorders in the foetus.
So amniocentesis is a pre-natal diagnostic technique.
Amniocentesis Procedure. It involves the following steps:
- The location of the foetus is determined by a technique called sonography (using high-frequency ultrasound waves) to prevent accidental damage to the foetus.
- A fine hollow needle is passed through the abdominal and uterine wall of a pregnant female (about the 14th or 15th week after conception) into the amniotic cavity.
- A small amount of amniotic fluid is withdrawn. It contains foetal skin cells and a number of proteins, especially enzymes. The cells can be cultured in vitro for further examination.
Community Health Mcqs For Neet
Amniocentesis Significance:
To know the sex of the baby, congenital genetic diseases and metabolic disorders in the developing foetus, the technique known as amniocentesis is followed.
Thus amniocentesis is a pre-natal diagnostic technique. But the technique is being misused even to abort normal female foetuses. So it has been now banned. Karyotypic studies show that human females are homogametic while human males are heterogametic. It is the father who is biologically responsible for the sex of the child.
Test Tube Babies (In Vitro Fertilization)-IVF.
The Technique of in-vitro fertilization and in-vitro development followed by the embryo transfer in the uterus of the normal female to start the development and finally lead to normal birth is called test tube baby.
Test Tube Babies (In Vitro Fertilization)-IVF Procedure. It involves the following steps:
- Removal of unfertilized ovum from the reproductive tract of a female.
- Ovum is kept under aseptic conditions.
- Fusion of sperm and ovum in a culture medium, outside the female body, to form the zygote.
- The zygote is stimulated to develop in-vitro up to 32-celled stages.
- The developing embryo is implanted in the endometrium of the uterus at the 32-celled stage. So the pregnancy in the woman starts and further development of the child continues in the womb till it is bom.
Such a baby is called a test tube baby.
Test Tube Babies (In Vitro Fertilization)-IVF Significance
- It is a boon to infertile mothers.
- It can be used for men with oligospermia (low sperm count).
- Old superior cows can donate oocytes.
Embryos can be frozen and preserved in an embryo tank for 10 years for future use. In very rare cases, a surrogate mother may have to be used to bring up an in vitro fertilized ovum to maturity. Though the biological realization of a test tube baby is a remarkable achievement, it has raised several ethical and legal problems including the right over the child.
- The first test tube baby was bom to Lesley and Gilbert Brown on July 25, 1978, in Oldham, England. Mrs. Brown had obstructed Fallopian tubes. Dr. Patricke Steptoe and Dr. Robert Edwards both from England experienced Mrs. Brown successfully.
- The world’s first test tube baby (a baby girl) was named Louise Joy Brown. Later, test tube babies were also born in Australia, the United States and some other countries. India’s first test tube baby was bom on August 6, 1986, at K.E.M. Hospital, Mumbai. Her name is Kumari Harsha.
- Mental Health. Behaviour according to the accepted norms of society is termed mental health.
- Mental Illness. A person may be physically fit and not suffering from any disease but because of certain inhibitions, abnormal behaviour and abnormal reactions to normal situations of life.
- Mental Illness is mainly classified into psychosis, neurosis and other disorders such as mental retardation and epilepsy.
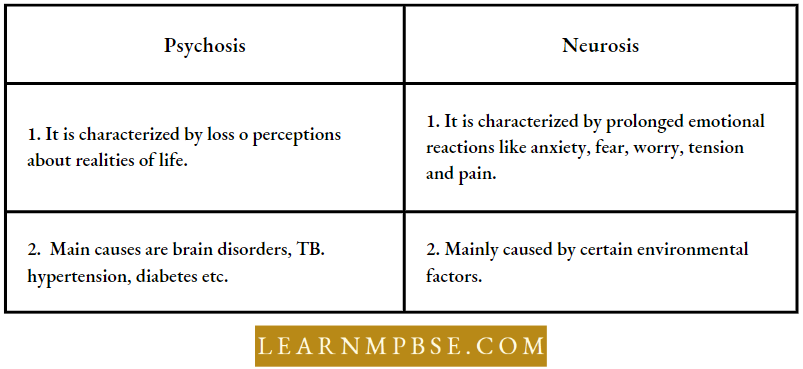
Differences Between Psychosis And Neurosis
Symptoms Of Mental Illness
- Depression.
