NEET Biology Nervous System
Systems of Coordination.
- Nervous system. Fast, specific with the electrochemical transmission, along nerve fibers
- Endocrine system. Slow, diffused with chemical transmission through body fluids.
- Immune system (antigen-antibody reactions)
- Neurology. Study of morphology, physiology, and pathology of the nervous system.
- Neurophysiology. Physiology or working of the nervous system.
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
Nervous System Notes For Neet
NEET Biology Role Of The Nervous System
- The nervous system illustrates the activities of different organs and the entire organism.
- The nervous system links the various organ systems and coordinates all their activities.
- It ensures the integrity of the organism.
- The unity of an organism and its internal environment is affected and maintained through the nervous system.
- Man’s brain is the material basis of thinking, memory, and good speech.
- It stimulates or inhibits the activities of muscles and glands to evoke a response to the received information.
- Special senses such as vision, hearing, smell, taste, and touch produced by information provided by sense organs are associated with the nervous system.
NEET Biology Nervous System Neuron
- The fundamental components of nervous tissue are neurons, which originate from the ectoderm. Each neuron comprises a cell body, or cyton, containing a nucleus and many nerve fibers, classified into two categories.
- An axon is an efferent process as it transmits impulses outward. The terminal branches of the axon, known as telocentric, possess end knobs that release neurotransmitters facilitating impulse conduction.
- The branching processes of dendrites are afferent as they receive impulses for the neuron.
- Nerve impulses are transmitted from the axon terminals of one neuron to the dendrites of another. The convergence of the two is referred to as a synapse.
NEET Biology Constituents Of the Nervous System
- A central nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. It contains nerve centers for all sensations. The brain and spinal cord are covered by protective membranes called meninges and their cavities are filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
- The peripheral nervous system consists of various nerves which conduct impulses to all parts (Spinal and Cranial nerves).
- The autonomic nervous system illustrates the working of viscera composed of sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
- The central nervous system is made of nerve bodies forming the grey matter and of nerve fiber tracts which form the white matter.
- The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves made of nerve fibers and nerve cell bodies located in the brain, spinal cord, and ganglia.
- The autonomic nervous system consists of nerve cell bodies, their nerve fiber, and nerve plexies. However, all three divisions of the nervous system are connected intimately both structurally and functionally.
Structure And Function Of Neurons NEET
Brain. The brain reaches its highest development in mammals with better intFor exploration and mastery over the environment. The cerebral hemisphere reaches the status of a dominant inter-example rating part of the brain and acts as a coordinating center of the brain.
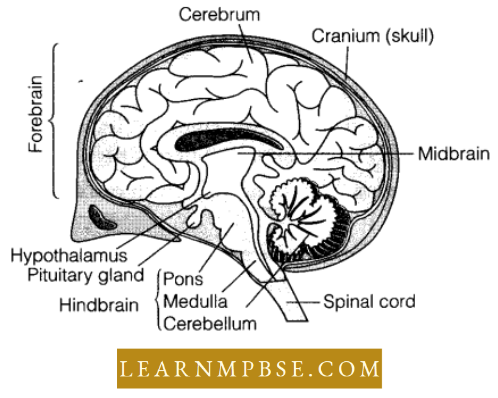
- The cerebral hemispheres are immense projecting forwards above the olfactory lobes and backward above the diencephalon and mid-brain. The two hemispheres are separated by it deep median fissure.
- Each hemisphere is further divided In an oblique Sylvimi (IsMire into an anterior frontal lobe and a posterior lateral temporal lobe
- The cerebrum or cerebral hemispheres have a thick roof called a ‘neopallium’ in mammals, it is formed by upgrowth of the lateral portions of the pallium, but it differs histologically from the pallium in having a larger number of neurons which are arranged in layers of the cortex and medulla.
- The cortex is further increased by many curved depressions or sulci and lobes or ‘gyri’ (absent in rabbits). Each hemisphere has a complex lateral ventricle, each ventricle has a middle body from which three prolongations come run forward, backward, and outward.
- Above the lateral ventricles is a band of nerve fibers called corpus callosum which joins the neopallium or cortex of the two cerebral hemispheres, the anterior part of the corpus callosum is bent to form ‘menu while the posterior part is bent downwards and forwards forming splenium.
- Below the corpus callosum is a band of longitudinal fibers forming the ‘fornix’. Its main body is formed by the union of two sets of fibers called fimbriae or taeniae hippocampi. Between the corpus callosum and fornix is a septum peculium having a small cavity called pseudocoel or 5th ventricle, which is not a true ventricle but a space between the two hemispheres.
- The floor of the hemispheres forms anterior corpora striata and postero-lateral hippocampus which serves as an olfactory center, the median commissure of it is called psalterium or lyra, and that of corpora striata is the anterior commissure.
- Running from the anterior commissure to the optic chiasma is a delicate membrane of the lamina terminals which marks the anterior boundary of the 3rd ventricle.
- The cerebral hemispheres receive impulses from visual, auditory, olfactory, tactile, and peripheral receptors and they initiate voluntary motor impulses which are carried by bundles of nerve fibers to muscles. The cortex For exampleates the impulses and organizes and for example, rates them into coordinated activities.
