NEET Biology Animal Nutrition and Digestive System Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Which of the following animal products can be used by an animal as a source of energy?
- Carbohydrates only
- Fats only
- Carbohydrates, fats or proteins
- Carbohydrates or fats.
Answer: 3. Carbohydrates, fats or proteins
Question 2. The inadequate amount of iodine in the diet would lead to an enlargement of:
- stomach
- thyroid gland
- gonad
- pancreas.
Answer: 2. thyroid gland
Question 3. The stomach of a ruminant is divided into:
- oesophagus and duodenum
- omasum, reticulum, abomasum and rumen
- ileum and duodenum
- omasum and abomasum chambers.
Answer: 2. omasum, reticulum, abomasum and rumen
Question 4. Glucose, galactose and fructose all have the same molecular size and composition and their absorption through the mucosal cells takes place :
- at the same rate
- glucose is absorbed most rapidly
- fructose is absorbed most rapidly
- galactose is absorbed most rapidly.
Answer: 4. galactose is absorbed most rapidly
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question and Answers
Question 5. A high carbohydrate, low protein diet for prolonged periods in children may lead to a deficiency disease called :
- marasmus
- rickets
- keratitis
- kwashiorkor.
Answer: 4. kwashiorkor
Digestive System MCQs NEET
Question 6. Which of the following hormones is not produced by the alimentary canal?
- Insulin
- Cholecystokinin
- Gastrin
- Secretin.
Answer: 1. Insulin
Question 7. The bile secreted by the liver cells passes into the gall bladder through :
- hepatopancreatic duct
- cystic duct
- hepatic duct
- hepato gall duct.
Answer: 2. cystic duct
Question 8. Removal of the stomach produces :
- dumping syndrome
- Turner’s syndrome
- emphysema
- midget.
Answer: 1. dumping syndrome
Question 9. Gastro-colic reflex is meant for :
- the removal of bacteria from the body
- the removal of faeces from the body
- the synthesis of vitamins in the body
- None of the above.
Answer: 4. None of the above
Question 10. The enzyme which is found from Protozoa to Mammalia is known as :
- amylase
- trypsin
- pepsin
- lipase.
Answer: 2. trypsin
Question 11. The molecule used by most animals for long-term energy storage is :
- glycogen
- starch
- fats
- cholesterol.
Answer: 3. fats
Digestive System MCQs NEET
Question 12. A polypeptide secreted into the blood by the cells in the stomach wall stimulates the production of HCI by parietal cells of the stomach:
- gastrin
- secretin
- pancreozymin
- rennin.
Answer: 1. gastrin
Question 13. Which one of the following will not take place when glucose is taken as food?
- Ingestion
- Digestion
- Absorption
- Assimilation.
Answer: 2. Digestion
Question 14. The greenish faecal matter excreted by the newborn child is :
- meconium
- macrophages
- jaundice
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. meconium
Question 15. Energy is stored in muscles and the liver as :
- glycogen
- starch
- fats
- cholesterol.
Answer: 1. glycogen
Digestive System MCQs NEET
Question 16. Vermiform appendix in man is seen attached to :
- colon
- caecum
- rectum
- ileum.
Answer: 2. caecum
Question 17. Bile augments the digestion of:
- glycogen
- fat
- starch
- protein.
Answer: 2. fat
Question 18. Which of the following is not a human salivary gland?
- Parotid glands
- Submaxillary
- Sublingual
- Infraorbital.
Answer: 4. Infraorbital
Question 19. The chemical name of vitamin K is :
- plastoquinone
- plastocyanin
- phycocyanin
- phylloquinone.
Answer: 4. phylloquinone
Question 20. Which one of the following disaccharides gives rise to two molecules of glucose on hydrolysis?
- Lactose
- Sucrose
- Maltose
- Galactose.
