NEET Biology Notes For Reproductive Health
- Health is affected by the Following :
- Genetic disorders.
- Infection.
- Lifestyle including Food and water.
- Physical exercises.
- Genetic disorders: these are inborn errors. these are deficiencies with which a child is born. such as mongolism. genetic disorders also include deficiencies or defects which a child inherits From birth.
- Reproductive health: it means total well-being in all aspects of reproduction i.e. physical, emotional, behavioural and social.
- A society with people having physically and Functionally normal reproductive organs and normal emotional and behavioural interaction among them in all sex-related aspects is called a reproductively healthy society.
- Reproductive and Child Health Care (RCH) programmes are carried out at the National Level to look after these problems.
- Sex education: Sex education is concerned with creating awareness among people about reproductive organs, adolescence and associated changes, safe and hygienic practices, and sexually transmitted diseases including AiDS.
- Significance of Reproductive Health in a Society: A reproductively healthy society’ survives in a normal way. Reproductive health ensures that all individuals in the reproductive age group are Fertile and able to carry on the human race Further.
- Individuals should be educated about reproduction-related aspects like controlled population, absence of sex abuses and sex-related crimes in society and enable people to think and take up necessary steps to build up a reproductively healthy society.
- Aspects of reproductive health need to be given special attention in the present scenario: ConFerring upon the demands of the present situation of our country, the following aspects of reproductive health should be given special attention :
Reproductive Health Neet Important Points
- Control of the human population.
- Creation of awareness about reproduction-related aspects among people including sex education to students.
- implementation of various action plans to attain reproductive health.
- Continued research on reproduction-related areas.
- Measures of birth control.
- Sex education should be encouraged in schools: Sex education should be encouraged in schools to give the right information to young minds to save them From myths and misconceptions about sex-related aspects.
- Proper information about reproductive organs, adolescence and related changes, safe hygienic sexual practices, and sexually transmitted diseases like AiDS would help people to lead a reproductively healthy life
- Thus sex education is necessary to make society reproductively healthy.
- Reproductive health in our country has tremendously improved in the past 50 years and the Following are some areas of improvement.
- Improved Medical Facilities available For the treatment of diseases.
- Rapid decline in death rate.
- Success oF programmes like Family planning and Reproductive and Child Health Care Programmes.
- Increased awareness among people about reproduction-related aspects.
- RCH programmes also include providing medical Facilities and care to persons about problems like menstrual irregularities, pregnancy-related aspects, MtP, StD, birth control and infertility.
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
NEET Biology Reproductive Health Objectives OF RCH
- creating awareness about canon* reproduction-related problems.
- Providing Facilities and support to the building, up a reproductively healthy society.
- Providing audio-usual and print media support to various government and non-government organisations.
- Educating the people and providing the right information to them From myths and mis- mis-misconceptions
- Providing project education regarding reproductive organs, adolescence and related changes, and safe and hygienic sexual practices.
- Providing information regarding the danger of sexually transmitted diseases, AiDS etc.
Various contraceptive options:
Various contraceptive options are available now such as natural/ traditional, barrier, and lUDs. pills, injectables, implants and surgical methods. though there are certain ill-elFects For some of these methods, they are not very significant. they have to be used under strict medical guidance and supervision only.
Different types oF lUDs:
Different types oF lUDs are presently available such as the non-medicated IUDs example. i-pipes loop), copper-releasing lUDs (CUt, CU 7, Multiload 375) and hormone-releasing ones (Progestasert, LNG-20)
Functions:
IUDs increase phagocytosis oF sperms within the uterus and the Cu ions released by some suppress sperm motility and the Fertilising capacity oF sperms. the hormone-releasing iUDs. in addition, make the uterus unsuitable For implantation and the cervix hostile to the sperm.
Advantages:
IUDs are ideal contraceptives For Females who want to delay pregnancy and space children. it is one of the most widely accepted methods of contraception in India.
Oral Contraceptives:
- The oral administration of low dosages of progestagens or progestagen-estrogen combos constitutes an alternative contraceptive strategy utilized by females.
