NEET Biology Respiration In Plants Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. While a muscle is in the process of reducing an oxygen debt :
- Lactate is converted into pyruvate
- All the NAD* is in the reduced form
- Pyruvate is converted into lactate
- NADH acts as an oxygen acceptor.
Answer: 1. Lactate is converted into pyruvate
Question 2. NAD functions in cell respiration as a (an):
- energy currency
- enzyme
- coenzyme
- hydrogen donor.
Answer: 3. coenzyme
Respiration In Plants MCQs For NEET
Question 3. Which of the following statements about oxidative phos¬phorylation is not true?
- More of the ATP in a normal cell is formed by oxidative phosphorylation via the electron transport chain than by substrate-level phosphorylation UJ;
- In eukaryotes, the formation of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation requires that the inner mitochondrial membrane remains intact
- NAD is a carrier molecule that travels down the electron transport chain to release ATP during oxidative phosphorylation
- In eukaryotes, the electron transport chain and the enzymes of the citric acid cycle are located in nvmitoc- conidia whereas the enzymes of glycolysis are located in the cytoplasm
- The role of oxygen is to act as an acceptor for electrons.
Answer : 3. In eukaryotes, the electron transport chain and the enzymes of the citric acid cycle are located in nvmitoc- conidia whereas the enzymes of glycolysis are located in the cytoplasm
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question and Answers
Question 4. Transfer of energy in animal cells is in the form of:
- ATP
- ADP
- Protein
- Monohexose phosphate.
Answer: 1. ATP
Question 5. Directly largest amount of phosphate bond energy is produced in the process of respiration during the:
- Glycolysis
- Anaerobic respiration
- Krebs’ cycle
- Fermentation.
Answer: 1. Glycolysis
Question 6. The end products of Krebs’ cycle are :
- 3 (NADH2), 1 FADH2,2 GTP
- 4(NADH2),1GTP
- 2 (NADH2), 2(FADH2), 1 GTP
- 3 (NADH2), 1 (FADH2), 1 GTP.
Answer: 4. 3 (NADH2), 1 (FADH2), 1 GTP.
Question 7. One NADH2 yields how many ATP molecules?
- Three
- Six
- Four
- One.
Answer: 1. Three
Respiration In Plants MCQs For NEET
Question 8. Acetyl Co-A combines with which of the following compounds to form citric acid :
- Oxalosuccinic acid
- Oxaloacetic acid
- Citric acid
- Ketoglutaric acid.
Answer: 2. Oxaloacetic acid
Question 9. Respiratory quotient (RQ) is represented by C02/02 and R.Q. for organic acid is :
- more than one
- less than one
- One
- infinity.
Answer: 1. more than one
Question 10. Oxidative phosphorylation is the formation of :
- NADPH2 in respiration
- ATP in respiration
- NADH2 in photosynthesis
- ATP in photosynthesis.
Answer: 2. ATP in respiration
Question 11. In the process of respiration, the potential energy stored in organic compounds is released in the form of:
- physical energy
- chemical energy
- kinetic energy
- radiant energy.
Answer: 2. chemical energy
Question 12. Glycolysis operates in :
- cytoplasm
- endoplasmic reticulum
- perinuclear space
- Golgi body.
Answer: 1. cytoplasm
Question 13. The process of respiration which results in the formation of pyruvic acid is :
- phosphorylation
- glycolysis
- photorespiration
- Krebs’ cycle.
Answer: 2. glycolysis
Question 14. Respiratory Quotient (R.Q.) is the ratio of:
- 02 consumed to C02 evolved
- water and C02
- carbohydrates and 02
- C02 evolved and 02 was consumed.
Answer: 4. C02 evolved and 02 was consumed.
Respiration In Plants MCQs For NEET
Question 15. In anaerobic respiration, the end product is :
- starch
- pyruvic acid
- sugar
- ethyl alcohol and C02.
Answer: 4. ethyl alcohol and C02.
Question 16. Energy-rich compounds produced in respiration are:
- adenosine diphosphate
- adenosine triphosphate
- adenosine monophosphate
- adenosine acetate.
Answer: 2. adenosine triphosphate
Question 17. One molecule of glucose on complete oxidation releases how much energy?
- 2870 KJ
- 1292 KJ
- 247 KJ
- 3800 KJ.