Answer: 3. Maltose
NEET MCQs On Digestive System
Question 21. An animal with a diet deficient in at least one essential nutrient is said to be :
- starving
- undernourished
- malnourished
- suffering from Kwashiorkor disease.
Answer: 3. malnourished
Question 22. The liver is called the reticular gland because :
- it contains reticular tissue
- its shape is reticular
- lobules branches and anastomoses with one other to form a network
- hepatic duct and cystic ducts unite to form bile ducts.
Answer: 3. lobules branches and anastomoses with one other to form a network
Question 23. Brunner’s glands secrete :
- mucus
- secretin and cholecystokinin
- enterokinase
- hydrochloric acid.
Answer: 1. mucus
Question 24. Which of the following vitamins serves as a coenzyme?
- Vit. B,
- Vit. B2
- Niacin
- All the above.
Answer: 1. Vit. B
NEET MCQ Question 25. Choose the wrong statement.
- Lipases and nucleases are not present in pancreatic juice.
- Goblet cells secrete mucus.
- Brunner’s glands are sub-mucosal glands.
- Carboxypeptidase catalyses the conversion of proteins.
- Bile contains no enzymes.
Answer: 2. Goblet cells secrete mucus
NEET MCQs On Digestive System
Question 26. The alimentary canal of prawn is:
- incomplete
- complete
- long
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. complete
Question 27. How many of the 20 amino acids are essential amino acids for an adult human?
- Eight
- Six
- Thirteen
- Fourteen.
Answer: 1. Eight
Question 28. The gastric juice secreted by gastric glands is :
- alkaline
- neutral
- acidic
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. acidic
Question 29. Most vitamins function as :
- lubricant for active transport
- a foundation for building bones
- transport molecules within the plasma membrane
- coenzymes.
Answer: 4. coenzymes
NEET MCQs On Digestive System
Question 30. The three secretions that mix with food in the small intestine are :
- saliva, gastric juice and bile
- gastric juice, bile and pancreatic juice
- bile, pancreatic juice and intestinal juice
- pancreatic juice, intestinal juice and gastric juice.
Answer: 3. bile, pancreatic juice and intestinal juice
Question 31. Enzymes are organic(proteinaceous) chemicals which accelerate biochemical reactions in cells by :
- increasing the temperature of cells
- increasing the energy of activation of the reacting molecules
- lowering the pH of the cells
- decreasing the energy of activation of reacting molecules.
Answer: 4. decreasing the energy of activation of reacting molecules
Question 32. The cells that produce dilute hydrochloric acid in the stomach are:
- parietal cells
- goblet cells
- digestive cells
- paneth cells.
Answer: 1. parietal cells
Question 33. The isolated patches of lymphoid tissue of the intestine are known as :
- hepatic cells
- Islets of Langerhans
- Peyer’s patches
- Kupffer cells.
Answer: 3. Peyer’s patches
Question 34. Gastric juice contains :
- ptyalin
- pepsin
- erepsin
- lipase.
Answer: 2. pepsin
Question 35. Bile is:
- acidic
- alkaline
- neutral
- None of these.
Answer: 2. alkaline
NEET Important Questions on Animal Nutrition
Question 36. Salts and digestive enzymes present in pancreatic juice amount to :
- 5%
- 3%
- 2%
- 8%.
Answer: 3. 2%
Question 37. Which one is a nitrogenous polysaccharide?
- Chitin
- Cellulose
- Glycogen
- Starch.
Answer: 1. Chitin
Question 38. A mineral is an atom that can be used by an animal in a form that is:
- an organic molecule
- an inorganic molecule or ion
- bonded 6 vitamins.
- bonded to several water molecules.
Answer: 2. an inorganic molecule or ion
Question 39. How many teeth in a man are grown twice in life?
- 32
- 28
- 20
- 12.
Answer: 3. 20
Question 40. The swallowing of bolus food in rabbits is called :
- defaecation
- deglutition
- regurgitation
- digestion.