- Insomnia or excessive sleeping.
- Compulsive action.
- The feeling of hopelessness.
- Serious thoughts of suicide.
- Unreasonable phobias.
Community Health Mcqs For Neet
List Of Common Problems Of Adolescence
- Anxiety
- Hypochondria
- Loneliness
- Neurasthenia
- Phobias
- Post-traumatic stress.
Drug Abuse. The constant use of certain drugs forms a habit and one becomes a drug dependent.
- This is called drug dependency or drug addiction or drug abuse. Such drugs act on the brain and change the behaviour, consciousness and power of perception of an individual, and are called mood-altering or psychotropic drugs.
- The drugs of abuse are often taken with alcohol or with common medicines such as aspirin. It increases sedation.
- Drug abuse is not found among well-adjusted, satisfied and happy people. It is more common among those who are under stress and feel insecure.
Anxiety Disorders. These may be
- Neurotic anxiety or
- Separation anxiety or
- School phobia. These disorders are due to overreaction to stress conditions. The symptoms are palpitation, sweating, nausea, trembling, diarrhoea and muscular tension.
Schizophrenia.
It is characterized by the following:
- Distorted thoughts
- Laughing or crying at an inappropriate time disturbs emotion
- Incoherent and bizarre behaviour lasting for a week or more
- Auditory hallucination.
- Delusion.
- List Of Psychological Disorders
- Anxiety disorders
- Obsessive-compulsive disorders
- Attention deficit disorders
- Mood disorders
- Schizophrenia
- Borderline personality disorders
- Addictive disorder
Obsessive-compulsive Disorders. These disorders cause total disability and affect a person’s working hours. Affected persons manifest overwhelming obsessions and compulsions.
- They are compelled to perform an action or an idea despite their own attempt to resist it (compulsion).
- The most common obsessions are violence, concern about infection by germs or dirt, and constant doubts (obsessions).
Mental Health Neet Biology Notes Pdf
Mental Health And Community Health For NEET Drugs
Drugs are substances used to treat diseases or to replace a missing substance essential for growth or combat against genus-causing infection. Another category of dmg includes those substances which work on the nervous system and act either as stimulants or as depressants.
Drug Dependence Or Drug Addiction. It is defined as self-administration of damage for a long period which leads to dependence of the body on them and may cause various disorders.
Drugs are classified on the basis of their action as follows:
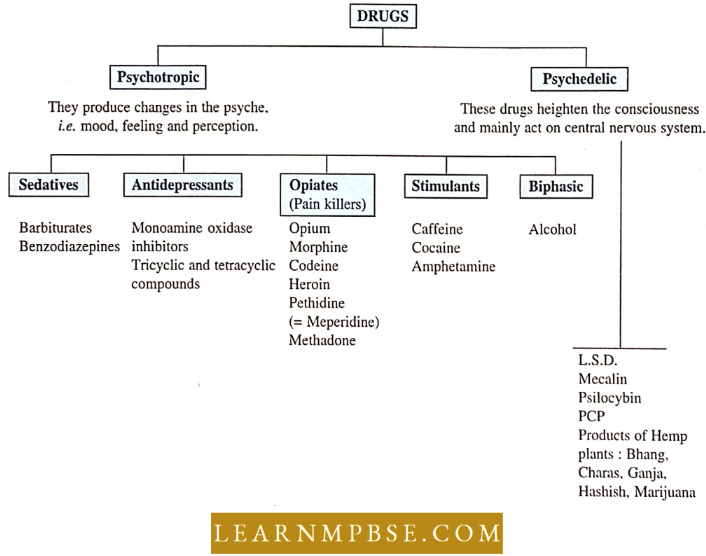
- Tranquillisers. They slow down the high centres of the brain and relieve worries. They influence only mental activity but do not affect working efficiency, for example, alcohol, compose, diazepam, Librium (chlordiazepoxide) and luminal.
- Depressant. Depressants are used to calm anxiety. They produce drowsiness and a feeling of confusion, for example, Barbiturates are used as depressants or sedatives.