- They are administered in tablet form, commonly referred to as ‘pills.’ Pills must be taken daily for two consecutive days, preferably between the first five days of the menstrual cycle.
- Following a 7-day interval (during which menstruation transpires), the procedure must be resumed in the same sequence until the intended duration of contraception is achieved. They impede ovulation and implantation, as well as modify the quality of cervical mucus to obstruct or delay the entry of sperm.
- Pharmaceuticals demonstrate high efficacy with little adverse effects and are widely accepted by females.
NEET Biology Notes
Advantages of Saheli:
A‘Saheli’, the new oral contraceptive For females contains a non-steroidal preparation called ‘centchroman’. it is a ‘once a week’ pill with very Few side effects and high contraceptive value.
Medical termination of Pregnancy:
- Medical termination of Pregnancy (MTP) is the intentional termination of pregnancy before Full term. MtP is legalised in our country with certain strict conditions to avoid its misuse. MTP is generally performed to get rid oF unwanted pregnancies due to rapes, casual relationships etc.
- It is also used in certain cases when the continuation of the pregnancy could be harmful or even fatal to either the mother the Foetus or both. MTPs are formed by qualified medical professionals preferably during the First trimester.
- Avoiding sexual intercourse with unknown/multiple partners, and using oF condoms during coitus are some of the simple tips to avoid contracting STDs.
- inability to conceive or produce children even after 2 years of unprotected sexual cohabitation is called infertility. Various methods are now available to help such couples.
- Population: Population is defined as a group of organisms or the same species within which individuals may change genetic information occupying a particular space.
- Demography: Demography deals with the statistical study of the population.
- The population has characteristics which are a Function of the whole group and not of the individuals these are population density, birth rate, death rate, potential oF dispersion and growth Form.
- The population is defined as the total number of individuals of a species present lit a particular area: lie enemies in a population have some common characteristics, share a common pone pool and are capable of interbreeding among themselves to produce let tile ollspimgs
- Aim of Population Study: The alarming rise in the human population has created many scrum problems, l herblore, population education has been introduced into the school and college curricula. Population education is aimed at making students aware of the following:
- consequences of uncontrolled population growth such as environmental pollution, depletion of natural resources, extinction of species, etc ;
- Benefits oF lowering population growth rate to the biosphere ;
- advantages of a small Family to humans ;
- growth, distribution and density of population ;
- relation oF population to the standards oF liFe.
- Aspects of Demography.
- Demography: The scientific study of the human population is called demography. it deals with three phenomena :
- Changes in population, i.e., growth or decline.
- Composition of the population, i.e., age groups, and sex ratios.
- Distribution of the population in space.
- Demographic study is carried out through census, and registration of births and deaths.
- Census: Census is the counting of population, age and sex of individuals, marital status, number of children per couple, number of dependents, number of earning hands, education, literacy, mother tongue, religion, race, occupation, type of employment, mortality, etc.
- India, census is undertaken every ten years, for example, i97i, i98i, i99i. it takes over one year For the completion oF census. The Census of our country was carried out in February 2001 it is over one billion.
- Population density: Population density of a species is the number of individuals of a species per unit area or volume example, the number of animals per square kilometre; the number of trees per acre of a Forest etc. For instance, the number of people per square kilometre in 1991.
- If the total number of individuals is represented by the letter N and the number oF units oF space by the letter S, the population density D can be obtained as D = N/S.
- Consequences OF Higher Population Density
Neet Reproductive Health Chapter Notes
As the population density increases in a country beyond its means; it brings the following problems:
- Per capita income comes down
- Natural resources like land, minerals, wood, Fuel, etc. decrease
- general health goes down
- The large population of a country is the result of having large Families and the quality of life deteriorates accordingly.