Answer: 2. deglutition
Question 41. The pancreatic juice does not contain :
- trypsin
- amylopsin
- pepsin
- lipase.
Answer: 3. pepsin
Human Digestive System MCQs For NEET
Question 42. The blood capillaries of intestinal villi absorb all but:
- amino acids
- glucose
- salts
- fatty acids and glycerol.
Answer: 4. fatty acids and glycerol
Question 43. The factor which governs the absorption of digested food by intestinal villi is:
- peristalsis
- osmosis
- emulsification
- selective absorption.
Answer: 4. selective absorption
Question 44. Caecum in rabbits is concerned with :
- digestion of starch
- digestion of cellulose
- digestion
- digestion of lipids.
Answer: 3. digestion
Question 45. In the pancreas, pancreatic juice and hormones are secreted by:
- same cells
- different cells
- same cells at different times
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. different cells
Question 46. The dental formula of man is:
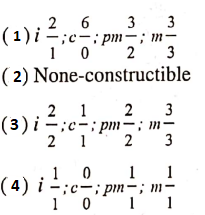
Answer: 3.
Question 47. Teeth are derivatives of:
- epidermis of skin
- dermis of skin
- The bone of the skeleton of the jaw
- Both and (B).
Answer: 2. dermis of skin
Human Digestive System MCQs For NEET
Question 48. Teeth are :
- living structure
- dead structure
- partly dead and partly living
- exact nature is not known.
Answer: 3. partly dead and partly living
Question 49. Another term for digestion is:
- dehydration synthesis
- absorption
- hydrolysis
- monomer interchange.
Answer: 3. hydrolysis
Question 50. Diastema is the toothless gap in ambit
- between right ami left incisor
- between incisors ami premolars
- between premolars and molars
- behind the molars.
Answer: 2. between incisors ami premolars
Question 51. Teeth of frog are :
- diphyodont
- pleurodont
- acrodont
- thecodont.
Answer: 3. acrodont
Question 52. The tube that connects the pharynx to the middle ear is called:
- Eustachian tube
- omentum tube
- pharyngcoacoustic tube
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. eustachian tube
Question 53. The Alimentary canal runs in between :
- oesophagus to stomach
- oral aperture to the anus
- stomach to anus
- mouth to cloaca.
Answer: 4. mouth to cloaca
Question 54. The pan of intestine that is ‘U’ shaped is called :
- pyloric intestine
- duodenum
- ileum
- colon.
Answer: 2. duodenum
Human Digestive System MCQs For NEET
Question 55. The pans of the small intestine are :
- duodenum and colon
- colon and rectum
- jejunum, duodenum and ileum
- ileum and colon.
Answer: 3. jejunum, duodenum and ileum
Question 56. The large intestine of man is composed of :
- rectum and colon
- ileum and colon
- rectum and ileum
- caecum, colon and rectum.
Answer: 4. caecum, colon and rectum
Question 57. Opening of the stomach into the duodenum is guarded by :
- pyloric valve
- ileocecal valve
- stomach valve
- cardiac valve.
Answer: 1. pyloric valve
Question 58. Digestion is brought about by :
- enzymes
- acids
- vitamins and minerals
- alkaline solution.
Answer: 1. enzymes
Best MCQs For NEET Biology
Question 59. Which of the following characters is shared by the liver of the frog and man?
- Glisson’s capsule
- Presence of hepatic cord cells
- Secretion of bile
- Five lobes.
Answer: 2. Presence of hepatic cord cells
Digestive System MCQ Question 60. Pancreatic juice contains :
- Trypsin, Lipase and Maltase
- Pepsin, Trypsin and Maltase
- Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Amylase and Lipase.
- Trypsin, Pepsin and Amylase.
Answer: 3. Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Amylase and Lipase
Question 61. Which of the following is not a protein-digesting enzyme?
- Trypsin
- Rennin
- Pepsin
- Ptyalin.
