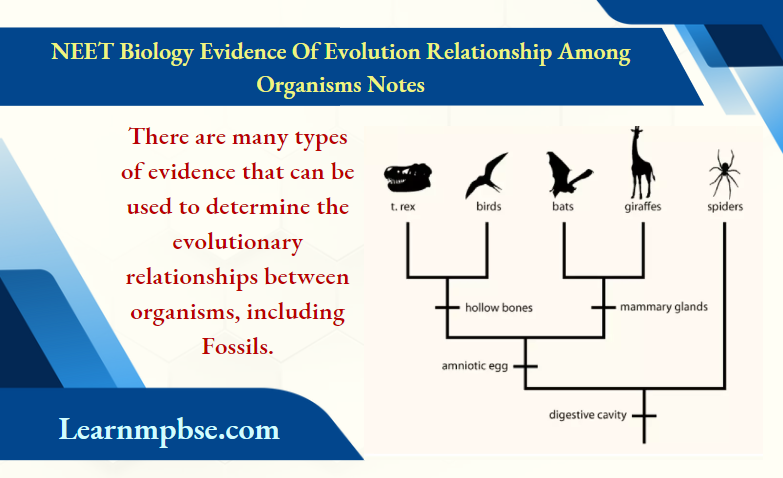
NEET Biology Evidence Of Evolution Relationship Among Organisms
Organic evolution is also stated as ‘Descent with modification’ (Darwin, 1859)
Empedocles (493—435 B.C.). Founder of the concept of Evolution.
Herbert Spencer (1820-1903). Coined the term evolution.
Biological evolution has given rise to a large number of different kinds of organisms.
NEET Biology Evidence Of Evolution Evidence In Support Of Evolution
The types of evidence which support organic evolution are, morphological, anatomical, embryological, palaeontological, biogeographical, physiological, and biochemical.
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
NEET Biology Evidence Of Evolution From Taxonomy
Classification of animals both present and extinct is based upon their natural similarities and dissimilarities which establish their genealogical relationship and common ancestry.
Palaeobiological study helps in understanding and locating hydrocarbon sources.
Evidence Of Evolution NEET Notes
Palynofossils—the tiny microscopic spores, pollen, and other vegetal remains of the past—assist us in interpreting ancient environmental conditions favourable for organic matter accumulation and its conversion to fossil fuels by transformation and subsequent thermal alteration.
Genclogieal lice was first drawn by Lamarck (1809).
- The levels of classification are Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species.
- All similar species are grouped together in one genus, all such genera in one family and so on.
Evolution Of Plants
- Diverse life processes, including energy transformation, macromolecule synthesis, genetic coding, and various biochemical reactions, exhibit similarities among diverse creatures.
- The parallels in biological processes reinforce the notion that every living being originated from a shared primordial ancestor and emerged through evolution.
- Evolutionary change is an essential trait of all living species.
NEET Biology Evidence Of Evolution Morphological And Anatomical Evidence
Body Organisation. Body of all multicellular animals: cell organelles → cells → tissues → organs → systems.
Vertebrate Organs. Certain organs (for example Heart) show gradual modifications.
- Fish’s Heart. 2 chambered (1 auricle + 1 ventricle)
- Amphibian’s Heart. 3 chambered (2 auricles + 1 ventricle)
- Reptilian Heart. Incompletely 4 chambered (2 auricles + partly divided ventricle).
- A crocodile is a reptile, but it has a 4 chambered heart with completely divided ventricles.
- Mammals And Aves. 4 chambered hearts (2 auricles + 2 ventricles).
Homologous And Analogous Organs NEET Biology
Homologous Organs. Organs which look different and perform different functions but have the same basic structure and origin are called homologous organs. They are evidence in support of divergent evolution Examples,
- Forelimbs of vertebrates such as seal (flipper), bat (patagium), horse (forelimb), man (arm).
- Thom of ‘glory of the garden’ ( Bougainvillea) and tendril of Passiflora. Both look different and help in climbing in a different manner. But both arise in the axillary position and are modified branches.