- Stimulants (Antidepressants). These drugs temporarily increase mental alertness or self-confidence. They are also called Mood elevators or Superman drugs, for example. Amphetamines, cocaine, coffee and tea also contain small amounts of stimulants.
- Narcotic. It is a drug or chemical which depresses the activities of the central nervous system.
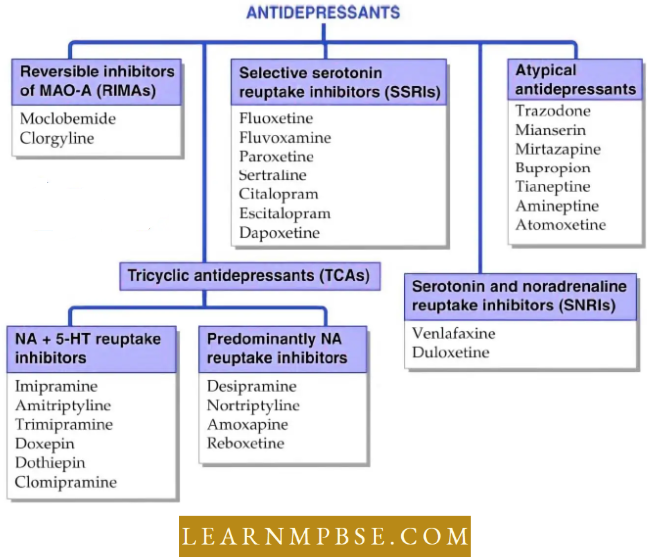
Antidepressants: They are essential for the treatment of severe cases of depression and are prescribed in most cases of clinical depression. Four types are in use as given
Mental Health and Community Health For NEET Psychedelic Or Producing Drugs
These drugs have a strong effect on the cerebrum and sense organs and take the user to a world of fantasy giving him false and temporary happiness. The individual may sense strong colours and strong sounds even though nothing is there. They include LSD (Lysergic acid Diethyl amide), Marijuana and Hashish.
