NEET Biology Agricultural Chemical Pesticides Plant Pests
Agricultural:
Agricultural chemicals, including fertilizers, plant growth regulators, and insecticides, are employed to enhance the production potential of crops.
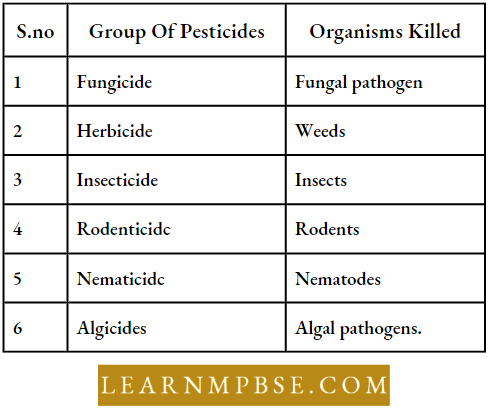
Fertilizers restore soil nutrients, growth regulators facilitate plant development, and insecticides safeguard plants against diseases and pests. c Pesticides encompass fungicides, herbicides, rodenticides, insecticides, nematicides, and algicides.
Major Groups Of Pesticides
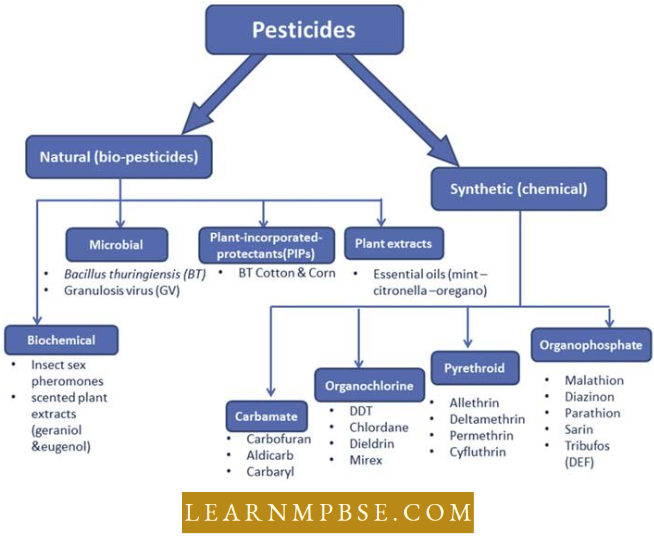
Agricultural Chemical Pesticides NEET Notes
As regards the mode of action pesticides attack the nervous systems and respiratory systems and herbicides damage the photosystem 2 of photosynthesis and translocation. Pesticides are capable of damaging the ecosystem and in the long run render agriculture non-sustainable.
- All pesticides are poisons. They upset the food web in nature.
- Some resistant pests survive even after pesticide application, thus higher doses are required to kill them.
- The major problem with the application of pesticides is bioconcentration in the bodies of animals.
- Due to the lack of safety measures in the use of pesticides, they pose adverse health effects on people.
- Owing to the lack of stringent measures in the manufacture of pesticides, there may be grave consequences such as the recent Bhopal gas tragedy. (1984)
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a combination of techniques such as biological control, mechanical control and carefully timed application of pesticides along with sound cultural practices,
NEET Biology Agricultural Chemical Pesticides
Pesticides are capable of damaging the ecosystem and in the long run render agriculture non-sustainable.
All pesticides are poisonous; they are not specific to the target organism and they may kill useful organisms. They upset the food web in nature.
Examples of Classes of Pesticides
- Organochlorides – DDT, BHC, Aldrin, Endosulphanc.
- Organophosphate – Maiathion, Parathion and Fenitrothion.
- Carbamates – Carbofuran, Aldicarboropoxus.
- Triazincs – Simazines, Atrazinc
- Pyrethroids – Pyrethrin
Types Of Pesticides NEET
Types Of Pesticides
Various Organic Compounds With Heavy Metals, Commonly Used As Fungicides Are:
- Agrosan GN, Ceresan, and Tillex are compounds of mercury used in seed treatment.
- Dithane M-45 and Dithane Z-79 control the tikka disease of groundnut.
Burgundy Mixture. It is an important copper fungicide. Its nature and function are the same as the Bordeaux mixture.
Biocides The pesticides that affect useful plants and animals including human beings.
Organochlorides are lipophilic in nature; hence, show a great affinity for fatty tissues. These decompose very slowly; therefore, get accumulate in the environment posing serious problems.
- Organophosphates are organic esters of phosphoric acid, thiophosphoric acid and other phosphoric acids. These are sold under the names-organic phosphates, phosphorus insecticides, nerve gas relatives, phosphates, and phosphate insecticides.
- These are the most toxic pesticides to vertebrates e.g., Parathion, Malathion, Fernethion, Trithion, TEPP and Ethion.
- Organophosphates act on the central nervous system, combining with the phosphorus molecule of the enzyme cholinesterase inhibiting its normal functioning. As a result, the breakdown of acetylcholine stops.
- The accumulation of acetylcholine leads to a barrage of extraneous nervous impulses. It causes acute toxicity resulting in convulsions, paralysis and death. The recognition of this property led to the development of nerve gas used in World War 2.
