NEET Biology Evolution Of Man
Male Primula is positioned to inquire about his origin.
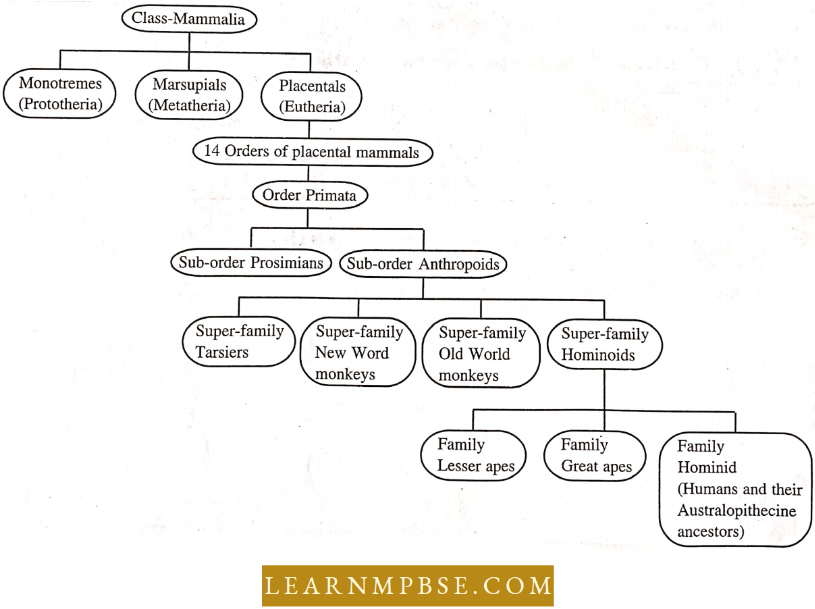
- Male Is classified within the order Primates alongside monkeys and apes.
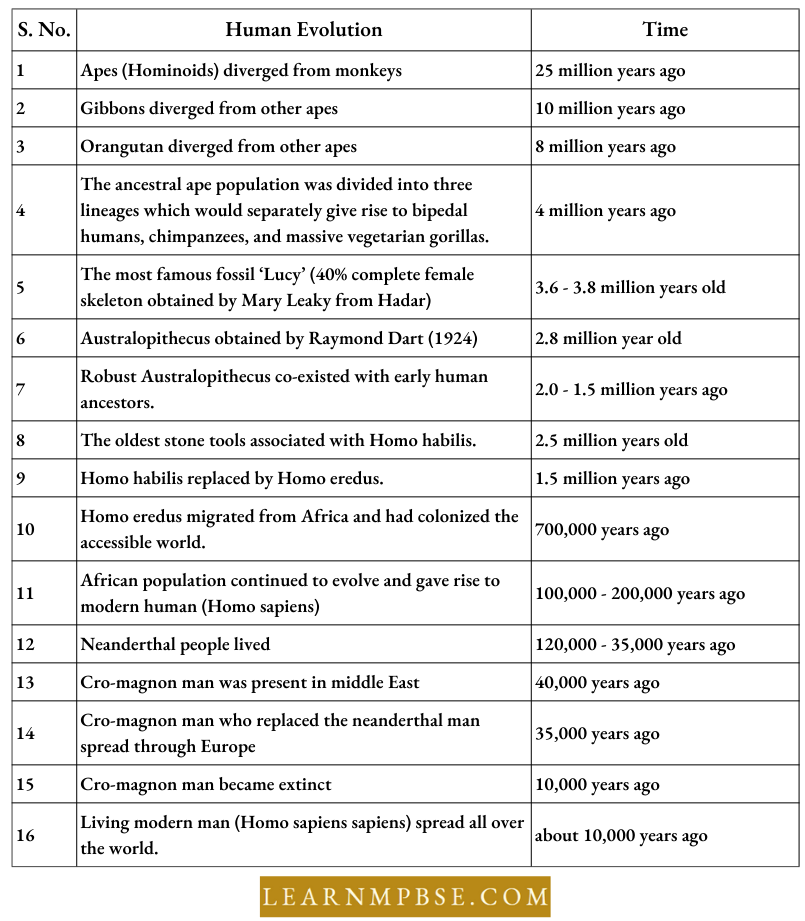
- The ancestors of humans and other comparable species developed approximately 24 million years ago.