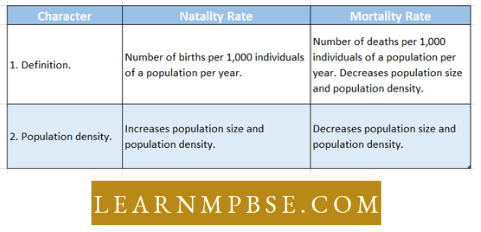
Birth or Natality rate:
It is often measured as the number of births per 1,000 individuals in a population annually. It increases both the population size and population density.
- The national average birth rate in India is roughly 28.6 births per 1,000 inhabitants each year. Kerala has the lowest birth rate among Indian states at 18 per 1,000, whilst Uttar Pradesh has the highest at 34.8 per 1,000.
- The total number of live births in a year is equal to the mid-year population multiplied by the mortality rate.
- It is the opposite of the birth rate. It is sometimes measured as the number of deaths per 1,000 residents in a population per year
- It is often measured as the number of births per 1,000 individuals in a population annually. It increases both the population size and population density.
- The national average birth rate in India is roughly 28.6 births per 1,000 inhabitants each year. Kerala has the lowest birth rate among Indian states at 18 per 1,000, whilst Uttar Pradesh has the highest at 34.8 per 1,000.
- The total number of live births in a year is equal to the mid-year population multiplied by the mortality rate.
- It is the opposite of the birth rate. It is sometimes measured as the number of deaths per 1,000 residents in
Difference between Natality Rate And Mortality Rate
- Population growth: Population growth is determined by several individuals added to the population by births (natality) and immigration (entry of individuals of the same species into an area From outside). it increases the population size. the number of individuals lost From the population by deaths (mortality) and emigration (departure of individuals of the same species From one area to outside). it decreases the size of the local population but the species spreads to new areas.
- If more individuals are added than lost, the population will show positive growth.
- But if more individuals are lost than added, then the population shows negative growth.
- But if the two rates are equal, then the population will become stationary and is called zero growth.
- Population growth = (Births + immigration) – (Deaths + emigration).
Migration involves the two-way movement of a whole population From one area to another area. Migration is not considered as a Factor determining the population size.
- Growth Rate: it is the increase in the number of individuals per unit time per unit number of individuals due to natality being higher than mortality. in other words, the growth rate is the difference in the birth rate and death rate in a population. the growth rate of the human population is 2%; 0.8% in developed countries and 2.5% in developing countries.
it is i.7% in India as per census oF 200i. - Reasons for an overpopulation
- Religious Beliefs. Certain religions Forbid Family planning. Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates have a population growth rate of 3% despite being among the richest and most educated countries.
- Education: It is found that population growth is inversely related to the degree and percentage of education. Over 50% of the Indian citizens are illiterate. Most of them believe that a higher number of children are a blessing to God.
- Early Marriage: In most developing countries, marriages are solemnised at an early age between i5-20 years.
- Child-Labour. In many families, children are asked to work to earn a livelihood. Such Families consider a larger number of children to be an asset.
- Decreased Mortality: The death rate has Fallen in most countries including India mostly due to the spread of medical Facilities and awareness of care For Infants.
- increased Average Life Span: The average life span of human beings is steadily rising in most countries. it has reached a Figure of more than 75 years in developed countries and around 56 years in developing countries like India.
- incidence of Epidemics: they have come down due to the increased spread of health services and, the stress of government and civic agencies on sanitation and vaccination.
- Famine and Floods. Previously innumerable deaths used to occur due to these two reasons Advancement of technology has made it possible to Forecast impending disasters and take preventive as well as remedial measures.
- increased Facilities. Every government pays special attention to building Facilities like transportation, health services, proper storage and distribution of Food, housing and other Facilities For the poor
Reproductive Health NEET Notes
Major Disadvantages OF Large Families :
The major Disadvantages OF Large Families are
- The mother may suffer From ill health due to Frequent pregnancies.
- Economically weak parents cannot maintain their standard of living.
- Children do not get nutritious Food, proper clothing, proper medical Facilities and good education.
- over the health of the mother leads to less attention to children.
- Overcrowding leads to problems of sanitation, sewage, transportation, environmental and noise pollution, and various socio-economic problems related to juvenile delinquency and crime.