Answer: 1. 2870 KJ
Question 18. Which mineral acts as an activator in isocitric acid de-hydrogenase enzyme in Krebs’ cycle?
- Mn
- Fe
- Mg
- Mo.
Answer: 3. Mg
Question 19. During complete aerobic respiration, how much ATP is gained in prokaryotes?
- 40 ATP
- 8 ATP
- 38 ATP
- 24 ATP.
Answer: 3. 38 ATP
Question 20. In proteins, R.Q. value is:
- Less than unity
- More than unity
- Zero
- Unity.
Answer: 1. Less than unity
Respiration In Plants MCQs For NEET
Question 21. The inner membranes of mitochondria and chloroplasts :
- are relatively permeable to H+
- have ATP enzymes attached to one face only
- contain molecules of the electron transport system
- All the above.
Answer: 4. All the above.
Question 22. K (J is found to be always unity in :
- Fats
- carbohydrates
- proteins
- organic acids.
Answer: 2. carbohydrates
Question 23. How much ATP is produced during anaerobic respiration?
- 8 ATP
- 2 ATP
- 5 ATP
- 6ATP.
Answer: 2. 2 ATP
Question 24. If naked peas sce<ls are kept in four respiratory flasks then they would germinate best if the flask contains :
- C02
- N2
- 02
- H2
Answer: 3. 02
Question 25. What is the link between glycolysis and Krebs’ cycle?
- oxaloacetic acid
- Acetyl CoA
- citric acid
- pyruvic acid.
Answer: 2. Acetyl CoA
Question 26. Name the scientist who found how the energy of glucose was released in aerobic respiration.
- Pasteur
- Calvin
- Krebs
- Hopkins
Answer: 3. Krebs
Question 27. In glycolysis the net gain is two ATP molecules and two molecules are released:
- NAD
- FADH
- NADH2
- FAD.
Answer: 3. NADH2
Plant Respiration NEET Questions
Question 28. The scries of reactions in the TCA cycle take place in :
- ribosome
- grana
- mitochondria
- endoplasmic reticulum.
Answer: 3. mitochondria
Question 29. In the Krchs’ cycle, citric acid is activated by :
- aconitase
- malate dehydrogenase
- succinyl coenzyme A
- coenzyme A.
Answer: 1. aconitase
Question 30. In the ‘FCA cycle, the acid reacts with acetyl coenzyme A:
- fumaric acid
- succinic acid
- oxaloacetic acid
- malic acid.
Answer : 3. oxaloacetic acid
Question 31. Oxidative phosphorylation is the synthesis of :
- ADI* during the aerobic respiration
- NADP during the anaerobic respiration
- ATP during aerobic respiration
- phytochrome.
Answer: 3. ATP during the aerobic respiration
Question 32. When two molecules of Tripalmitin are used as a respiratory substrate the RQ is:
- 4
- 0.7
- 1
- Infinity.
Answer: 2. 0.7
Plant Respiration NEET Questions
Question 33. Glucose is converted into pyruvic acid through a series of reactions with a net gain of: ,
- 2 molecules of ATP
- 36 molecules of ATP
- 4 molecules of ATP
- 38 molecules of ATP.
Answer: 1. 2 molecules of ATP
Question 34. The maximum rate of respiration in many plants of the tropics can be observed in the range of:
- ()°C—25°C
- 20° C to 45° C
- 60°C—IOO°C
- Above 100° C.
Answer: 2. 20° C to 45° C
Question 35. In woody stems, respiration takes place through :
- pores
- stomata
- lenticels
- injured parts.
Answer: 3. lenticels
Question 36. During ATP synthesis electrons pass through :
- phytochromes
- cytochromes
- water
- oxygen.
Answer: 2. cytochromes
Question 37. R.Q. for Oxalic acid is :
- 4
- I
- Infinity
- 0.9.
Answer: 1. 4
Question 38. In plants glucose used as a respiratory substrate is derived from :
- starch
- maltose
- sucrose
- galactose.
Answer: 3. sucrose
Plant Respiration NEET Questions
Question 39. During glycolysis, fructose 1,6 biphosphate is produced by the action of which enzyme?
- Mutase
- Phospho fructokinase
- Invcrtasc
- Hexokinase.