Answer: 4. Ptyalin
Question 62. The final product of protein digestion is :
- amino acids
- glucose
- peptones and proteoses
- peptide.
Answer: 1. amino acids
Question 63. The exact sequence of events during the digestion of proteins is :
- proteins → peptones → amino acid → metaproteins and peptides
- proteins → proteases and peptones → peptides → amino acids
- proteins → acid metaprotcins → proteo¬ses → amino acids → peptides
- proteins -A primary proteins → peptides → amino acids.
Answer: 2. proteins → proteases and peptones → peptides → amino acids
Question 64. Enterogasterone stops the secretion of :
- trypsin
- gastric juice
- bile
- pancreatic juice.
Answer: 2. gastric juice
Best MCQs For NEET Biology
Question 65. Cholecystokinin brings the release of :
- pancreatic juice
- gastric juice
- intestinal juice
- bile.
Answer: 4. bile.
Question 66. Proenzyme pepsinogen is activated by :
- Enterokinase
- Enterocrinin
- HCL
- Gastrin.
Answer: 3. HCL
Question 67. Secretin and pancreozymin bring the release of :
- pancreatic juice
- gastric juice
- bile
- intestinal juice.
Answer: 1. pancreatic juice
Question 68. Digestion within a digestive tract is :
- incomplete
- same as absorption
- extracellular
- an irreversible process.
Answer: 3. extracellular
Best MCQs For NEET Biology
Question 69. The liver can synthesize :
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin K.
Answer: 3. Vitamin A
Question 70. Absorption of glucose involves :
- hydration
- dehydration
- phosphorylation
- sulphonation.
Answer: 3. phosphorylation
Question 71. Vitamin B is :
- fat-soluble
- water-soluble
- insoluble
- no change.
Answer: 2. water-soluble
Question 72. The one difference between a frog and a man is that the frog has no :
- pancreas
- thyroid
- salivary gland
- adrenal gland.
Answer: 3. salivary gland
Question 73. Rickets, scurvy and poor vision are caused by to deficiency of:’ ‘
- vitamins D, C and A
- vitamins BJ2 B6andC
- vitamins B6, B12 and A
- vitamins B, D and A.
Answer: 1. vitamins D, C and A
Question 74. Gastric secretion is regulated by :
- neural mechanism
- hormonal mechanism
- neural and hormonal control
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. neural and hormonal control
Question 75. Iron is needed in the diet mainly to :
- synthesize haemoglobin
- aid the healing of wounds
- clean the blood
- strengthen the bones.
Answer: 1. synthesize haemoglobin
Best MCQs For NEET Biology
Question 76. With regard to nutrient-eating habits a human is.
- a herbivore
- an omnivore
- a carnivore
- a granivore
Answer: 2. an omnivore
Question 77. The abnormal metabolism of one of the following causes Gaucher’s iliscave :
- fats
- proteins
- carbohydrates
- All the above
Answer: 1. fats
Question 78. The main motion of lacteal is to both
- lipids
- glycogen
- milK
- proteins.
Answer: 1. lipids
Question 79. The main function of prolonged chewing is to rupture :
- membrane
- muscle bundles
- connective tissue
- cell walls.
Answer: 4. cell walls
Question 80. Which one of the following arcs is reabsorbed in the alimentary canal as such?
- Albumen of egg
- Polysaccharide
- Fat-soluble vitamin
- Protein.
Answer: 3. Fat-soluble vitamin
Question 81. Islets of Langerhans are :
- exocrine
- excretory
- endocrine
- digestive.
Answer: 3. Endocrine
Digestive System MCQs NEET
Question 82. What makes the chyme in human digestion move to the duodenum from the stomach?
- Peristaltic movement
- Gravitational pull
- Circulation of blood
- Gravitational push.
Answer: 1. Gravitational pull
Question 83. The activator of intestinal juice is :
- succus entericus
- secretin
- enterozymase
- enterocrinin.