- Disadvantages of Large Population
- Deficiency oF the essential commodities oF liFe viz. Food, clothes and shelter.
- Depletion of resources.
- Unemployment.
- Poverty.
- StriFe among different groups.
- Lack of interest towards life.
- Crime and addictions.
- Abortion.
- Restrict the Family to two children.
- Family Planning”.The main objective of family planning or family welfare programmes is to prevent the fertilization of the dead ovum by the male sperm and stop the increase in population growth by various methods, such as contraceptives, intrauterine devices, vasectomy and tubectomy.
- Contraceptives (Anirudh) for males and intrauterine devices, loop for females are used to avoid pregnancy. Vasectomy is the method of sterilizing a male by surgical operation of the sperm duct or vas deferens. Tubectomy is the method of sterilizing a female by the surgical operation of fallopian tubes. Whatever the method employed, it must take care of the health of the persons concerned.
- Because of the family planning methods, the birth rate in India is reduced to some extent. The government gives incentives to those who adopt family planning.
- Ways of Family Planning
- Late marriage for young persons.
- Increase in the sources of recreation to divert the attention from sex.
- The couple should not mate between the 8th and 18th day from the start of the menstrual cycle.
- Use of contraceptives.
- Sterilization
- Use of drugs.
- Strife among different groups.
- Crime and addictions
- Population Control
Population explosion can be checked by two methods—population education and birth control.
- Population Education
The knowledge about the relationship between population size and the availability of resources For the welfare of the society is called population education.
- the students should be convinced about the relationship between overpopulation and unemployment.
- the citizens should be told how the large size of the population is eating away at the resources of the state and the reasons For the limited availability of health care, education Facilities and other welfare schemes.
- People should be made aware of how a large number of children eat away the meagre resources of the Family with nothing left For bad days, how large Families rely on indebtedness to meet emergencies.
- How child bread earners do not improve the conditions of the Family, how uneducated children remain a burden on society, etc. they should be convinced that a small Family can live comfortably even with meagre resources.
- Mass Media of Communication. Radio, television, newspapers, magazines, hoardings and posters should be employed to spread the message of Family planning and birth control and its advantages.
- The future of mankind depends on the stabilisation of the human population at a level that ensures the necessities of life, employment and happiness.
- The law about marriageable age should be widely published and strictly enforced (2 years For boys and 8 years For girls). In developed countries, women marry at the age of 25-35.
- As far as possible. miss should bo laid on (hr mini Ftlnln% ul ilic women. Women 2veing higher Mvia! Matu is perfect for small Families. Stub women gc2nnlly matiy late.
- Remove the Mi|vititionv ami wrong beliefs in the society higher number oF children hong ihvl’s pill connected with the earthly or heavenly prosperity.
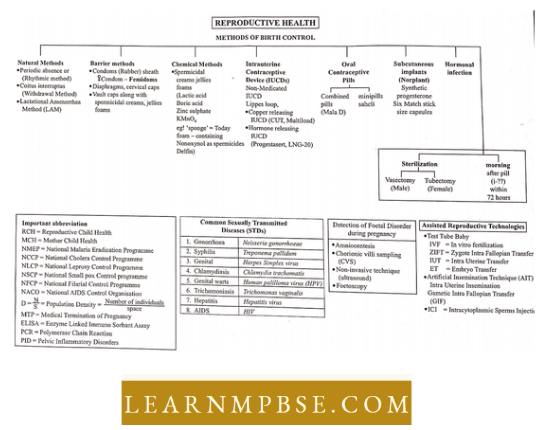
The various methods of birth control
- Use oF Contraceptives means prevention oF conception ;
The following contraceptives are popular :
- Diaphragm: Hie vaginal diaphragm is a rubber cup stretched over a collapsible metal spring coil. it is designed to fit over the cervix, i.e. the mouth of the uterus which prevents Fertility or conception.