- Insect Legs. They are used in squatting in mosquitoes, collection of pollen in bees, clinging in lice, grasping in praying mantis and digging in mole cricket. However, in each case, it has five parts – coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia and 1-5 jointed tarsus.
- Insect Mouth Parts. They have a labrum, two mandibles and two pairs of maxillae. Mouth parts are specialised for chewing and biting in cockroaches, chewing and lapping in Honey bees, sponging in Housefly, piercing and sucking in Mosquito and siphoning in Butterfly.
Differences in homologous organs are examples of divergent evolution/adaptive radiation. The occurrence of similar types of biomolecules in various groups of organisms is called molecular homolog}’, for example, blood proteins in humans and apes, hormones in mammals, and Rubisco in plants.
Analogous Organs. Organs which have the same function and look superficially alike but are quite different in fundamental structure and embryonic origin are called analogous organs and support convergent evolution. Examples,
- Wing of an insect and that of a bat.
- Fins of fishes and flippers of whales have similar functions and are structurally quite different,
- Stings of Honey bee and Scorpion have similar functions but are modifications of the ovipositor and last abdominal segment respectively,
- Photosynthesis is performed by different structures in Wild peas (stipules). Australian acacia (petiole) and Ruscus (cladodes).
Connecting Links are the living animals which possess the characteristics of two different groups of animals known as the connecting links. Examples
- Lung Fishes — connecting link between fishes and amphibians.
- Resemblance With Fishes — paired fins, gills and dermal scales.
- Resemblance With Amphibians — internal nares, 3 chambered heart single or double lung for breathing.
- Egg Laying Mammals — spiny ant eater, duck-billed platypus. Link mammals with reptiles.
Mammalian Features — hair, mammary glands, diaphragm, single aortic arch.
Reptilian Features — lay large eggs, presence of cloaca, large coracoid in pectoral girdle.
Some Other Connecting Or Missing Links
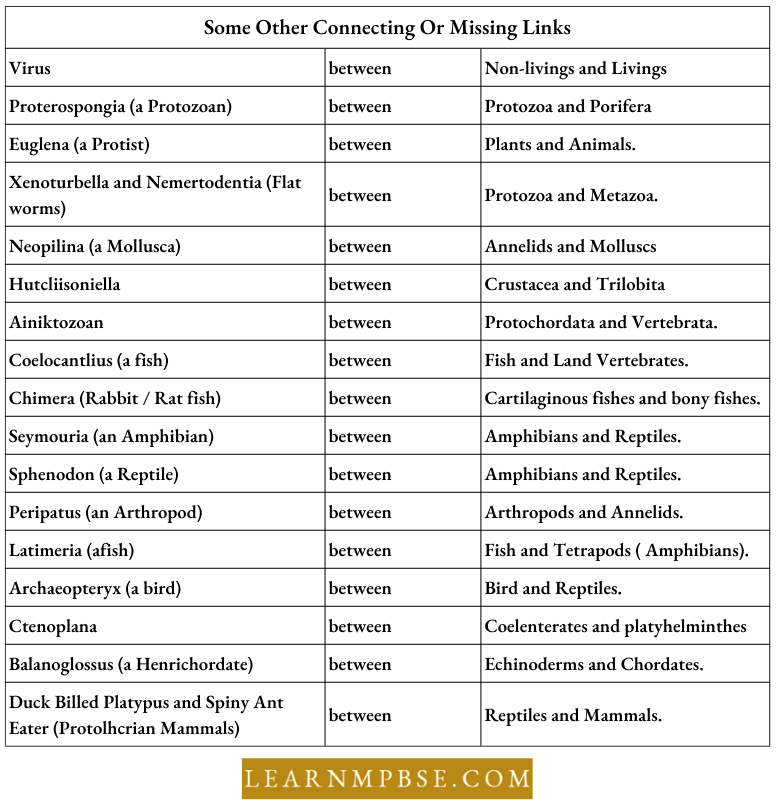
Missing links are the extinct animals which possess characters of two different groups of animals.