Carbamates are organic esters of hypothetical carbanic acid. Isolan, carbaryl, carbofuran, aldicarb, and propoxur are widely used.
Pyrethroids are synthetic derivatives of pyrethrin—a chemical extracted from an annual plant Chrysanthemum cinerarifolium, C. narshallii, and C. coccinium.
Triazines are a group of herbicides which are derived from urea, for example, Simazines and atrazine.
Effects Of Chemical Pesticides NEET
NEET Biology Agricultural Chemical Pesticides Plant Diseases
When the favourable conditions of life are so seriously affected by any agency that the life of a part of a plant or whole plant is threatened, we call it plant disease. or
Plant disease can be defined as a condition in which the structure and function of a plant are disturbed and threaten the life of a plant.
- A diseased plant can be differentiated from a healthy plant because of a disturbed morphological and physiological state.
- Pathogens are the disease-causing organisms. There are numerous different types of pathogens. They are classified as animate, viral and inanimate pathogens.
- Animate Pathogens. They are generally microbial in nature. Nematodes and insects are the other pathogens of animal origin. The fungus Puccinia graminis tritici causes black rust in wheat. A bacterium Xanthomonas ciiri causes citrus canker. Mites cause Mango malformation.
- Viral Pathogens. Certain viruses act as pathogens. A few viral plant diseases arc mosaic, vein-clearing, chlorosis and leaf curl of potato.
- Inanimate Pathogens. There are certain plant diseases whose causes cannot be attributed to any pathogens. Molybdenum deficiency in the soil causes whip tail of cauliflower. The black tip of mango and scabs are caused by gases released from chimneys and respiratory gaseous products in cold storage respectively.
Chemical Method To Control Plant Diseases
- Bordeaux Mixture. It is a mixture of copper sulphate and lime in the ratio 4:4 dissolved in 50 gallons of water. It was first used in controlling many types of crop diseases by French Prof. Mallardet of the University of Bordeaux in 1878.
- Burgandy Mixture. It is a mixture of copper sulphate 5 lbs, sodium carbonate 0.25 lbs and water 50 lbs
- Ammonical Copper Carbonate (3 oz. copper carbonate, 5 pints ammonia and 50 gallons of water.
- Sulphur Dust. Inorganic dust is one of the oldest and most widely used fungicides. It can be used as a powder or in the wettable form.
- Antibiotics. Several antibiotics are used to control various plant diseases. Penicillin, streptomycin, cycloheximide, griseofulvin, viridin, blasticidin, agrimycin are the most common effective antibiotics.
- Commonly Used Fungicides Are:
- Agrosan GN Ceresan Tillex are compounds of mercury used in seed treatment.
- Dithane M-45, Dithane Z-79 Control tikka disease of groundnut.
- Pyrethroids
Agricultural Chemicals And Their Impact
NEET Biology Agricultural Chemical Pesticides Plant Pests
Pests. Pests are animals or plant organisms which damage cultivated plants or plant products.
Types Of Pests. Pests are of the following types: Arthropods (invertebrates with jointed appendages)
- Insects like grasshoppers, bugs, beetles, weevils, caterpillars and grain moth.
- Non-insect arthropods, like crabs, ticks and mites,
- Molluscs like snails and slugs.
- Birds such as pigeons, parrots, sparrows and crows,
- Mammals like rodents, monkeys and wild elephants.
- Pests Of Maize.
- Maize stems Borer (Chilo-Cornelius).
- Pink Borer (Sesamia inferens).
- Pests Of Millets.
- Deccan wingless grasshopper (Calemania sphenarroides)
- Greasy cutworm (Agrotis physilon).
- Pests Of Sugarcane.
- Top shoot Borer (Scirpophaga nivella)
- Stem Borer (Diatoroea venosata).
- Pests Of Cotton.
- Spotted Bollworm (Earias fabla).
- Pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella.)
Various Stored Grain Pests
- Rice Weevil (Calandra oryzae): A little bug, reddish-brown in color, measures approximately 2.5 mm in length.
- Angoumois Grain Moth (Sitotroga cerealella): It is a 12 mm long, lustrous buff-colored moth with pointed, slender wings featuring broad fringes.
- Puke Beetle (Bruchus sp.)is a 3.00 mm: Long insect characterized by elongated antennae and a chocolate-colored body, which inflicts significant damage to crops and stored grain.
- Lesser Grain Borer (Rhizopertha dominica): The beetle measures approximately 1.5 mm in length, with a coloration ranging from black to brown, and possesses a globular head.
- Red Grain Beetle (Tribolium castaneum): The adult measures 1.5 mm in length and exhibits a reddish-brown hue, but the larva is pale yellow.
- Khapra Beetle (Trogoderma granarium): It is a brown-oval beetle that inflicts damage on wheat, as well as pulses, maize, and cereals. Only grubs inflict the injury.
- Rice moth (Coreyra cephalonica).
