MPBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Coordination In Plants Question and Answers
Question 1. What are plant hormones?
Answer:
Plant hormones or phytohormones are non-nutrient diffusible chemical substances that control the activities of plants like growth, development, differentiation, movements, and other physiological processes.
Question 2. How is the movement of the leaves of a Sensitive Plant different from the movement of the shoot toward light?
Answer:
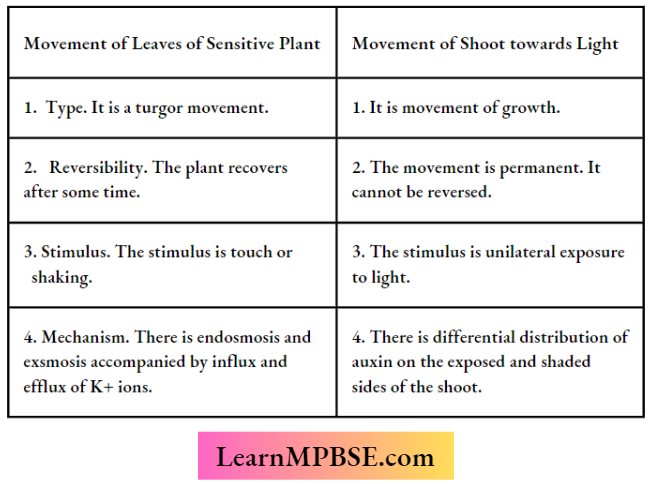
- Leaves of sensitive plant (Mimosa pudica) droop down on being touched or shaken. It is a harmonistic or seismonastic response where the direction of movement is predetermined by the presence of a turgor cell.
- The movement of the shoot toward light is a growth movement caused by the differential distribution of auxin.
Question 3. Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Answer: Auxin (IAA)/Gibberellins (GA).
Question 4. How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
Answer:
- In the region of contact, there is less availability of auxin as compared to the free side. Because of this, there is more growth on the free side.
- The tendril, therefore, bends over the support. The process continues and several coils are produced.
Coordination In Plants Class 10 Questions And Answers
Question 5. Explain the cause of shoots of the plant bending towards light.
Answer:
- The bending of the shoot towards unilateral light is caused by the effect of light on auxin distribution.
- There is less auxin on the illuminated side and more auxin on the shaded side. Therefore, there is more growth on the shaded side and the shoot bends in the other direction.
Question 6. What are nastic and curvature movements? Give one example of each.
Answer:
- Nastic Movements. They are non-directional movements in which the direction of movements is determined by the structure of the responding organ, for example., the opening of flowers, haptonasty in the Sensitive Plant. Nastie movements can be due to growth or turgor changes.
- Curvature Movements. They are directional growth movements in which the response of the plant organ is determined by the direction of the stimulus, for example., positive phototropism of shoot.
Question 7.
- What are plant hormones?
- Write two functions of auxin.
Answer:
- Plant Hormones. Plant hormones or phytohormones are non-nutrient diffusible chemical substances that can control various activities of plants like growth, differentiation, movements, development, and other physiological processes.
- Functions of Auxin.
- Auxin induces cell enlargement.
- It prevents premature falling of leaves and fruits.
Question 8.
- What is tropism?
- How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
Answer:
- It is the directional curvature movement of generally cylindrical plant organs with the direction of stimulus determining the direction of movement.
- More auxin is present on the side of the tendril away from the point of contact. Therefore, there is more growth on the free side as compared to the contact side. The more growth on the free side causes the tendril to coil around the support.
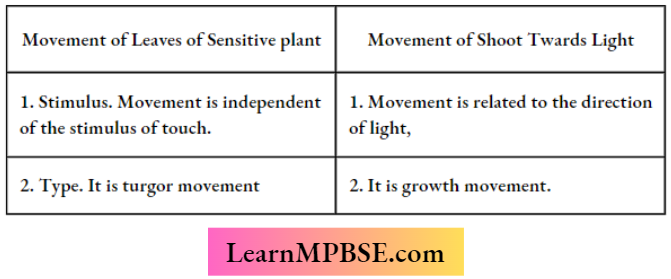
Question 9. How is the movement of leaves of sensitive plants different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
Answer:
Coordination In Plants Class 10 Questions And Answers
Question 10. Which plant hormone
- Inhibits the growth of plants
- Increases yield
- Controls cell division.
Answer:
- Abscisic acid
- Gibberellin
- Cytokinin.