NEET Biology Evolution Of Man Relationship Of Man With Other Primates
The older primate includes three sub-orders. Leinuroidac, Tarsioidac, and Anthropoidae. The Leminoidne and Tarsioidac are collectively called prosimians and Anthropoidae are called simians.
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
- The first mammal was 210 million years old, the first primate 80 million years, the first anthropoid apes 36 million years, and the first hominids 24 million years ago.
- The three families of modern hominids are the Hominidae (the family of man), llylobatidae (Gibbous), and the Pongidne (chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans).
- The unique features of the man are erect posture, shorter arms, and a large brain, and can fabricate special tools, use spoken language, and practice prolonged parental care.
- The evolutionary history of man has been built up from the study of fossils and molecular homology.
- Human evolution took place in Africa and Asia.
- A common ancestry for great apes and man has been deduced from similarities in DNA contents, chromosome number, and banding pattern.
NEET Biology Human Evolution Notes
NEET Biology Evolution Of Man Human Evolution
The evolution of man is associated with intelligence and bipedal locomotion
- TA. Huxley (1863)– Book ‘Man’s Place in Nature’ Charle’s Darwin (1971) – ‘Descent of Man’.
- Darwin suggested Man, Apes, and monkeys had a common ancestor.
- Mammals evolved in the early Jurassic period about 210 million years ago from Cynodont Reptiles.
Cotylosaurs → Cynodont → Mammals (Stem reptiles) (reptiles)
Early History
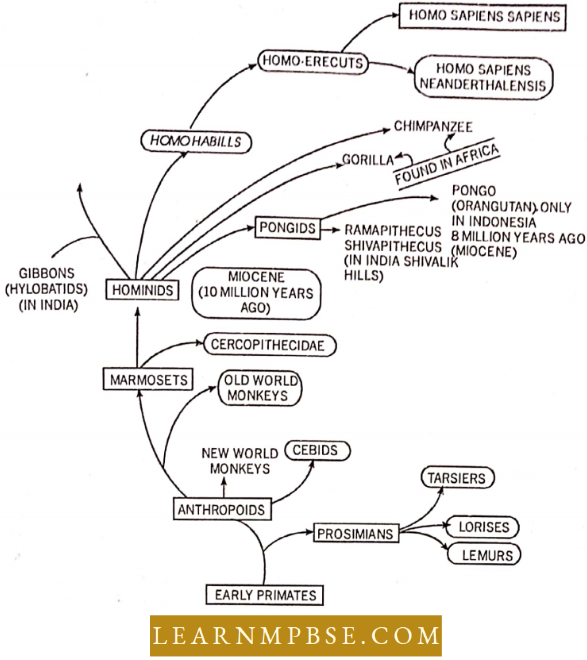
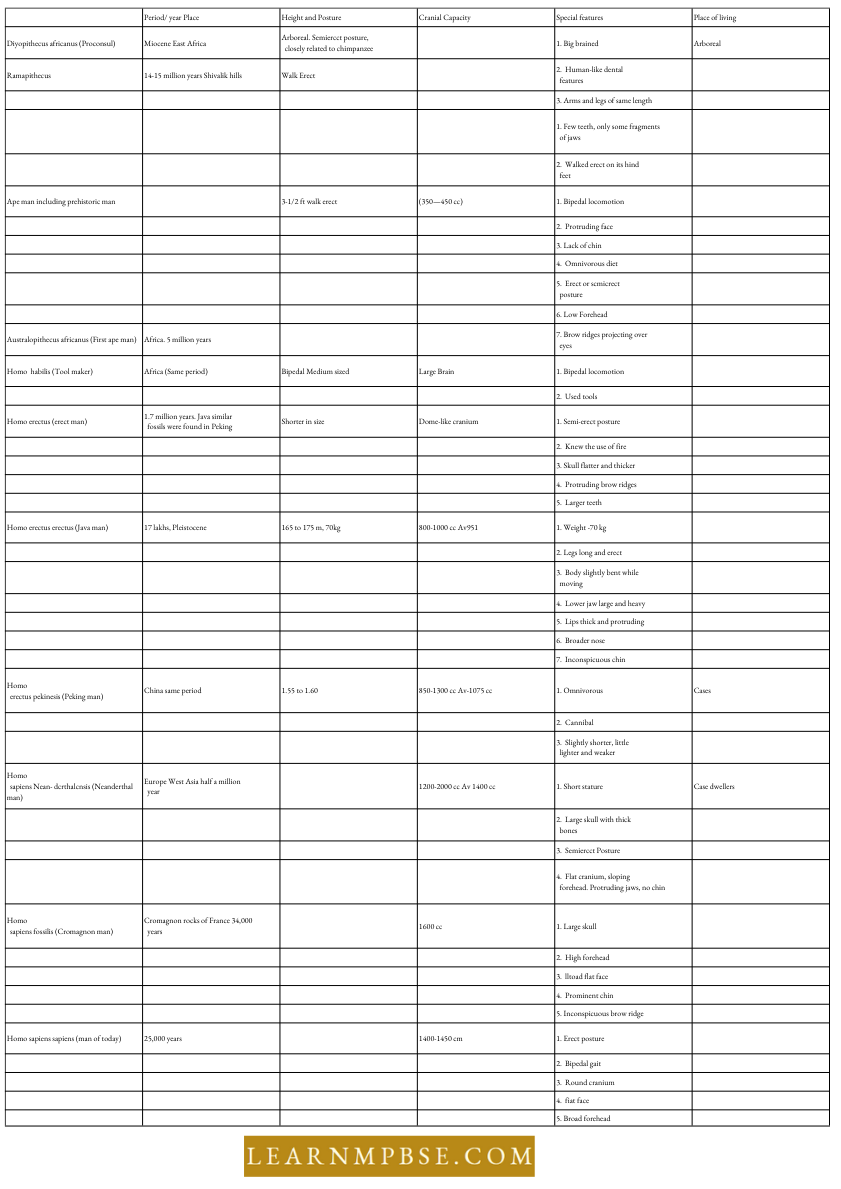