Barbiturates. They are the synthetic drugs. They are sedatives and are the major components of sleeping pills. Its use produces drowsiness, feelings of confusion and sleep. Its withdrawal causes epilepsy.
Cannabis. It is the most ancient drug-yielding plant. Three kinds of drugs are obtained from these plants (Derivation of Cannabis indica).
- Hashish or Cliaras is obtained from the flowering tops of female plants.
- Bhang is obtained from dry leaves.
- Ganja. It is obtained from small leaves and bracts of inflorescence.
Marijuana is another drug obtained from Cannabis sativa. The common reaction of these drugs is relaxation, euphoria, laughing tendency, and rise in blood sugar level.
Human Population Growth Historical Perspective
Kinds And Effects Of A Few Drugs
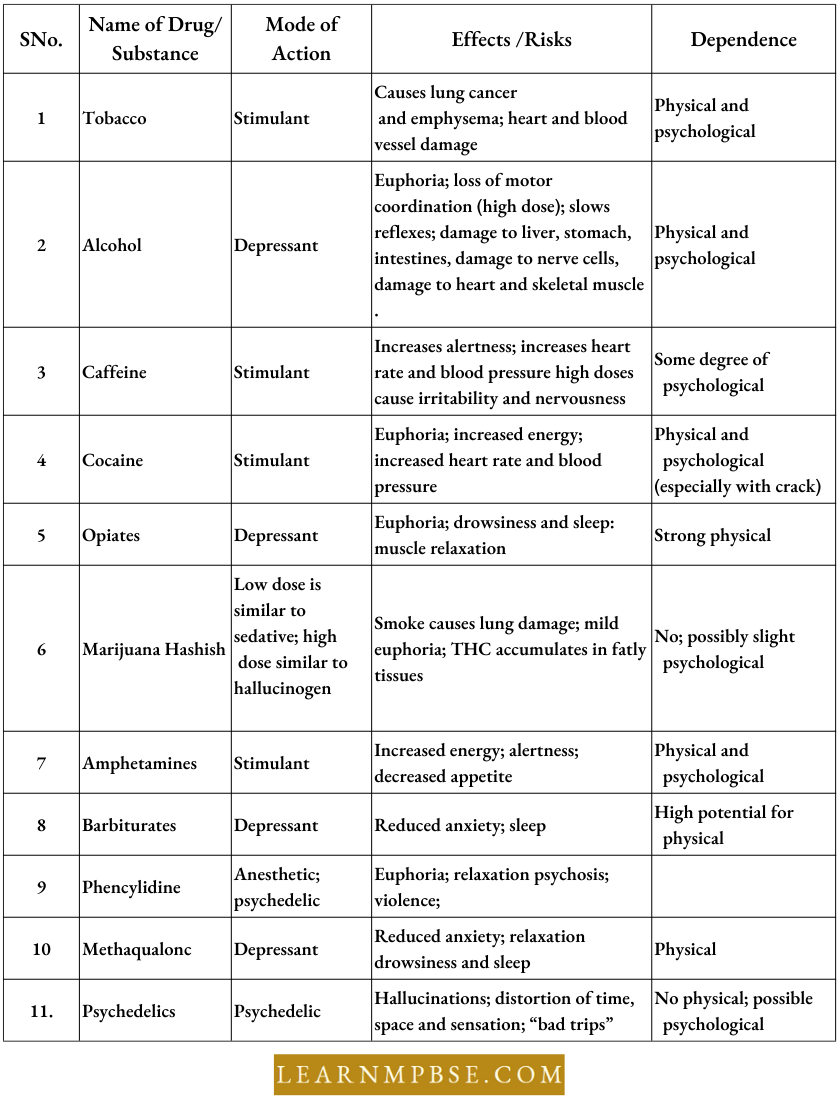
Classes Of Psychoactive Drugs
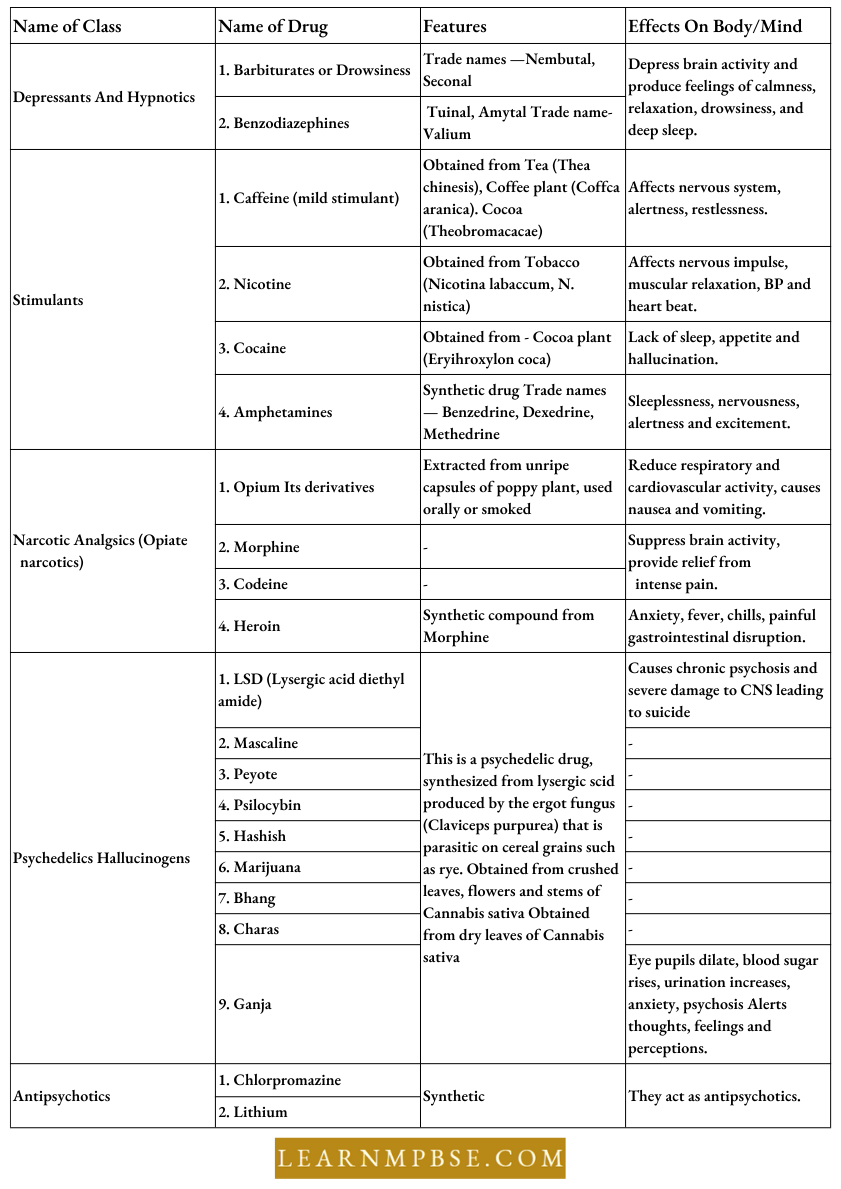
Mental Health and Community Health For NEET Tobacco Addiction
The tobacco plant is a native plant of tropical America.
