P-Block Elements Class 11 Notes
Class 11 Chemistry Some P Block Elements Long Questions And Answers
Question 1. Unlike diamond, graphite is a good conductor of electricity —explain.
Answer:
In a diamond crystal, each carbon atom is sp³-hybridized, meaning that all electrons in the valence shell of the carbon atom engage in the formation of sigma bonds with four adjacent carbon atoms.
- Consequently, there are no free electrons remaining in the lattice, rendering the diamond incapable of conducting electricity.
- Conversely, each carbon atom in graphite, being sp²-hybridized, utilizes three of its valence electrons to establish three σ-bonds with three adjacent carbon atoms.
- The fourth electron in the 2pz orbital, oriented perpendicularly to the carbon layer, establishes an n-bond through lateral overlap with the 2pz orbital of any of the three neighboring carbon atoms.
- The electrons of the π-bonds are delocalized throughout the entire crystal via resonance. Graphite exhibits excellent electrical conductivity owing to the existence of mobile electrons.
Read and Learn More Class 11 Chemistry
Question 2. Diamond is extremely hard but graphite is soft and slippery —explain with reason.
Answer:
In diamond crystal, each sp³-hybridized carbon atom is tetrahedrally bonded to four other carbon atoms via covalent connections.
- A multitude of tetrahedral units interconnected to create a three-dimensional extensive array of molecules with robust bonds extending in all directions. Due to its three-dimensional network of robust covalent connections, diamond exhibits exceptional hardness.
- Conversely, in graphite crystals, each sp²-hybridized carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms, creating a network of planar hexagons.
- These two-dimensional layers are arranged in parallel planes, positioned horizontally above one another at a distance of 3.35 Å.
- Due to the weak van der Waals forces binding these layers, one layer can effortlessly glide over another with minimal pressure applied. This elucidates the reasons behind graphite’s softness and lubricity.
P-Block Elements Class 11 Notes
Question 3. Carbon monoxide possesses both oxidising and reducing properties—why?
Answer:
The oxidation slate of carbon in carbon monoxide is +2. It stands in between its highest oxidation state (+4) and lowest oxidation state (-4). As a result, in chemical reactions, the carbon atom in CO may increase its oxidation number from +2 to +4 or it may decrease its oxidation number from +2 to -4. When the oxidation number increases, CO is oxidised and plays the role of a reducing agent. For example, at high temperatures, CO reduces black CuO to red metallic Cu.

On the other hand, in case of a decrease in the oxidation number of carbon, carbon monoxide undergoes reduction, i.e., it acts as an oxidising agent. For instance, in the following reaction, carbon monoxide oxidises hydrogen-producing water and itself gets reduced to methane

Question 4. How will you convert a mixture of CO and CO2 completely into
- CO2 and
- CO?
Answer:
When a mixture of CO2 and CO is passed over strongly heated CuO and kept in a combustion tube, CO2 remains unchanged while CO gets oxidised to CO2. As a consequence, only CO2 comes out of the combustion tube. In this way, the mixture is completely converted into CO2
| Class 10 Science | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Transformation of Sentences |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Science |

On the other hand, when a mixture containing CO and CO2 is passed over white-hot coke, CO remains unchanged but CO2 gets reduced to CO. In this way, the mixture is completely converted into CO.

Mpbse Class 11 Chemistry P-Block Solutions
Question 5. Mention 3 similarities like B and Si.
Answer:
Three similarities between boron and silicon are
1. Both boron and silicon react with caustic soda to form H2 gas.
2B + 6NaOH → + 3H2
Si + 2NaOH + H2O → Na2SiO3 + 2H2
2. Halides of both boron and silicon undergo hydrolysis to form weak acids
BCl3 + 3H2O→H3BO3+ 3HCl
SiCl4 + 4H2O→ H4SiO4 + 4HCl
3. Halides of both boron and silicon form complex compounds
BF3 +HF → HBF4; SiF4 + 2HF → H2SiF6
Question 6. When boron trichloride reacts with water, it only B3 forms [B(OH)4]– whereas aluminium trichloride forms [AI(H2O)4]3+ in acidified aqueous solution. State the hybridisation of boron and aluminium in these species and explain your answer
Answer:
Boron trichloride (BCl3 ) undergoes hydrolysis to form orthoboric acid [B(OH)3] at first As the atomic size of B is small and its electronegativity is high, B(OH)3 polarises HO molecule by accepting an OH– ion thereby forming [B(OH)4]– and releasing a proton.
BCl3 + 3H2O→B(OH)3 + 3HCl
B(OH)3 + H2O→[B(OH)4]–+ H+
There are no vacant d -orbitals in B as it lies in the second period and has only one s – and three p – orbitals. So, B can have four pairs of electrons in its valence shell, i.e., its maximum coordination number is 4.
For this reason, B(OH)3 accepts one OH” ion to form [B(OH)4]- in which B-atom is sp³ -hybridised. On the other hand, AlCl3 undergoes hydrolysis in acidic medium to form [Al(H2O)g]3+
AlCl3 + 6H2O →[Al(H2O)6]3+ + 3Cl(aq)–
In an acidic medium, the concentration of OH– ions is lower than H+ ions. Thus, Al3+ ions coordinate with H2O molecules and not with OH– ions. Due to the availability of vacant d -d-orbitals in Al3+ ions, it can expand its coordination number from 4 to 6. Thus, it can form the complex ion, [Al(H2O)6]3+ in which hybridisation state of Al is sp³d²
Chemical Properties Of P-Block Elements Class 11
Question 7. Give reasons for the following:
- Diamond-tipped tools are used for drilling and cutting purposes.
- Graphite is used as a lubricant.
- Silicones are water-repelling in nature.
- CO gets absorbed by ammoniacal cuprous chloride to form a complex but CO2 does not
Answer:
1. Diamond has the highest thermal conductivity among all known substances. Because of its high thermal conductivity, diamond-tipped tools do not overheat. Diamond is extremely hard as well. For these reasons, diamond-tipped tools are extensively used for drilling and cutting purposes.
2. Graphite has a layered structure in which any two successive layers are held together by weak van der Waals forces of attraction and thus one layer can smoothly slide over the other. For this reason, graphite acts as a lubricant.
3. Silicones are water-repelling in nature because they are surrounded by non-polar alkyl groups.
4. Carbon monoxide acts as a Lewis base due to the presence of a lone pair of electrons on carbon :C=0: and forms a soluble complex with ammoniacal cuprous chloride (CuCl).
CuCl + NH3 + CO→ [Cu(CO)NH3]+Cl–
On the other hand, carbon dioxide ![]() does not have a lone pair ofelectrons on carbon and cannot form complexes.
does not have a lone pair ofelectrons on carbon and cannot form complexes.
Question 8. What happens when
- A mixture of sand and sodium carbonate is melted on heating. 0 At 200°C and under high pressure, carbon monoxide is passed through caustic soda solution and the product is heated to 300°C.
- At high temperatures, metallic calcium is made to react with carbon and the product obtained is treated with water.
- Potassium ferrocyanide is heated in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 and the gas thus obtained is passed over finely divided nickel powder at 50°C.
- Silicon is heated with methyl chloride at high temperatures in the presence of copper.
- SiO2 is treated with HF.
Answer:
1. When a mixture of sand and sodium carbonate is melted by tremendous heat, sodium silicate and carbon dioxide are obtained.
SiO2 + Na2 CO3 → Na2SiO3 + CO2↑
2. When CO is passed through NaOH solution at 200°C under high pressure, sodium formate is produced.
NaOH + CO→ HCOONa
When sodium formate is heated at 300°C, sodium oxalate and hydrogen gas are formed.