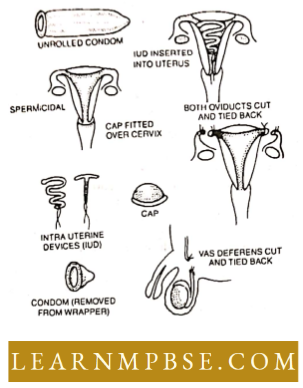
- Condom: The condom is a sheath oF rubber which Fits on the erect penis. it is put on the penis beFore it is introduced into the vagina during intercourse.
- Jellies, creams and Foams: Several different spermicidal jellies, creams and Foams are available For use as contraceptive agents. These jellies, creams and Foams are inserted into the vagina Five to FiFteen minutes beFore ejaculation takes place.
Importance Of Reproductive Health NEET
Introduction oF copper ‘t’: or loop in the Female uterus prevents the entry oF sperms in the uterus iUD (intra-uterine device).
- Oral contraceptives. these are popularly known as “pills” and are combinations of synthetic sex hormones which suppress the production of ovum. these pills alter the ovulation cycle.
- Sterilization. it is the surgical technique by which the passage of sperm or ovum is discontinued. Both men and women can be sterilized without losing their ability to function sexually.
- Vasectomy: In men, the sterilization procedure is called vasectomy.
- tubectomy: In women, part of the Fallopian tube is cut and tied.
- Laparoscopy: it is the mechanism of tying the oviducts or tubal ligation and hence blocking them with the help of an instrument called a laparoscope. Because oF ligation, the ovum cannot pass into the uterus nor the sperm reach the egg For Fertilization.
- Medical termination of pregnancy (MTP). it is the cessation of pregnancy by surgery, suction or by other means.
- Other measures
- Abstinence: Abstaining From intercourse.
- Coitus interrupts: It involves the withdrawal of the penis From the vagina beFore ejaculation occurs.
- Zero ‘O’ method: This is a natural effective and practical method where the woman has to Find Herself in the Fertile and infertile period, by keeping a close watch on the uterine charge. the safest period to avoid pregnancy is From the beginning of mucus discharge next Four days after the discharge has stopped.
NEET Biology Reproductive Health Questions From Competitive Examinations
Question 1. Which of the following is a convincing reason for Kuion’s growth as a country?
- High birth rate
- Low mortality rate
- Low population of old people
- High population of young children.
Answer: 4. High population of young children.
Question 2. If the rate oF addition oF new members increases concerning the individual host oF the same population, then the graph obtained has :
- Declined growth
- Exponential growth
- Zero population growth
- None of these.
Answer: 2. Exponential growth
Question 3. Copper-t prevents :
- Ovulation
- Fertilization oF egg
- Implantation
- Both B and C.
Answer: 4. Both B and C.
Question 4. Which is related to males?
- Oral pill
- tubectomy
- Vasectomy
- None of these.
Answer: 3. Vasectomy
Question 5. Study oF population trends is:
- Kalography
- Psychobiology
- Biography
- Demography.
Answer: 4. Demography.
Importance Of Reproductive Health NEET
Question 6. July 11 is :
- World Environment Day
- World Population Day
- World AIDS Day
- World Education Day.
Answer: 2. World Population Day
Question 7. A method of birth control is :
- GIFt
- Zift
- IVF-Et
- IUDs
Answer: 4. IUDs
Question 8. What is the Function of copper t?
- Prevents mutation
- Prevents Fertilization
- Prevents zygote Formation
- B and C.
Answer: 4. B and C.
Question 9.In the production oF test tube babies:
- Fertilization is external and Foetus Formation is internal
- Fertilization is internal and Foetus Formation is external
- Fertilization and Foetus Formation are external
- Fertilization and Foetus Formation are internal.
Answer: 1. Fertilization is external and Foetus Formation is internal
Question 10. Certain characteristic demographic Features of developing countries are :
- High Fertility, high density, rapidly rising mortality rate and a very young age distribution.
- High infant mortality rate, low Fertility, uneven population growth and a very young age distribution.
- High mortality, high density, uneven population growth and a very old age distribution.