Answer: 2. Phospho fructokinase
Question 40. In the conversion of pyruvic acid to C02, which does not take place :
- pyruvic acid to succinic acid
- pyruvic acid to lactic acid
- pyruvic acid to malic acid
- None of these.
Answer: 1. pyruvic acid to succinic acid
Question 41. The function of cellular respiration is to :
- make NADH
- make ATP
- gel rid of glucose
- get rid of C02
Answer: 4. get rid of C02
Question 42. It is not advisable to sleep under trees at night because :
- They release 02 at night.
- They release C02 at night.
- They release both CO-> and 02 at night
- They produce none of the above.
Answer: 2. They release C02 at night.
Question 43. The function of mitochondrial cristae is to.
- increase the availability of phospholipids
- store coenzyme A
- increase the surface area of the inner membrane
- prevent the escape of 0-> gas.
Answer : 3. increase the surface area of the inner membrane
Question 44. The number of molecules of pyruvic acid formed from one molecule of glucose at the end of glycolysis is :
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4.
Answer: 2. 2
Question 45. Oxidative phosphorylation takes place on :
- grana
- crista
- mitochondrial matrix
- ribosomes.
Answer: 3. mitochondrial matrix
Plant Respiration NEET Questions
Question 46. Which among the following is the most appropriate rea¬-‘ son for storing green-colored apples at low temperatures?
- The rate of respiration is reduced
- The rate of photosynthesis is reduced
- The rates of photosynthesis and respiration are reduced
- Respiration and photosynthesis are completely inhibited.
Answer: 2. The rate of photosynthesis is reduced
Question 47. The other name of Glycolysis is :
- BMP pathway
- TCA pathway
- I IMP pathway
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. BMP pathway
Question 48. One molecule of ATP yields how much energy?
- 8.9 K cal
- 6.5 K cal
- 34KJ
- 3.4 KJ.
Answer: 3. 34KJ
Question 49. In which kind of plants CO, compensation is usually higher:
- C4 plants
- C3 plants
- CAM plants
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. CAM plants
Question 50. ATP is:
- an enzyme that brings about oxidation
- a hormone
- a molecule with high energy phosphate bond
- a protein.
Answer: 3. a molecule with high energy phosphate bond
Question 51. Which of the following processes make direct use of oxygen?
- Glycolysis
- Fermentation
- Krebs’ citric acid cycle
- Electron transport.
Answer: 4. Electron transport.
Question 52. Which of the following is not true of glycolysis?
- Substrate-level phosphorylation takes place
- CO and 11,0 are end products
- ATP is generated
- ATP is used.
Answer: 2. CO, and 11,0 are end products
Question 53. When a yeast is producing wine, which of the following is not produced?
- Pyruvic acid
- Ethanol
- CO,
- Acetyl Co A.
Answer: 4. Acetyl Co A.
NEET Important Questions On Respiration
Question 54. In the conversion of pyruvic acid to acetyl CoA, pyruvic acid is :
- oxidized
- reduced
- broken into one carbon fragment
- isomerized.
Answer: 2. reduced
Question 55. The function of coenzyme A is to :
- isomerize pyruvic acid
- isomerize NAD
- activate acetyl group
- facilitate oxidative phosphorylation.
Answer: 3. activate acetyl group
Question 56. How many carbon atoms are in an oxaloacetic acid molecule, which joins with an acetyl group during step 1 of the Kerbs’ citric acid cycle?
- 6
- 4
- 3
- 2.
Answer: 2. 4
Question 57. At the end of the Krebs’ citric acid cycle, most of the energy removed from glucose molecule has been transferred to :
- Citric acid
- Oxaloacetic acid
- ATP
- NADH2 and FADH2
Answer: 2. Oxaloacetic acid
Question 58. In ETS, the final acceptor of protons is :
- Cyt. b
- Cyt. a3,
- Oxygen
- Ubiquinone (substance).
Answer: 3. Oxygen
Question 59. The atom within each cytochrome molecule that actually accepts and releases electrons is :
- Carbon
- Iron
- Zinc
- Oxygen.
Answer: 2. Iron
Question 60. Oxygen which forms part of the ETS, enters the mitochondrion as an atom in :
- Glucose
- Pyruvic acid
- C02
- Oxygen gas.