- Dryopithecus (Proconsul, 18-24 million years)—Common ancestor of humans and apes that lived in Asia as well as Africa. Common species D. africanus. Semi-erect, with hind limbs and forelimbs of the same size.
- Ramapithecus (Kenyapithecus, 8-15 million years)—It was the earliest man like Primate which probably walked on its legs and possessed dentition similar to humans.
- Australopithecus (Southern ape, First ape-man, 2-5 million years)—A. africanus was lightly built and omnivorous while weight was 20-30 kg.
- A. robustus was heavily built and vegetarian, height-120 cm, Cranial capacity-380-430 cm.
- Face-Prognathous (Projecting Type)—Low forehead, prominent brow ridges, no chin, bipedal locomotion but with bent knees, used crude tools.
- Homo Habilis (2 Million Years)—Bipedal Locomotion with 150 cm height, (40-50 kg) Cranial capacity 680 cm3, Prominent brow ridges and hominid teeth. He was the first toolmaker. Used chipped stone tools.
- Homo erects (1.7 Million Years, Erect man)—It walked on erect long legs, 150 cm, cranial capacity 775-1225 cm³, prominent brow ridges, no chin, massive jaws, and longer teeth. Semi-erect posture made more elaborate tools, hunted big game birds, used lire, and primitive speech.
- Java man (Homo Crectus Credits)—had a smaller cranial capacity (775-900 cm³)— first used fire for cooking and protection.
- Peking Man (Homo Erectus Pekinesis)—(H. eredus Sinanthropus) had sharp and chisel-shaped tools. Large cranial capacity (915-1225 cm³) Neanderthal Man (Homo sapiens neanderthalcnsis)-30,000-50,000 years ago. 150 cm, Cranial capacity (1300-1600 cm³), sloping forehead, brow ridges, chin, and thick bones of the skull which protruded behind strong shoulders and arms, used tools, and animal hides. Lived in caves and probably built hut-like shelters-had religious feelings and burial customs.