Fossil Evidence Supporting Evolution NEET Study Material
Vestigial Organs. The organs which occur in reduced form and are useless to the possessor, but correspond to the fully developed functional organs of their ancestors called vestigial organs. For example, the Human body has about 90 organs which are vestigial.
- Tail Bone (Coccyx)
- Wisdom Tooth
- Nictitating Membrane. (Plica semilunaris) also called the third eyelid. Used in cats, eels, pigeons and frogs for cleaning the cornea. In men, this function is carried out by the upper eyelid.
- Auricular Muscles. Three in mammals such as dog, cow, rabbit etc. ( Anterior, superior and posterior).
- Caecum And Vermiform Appendix
Examples In Other Animals
- Whales. Whales possess vestigial pelvic girdle and vestigial ear pinna (reduced).
- Pythons and Boas possess vestigial, greatly reduced pelvic girdles.
- The splint bones of horses represent the vestigial second and fourth toe.
- Eyes have become vestigial in deep sea-dwelling animals like crayfish, salamanders etc.
Examples Of Vestigial Organs Of Plants. Leaves are reduced to scales in Ruscus and Asparagus. Pistil is reduced in ray florets of sunflower.
Atavism (Reversion ). It is the reappearance of certain ancestral (not parental) structures which have either completely disappeared or greatly reduced.
NEET Biology Evidence Of Evolution Embryological Evidences
Embroyological Evidence includes similar early development; similar vertebrate embryos, temporary embryonic structures; recapitulation theory and development of certain organs.
- Development of all triploblastic animals starts from a zygote and undergoes similar processes to form gastrula having-3 primary germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm) which have the same fate in organogenesis.
- Early embryos of different vertebrates are similar in having similar structures like gill slits, notochord, tail etc. and are indistinguishable from one another. All these support organic evolution.
- It is also supported by recapitulation theory by Von Baer (modified into Biogenetic Law by Haeckel) which states “Ontogeny repeats phytogeny” example, a tadpole larva of the frog.
NEET Biology Evidence Of Evolution Palaeontological Evidence
Palaeontological evidence includes missing links; distribution of fossils in the rocks of different periods, ancestries of animals etc.
- Vinci (1452-1519) is regarded father of palaeontology. Palaeontological evidences are based on a comparative study of fossils of different animals. Fossils are the remains or impressions of harder parts of past animals preserved in sedimentary rocks or other media.
- The age of the fossil is determined either by C14 – dating technique or the amount of lead in a rock.
Radioactive Carbon Method: The radioactive carbon method was discovered by W.F. Libby.
- Half half-life of radioactive carbon is 5730 years which was found in very minute quantity i.e. 0.1 % in the atmosphere and continuously produced from cosmic ray bombardment on earth’s upper atmosphere.
- Living organisms absorb radioactive carbon (C14) throughout their life from the environment in the form of CO2 and organic molecules which signal death.
- After the death of organism, C14 began to decay according to its half-life i.e., 573 x 103 years. It means 100 grams C14 will remain 50 grams in 5.73 x 103 years and 25 grams in another 5.73 x 103 years.
- By measuring the amount of C14 in a fossil relate this amount with the amount of C14 in a living organism, the age of the fossil can be estimated.
- This method is useful only to determine the age of actual remains and useless for moulds, casts or impressions.
- The C14 Radioactive carbon method can be used to determine the age of younger fossils that are not older than 70,000 years.
- This method is used for dating not only fossils but also archaeological remains.
Fossil Evidence Supporting Evolution NEET Study Material
Radioactive Clock Method: This method was discovered by Boltwood (1907) and is based on the disintegrating property of radioactive elements. These elements disintegrate at a steady rate into a stable substance for example in the U238 – Pb206 method the following decay takes place.
Uranium238 → Radium226 →Polonium218 → Lead206 → Polonium210 → Astatine218
- One-half of uranium238 atoms will convert into Lead206 after 4.5 billion years (4.5 x 1010 years).
