NEET Biology Respiratory System In Animals Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. An increase in the CO2 concentration shifts the shape of the oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve to the light. This phenomenon is known as
- Bohrs effect
- Hamburfurs effect
- Newtons effect
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Bohrs effect
Question 2. What are the respective percentages of O2 in air we inhale and exhale?
- 16.3, 3.00
- 20.94, 16.30
- 20.94,00
- 20.3, 3.00.
Answer: 2. 20.94, 16.30
Question 3. According to modern view, the blood that enters the Kings of Frogs is:
- Oxygenated
- Mixed
- Deoxygenated
- Low in glucose level.
Answer: 2. Mixed
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question and Answers
Question 4. This stage when a lung collapses, especially the alveoli is:
- Atelectasis
- Poliomyelitis
- Asthma
- Cpistasis.
Answer: 1. atelectasis
Question 5. Oxyhaemoglobin is an unstable compound because :
- One haemoglobin molecule binds 4 molecules of oxygen
- Haemoglobin is a complex pigmented protein
- Haemoglobin is contained within RBCs
- Oxygen and haemoglobin are not chemically bound but only physically combined.
Answer: 4. Oxygen and haemoglobin are not chemically bound but only physically combined.
Question 6. Carboxyhaemoglobin is formed due to the combination of haemoglobin with :
- CO
- HCN
- CO,
- CH4
Answer: 1. CO
Respiratory System MCQs For NEET
Question 7. Mouth-to-mouth breathing proves useful in the resuscitation of a drowned person because expired air from the resuscitator:
- does not contain any oxygen
- contain a considerable amount of oxygen
- contain considerable oxygen and CO2, to stimulate breathing
- contain largely N0 and traces of CO2
Answer: 3. contain considerable oxygen and CO2, to stimulate breathing
Question 8. During one circuit of blood from the lungs to the tissue and back through the circulatory system, the percentage of haemoglobin giving up oxygen is:
- 50%
- 25%
- 75%
- 100%.
Answer: 2. 25%
Question 9. Among all the systems of an organism the one which is not concerned with respiration is:
- Nervous
- Digestive
- Excretory
- Endocrine.
Answer: 3. Excretory
Question 10. Which of these does not apply to the air that reaches into the lungs of rabbits, when compared with the air of the atmosphere?
- Its temperature is equal to that of the animal’s body
- It contains no bacteria, virus or spores
- It is quite dry
- It is moist.
Answer: 3. It is quite dry
Question 11. Which Of the following statements is correct?
- Anaerobic respiration yields considerably more energy
- Aerobic respiration yields more energy than anaerobic respiration
- Both release equal amounts of energy
- Anaembie respiration yields slightly more energy than Aembie respiration.
Answer: 2. Aerobic respiration yields more energy than anaerobic respiration
Question 12. Vocal cords are :
- two folds of mucous membrane
- four folds of mucous membrane
- two folds of cartilage
- four layers of cartilage.
Answer: 1. two folds of mucous membrane
Respiratory System MCQs For NEET
Question 13. The carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is almost entirely produced by :
- Forest Ore
- Respiration by plants and animals
- Microbial activity
- Furnaces of industries.
Answer: 2. respiration by plants and animals
Question 14. What structures are responsible for raising of throat in frogs?
- Hyoglossal muscles
- Stemohyal muscles
- Petrohyal muscles
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Petrohyal muscles
Question 15. During hibernation frog respires by :
- Lungs
- Lining of buccal epithelium
- Skin
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. skin
Question 16. Respiratory organs should be :
- thin-walled
- thick-walled
- non-vascular
- covered by scales.
Answer: 1. thin-walled
Question 17. In addition to other gases and water vapours, expired air contains:
- Cl2
- SO2
- CO2
- O2.
Answer: 3.CO2
Respiratory System MCQs For NEET
Question 18. During external respiration, oxygen is first accepted by :
- lungs
- alveolar capillaries
- W.B.C.s
- R.B.C.s.
Answer: 4. R.B.C.s
Question 19. In humans, the bulk of C09 released in tissue respiration is transported by blood as:
- carbonic acid in plasma
- sodium bicarbonate in erythrocytes
- carbamino haemoglobin in erythrocytes
- ammonium bicarbonates in erythrocytes.
Answer: 2. sodium bicarbonate in erythrocytes
Question 20. The rate of respiration increases due to :
- exercise
- rest
- sleep
- None of these.