- Cro-Magnon Man (H. sapiens Fossilis) 20,000-50,000 years back, 180 cm, Cranial capacity-1600 cm³, Broad forehead but arched, brow ridges moderate, strong jaws with man-like dentition, and a well-developed chin. The face was perfectly orthognathous with an arrow and elevated nose. Cave dwellers, the hunter with the domesticated dog, used stone spears and arrowheads, paintings, etc.
- Modern Man (H. sapiens Sapiens): evolved about 25,000 years ago and spread only about 10,000-11,000 years ago. Cranial capacity- (1400-1450 cm³). Four flexes in the vertebral column, a slight raising of the skull cap.
Time Scale Related To Human Evolution
NEET Biology Evolution Of Man Evolutionary Changes During Human Evolution
- Skull And Brain. Increase in size, complexity, and intelligence.
- Bipedal Locomotion. Due to bipedal locomotion forelimbs became free.
- Forelimbs. Modified into organs of manipulation and lengthening of hindlimbs and shortening of forelimbs.
- Thumb. Perfection of thumb opposability in forelimbs.
- Toe. Loss of opposability of great toe in hind limbs.
- Upright posture. Erect posture by the development of lumbar curve.
- Jaw. Jaw power reduced.
- Teeth. Due to omnivorous feed habits, the size of incisors and canines is reduced.
- Chin. Development of chin.
- Pelvic Girdle. Development and broadening of iliac bones of the pelvic girdle.
- Social organization and cultural evolution.
NEET Biology Important Notes PDF
Evolution Of Man
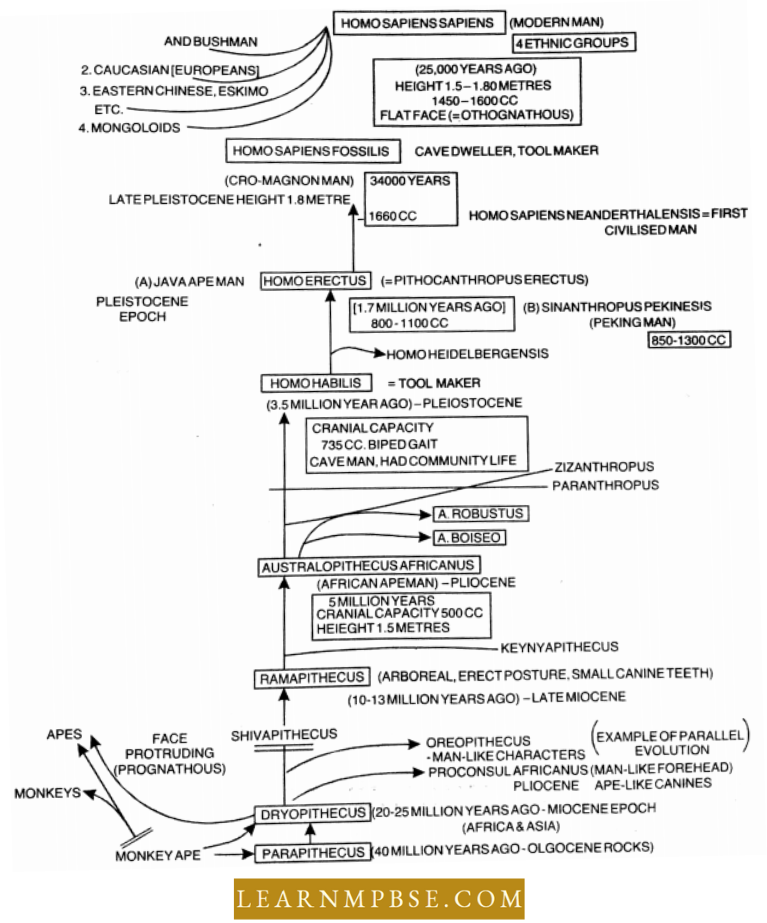
Early Human Evolution
NEET Biology Evolution Of Man Synopsis
Evolutionary History Of Man
- The evolution of hominids occurred in Africa and Asia.
- The evolution of man took place in Africa.
- Dnvpiihecus and Ramapithccus lived about 15 million years ago; they were hairy and walked like apes.
- 3-4 million years before man-like primates walked in Eastern Africa; they were about 4 feet tall and walked upright.