- The age of the rock can be calculated by estimating the uranium and lead quantity.
- This method is used for igneous rocks containing minerals and is useless for determining the age of sedimentary rock and fossils directly.
It is based on the fact that the older rock is less radioactive.
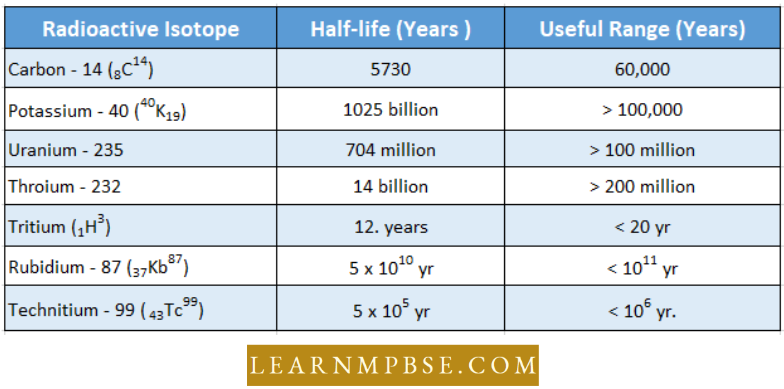
Potassium-argon Method: The transformation of radioactive potassium K40 to argon and rubidium to strontium has been used for dating fossil-bearing rocks of any age and any type. Due to the greater concentration of potassium in most rocks, it is a more accurate method of dating fossils than uranium, a relatively rare element.
- It is the latest method to estimate the age of fossils.
- The half-life of potassium is 1.3 x 109 years.
- Ordinary potassium contains 0.01 % of radioactive isotopes which disintegrate into calcium and argon.
- The age of the earliest known fossil of hominids in East Africa has been estimated by this method recently.
- It is possible to date very old rocks i.e. over three billion years by this method. Electron spin resonance dating
Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) dating is a relatively new, more precise and most accurate method of dating. It is based on the fact that background radiation causes electrons to dislodge from their normal positions in atoms and become trapped in the crystalline lattice of the material.
- When odd numbers of electrons are separated, there is a measurable change in the magnetic field (or spin) of the atoms.
- Since the magnetic field progressively changes with time in a predictable way as a result of this process, it provides another atomic clock or calendar, that can be used for dating purposes. ESR is used mostly to date Calcium carbonate in limestone, coral, fossil teeth, molluscs and egg shells. This method can date quartz and flint.
- This method has been used by palaeontologists mostly to date samples from the last 300,000 years.
- Missing Links. They are those extinct organisms which had the characteristics of two different groups of animals. These also show the path of evolution. Archaeopteryx (lizard-bird) is a missing link between the reptiles and the birds.
- They are the transitional forms between two present-day groups of organisms, for example, Pteridosperms (Pteridophytes and gymnosperms).
- Toothed birds Reptiles and birds.
- Archaeopteryx (Wagner 1861)
- Reptilian Characters—toothed jaws, non-pneumatic bones, keel-less sternum, free caudal vertebrae, free clawed fingers.
- Avian Characters—Fore limbs forming wings, feathers, beak, rounded cranium, fused skull bones.
- Geological Succession Of Fossils shows that fossils have become more in number and show gradually increased complexity from the earliest to recent rocks.
- Dinosaurs were highly flourished, giant reptiles of the Jurassic period (Age of Reptiles) of the Mesozoic era. These became extinct probably due to the direct hitting of a comet or a meteorite having rich amounts of iridium and global cooling.
- Geological Time Scale is the tabulated form showing the sequence and duration of different eras and periods with their dominant form of life. It was proposed by Giovanni Avaduina (1760). It has 5 principal eras: Archaeozoic; Proterozoic; Palaeozoic; Mesozoic and Coenozoic. Another era is Azoic 4200- 4600 million years ago in which no life existed.