Answer: 4. Oxygen gas.
NEET Important Questions On Respiration
Question 61. Fatty acids enter cellular respiration as :
- one carbon fragment
- two carbon fragments
- long chains of 16-20 carbon atoms
- three-carbon fragments.
Answer: 2. two carbon fragments
Question 62. Within the mitochondrion, the proton gradient develops across the :
- inner membrane
- outer membrane
- intermembrane space
- matrix.
Answer: 3. intermembrane space
Question 63. Match the items in Column 1 with those in Column 2 :
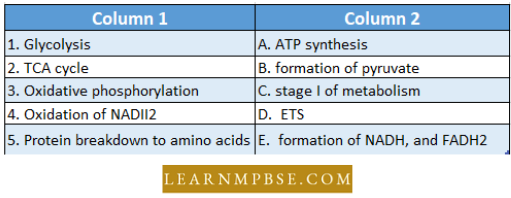
- (1—E), (2—B), (3—D). (4—A), (5—C)
- (1—A). (2—C). (3—A). (4—D), (5—C)
- (1—B), (2—D), (3—A). (4—E), (5—C)
- (1—B), (2—C). (3—D), (4—A), (5—E),
Answer: 2. (1—A). (2—C). (3—A). (4—D), (5—C)
Question 64. Which is true for glycolysis under aerobic conditions?
- Only ATP is produced
- Only NADH2 is produced
- Both ATP and NADH2 arc produced
- Neither ATP nor NADH is produced.
Answer: 3. Both ATP and NADH2 arc produced
Question 65. Which is not true for the TCA cycle when one acetyl group is oxidized?
- Two CO, molecules are released
- Three NADf molecules and one FAD molecule are reduced
- One GTP molecule is produced
- 38 ATP molecules are produced.
Answer: 4. 38 ATP molecules are produced.
Question 66. An organism which does not produce water as a waste of the respiratory process is likely to be :
- green plant
- autotroph
- anaerobe
- aerobic organism.
Answer: 3. anaerobe
NEET Important Questions On Respiration
Question 67. A high concentration of oxygen above 25% :
- reduces respiration
- increases respiration
- does not have any effect
- leads to the bursting of cells.
Answer: 1. reduces respiration
Question 68. If CO, is given off in respiration, why does the amount of CO, in the atmosphere remain relatively constant?
- CO, forms carbonate rocks
- CO is a buffer
- CO is converted in photosynthesis to carbohydrates
- CO is split up during photosynthesis.
Answer: 3. CO, is converted in photosynthesis to carbohydrates
Question 69. How many molecules of ATP are produced directly from one molecule of glucose during glycolysis :
- 6
- 8
- 0 2
- 38.
Answer: 3. 0 2
Respiration in Plants NEET Questions MCQ Question 70. In ETS, complex IV refers to :
- succinate dehydrogenase
- cytochrome oxidase
- ATP synthetase
- Ubiquinone.
Answer: 2. cytochrome oxidase
Question 71. Sir Hans Adolf Krebs (1900-1987) shared the Nobel Prize for Physiology and Medicine (1953) along with :
- A. Todd.
- 11. Theorell.
- Fritz Lipmann
- Linus Pauling.
Answer: 3. Fritz Lipmann
Question 72. The end product of the fermentation of sugars by Psuedomoiuts bacteria is :
- lactic acid and alcohol
- CO2
- ethyl alcohol +C02
- butyl alcohol.
Answer: 1. lactic acid and alcohol
Question 73. Which of these is not true for fermentation?
- NADH donates electrons to the ETS
- beginning with glucose
- Net gain of only 2 ATP
- Occurs in cytosol.
Answer: 1. NADH donates electrons to the ETS
Aerobic And Anaerobic Respiration MCQs
Question 74. Protein-rich pulses have R.Q. equal to :
- One
- More than one
- Less than one
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Less than one
Question 75. The mineral activator needed for the enzyme carboxylase of the TCA cycle is :
- Mg
- Fe
- Mo
- Mn
Answer: 1. Mg
Respiration in Plants NEET Questions MCQ Question 76. A huge amount of starch is stored in potatoes, which are underground. This is made possible by :
- Synthesis of sugar in potatoes
- Migration of starch from aerial parts to the tubers
- Migration of starch from dead soil into the tubers
- The activity of enzymes that convert starch into sugar and back to starch after it has reached the potato.