WHO report states that in India, about one million people die every year (2,200 Indians die every day) due to tobacco-related diseases.
Tobacco smoke mutates and inactivates the P-53 gene which checks cancer growth.
Benzpyrene. Carcinogen present in tobacco. About 33 per cent of all cancers are caused by tobacco.
In India, about 19 per cent of women workers engaged in beedi making, have one of four miscarriages at three to four months of pregnancy.
Byssinosis. Acute bronchitis is associated with generalized airflow obstruction.
No Tobacco Day: 31st May. Tobacco is commonly called killer weed.
1996- The Olympics held in Atlanta (USA) had been declared smoke-free.
Health Care Foundation of India (HCFI) has suggested that tobacco should be treated like any other narcotic as regular nicotine use may also lead to addiction.
In India, the graph of smokers skyrocketed by 400 per cent during the 1970-80 period alone. Meanwhile, a six-fold increase in mortality from bronchitis and emphysema was also noted in India.
An “ Anti-tobacco Bill” has been long pending before Parliament.
- One out of 20 children are tempted by cigarette advertisements.
- India is one of the top consumers of cigarettes. Over 142 million men and 37 million women above 15 years of age are regular smokers.
Lung Cancer mortality risk for a heavy smoker is 20-30 times greater than that of a non-smoker.
- China has the biggest cigarette market.
- According to WHO, by 2025 AD only 15 per cent of the world’s smokers will be in the rich countries compared to the present 28 per cent, while in the Third World, the percentage of smokers will rise from 72 to 85 per cent.
Central Tobacco Research Institute is located at Rajahmundry (A.P.)
Mental Health and Community Health For NEET Alcoholism
Alcoholism. The habit of drinking alcohol is called alcoholism. Alcoholism as a disease was declared by WHO in 1964.
Sedative. Which depresses functional efficiency.
Depressant. Lowers the activities of CNS.
Beer, Wine And Whisky contain 3%, 10% and 40% alcohol.
Mental Health Neet Biology Notes Pdf
Anaesthetic. Causes loss of sensation.
Hangover. Mild effects of alcohol even after a long period of its consumption.
Polyneuropathy. A degenerative disease of the nervous system associated with chronic alcoholism.
The most common form of cirrhosis is known as Lenmec’s cirrhosis.
Alcoholism also causes a reduction in life span of 10 to 12 years.
Treatment Of Alcoholism: Abstaining from alcohol; general psychological rehabilitative treatments; use of drugs like Antabuse (disulfiram) and Temposil (Citrated calcium cyanide); aversion therapy; etc.
Mental Health and Community Health For NEET Community Health
The sum total of all the activities that contribute to the improvement of the health of the community.
Vaccination. The introduction of antigens into the body induces the production of specific antibodies, either to confer immunity against subsequent infection by the same antigen or, less commonly, to treat a disease.
Sanitary. Free from dirt and germs that might cause disease.
Sanitation. All the arrangements provide sanitary conditions.
Sterilization. A process which makes things free from germs.
National Programmes: The Government of India has launched various national programmes to eradicate and control some of the major communicable diseases. These are
- National Malaria Eradication Programme (N.M.E.P)
- National Filaria Control Programme (N. F. C. P.)
- National Leprosy Control Programme (N.L.C.P.)
- National Smallpox Eradication Programme
- National Cholera Control Programme (N.C.C.P.)
- Tuberculosis Programme
- Other diseases—Trachoma, Cancer, V.D, T.B.