- Rcmuipithecus and Sivapithecus lived in Africa and Asia and were the forerunners of hominids.
- Genus Australopithecus appeared in Africa about 5 million years ago.
- The genus Homo appeared about 2 million years ago.
- Homo habilis lived in Africa about 2 million years ago and was characterized by a larger brain; could use tools.
- Homo credits appeared about 1.7 million years ago and believed to have migrated to Asia and Europe.
- As a result of the abrupt transition that occurred in Europe about 84000 years ago, Neanderthal man was wiped out and gave way to more efficient Cro-Magnon.
- Homo sapiens evolved about 10000 years ago.
- Leaky (1930) excavated the first fossil ape Proconsul from early Miocene rocks around Lake Victoria of Kenya. It had 5 cusped molars.
- Leaky (1959) excavated fossils of Zijanthropus (15.5 lakhs year old rocks).
- Leaky (1960) excavated fossils of Homo habilis. (16 to 18 lakhs yrs old).
- Dryopithecus. This fossil ape is known from middle Miocene or early Pliocene rocks
- Sivapithecus was excavated from the middle and late Pliocene rocks of the Shivalik hills of India.
- Fossils Of Ramapithecus And Kenyapithccus were excavated by Lewis (1930) and Leaky (1955) from about 1.2 to 1.4 crore-year-old rocks from Kenya, China, and India.
- Raymond Dart 1924 excavated a fossil baby skull (Tuang baby) from the Pliocene rocks of Australopithecus near Tuang in Africa.
- Robert Brown (1936 onward) excavated fossils of Paranthropus (10-18 yrs old, Pleistocene rocks of Africa).
The most primitive and earliest ape during the Oligocene is called Parapithccus.
- Linnaeus was the first scientist who placed human beings along with monkeys and apes.
- The skull of Pithecanthropus was found in Java.
- Geological evidence for the most primitive numerals found in C. Africa.
- Apes are characterized by the absence of a tail.
- The most primitive ape is Gibbon while the most advanced is Gorilla.
- Old-world Monkeys (Ceboids). Long prehensile (grasping) tails and flat noses, ground dwellers example, Baboons, Rhesus monkeys
New World Monkeys (Ccrcopithecoids) have No such tails but have protruding noses example, spider monkeys, organ grinder’s monkeys (capuchin)
- The first evidence of Australopithecus was the skull of a child discovered by Raymond Dart. Later in 1974 a complete skeleton named Lucy was found by Donald Johanson and Timothy white
- Mitochondrial Eve—A member of archaic Homo sapiens
- The Efe pygmies of Zaicr’s Itwi Forest are among the world’s shortest people, with males reaching an average of 4. 8″ (1,42m) and females reaching 4′ 5″ (1.35 m)
- Piltdown man. It is hypothetical and developed on the basis of artifacts consisting of fragments of skull at Piltdown England
Theories of Human Evolution NEET
Cultural Evolution Is Divided Into Three Phases:
Paleolithic Era. The evolution of knowledge regarding rudimentary hunting implements and primitive language: the human species was Homo habilis.
- Mesolithic Period. Development of intricately designed implements for collective hunting, pyrotechnology, animal skin processing, lithic artistry, and ivory craftsmanship.
- The primary human kinds were Neanderthals and Cro-Magnons.
- Neolithic Period. Progressive development of agriculture, animal domestication, matrimonial practices, education, science, and technology.
- The Indian subcontinent and the Middle East are the initial locations of agriculture. This phase encompassed Homo sapiens.
Percents Of Bands Common Among Humans
- Chimpanzees: 99 %
- Gorillas: 99%
- Orangutans: 99%
- African Green Monkeys: 95%
- Domestic Cats: 35%
- Mice: 7%
Cranial Capacities
- Chimpanzee (Ape): 400 cc
- Gorilla (Gorilla): 650 cc
- Australopithecus: 300-500 cc
- Java ape Man (Pithecanthropus): 800-1000 cc
- Peking Man (Sinanthropus): 1075 cc
- Neanderthal Man: 1400 cc
- Rhodesian Man: 1280 cc
- Cromagnon Man: 1600 cc
- Modern Man (Homo sapiens): 1900-1450 cc