- The diencephalon is small and hidden dorsally by the hemispheres, it has a laterally compressed third ventricle or diaconal whose roof is formed by a delicate velum interpositum.
- The side walls of the diencephalon or optic thalami are made of a thick mass of white and grey matter on the external surface of each thalamus near the anterior end is a rounded corpus geniculatum. The floor of the diencephalon is called the hypothalamus.
- Recently a potent substance called hypothalamic D has been extracted from the hypothalamus which stimulates the production of adrenotrophic hormone of the pituitary gland.
- The hypothalamus is composed of four parts optic chiasma, infundibulum and tuber cinereum, pituitary gland, and corpus albicans.
- The diencephalon is a relay center of impulses from the posterior For example going to the cerebral cortex, the thalami are the centers of exploration and activity and for recognition of sensations of heat, cold, pain, and body movements.
- Mid brain has two pairs of optic lobes called corpora quadri gemina. The floor of the mid brain is called crura cerebral which contains bundles of fibers. The canal which connects the 3rd ventricle with the 4th ventricle is called iter. Vision is controlled by the cerebrum and anterior parts of the anterior optic lobes.
- The posterior optic lobes are auditory in function. The highly developed cerebellum is divided to form five lobes, central lobe vermis, two lateral lobes, and two outer floccular lobes.
- In section, the cerebellum shows an outer thick layer of grey matter and a central mass of white matter, the two exhibit a tree-like pattern called arbor vitae.
- The cerebellum is concerned with equilibrium and co-ordination of muscles and responses initiated by the cerebral hemispheres and carried out through the cerebellum Medulla oblongata lias a posterior choroid plexus below which is the fourth ventricle joined in front to the iter and behind to the central canal.
- The medulla controls respiration, heartbeat, and blood vessels, it also has conduction pathways for impulses passing from cerebral hemispheres to the spinal cord and again in the opposite direction.
Neet Biology Nervous System Notes Pdf
NEET Biology Nervous System Spinal Cord
- It is a cylindrical, cord-like, homogeneous extension of the medulla oblongata, measuring 42 to 45 cm in length and 2 cm in thickness in humans, extending from the neck to the lumbar region.
- For instance, it traverses the neural canal of the spinal column and culminates in a slender extension known as the filum terminale. Growth ceases around 4 to 5 years of age.
- In this structure, the white matter is located externally, while the H-shaped grey matter is situated internally, which is the inverse of the brain’s configuration.
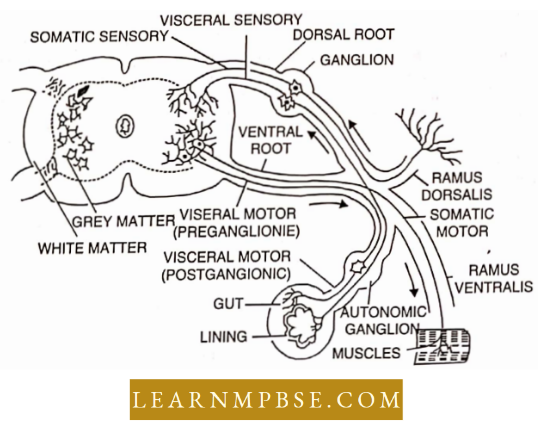
NEET Biology Nervous System Peripheral
- Cranial nerves. The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves connected to or arising from the central nervous system, it has cranial and spinal nerves. Twelve cranial nerve 1 – Olfactory (sensory). 11-Optic (sensory), lH-Oculomotor (motor), IV-Trochlear (motor), V-Trigeminal (mixed ), Vl-Abducens (motor), Vll-Facial (mixed), VIII-Auditory (sensory), IX- Glossopharyngeal (mixed), X-Vagus (mixed), Xl-Spinal accessory and XII-Hypoglossal (motor).
- Sensory Cranial Nerves. Olfactory, Optic, and Auditory.
- Motor Cranial Nerves. Oculomotor, Pathetic/Trochlear, Abducens, Accessory Spinal and Hypoglossal.
- Mixed Cranial Nerves. Trigeminal, facial, Glossopharyngeal and Vagus,
- Dentist’s nerves. Trigeminal (Vth nerve) [Has a swelling called gasserian ganglion from where it divides into 3 branches]
- Number of Cranial Nerves. 10 pairs in amniotes (fishes and amphibians) and 12 pairs in amniotes (reptiles, birds, and mammals).
- The facial nerve in frogs passes through the Gasserian ganglion but in mammals, it passes out through the Geniculate ganglion.
- Glossopharyngeal and Vagus nerves in frogs pass out through the jugular ganglion but in mammals, they pass through the vagus ganglion. All are situated within the cranium.
- The motor component of the vagus nerve controls sound production.
NEET Biology Nervous System Spinal Nerves
- They originate from the spinal cord. Humans possess 31 pairs of spinal nerves.
- Each spinal nerve comprises two roots: sensory (afferent) and motor (efferent) roots.
- All spinal nerves possess a mixed composition. Each spinal neuron is partitioned into three rami.
- The filum terminale and several posterior spinal nerves create a horse-tail-like structure known as the cauda equina within the neural canal.