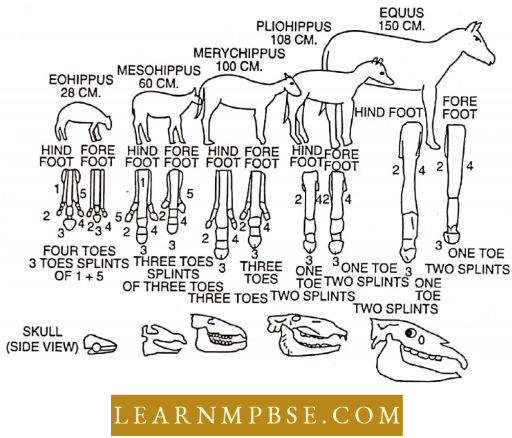
- Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of an organism. The Palaeontologists have traced the ancestries of horses, elephants, camels etc. The evolution of horses started in North America about 60 million years ago.
- The original dawn horse (Eohippus) has passed through stages like an intermediate horse (Mesohippus), ruminating horse (Merychippus) and Pliocene horse (Pliohippus) to transform into a modern horse (Equus).
- These stages confirm the occurrence of changes like an increase in height, a reduction in the number of functional digits and an increase in the size of the crown of the molars.
NEET Biology Evidence Of Evolution Type Of Fossils
- Unaltered. Woolly mammoth buried in ice.
- Petrified. Replacement of organic parts by mineral
- Moulds and casts
- Prints. Footprints, prints of leaves, stems etc.
Types Of Rocks
- Igneous Rocks. Rocks which are formed by the solidification of the original molten earth are called igneous rocks.
- Sedimentary Rocks. Rocks formed due to deposition and subsequent stratification of soil particles over a long period of time are sedimentary rocks.
- Metamorphic Rocks. These rocks are sedimentary rocks that are changed by heat and pressure.
In passing from the earliest to recent rocks, the fossils become more numerous and also progress from simple to more complex types.
Geological Time Scale
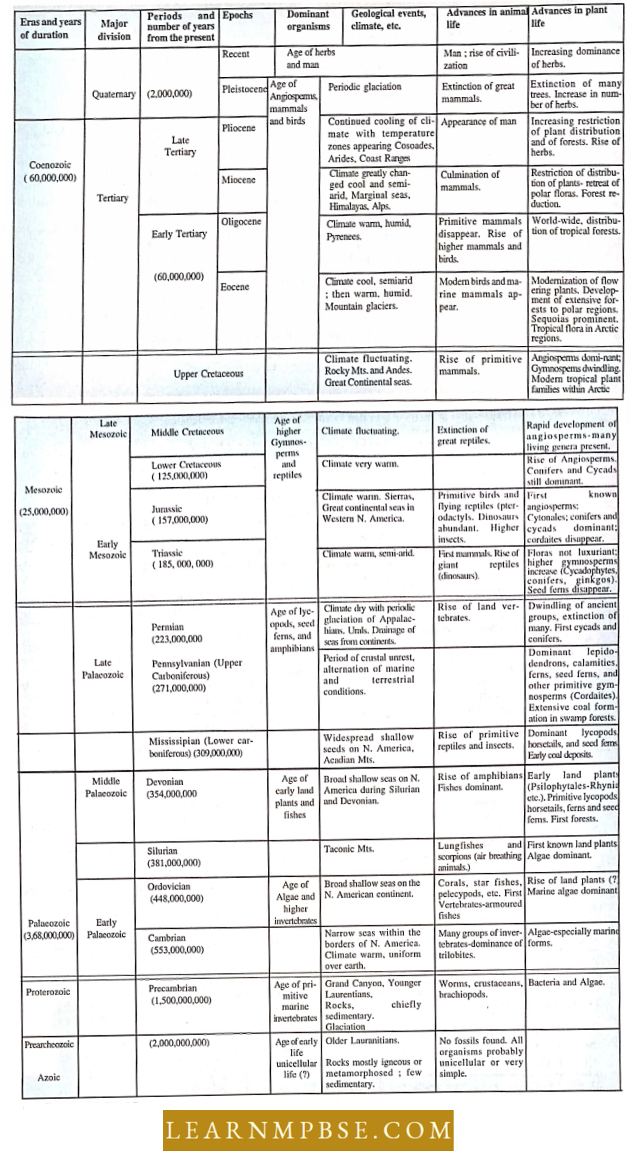
NEET Biology Evidence Of Evolution Biogeographical Evidence
- Biogeography. The study of the distribution of animals and plants in the world is called biogeography.