Answer: 4. Activity of enzymes that convert starch into sugar and back to starch after it has reached the potato.
Question 77. Which of the following leaves will show the maximum rate of respiration?
- Young leaves
- Mature leaves
- Senescent leaves
- None of these.
Answer: 1. Young leaves
Question 78. Respiration in methane-forming bacteria and de-nitric-flying bacteria is :
- Aerobic
- Facultative aerobic
- Facultative anaerobic
- Obligatory anaerobic.
Answer: 4. Obligatory anaerobic.
Question 79. During respiration, there are:
- gain in the dry weight
- loss in the dry weight
- no change in the dry weight
- all the above are correct depending on the type of respiratory substrate.
Answer: 2. loss in the dry weight
Best MCQs For NEET Biology
Question 80. In animal cells, the first phase in the breakdown of glucose is :
- Fermentation
- ETS
- Krebs’ cycle
- Glycolysis.
Answer: 4. Glycolysis.
Respiration in Plants NEET Questions MCQ Question 81. A molecule of ATP is formed when an electron passes from :
- Cyt. c to Cyt. a
- Cyt. b to Cyt. c
- Cyt. a to Cyt. c
- Cyt. c to Cyt b.
Answer: 2. Cyt. b to Cyt. c
Question 82. Most of the energy is supplied by mitochondria through :
- Breakdown of proteins
- Reduction of NADP
- Breakdown of sugars
- Oxidizing TCA substrates.
Answer: 4. Oxidising TCA substrates.
Question 83. The end product of glycolysis is :
- Glucose
- Pyruvic acid
- Ethyl alcohol
- Carbon dioxide.
Answer: 2. Pyruvic acid
Question 84. Which is the link between glycolysis and Krebs’ cycle :
- Glucose
- Cytochrome
- Acetyl Co A
- Pyruvic acid.
Answer: 3. Acetyl Co A
Question 85. The end products of fermentation are :
- 02 and ethyl alcohol
- 02 and acetaldehyde
- C02 and ethyl alcohol
- C02 and acetaldehyde.
Answer: 3. C02 and ethyl alcohol
Best MCQs For NEET Biology
Question 86. In eukaryotes, a net gain of ATP in the complete oxidation of one molecule of glucose is:
- 20 ATP
- 36 ATP
- 38 ATP
- 56 ATP.
Answer: 2. 36 ATP
Question 87. In ETS, which is the cytochrome that reacts with oxygen?
- Cyt a
- Cyt b
- Cyt b6
- Cyt a3
Answer: 4. Cyt a3
Question 88. Instantaneous sources of energy are:
- Starch
- Protein
- Glucose
- Sucrose.
Answer: 3. Glucose
Question 89. R.Q. is less than one in succulent plants because of:
- incomplete reduction
- complete reduction
- incomplete oxidation
- complete oxidation.
Answer: 3. incomplete oxidation
Question 90. Oxidative phosphorylation is the formation of :
- NADPH2 in respiration
- ATP in respiration
- NADPH2 in photosynthesis
- ATP in photosynthesis.
Answer: 2. ATP in respiration
Question 91. In hexose monophosphate shunt the number of C02 molecules evolved is :
- Same as in glycolysis
- Less than glycolysis
- More than glycolysis
- Much less than glycolysis.
Answer: 3. More than glycolysis
Question 92. Which of the following observations most strongly support the view that mitochondria contain electron-transfer enzymes aggregated into compact associations?
- A contractile protein capable of utilizing ATP has been obtained from mitochondria
- Mitochondria have a highly folded inner wall
- Disruption of mitochondria yields membrane fragments which are able to synthesize ATP
- Mitochondria in animal embryos have a tendency to concentrate in cells which become part of locomotory structures.
Answer: 3. Disruption of mitochondria yields membrane fragments which are able to synthesize ATP
Question 93. Maximum energy becomes available per mole of glucose when it is metabolized through :
- Glycolysis in the skeletal muscle of a sprinter
- Fermentation into ethanol by yeast
- Fermentation into methanol by enteric bacteria
- Aerobic respiration.
Answer: 4. Aerobic respiration