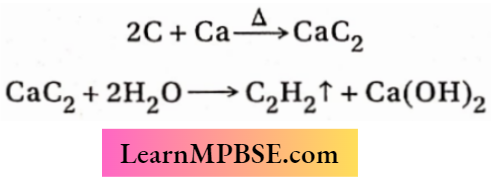
3. Metallic calcium reacts with carbon at high temperatures to form calcium carbide. Calcium carbide on treatment with water produces acetylene and calcium hydroxide
4. When potassium ferrocyanide is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid, potassium sulphate, ammonium sulphate, ferrous sulphate and carbon monoxide are formed. When the resulting CO gas is passed over finely divided nickel at 50°C, nickel tetracarbonyl (a coordinated complex) is formed
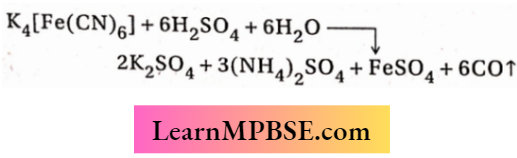
Ni + 4CO →(50°C) Ni(CO)4
5. When silicon is heated with methyl chloride at high temperature in the presence of copper, a mixture of mono-, di- and trimethylchlorosilane along with a small amount of tetramethylsilane is obtained
![]()
SiO2 reacts with HF to form silicon tetrafluoride. The initially formed SiF4 dissolves in HF to form hydrofluorosilicic acid.
SiO2 + 4HF→SiF4 + 2H2O ; SiF4 + 2HF → H2SiF6
Electronic Configuration Of P-Block Elements
Question 9. Starting from boric acid how can you prepare—
- Boric anhydride
- Boron trichloride
- Boron trifluoride
- Meta and tetraboric acid
- Boron hydride
- Ethyl borate
Answer:
1. Boric anhydride is prepared by heating boric acid at high temperatures

2. Boric acid is first converted to boric anhydride, which on heating with Cl2 forms boron trichloride.
B2O3 + 3C + 3Cl2→2BCl3 + 3CO
3. Boric acid, on heating with CaF2 and cone. H2S04 forms boron trifluoride.
CaF2 + H2SO4→CaSO4 + H2F2
2H3BO3 + 3H2F2 → 2BF3 + 6H2O
4. Orthoboric acid on heating at 100°C and 160°C forms metaboric acid and tetraboric acid respectively.
Metaboric Acid:

Tetraboric Acid:

5. Boric acid is first converted to boric anhydride which on heating with Mg-powder forms magnesium boride. On reacting dilute HCl with magnesium boride, boron hydrides are formed.

Ethyl borate is formed by heating a mixture of boric acid and ethanol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4.
3C2H5OH + H3BO3 → (C2H5)3BO3 + 3H2O
Electronic Configuration Of P-Block Elements
Question 10. Consider the compounds, BCI3 and CCl4. How will they behave with water? Justify.
Answer:
BCl3 is an electron-deficient molecule because the core boron atom possesses only six electrons in its valence shell. Consequently, it can take a pair of electrons provided by water and undergo hydrolysis to produce boric acid (H3BO3) and HCl.
The central atom of the molecule, designated as atom B, possesses six valence electrons. Shell
Conversely, the carbon atom in CCl4 possesses 8 electrons in its valence shell and lacks unoccupied d-orbitals to expand its octet. CCl4 cannot take a pair of electrons from H2O; therefore, it does not undergo hydrolysis.