Answer: 4. enterocrinin
Question 84. Which of the following is related to the digestive system in molluscs?
- Byssus Thread
- Osphradium
- Statocyst
- Radula.
Answer: 4. Radula.
Question 85. The nutrition in Hydra is holozoic. The entire process may be divided into four parts :
A. ingestion
B. digestion
C. excretion
D. egestion
- A, C, and D are correct
- A, B, and D are correct
- A, B, and C are correct
- A, C, and D are correct.
Answer: 2. A, B, and D are correct
Question 86. In man, the bile juice secreted by the liver per day is :
- 250 ml
- 600 ml
- 1000 ml
- 1,500 ml.
Answer: 2. 600 ml
Question 87. The method of intake of food in the case of ciliate paramecium is :
- holozoic
- saprozoic
- saprophytic
- holophytic.
Answer: 1. holozoic
Digestive System MCQs NEET
Question 88. The dental formula indicates the type of teeth and their number in sequence. Which sequence below is correct?
- Incisors, premolars, canines and molars
- Incisors, canines, premolars and molars
- Incisors, premolars, molars and canines ,
- Canines, incisors, prcmolars and molars..
Answer: 2. Incisors, canines, premolars and molars
Question 89. Carbohydrate splitting enzyme is secreted by :
- liver
- zymogen veils of gastric glands
- salivary glands
- crypts of lieberkuhn
Answer: 3. salivary glands
Question 90. The major utility of breaking lift of fond into small bits during chewing is :
- to reduce the area of food eaten up l
- to increase the surface area of food eaten up
- to enjoy the taste of food
- to make flic food soluble.
Answer: 2. to increase the surface area of food eaten up
Question 91. Peyer’s patches produce :
- enterokinase
- lymphocytes
- mucus
- trypsin.
Answer: 2. lymphocytes
Question 92. In the colon constriction of its surface forms a series of small pockets called :
- taeniae
- crypts of Lciberkuhn
- sacculus rotundas
- haustra.
Answer: 4. haustra
NEET MCQs On Digestive System
Question 93. The dietary component which is assimilated without any change is :
- cane sugar
- milk
- vitamins
- maltose.
Answer: 3. vitamins
NEET Digestive System Question 94. Gastric juice has a pH of about:
- 10
- 8.8
- 6
- 2.
Answer: 4. 2
Question 95. The glucagon is produced by :
- P-cells of the endocrine pancreas
- exocrine pancreas
- a-cells endocrine pancreas
- pancreatic duct.
Answer: 3. a-cells endocrine pancreas
Question 96. Pepsin changes :
- proteins into peptones
- fats into fatty acids
- milk into curd
- starch into sugar.
Answer: 1. proteins into peptones
Question 97. Lipase changes :
- proteins into peptones
- starch into sugar
- fats into fatty acids
- None of these.
Answer: 3. fats into fatty acids
NEET MCQs On Digestive System
Question 98. Trypsin reduces proteins and peptones to :
- amino acids
- nucleic acids
- glycogen
- None of these.
Answer: 1. amino acids
Question 99. Succus entericus acts in :
- alkaline medium
- strongly acidic medium
- neutral medium
- weakly acidic medium.
Answer: 1. alkaline medium
Question 100. The function of the bile salts is:
- to catalyse chemical reactions
- to emulsify the fats
- absorption of fat-soluble nutrients
- Both (2) and (3).
Answer: 4. Both (2) and (3)
Question 101. The gastric enzyme pepsin can shrink down protein into peptones in a medium which is:
- strongly alkaline
- weakly alkaline
- acidic
- at a neutral pH
Answer: 3. acidic
Question 102. liver, the biggest gland in the body, is concerned with the secretion of:
- hormones controlling digestion
- digestive enzymes
- bile
- mucus.