- Pangaea. It is held that around the carboniferous period ( about 375 million years back) or slightly earlier, all the present-day continents formed a single large irregular-level mass called Pangaea.
- Realms Of Life. Sclater ( 1858) divided the earth into six realms for the distribution of birds while Wallace (1923) divided the earth into six realms for the distribution of both plants and animals.
- Nearctic
- Palaearctic
- Neotropical
- Oriental
- Ethiopian
- Australian
- Discontinuous Distribution. Descendants of a common ancestor in some cases inhabit different continents and also differ from each other.
- Even with the same climate and topography, different realms have different types of flora and fauna. Central Africa has lions, elephants, antelope, and giraffes while Brazil has tapir, sloths, opossums, and llamas. The deserts of the two realms also differ with cacti in America and euphorbias in Africa. It is believed that at one time the whole land mass was one piece of Pangaea.
- About 200 million years back, it broke up into northern Laurasia and southern Gondwanaland. Laurasia further split up to form Eurasia, Greenland, and North America. Gondwanaland formed South America, South Africa, Australia, New Zealand and India.
- Another reorientation occurred 135 million years back when India was pushed upwardly to rest against Eurasia, South Africa joined North Africa and South America came close to North America.
- The degree and period of separation of an area from another correspond to species diversity.
- Double coconut occurs only on Seychelles Island. Egg-laying mammals are restricted to Australia, Tasmania, and New Guinea. Kangaroo and Koala are marsupials found in Australia while Opossum is found in S. America.
- The two sides of the isthmus of Panama separated only a few million years back. They possess different but related species of invertebrates.
- Galapagos Islands is a group of 14 islands situated 800-960 km off the west coast of South America. Darwin visited the islands and called them living laboratories of evolution. The islands have 23 different species of birds and 11 types of tortoises.
- Amongst the birds are 14 species of finches (named Darwin’s finches by David Lach, 1947), a group of small birds which resemble the mainland seed-eating ground finches in general body pattern but differ in food habits, types of beaks, and several other physical features to appear distinct species.
- The finches must have come from the mainland but different islands of the Galapagos provided different types of environmental conditions so that the common stock became diversified due to genetic drift and adaptation to different food habits. It is an example of adaptive radiation/divergent evolution. Example,
- Alligators – occur only in the S.E. U.S.A. and Eastern China.
- Restricted Distribution. The parts separated from the rest of the world long have unique fauna and flora example, Australia.
NEET Biology Evolution Notes
NEET Biology Evidence Of Evolution Biochemical Evidences
- Enzymes
- Hormones
- Blood proteins– of various mammals are similar to a large extent but are sharply distinguishable from those of other vertebrates. Man is nearest to the great apes (Chimpanzees and gorillas) and next in order are the old-world monkeys, the new-world monkeys and the tarsiers.
- Molecular Homology. Similarity among animals at the molecular level is called Molecular Homology.
NEET Biology Evidence Of Evolution Cytological Evidence
All the living organisms are similar in being:
- Cellular in nature and are formed of one (protozoans) or more cells (metazoans).
- Presence of similar organelles having similar ultrastructure and functions.
- All, the cells are formed of similar material called protoplasm having similar physical, chemical, and biological properties.
- Basic metabolic cellular functions are performed similarly.
This supports that all the organisms are interrelated and have a common ancestry.
NEET Biology Evidence Of Evolution Comparative Physiology
All living organisms exhibit similarities in their chemical structure and function i. e., the biochemical composition and physiological activities, for example, the blood as regards cell and plasma, is markedly similar in different groups.