Harmful Effects Of Pesticides NEET
List Of Some Of The Insect Pests That Destroy Crops In The Fields
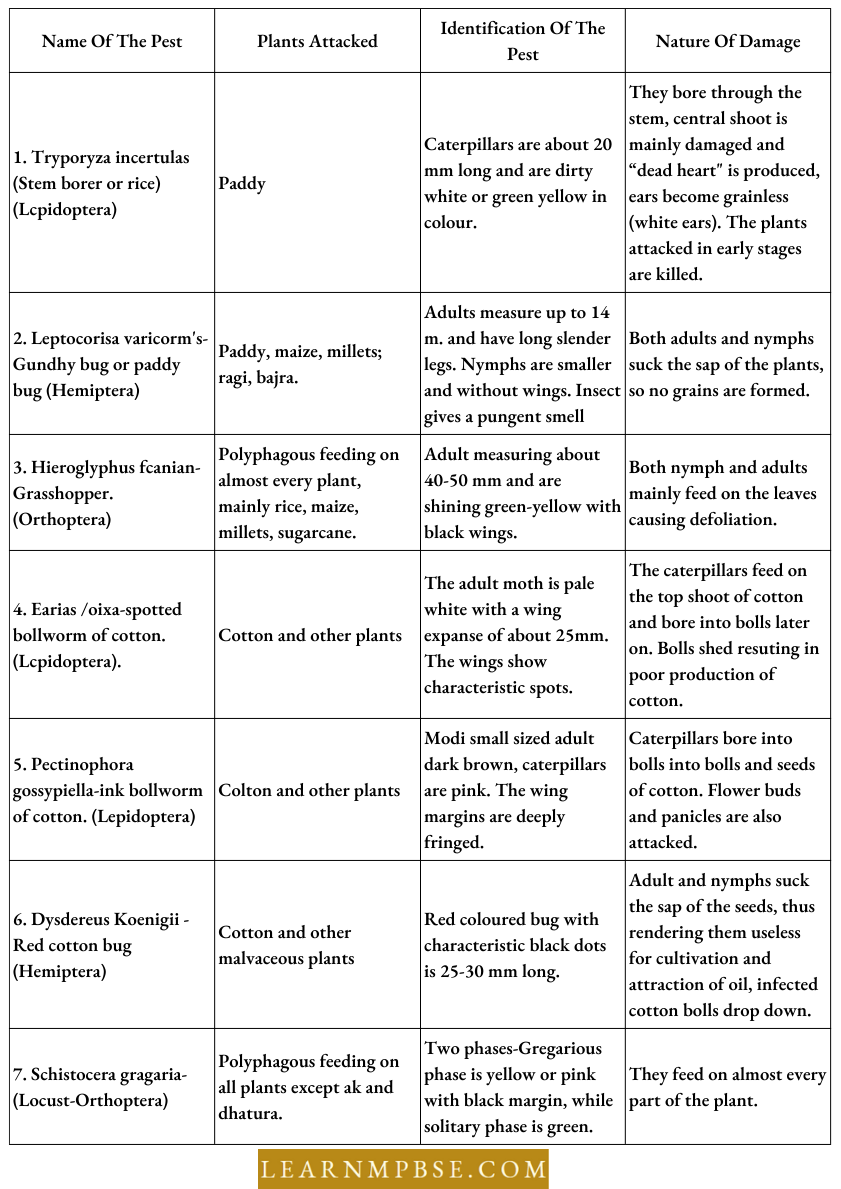
Agricultural Chemical Pesticides Class 12 Notes For NEET
NEET Biology Agricultural Chemical Pesticides Synopsis
Common Examples Of Organochlorides Are:
- BHC
- DDT
- Heptachlor
- DDE
- Chlordane
- Endosulfan
- Aldrin
- Dieldrin
- Endrin.
Carbofuran is sold as furadan, propoxur as Baygon and aldicarb as Temik.
Role Of Pesticides In Agriculture NEET
Pesticide Treadmill Effect:
The usage of pesticides results in farmers allocating a greater amount of their income to these chemicals without achieving higher yields. This has occurred with cotton in India.
- A fish residing in water contaminated with DDT can accumulate a concentration of DDT that is 1,000,000 times greater than that present in the water.
- DDT disrupts the correct production of eggshells in birds, resulting in the destruction of deposited eggs prior to hatching.
- Peregrine falcons, Ospreys, and bald eagles have nearly become extinct due to DDT. Gambusia fish have been employed to manage mosquito populations within Integrated Pest Management (IPM).
- Algicides are insecticides that eliminate algal diseases and blooms, such as Copper Sulphate.
The inaugural commercial bioinsecticide is Sporeine, which was developed in Germany.
Organophosphates are biodegradable.
Dioxan is present as an impurity in 2,4,5 -T It is highly toxic and Carcinogen also causes kidney/ liver disorders.
Bioinsecticides of Plant Origin
- Rotenone from roots of Derris elliptica
- Cinerin and Pyrethrin from Chrysanthamum cinnarifolium
- Thurioside and Sporeine from Bacillus thringenesis
- Azadirachtin from Azadirachta indica
- Squill from Sea Onion
- Nicotine from Nicotiana species.
Phenylcarbamates and thiocarbamates are used as herbicides while Dithiocarbamates are used as fungicides.