AIDS etc. are also covered under various National Programmes
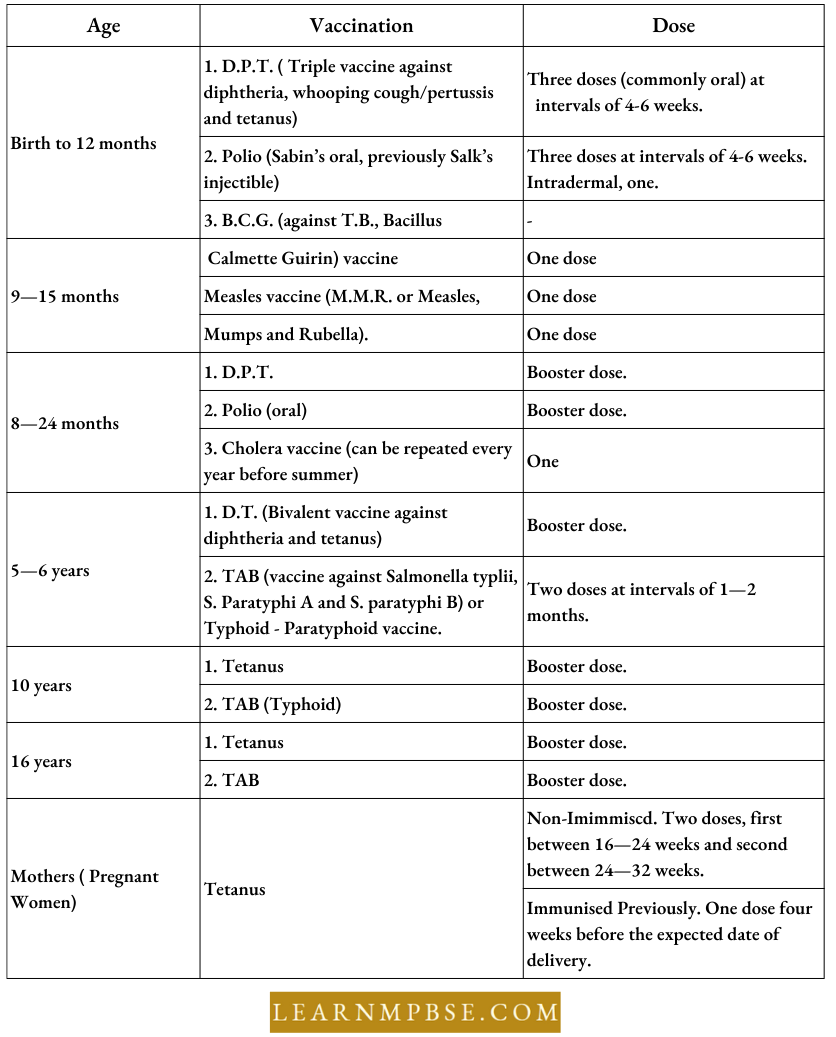
Universal /National Immunisation Programme:
The success of the smallpox eradication program has catalyzed efforts to eliminate six avoidable illnesses via the universal immunization initiative. The six diseases are diphtheria, pertussis (whooping cough), poliomyelitis, tetanus, TB, and measles.
- The program was initiated by the World Health Organization in May 1974 and aims to reach every kid by the year 2000 A.D.
- It was launched in India in 1985 and reached every child by 1992. India has designated the year 2000 A.D. as the year for universal health. The immunization timetable for six selected diseases and two supplementary ones
- Cholera and
- Typhoid
Community Medicine And Mental Health Neet
The Human Population Increased To An Unmanageable Proportion In Recent Times Due To The Following Reasons:
- Enhanced longevity has contributed to the population explosion.
- Advances in medicines and surgery have made it possible to save thousands of lives.
Human Population Growth Curve Assumes T Shape And Sigmoid Or ‘S’ Shape: When the food supply becomes insufficient in comparison with population, mass starvation death results. The graph of population growth will become T -shaped. When there is no increase in population and the environment can sustain a limited population, the growth curve will become ‘S’-shaped.
Reasons For Depletion Of Environment:
- Excessive deforestation,
- Indiscriminate mining operations,
- Excessive use of fossil fuels.