NEET Biology Evidence Of Evolution Genetics
The selection and interbreeding of domestic animals by man has led to the establishment of new races. This has been possible because of the changes occurring in genes producing mutations and variations in changed environments.
The natural forces of isolation and natural selection operate on these variations and some of them become heritable, leading to the formation of new races. The same process of gene mutation, variations, selection and interbreeding might have occurred on a large scale in nature leading to the establishment of new species.
Great Chain Of Being Or Aristotle’s Ladder Of Nature:
To express ideas about evolution various naturalists explained their different views. About 2000 years before Darwin explained his theory others expressed their views. According to Plato (428-348 BC), each species was an unchanging ideal form. All earthly representatives are imperfect imitations of such true essence of an ideal unseen world.
- As God is perfect, everything that existed on earth was His ideas. Later on, Aristotle (384-322 B.C.) further explained Plato’s idealistic concept to chain like a series of forms, each form representing a link in the progression from most imperfect to perfect. He called this chain as Ladder of Nature or Scala Naturae. It is also known as the “Great Chain of Being”
- Plate Tectonics: The concept of plate tectonics supposes that the surface layers of the Earth fit together like a spherical zig-zaw puzzle, and the individual pieces are on the move about one another.
- Continental Drift is the process in which it is supposed (from recent geological and other evidence) that the continental land masses have not always occupied their present position on the globe and that, powered by processes within the Earth itself, they are slowly and continuously on the move.
- In this way new land masses are created and destroyed, split apart and joined, over geological time. This hypothesis was first proposed by Snider in 1858 but developed by Taylor in America and Wagner in Germany in the late 1800s.
- Significance. Continental Drift is one of the processes that can lead to geographical isolation.
- K-T Boundary. The boundary between rocks of the cretaceous and tertiary periods, about 65 million years, often having iridium and marketing the extinction of dinosaurs.
- Magma. It is the molten rock material present in the earth’s interior from which igneous rocks have been formed. Lava is also magma that has reached the surface of the crater of a volcano.
- Aeon Or Eon. It is the geological age consisting of one or more eras, viz., archaean, Proterozoic, and phanerozoic. Phanerozoic eon has three eras-palaeozoic, Mesozoic, and economic.
Evidence of Evolution NEET Notes
Evolution Of Horse:
The primary tendencies observed in equine evolution pertained to movement and alimentation.
They signify adaptations to fluctuating environmental conditions and can be summarized as follows:
- Augmentation in dimensions
- Elongation of extremities and feet
- Reduction of lateral digits.
- Augmentation in length and girth of the third digit
- Alignment and rigidity of the spine
- Enhanced sensory organs
- Expansion in size and intricacy of the brain correlated with the evolution of sensory organs.
- Broadening of incisors, substitution of premolars with molars, elongation of teeth, elevation of molar crown height, augmented lateral support of teeth through cement, and expanded cusp surface areas due to enamel ridge exposure.
The Basic Timeline Of A 4.6 Billion-Year-Old Earth, With Approximate Dates:
- 2 billion years of complex cells (eukaryotes),
- 1 billion years of multicellular life,
- 1000 million years of simple animals,
- 570 million years of arthropods (ancestors of insects, arachnids and crustaceans),
- 550 million years of complex animals,
- 500 million years of fish and proto-amphibians,
- 475 million years of land plants,
- 400 million years of insects and seeds,
- 360 million years of amphibians,
- 300 million years of reptiles,
- 200 million years of mammals,
- 150 million years of birds,
- 130 million years of flowers,
- 65 million years since the dinosaurs died out,
- 2.5 million years since the appearance of the genus Homo,
- 200,000 years of anatomically modern humans,
- 25,000 years since the disappearance of Neanderthal traits from the fossil record.
- 13,000 years since the disappearance of Homo floresiensis from the fossil record.