Answer: 1. exercise
Question 21. Gas used up during respiration is:
- CO2
- O2
- N2
- Ozone.
Answer: 2. O2
Question 22. The index of pulmonary function is the :
- air left in the lung after a maximum forced exhalation
- the greatest amount of air that can expire after a maximal inspiratory effort inspiration
- amount of air that moves out with normal inspiration.
- amount of air present in the lung at a time.
Answer: 2. the greatest amount of air that can expire after a maximal inspiratory effort inspiration
Respiratory System MCQs For NEET
Question 23. Epiglottis guards the opening of the :
- pharynx
- larynx
- gullet
- trachea.
Answer: 2. larynx
Question 24. The exchange of gases between the alveolar air and alveolar capillaries takes place by :
- Exosmosis
- Diffusion
- Active transport
- Endosmosis.
Answer: 2. Diffusion
NEET Respiratory System Question 25. Haemoglobin has an affinity for :
- CO2
- O2
- N2
- None of these.
Answer: 2. O2
Question 26. Pneumonia is a disease of:
- Alimentary canal
- Heart
- Brain
- Respiratory tract.
Answer: 4. Respiratory tract
Question 27. Trachea is supported by :
- Bone
- Cartilage
- Cardiac muscles
- None of these.
Answer: 2. Cartilage
Question 28. With the increase in temperature, the respiratory rate will:
- increase
- decrease rapidly
- remain unaffected
- decrease slowly.
Answer: 1. increase
Respiratory System MCQs For NEET
Question 29. The end product of anaerobic respiration is :
- C09 and H20
- Fumaric acid
- Arctic acid
- Acetic acid.
Answer: 3. Lactic acid
Question 30. The gas exchange surface for most large aquatic animals are:
- trachea
- gills
- book lungs
- malpighian tubules.
Answer: 2. gills
NEET Important Questions On Respiration
Question 31. An advantage of gas exchange in aquatic habitats as compared with terrestrial habitats, is that it is easier to keep gas exchange surfaces:
- wet
- ventilated
- free of injury
- saturated with oxygen.
Answer: 1. wet
Question 32. A disadvantage of gas exchange in aquatic habitats, as compared with terrestrial habitats, is that:
- gas exchange surface tends to collapse
- oxygen concentration in water is much lower than in air
- CO2 concentration is much lower in water than in air
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. oxygen concentration in water is much lower than in air
Question 33. An animal has some way of moving air or water across its gas exchange surface, a process known as:
- counter-current exchange
- ventilation
- facilitated diffusion
- active transport.
Answer: 2. ventilation
Question 34. A frog cannot live long unless it resorts to :
- cutaneous respiration
- pulmonary respiration
- buccal respiration
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. cutaneous respiration
NEET Important Questions On Respiration
Question 35. Frogs while completely submerged in water respires through :
- Skin
- Skin and lining of the buccal cavity
- Lung
- skin, the lining of the buccal cavity and the lung.
Answer: 2. skin and lining of the buccal cavity
Question 36. The expiration in human lungs is due to :
- Contraction of lung
- Lowering of hyoid cartilage
- Ribs and their intercostal muscles
- Contraction of the lung and raising of hyoid cartilage.
Answer: 3. ribs and their intercostal muscles
Question 37. The percentage composition of carbon dioxide in the expired air is about:
- Two
- Four
- One
- Seven.
Answer: 2. Four
Question 38. The percentage composition of oxygen in the expired air is about:
- twenty
- ten
- sixteen
- eight.
Answer: 3. sixteen
Question 39. The volume of air that can be expired after a maximal inspiratory effort is :
- residual volume
- expiratory reserve volume
- inspiratory reserve volume
- lung volume.
Answer: 2. expiratory reserve volume
Question 40. The meeting point of all metabolic pathways is :
- lactic acid
- citric acid
- ornithine cycle
- acetyl Co-A.
Answer: 4. acetyl co-A
Question 41. The major fraction of CO2 produced and released during cell respiration is transported to the respiratory site in frogs:
- as carbonic acid
- as free CO2
- in combination with Hb
- in the form of bicarbonate ions.
Answer: 4. in the form of bicarbonate ions
Types Of Respiration In Animals MCQs
Question 42. Both hyperventilation and holding of one’s breath can cause loss of consciousness. Under normal circumstances, why does this happen?
- Alteration of carbon dioxide levels in the blood
- Alteration of oxygen levels in the blood
- Loss of haemoglobin from red blood cells
- Excess dissociation of oxygen from haemoglobin.