- High Fertility, low or rapidly Falling mortality rate, rapid population growth and a very young age distribution.
Answer: 4. High Fertility, low or rapidly Falling mortality rate, rapid
population growth and a very young age distribution.
Question 11. Oral contraceptives are prescribed in Females to check :
- Ovulation
- Fertilization
- Implantation
- Entry oF sperms in the vagina.
Answer: 1. Ovulation
Question 12. Zero growth means :
- Natality is zero
- Natality balances mortality
- Natality is less than mortality
- Natality is more than mortality.
Answer: 2. Natality balances mortality
Question 13. The following is a technique for direct introduction of gametes into the oviduct:
- MtS
- Et
- IVF
- Post.
Answer: 3. IVF
Question 14. Which of the following is a mechanical barrier used in birth control:
- Loop
- Copper-t
- Diaphragm
- Dalcon shield.
Answer: 3. Diaphragm
Question 15. Which of the following is the most sparsely populated state of India?
- Manipur
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Rajasthan
- Meghalaya.
Answer: 2. Arunachal Pradesh
Question 16. Maximum growth rate occurs in :
- Lag phase
- Exponential phase
- Stationary phase
- Senescent phase.
Answer: 2. Exponential phase
Reproductive Health PDF NEET
Question 17. In a population, the condition at which the rate of addition of new members is more than the rate of individuals lost indicates :
- Zero population growth
- Exponential growth
- Fluctuating growth
- Declining growth
- None of these.
Answer: 2. Exponential growth
Question 18. The growth curve is normally :
- J-shaped
- V-shaped
- S-shaped
- C-shaped.
Answer: 3. S-shaped
Question 19. The greatest biological problems Faced by human beings are:
- Population explosion
- Depletion of the ozone layer
- Depletion of natural resources
- Land erosion.
Answer: 1. Population explosion
Question 20. The formula For exponential population growth is:
- dl/clN = rN
- c/N/rN = dt
- rN/r/N = dt
- dN/dt = rN.
Answer: 4. dN/dt = rN.
Question 21. Human population growth is :
- Lag
- Stationary
- Exponential
- None of these.
Answer: 3. Exponential
Question 22. Which of the Following birth control measures can be considered the safest?
- the rhythm method
- the use oF physical barrier
- termination oF unwanted pregnancy
- Sterilization techniques.
Answer: 2. the use of a physical barrier
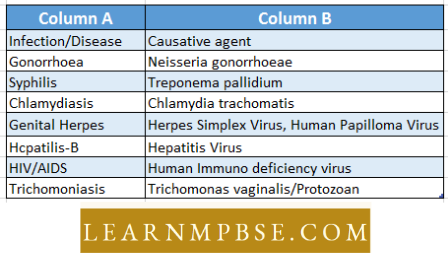
Question 23. Write one of the Following concretely mulched Sexually transmitted Diseases (S tD) with its pathogen.
- AIDS—Fiacillus anthraeis
- Syphilis—7’irponcma
- pallidumUirlhcrilis—Entamoeba gingivalls
- Gonorrhoea—Leislimania donovani.
Answer: 2. Syphilis—7’irponcma
Question 24. lire most important component of contraceptive pills is: .
- Progesterone
- Growth hormone
- Thyroxine
- Luteinising hormone.
Answer: 1. Progesterone
Question 25. Chancroid is a sexually transmitted disease caused by :
- treponema
- Haemophilus
- Nlisseiria
- Chlamydia
- trichomonas
Answer: 4. trichomonas
Question 26. Which of the following causes abortion in ladies?
- Viruses
- Bacteria
- Mycoplasma
- None of these.
Answer: 3. Mycoplasma
Question 27. Which one of the following statements is incorrect about menstruation?
- At menopause in the Females, there is an especially abrupt increase in
gonadotropic hormones - the beginning of the cycle of menstruation is called menarche
- During normal menstruation about 40 ml of blood is lost
- the menstrual Fluid can easily clot.
Answer: 4. the menstrual Fluid can easily clot.