Answer: 3. bile
NEET MCQs On Digestive System
Question 103. The precursor of trypsin is synthesized in the :
- stomach
- duodenum
- liver
- pancreas.
Answer: 4. pancreas
Question 104. The enzyme crepsin helps the breakdown of peptones into amino acids in the :
- stomach
- duodenum
- large intestine
- pancreas.
Answer: 3. large intestine
Question 105. The muscular movement of the alimentary canal is known as :
- cyclosis
- peristalsis
- maceration
- metachronal waves.
Answer: 2. peristalsis
Question 106. Deficiency in the quantity of vitamin D causes :
- haemorrhage
- rickets
- scurvy
- beri-beri.
Answer: 2. rickets
Question 107. Deficiency in the quantity of vitamin C causes :
- haemorrhage
- scurvy
- muscular dystrophy
- reproductive impairment.
Answer: 2. scurvy
Question 108. Bile is green in colour due to the presence of:
- bilirubin and biliverdin
- haemoglobin
- sodium glycocholate
- sodium taurocholate.
Answer: 1. bilirubin and biliverdin
NEET Important Questions on Animal Nutrition
Question 109. The hard substance that forms teeth is :
- bone
- enamel
- dentine
- tendon.
Answer: 3. dentine
Question 110. The teeth which are embedded in sockets are called:
- homodont
- thecodont
- diphyodont
- heterodont.
Answer: 2. thecodont
Question 111. Which of the following components of food can be directly absorbed by blood without any chemical breakdown in the alimentary canal?
- proteins
- fats
- vitamins
- starch.
Answer: 3. vitamins
Question 112. The animals that can eat various plants and animal materials are called:
- cannibal
- carnivorous
- omnivorous
- herbivorous.
Answer: 3. omnivorous
Question 113. In which part of the alimentary canal is NH3 produced during the digestion of food?
- Liver
- Intestine
- Stomach
- Caecum.
Answer: 4. Caecum.
Question 114. A principal gastrointestinal hormone is :
- prolactin
- choline esterase
- secretin
- Acetyl Co-A.
Answer: 3. secretin
Question 115. The enzyme which coagulates milk is called :
- pepsin
- trypsin
- lactase
- renin
Answer: 4. renin
NEET Important Questions on Animal Nutrition
Question 116. The process involving the conversion of solid substances into liquid material finally results in the absorption along the gut wall, they are then incorporated into the cells as complex substances. The process is called :
- combination
- assimilation
- absorption
- defalcation.
Answer: 2. assimilation
Question 117. Acidic thick fluid food in the stomach is called:
- chyle
- chyme
- liquid
- vitaminous food.
Answer: 2. chyme
Question 118. A lubricant, mucin, in saliva, is made of:
- polyunsaturated fats
- glycoproteins
- actin and myosin
- phospholipid.
Answer: 2. glycoproteins
NEET Important Questions on Animal Nutrition
Question 119. Synthesis of glycogen from sugar in the liver is known as :
- Glycogenesis
- Glycolysis
- Glycogenolysis
- Glycogen.
Answer: 1. Glycogenesis
Question 120. About how much saliva does a person produce each day?
- 100 ml
- 1 to 1.5 litre
- 500 ml
- 250 ml.
Answer: 2. 1 to 1.5 litre
Question 121. Gastric juice contains the following enzymes :
- pepsin and rennin
- amylase and pepsin
- propepsin and prorenin
- insulin and glycogen.
Answer: 1. pepsin and rennin
Question 122. The function of HC1 in the stomach is to :
- kill micro-organisms
- convert pepsinogen to pepsin
- dissolve enzymes
- Both and (B).
Answer: 4. Both and (B)
Question 123. Amylase is an enzyme for which the substrate is :
- starch
- proteins
- cane sugar
- fats.
Answer: 1. starch
Question 124. A good source of lipase is :
- gastric juice
- saliva
- bile
- pancreatic juice.