Limiting Factors Which Prevent The Earth From Supporting a Human Population Of Indefinite Size:
The following are the limiting factors which prevent the Earth from supporting a human population of limited size
- Adequate food supply.
- The habitable area on the land is limited. If a man tries to create more habitable areas by cutting down trees in forests, it would lead to imbalances in the nature.
- Limited natural resources.
- The adaptability of an organism for growth to the conditions.
- Famine, floods and epidemic diseases.
- Adolescence is the period of rapid growth, and physical and mental development period between childhood and adulthood.
- Acne resulting from clogged pores of the skin is a common problem of adolescence in both sexes.
- Neurasthenia is characterized by the inability to concentrate on enjoying things. It may lead to irritability, fatigue, insomnia, depression and headache.
- Phobias are common in adolescents.
- Mental Illness is characterized by abnormal behaviour and talk resulting in social and vocational dysfunction.
Important Psychological Disorders Are:
Anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorders, attention deficit disorder, mood disorder, Schizophrenia, Borderline personality disorder (BPD) Youths are tempted to go for drugs for non-clinical use.
Psychotropic Drugs or mood-altering drugs are also addictive:
- The substances are classified as sedatives and tranquilizers, opiate narcotics, stimulants, and hallucinogens.
- Drugs can be administered via inhalation or oral ingestion. They may also be administered by injections.
- All pharmaceuticals influence the central nervous system. Prolonged usage is exceedingly harmful to health.
- Nonetheless, some of these medications are given by physicians in appropriate dosages for certain conditions.
- Alcohol is swiftly absorbed and enters the circulatory system. A multitude of metabolic diseases is linked to persistent and excessive alcohol consumption.
- These encompass fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, hypertension, cardiovascular disorders, gastric ulcers, and vitamin shortages.
- Overcoming addiction is feasible with medical supervision and social assistance.
- The concurrent use of drugs and alcohol
Community Medicine And Mental Health Neet
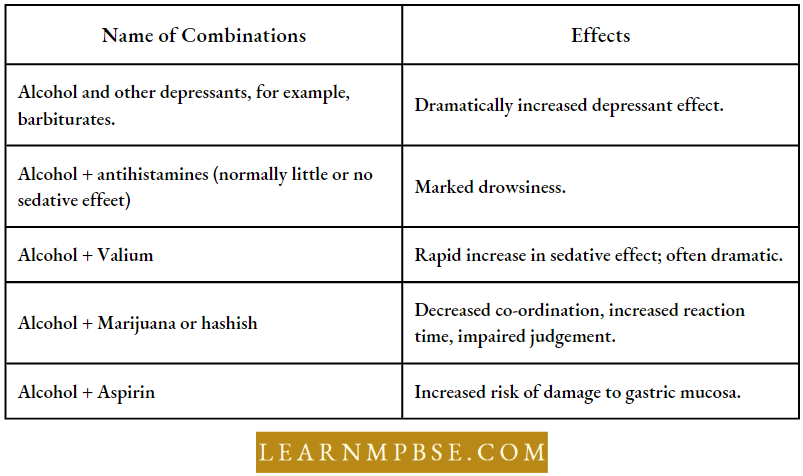
Major Groups Of Psychotropic Drugs, Examples And Effects

Interaction Of Alcohol With Some Common Drugs
Mental Health and Community Health For NEET Synopsis
WHO (World Health Organization) is a specialized, non-political health agency of the United Nations with its headquarters in Geneva. The constitution came into force on 7th April, 1948. Which is celebrated every year as ‘World Health Day’.
Alcohol is by far the number one foetal teratogen. Maternal alcohol intake and characteristic pattern of malformation in the foetus has recently been recognized called FAS, Foetal alcohol syndrome.
Symptoms of FAS include slow growth before and after birth, small head, facial irregularities like narrow eye slits, defective heart and other organs, malformed arms and legs, genital abnormalities and damage of the central nervous system and many, behavioural problems like hyperactivity and nervousness.
Cigarette smoke may be teratogenic and cause cardiac abnormalities and anencephaly (absence of cerebrum). Maternal smoking is also a significant factor in the development of cleft tip, palate and gastrointestinal disturbances. It is linked with sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
Anabolic Steroids misused by players are mainly Nandrolone, stanozolol, oxymetholone and methandie- nonc.