NEET Biology Evidence Of Evolution Synopsis
Mammals among animals and angiosperms among plants are the most advanced forms. The earliest era in the geologic record is Precambrian.
Phylogenetics = Cladistics. Some workers in cladistics equate homology with synapomorphy. In molecular biology, the term indicates a significant degree of sequence similarity between D.N.A. or protein sequences.
- Evolved from common ancestor = Monophyletic origin
- Dundee. It is the famous city of fossils in Italy
- Unaltered fossils of 25, 000 yrs old elephant woolly mammoths were found in ice of Siberia (Russia)
- Evolution Is Irreversible. Also called Dollo’s law (Dollo, 1893).
- Cope’s Law. In the course of evolution, there is a tendency for animals to increase in size.
- Bergman’s Law. Warm-blooded animals are larger in size in the colder regions as compared to hotter parts.
- Allen’s Law. Extremities like tails and ears become smaller in colder areas.
- Gloger’s Rule. Warm-blooded animals have more melanin in hot wet areas but develop yellow-red pigment in hot dry areas.
Paleontological Evidence Of Evolution NEET Preparation
Ontogeny Repeats Phylogeny
Recapitulation theory – Karl Von Baer
Biogenetic Law – Ernst Haeckel
- Biogenetic Law can be illustrated even with an example amongst plants. Seedlings of Acacia tree initially develop simple leaves which later transform into compound leaves. Another example is that modern-day oaks of the southern U.S.A. retain their foliage throughout the year whereas the oaks of the northern United States are deciduous and shed their leaves during winter.
- Dinosaurs. Extinct reptiles were of two types, lizard-hipped (order Saurischia) and bird-hipped (order ornithischian), originated about 230 million years back, both carnivorous and herbivorous, using four or two legs, brain small as compared to body, often with a long tail, smallest, with size of chicken (Compsogncithus) and the largest Brachiosaurus reaching 12.6 m and weighing 80 tonnes (some workers believe that the largest dinosaur was Apatosaurus = Brontosaurus that reached a length of 21 m having a weight of 30 tonnes). The teeth of carnivorous Tyrannosaurus were 16 cm long. Plesiosaur and Pilosaur are marine reptiles of the Jurassic and Cretaceous period.
The main factor responsible for the mass extinction of dinosaurs is suggested to be the hitting of the earth by a comet or a meteorite with rich amounts of metal- iridium. Another hypothesis, suggested for this mass extinction, is ‘global cooling’
- Pterosaurs are extinct flying reptiles of the Mesozoic age. Some of them had a wing span of 12 m.
- Synapsids/Synapsida. Mammal-like reptiles of carboniferous to Triassic (315-195 million years). Some of them gave rise to mammals (for example, Pelycosaurs and Therapsids). Synapsids were eliminated by dinosaurs.
- Convergence. Development of similarities between animals or plants of different groups resulting from evolution to similar habitats
- Latimeria (Coelocanth) is a lobe-finned (Cross- opterygian) fish in which fins arise from limb-like stalks and not directly from the body. It is the oldest living fish and once was believed to have become extinct about 70,000,000 years ago.
It is regarded as a “living fossil” as it has lived till today without undergoing any change in it. Other living fossils are Antedon (Feather star – echinoderm); Limulus (king crab -an arachnid); Cycas, etc.
- George Cuvier (1769 – 1832). Proposed the theory of catastrophism. Founder/father of modern palaeontology.
- Leonardo de Vinci ( 1452-1519). Father of palaeontology.
- The fossil-like impressions formed on certain rocks due to the deposition of minerals in rock crevices are called pseudofossils.
- The large-scale extinction of plants and animals within a short period is called mass extinction.
- Triassic. An epoch between 181 -225 million years ago with dry climate. Sandstone rocks are common. First mammals appeared.
- Palaccology. It deals with the study of ancient organisms and their environment.
- Hoofed animals like horses originated in the Eocene epoch in North America.
- Igneous rocks are devoid of fossils.
- A thorn of Bougainvillea and tendril in Cucurbita: Homologous