Question 11. What is phototropism?
Answer:
Phototropism. It is the directional growth movement of curvature that occurs in plant organs in response to unilateral light.
Question 12. What is hydrotropism?
Answer:
Hydrotropism. It is the tropic or directional movement of curvature that occurs due to unilateral exposure to water. Roots are positively hydrotropic.
Question 13. If you keep the potted plant horizontally for 2-3 days, what type of movements would be shown by the shoot and root after 2-3 days? Why?
Answer:
- The potted plant develops a geotropic response. It is different in shoot and root. The apical part of the shoot will bend upwardly.
- It is the negative geotropic response. The apical part of the root will bend downward. It is the positive geotropic response.
Question 14.
- Which plant hormone is present in greater concentration in the areas of rapid cell division?
- Give one example of a plant growth promoter and plant growth inhibitor.
Answer:
- Cytokinin hormone occurs in greater concentration in the areas of rapid cell division.
- Growth Promoter – Auxin
- Growth Inhibitor – Abscisic acid (ABA).
Mpbse Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Solutions
Question 15. Why does the shoot of the plant bend towards light when it is kept inside a cardboard box with a small hole?
Answer:
- Light coming from the hole functions as a unilateral stimulus. It results in passing auxin formed on the illuminated side to the shaded side.
- The shaded side comes to have more auxin. Therefore, it shows more growth. Due to this, the shoot bends to the other side or source of light.
Question 16. What is geotropism? Describe an experiment to demonstrate positive and negative geotropism.
Answer:
Geotropism. It is a tropic or growth movement of curvature which occurs in response to the vector of gravity. The main stem is generally negatively geotropic while the main root is positively geotropic.
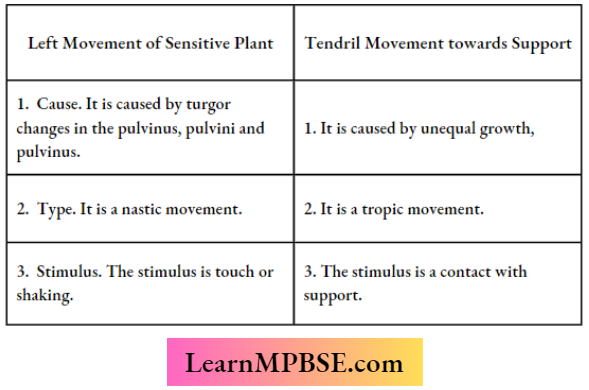
Question 17. List in tabular form three differences in the movement of leaves of Sensitive Plants when touched and the movement of tendrils towards the support.
Answer:
Question 18.
- Name the property that causes a tendril to circle the object.
- What is the benefit of it?
- Fill in the blank_____
Answer:
- Thigmotropism.
- By circling the support, the tendril can hold the plant to support and allow it to climb further to exposing the leaves properly
- Inhibits growth.
- Cytokinin.
Question 19. How does the sensitive plant detect the touch and how do the leaves move in response?
Answer:
- Touch is a stimulus that is converted into an electrochemical potential that reaches the bases of the leaflets and the leaf.
- The cells at the base show efflux of K+ and water. As a result, they shrink in size and cause the folding of leaflets and drooping of leaves.
Question 20. What are plant hormones? Name the plant hormones responsible for the following :
- Growth of stem
- Promotion of cell division
- Inhibition of growth
- Elongation of cells.
Answer: Plant hormones are non-nutrient, diffusible, chemical substances that control and coordinate growth, movements, and development.
- Growth of Stem. Gibberellin
- Promotion of Cell Division. Cytokinin.
- Inhibition of Growth. Abscisic acid.
- Elongation of Cells. Auxin.
Important Questions On Coordination In Plants Class 10
Question 21.
- Plants do not have any nervous system but yet if we touch a sensitive plant, some observable changes take place in its leaves. Explain how could this plant respond to external stimuli and how it is communicated.
- Name the hormone that needs to be administered to
- Increase the height of a dwarf plant
- It causes rapid cell division in fruits and seeds.
Answer:
Touching the sensitive plant creates an electrochemical impulse that travels from cell to cell quickly and reaches the bases of leaflets and leaves.
Special cells present at these bases shrink and cause bending movement of leaves and leaflets. Recovery occurs in about ten minutes when basal cells regain turgidity.
- Height of Dwarf Plant. Gibberellin.
- Rapid Cell Division. Cytokinin.