Age Distribution Pyramids. For constructing age pyramids, 3-age groups are taken into consideration.
- Pre-reproductive age (0-14 years).
- Reproductive age (15-60 years).
- Post Reproductive age (> 60 years).
There are 3-types of pyramids, i.e. Triangular, Bell-shaped and Urn-shaped
- Triangular Pyramid. It indicates an expanding population with a high growth rate.
- Bell-shaped Pyramid. It indicates a stable population with a zero growth rate.
- Urn-Shaped Pyramid. It indicates a declining population with a growth rate of minus.


P1 = Pre-reproductive age, P2 = Reproductive age. P3 = Post-reproductive age
Projected Growth Rates. Year 1999 = 1.4%, Year 2010 = 1.8%, Year 2030 = 0.5%
GIFT. Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT), a modified form of IVF, was developed in 1984 and is used when at least one fallopian tube is open.
- The sperms (gametes) are injected into the oviduct (fallopian tube) when the ovulation occurs.
- The difference between IVF and GIFT is that in GIFT fertilization occurs naturally within the body of a female partner, instead of in the laboratory in IVF.
ZIFT. Zygote intrafallopian transfer is another variation of IVF, and is also called ‘tubal embryo transfer’. In this case, after in vitro fertilization (in a Petri dish or test tube) the zygote is transferred into the fallopian tube. The difference between ZIFT and GIFT is that in ZIFT fertilization is observed/assured, whereas in GIFT it is not.
- The success of IVF/GIFT/ZIFT declines with the advancement of the age of the woman, perhaps due to poor quality of eggs; and if the success rate is improved, the chances of multiple births are increased.
- The present rate of growth of the human population is about 2 per cent per annum and in developing countries, it is 2.5% per annum.
- Sigmoid (S-shaped) and J-shaped growth curves are the two main kinds of growth curves.
- In a recent cyclone in Bangladesh over 50,000 people were killed but with a birth rate of 3.3 per cent per year, the number was replaced in 40 days.
- At the current rate of growth human population is doubling every 35 years.
If the 4.5 billion people in the world today continue to increase at the present rate, their combined mass will exceed the mass of the earth which is about 6.5 billion trillion tonnes in a period of 1550 years.
- Japan is the most densely populated country in the world.
- Australia is the most thinly populated country.
- Kerala is the most densely populated state of India. The complete count of individuals in an area is called a census.
Community Medicine And Mental Health Neet
The sex ratio in India is 929 females per 1,000 males. About 56% of the world’s population lives in Asia alone
- Harsha is the name of the first test tube baby bom in India (Kolkata)
- Laparoscopy involves tubular ligation (blocking fallopian tubes)
- Biologically females are superior to men because they nurse the foetus in the womb for about 280 days.
- The Red Cross was established in 1864
- There is a proposal to bring legislation to discourage the use of tobacco products including a ban on the use/consumption of tobacco in public places and on tobacco advertisements.
- Blood transfusion was first practised by James BledclI.
- The mechanism to preserve vaccines is called the cold chain.
- Amnesia. Loss of memory is associated with excessive alcohol intake.
- International Day against Drug Abuse and Illicit Trafficking is celebrated on June 27.
- IV-Drug: Any drug which is taken intravenously and includes addictive narcotic drugs like heroin.
- Drug phencyclidine is useful in controlling “rogue elephants.”
- “The Narcotics, Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act 1985” in India is one of the most powerful laws in the world to combat drug trafficking.
Teratogens. The drugs which cause foetal abnormalities when given to a pregnant mother are termed ter¬atogens. The placenta does not act as a barrier. Thalidomide is a well-known teratogen and causes phocomelia. Such drugs affect the foetus in three stages
- Fertilization and implantation
- Organogenesis
- Growth and development.
Other Known Teratogens Are LSD, morphine, methotrexate, stilboestrol, corticosteroids, warfarin, antithyroid drugs, tetracycline etc.
World Breastfeeding Week is celebrated every year from 1-7 August.
- WHO = World Health Organisation
- NICD = National Institute of Communicable Diseases
- ICMR = Indian Council of Medical Research
- ESI= Employees State Insurance