Answer: 1. Alteration of carbon dioxide levels in the blood
Question 43. The main difference between the insect tracheal system and most other types of respiratory system is :
- the tracheal system does not rely on the blood to transport oxygen to the tissues
- insects do not ventilate their tracheal system
- insects do not dispose of CO2via a tracheal system
- insects exchange both CO2 and O2 via their tracheal system.
Answer: 1. The tracheal system does not rely on the blood to transport oxygen to the tissues
Respiratory system NEET Biology Question 44. The membrane-bound enzyme involved in Krebs’ cycle is:
- malate dehydrogenase
- fumarase
- cis-aconitase
- succinic dehydrogenase.
Answer: 4. succinic dehydrogenase
Question 45. The blood leaving dead lungs leaves all its haemoglobin present in the oxygenated form and gives up oxygen to the tissues Ixvause :
- the tissue can absorb O2 from oxyhaemoglobin
- the reduction reaction of oxyhaemoglobin
- O2 conc. in the tissue is lower, CO2 conc. higher than in the lungs
- O2 conc. in the tissue is higher, CO2 conc. lower than in the lungs
Answer: 3. O2 conc. in the tissue is lower, CO2 conc. higher than in the lungs
Question 46. Breathing rate in human beings is :
- 16 times per minute
- 25 times per minute
- 72 times per minute
- 5 times per minute.
Answer: 1. 16 times per minute
Question 47. When the exchange of gases occurs between blood and tissue fluid, it is called :
- external respiration
- internal or tissue respiration
- cellular respiration
- All the above.
Answer: 2. internal or tissue respiration
Question 48. Blood has no role in the transport of oxygen in :
- lungfish
- molluscs
- insects
- leech.
Answer: 3. insects
Question 49. The surface area of human beings is made much larger by alveoli and is approximately the size of a :
- dinner plate
- drawing room
- tennis court
- four-person tent.
Answer: 3. tennis court
Question 50. Higher energy compounds are :
- which links the exergonic to the endergonic process
- produced in respiration
- produced when ATP loses two of its phosphate groups
- the oxidation of which releases large amounts of energy during respiration.
Answer: 4. the oxidation of which releases large amounts of energy during respiration
Types Of Respiration In Animals MCQs
Question 51. Chloride shift is essential for the transport of:
- CO2 and O2
- N2
- CO2
- O2
Answer: 3. CO2
Question 52. In the liver, the amino acids are oxidised resulting in the removal of amino groups from amino acids and the formation of ammonia and a keto acid. It is termed as :
- transamination
- ketosis
- deamination
- ketogenesis.
Answer: 3. ketogenesis
Respiratory system NEET Biology Question 53. The excess amino acids and fats are converted into carbohydrates in the liver. The process is known as :
- glycolysis
- glycogenosis
- gluconeogenesis
- glugogenesis.
Answer: 3. gluconeogenesis
Question 54. All land vertebrates essentially have :
- pharynx
- larynx
- gills
- lungs.
Answer: 4. lungs
Question 55. The lung is lined by :
- dry epithelium
- moist epithelium
- squamous epithelium
- endothelium.
Answer: 2. moist epithelium
Question 56. Under glycolysis, the pyruvic acid is reduced to lactic acid anaerobically in :
- liver
- muscles
- brain
- skin.
Answer: 2. muscles
Types Of Respiration In Animals MCQs
Question 57. On oxidation one of the billowing yields more water:
- sugar
- starch
- proteins
- Fats.
Answer: 1. sugar
Question 58. We get a major supply of energy from glucose via :
- fat metabolism
- Krebs’ cycle
- lactic acid
- pyruvic acid.
Answer: 2. Krebs’ cycle
Question 59. Real respiration involving energy release is:
- expiration
- breathing
- cell respiration
- inspiration.
Answer: 3. cell respiration
Question 60. The lungs of a frog are :
- thin-walled, inelastic and solid bags
- thick-walled, elastic and hollow bags
- thin-walled, elastic, hollow bags
- thick-walled, hollow and spongy.
Answer: 3. thin-walled, elastic, hollow bag
Question 61. Approximately, how many alveoli are present in each human lung?
- 100 million
- 150 million
- 200 million
- 300 million.
Answer: 2. 150 million
Question 62. Each lung is enclosed in a two-layered pleural membrane. The outer layer of the pleural membrane remains attached to:
- trachea
- wall of the thoracic cavity
- diaphragm
- ribs.