Answer: 4. pancreatic juice
Question 125. The formula for sucrose is C12H22On. This means sucrose is composed of:
- 3 elements
- 45 elements
- 1 element
- 22 elements
Answer: 1. 3 elements
Question 126. All enzymes are chemically speaking :
- carbohydrates
- proteins
- lipids
- lipoproteins.
Answer: 2. proteins
Human Digestive System MCQs For NEET
Question 127. The lacteals are central lymph vessels which are found in :
- liver
- pancreas
- spleen
- villi.
Answer: 4. villi
Question 128. Which of the following does not produce any digestive enzyme?
- Intestinal mucosa
- Gastric mucosa
- Liver
- Pancreas.
Answer: 3. Liver
Question 129. Surgical removal of gall bladder in human beings would lead to :
- impairment of digestion of fat
- jaundice
- impairment of digestion of protein
- No effect during digestion.
Answer: 4. No effect during digestion
Question 130. In the process of peristalsis :
- circular muscles of the digestive tube con¬tract and those directly in front of it relax
- the longitudinal muscles of the digestive tube contract and relax alternatively
- both processes occur simultaneously
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. circular muscles of the digestive tube con¬tract and those directly in front of it relax
Question 131. The spleen is attached somewhere to the alimentary canals of frogs and rabbits:
- has an important role in digestion
- has a semi-important role in digestion
- has no role in digestion
- checks the blood circulation in the alimentary canal.
Answer: 3. has no role in digestion
Question 132. The fundamental requirement of food is for:
- growth and metabolism
- hunger
- repair
- metabolism.
Answer: 1. growth and metabolism
Question 133. Pseudorumination is :
- eating the skin
- zymogens
- chewing the cud
- swallowing the food.
Answer: 2. zymogens
Question 134. Inactive enzyme precursors such as pepsinogen for pep¬sin are called:
- zymogens
- polyglycolide
- activates
- cholenzymes.
Answer: 1. zymogens
Question 135. Most digestion and all absorption of food takes place in the:
- stomach
- caecum
- small intestine
- large intestine.
Answer: 3. small intestine
Question 136. The main advantage of having a digestive tract with a mouth and anus is :
- it permits different parts of the gut to become specialized to perform different functions of the digestive process in turn
- it permits an animal without teeth to have a means of grinding its food.
- it permits animals to eat larger organisms as food
- it permits animals to eat food in larger chunks.
Answer: 1. it permits different parts of the gut to become specialized to perform different functions of the digestive process in turn
Human Digestive System MCQs For NEET
Question 137. In humans, the digestion of food is completed in the :
- mouth
- stomach
- small intestine
- large intestine
- rectum.
Answer: 3. small intestine
Question 138. A portion of the stomach that has evolved extremely thickened muscular walls and is quite efficient at grind¬ing hard food is called a (n):
- rumen
- gizzard
- crop
- omasum
- caecum.
Answer: 2. gizzard
Question 139. Which of the following is not a function of the mammalian liver?
- Secretion of digestive enzymes for export to the gut
- Regulation of blood glucose and amino acid contents
- Production of the nitrogenous waste urea
- Production of plasma proteins for the blood.
Answer: 1. Secretion of digestive enzymes for export to the gut
Question 140. Bacteria entered with contaminated food are killed in the stomach by ;
- MCI
- Pepsin
- Rennin
- Sodium bicarbonate.
Answer: 3. Rennin
Question 141. The pylorus in frogs is found between :
- stomach and duodenum
- duodenum and ileum
- ileum and colon
- oesophagus and stomach.
Answer: 1. stomach and duodenum
Human Digestive System MCQs For NEET
Question 142. Vitamins are :
- inorganic substances that cannot be syn¬thesized by animals
- inorganic substances that can be synthesized by the animals
- organic substances that can be synthesized by animals
- organic substances only synthesized in animal cells.
Answer: 3. organic substances that can be synthesized by animals
Question 143. In the ileum which of the following is absorbed?