Answer: 2. wall of the thoracic cavity
Question 63. Alveolar ducts which lead to alveoli are formed by the subdivision of:
- bronchi
- tracheoles
- bronchioles
- terminal bronchioles.
Answer: 4. terminal bronchioles
Human vs Animal Respiration NEET MCQs
Question 64. Which of the following is a step of the mechanism of respiration?
- Pulmonary ventilation
- Exchange of gases
- Transport of gases
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 65. The downward and upward movement of the diaphragm :
- lengthens and shortens the chest cavity
- only increases the chest cavity
- decreases the chest cavity
- No effect on the size of the chest cavity.
Answer: 1. lengthens and shortens the chest cavity
Question 66. During pulmonary ventilation, the diameter of the chest cavity is decreased by :
- elevation of ribs
- depression of ribs
- diaphragm becoming flat
- abdominal viscera moves down.
Answer: 2. depression of ribs
Question 67. Tidal volume and IRV are collectively termed :
- functional residual capacity
- pulmonary inspiratory capacity
- vital capacity
- ERV.
Answer: 2. pulmonary inspiratory capacity
Question 68. At a particular pressure, the diffusion of CO-, is how much faster as compared to diffusion of oxygen?
- 10 times
- 20 times
- 30 times
- Equal.
Answer: 2. 20 times
Question 69. During strenuous exercise, the Po, in the tissue falls, as a result of which, the blood at tissue level has merely 4.4 ml of oxygen/100 ml of blood. Thus how much oxygen is transported by the haemoglobin of blood during exercise?
- 15 ml
- 20 ml
- 30 ml
- 35 ml.
Answer: 1. 15 ml
Human vs Animal Respiration NEET MCQs
Question 70. What is the capacity of 1 gm of haemoglobin to combine with oxygen?
- 34 ml
- 1.34 ml
- 2.34 ml
- 3.12 ml.
Answer: 2. 1.34 ml
Question 71. Which one is correct?
- Respiratory centres are not affected by CO2 conc.
- During inspiration, the lungs act as a suction jump
- There are 103 alveoli in human lungs
- The vital capacity of a healthy person is 800 cc.
Answer: 2. During inspiration lungs act as a suction jump
Question 72. Which of the following represents the correct oxygen haemoglobin dissociation curve :
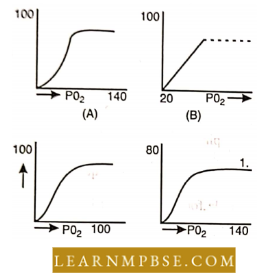
Answer: 3.
NEET Respiratory System Question 73. Which of the following is an occupational lung disease?
- Silicosis
- Asbestosis
- Minamata
- Both 1 and 2.
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2
Question 74. If O2 concentration in tissues were almost as high as at the respiratory surface :
- oxyhaemoglobin would dissociate to supply O2 to the tissues
- haemoglobin would combine with more O2 at the respiratory surface
- Oxyhaemoglobin would not dissociate to supply O2 to the tissues
- CO2 will interfere with O2 transport
Answer: 3. Oxyhaemoglobin would not dissociate to supply O2 to the tissues
Question 75. Match the structure listed under Column – 1 with the functional names given under Column – 2; choose the answer which gives the correct combination of the alphabets of the two columns
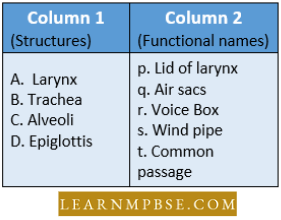
- A = r, B = t, C = q, D = s
- A = r, B = s, C = p, D = c
- A = r, B = s, C = c, D = c
- A = r, B = s, C = q, D = p.
Answer: 4. A = r, B = s, C = q, D = p
Question 76. Respiration is performed by the intestine in :
- Toad Pipa
- Fish, Misgumus
- Tortoise
- Toad Xenopus.
Answer: 2. Fish, Misgumus
Question 77. The structures participating in the air inhalation are :
- diaphragm and internal intercostal
- diaphragm and external intercostal
- abdominal muscles and internal intercostal
- All of the above.
Answer: 2. diaphragm and external intercostal
Question 78. In mammals, most of the CO2 is transported as NaHC03 and KHC03 in the blood. It is between :
- 10-30%
- 50 – 70%
- 80 – 85%
- 90 – 95%
Answer: 3 80 – 85%