- Vit. K
- Bile salts
- Glucose
- Fat.
Answer: 3. Fat.
Question 144. Casein contained in the milk is a :
- bacterium
- protein
- fat
- oligosaccharide.
Answer: 2. protein
Human Digestive System MCQs For NEET
Question 145. Cod liver oil is a rich source of:
- iodine
- vitamin A
- vitamin B
- vitamin C.
Answer: 2. vitamin A
Question 146. The vitamins we must consume daily are :
- fat-soluble
- water-soluble
- both (1) and (2)
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. water-soluble
Question 147. Enterokinase helps in the conversion of :
- caseinogen into casein
- proteins into polypeptides
- pepsinogen into pepsin
- trypsinogen into trypsin.
Answer: 4. trypsinogen into trypsin
Question 148. Match the items in column I (vitamin ) with those in column II (Deficiency diseases )
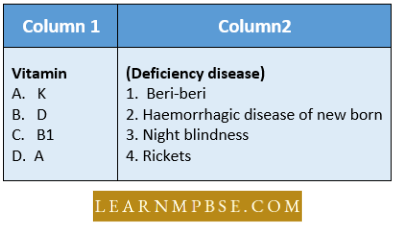
- A-3, B-2, C-4. D-1
- A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
- A-2, B-2, C-1, D-3
- A-3, B-4, C-4, D-2.
Answer: 3. A-2, B-2, C-1, D-3
Question 149. Substances which prevent deficiency diseases are called vitamins:
- Pavlov
- Funk
- Schwann
- Glisson.
Answer: 2. Funk
Question 150. Which one of the following statements about glycogen is correct?
- It is a disaccharide stored in the liver which can react with ammonia to form proteins.
- It is synthesised in the liver and takes part in the formation of bile and lipase,
- It is a polysaccharide which is synthesised and stored only in liver cells.
- It is synthesised in blood and stored in the liver and muscles to provide glucose in times of need.
Answer: 4. It is synthesised in blood and stored in the liver and muscles to provide glucose in times of need
Question 151. A dental disease characterised by mottling of teeth is due to the presence of a certain chemical element in drink¬ing water. Which is that element?
- Boron
- Chlorine
- Fluorine
- Mercury.
Answer: 3. Fluorine
NEET Digestive System Question 152. The saliva of man contains an enzyme known as:
- erepsin
- ptyalin
- amylase.
- maltase.
Answer: 2. ptyalin
Question 153. The human intestine lacks:
- symbiotic bacteria of human
- enzymes to digest cellulose
- developed vermiform appendix
- All the above.
Answer: 3. Developed vermiform appendix
Question 154. Canesugar injected into the blood is :
- changed to fructose
- changed to glucose and fructose
- undergoes no appreciable change
- changed to glucose.
Answer: 3. undergoes no appreciable change
Question 155. Fundus in sanguivorous animals is:
- round and tubular
- round and saccular
- long and branched
- long and tubular.
Answer: 4. long and tubular
Question 156. After digestion, amino acids are:
- absorbed into lymph
- absorbed into the portal circulation
- excreted to the extent of 50%
- converted into glucose in the intestine.
Answer: 2. absorbed into the portal circulation
Question 157. The rate of absorption of sugars by the small intestine is greatest for:
- pentoses
- hexoses
- disaccharides
- oligosaccharides.
Answer: 2. hexoses
Question 158. Which of the following are reabsorbed in the alimen¬tary canal as such?
- albumen of egg
- polysaccharides
- fat-soluble vitamin
- proteins.
Answer: 3. fat-soluble vitamin
Question 159. The activator of intestinal juice is :
- succus entericus
- secretin
- entero-zymase
- enterocrinin.
Answer: 4. enterocrinin
Question 160. Brunner’s gland is present in :
- duodenum
- jejunum
- ileum
- rectum.
Answer: 1. duodenum