Population Control Methods NEET
Question 28. Consider the statements given below regarding contraception and answer as directed thereafter:
(1)Medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) during the First trimester is generally safe
(2)Generally chances of conception are nil until the mother breast-feeds the Infants up to two years.
(3) Intrauterine devices like copper-t are effective contraceptives.
(4)contraception pills may be taken up to one week after coitus to prevent conception.
Which two of the above statements are correct?
- 1,3
- 1, 2
- 2, 3
- 3, 4.
Answer: 1. 1,3
Question 29. Given below are Four methods (a-d) and their modes of action (i-iv) in achieving contraception. Select their correct matching From the Four options that Follow.
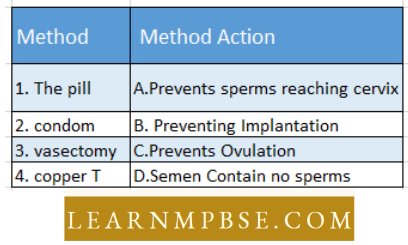
- 1-C, 2-D, 3-A, 4-B
- 1-B, 2-C, 3-A, 4-D
- 1-C, B-A, 3-D, 4-B
- 1-D, 2-A, 3-B, 4-C
Answer: 3. 1-C, B-A, 3-D, 4-B
Question 30. Medical termination of Pregnancy (M l P) is considered a sale tip to how many weeks of pregnancy?
- Eight weeks
- Twelve weeks
- Eighteen weeks
- Six weeks.
Answer: 2. twelve weeks
Question 31. Which one of the Following is the most widely accepted method of contraception in India, at present?
- Cervical caps
- tubectomy
- Diaphragms
- BJDs (Intrauterine devices).
Answer: 4. BJDs (Intrauterine devices).
Sexually Transmitted Diseases NEET
Question 32. The test-tube Baby Programme employs one of the following techniques?
- Intra uterine insemination (IUI)
- Gamete intra Fallopian transfer (GIFt)
- Zygote intra Fallopian transFer (Z1Ft)
- Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
Answer: 3. Zygote intra Fallopian transfer (Z1Ft)
Question 33. What is the Figure given below showing in particular?
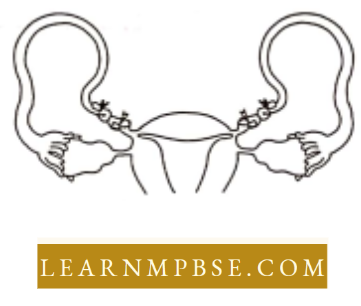
- Uterine cancer
- tubectomy
- Vasectomy
- Ovarian cancer.
Answer: 2. tubectomy
Question 34. Which of the following is wrongly matched?
- IUI – semen collected From the husband or donor is artificially introduced either into the vagina or into the uterus.
- GIFt – transFer oF embryos with more than 8 blastomeres into the Fallopian tube.
- ICSI – sperm directly injected into the ovum.
- ZIFt – transFer oF embryos with up to 8 blastomeres into the Fallopian tube.
- tVF – Fertilization outside the body in almost similar conditions as that in the body.
Answer: 2. GIFt – transFer oF embryos with more than 8 blastomeres into the Fallopian tube.
Question 35. One of the legal methods of birth control is :
- By abstaining From coitus From day 10 to 17 oF the menstrual cycle
- By having coitus at the time of daybreak
- A premature ejaculation during coitus
- Abortion by taking an appropriate medicine.
Answer: 4. Abortion by taking an appropriate medicine.
Question 36. Which of the following cannot be detected in developing
- Foetus by amniocentesis ?
- Sex of the Foetus
- Down syndrome
- Jaundice
- Klinefelter syndrome
Answer: 3. Jaundice
Question 37. Artificial insemination means:
- Transfer oF sperms oF husband to a test tube containing ova
- Artificial introduction oF sperm to a healthy donor into the vagina
- Introduction oF sperms to a healthy donor directly into the ovary
- Transfer oF sperms oF a healthy donor to a test
Answer: 2. Artificial introduction oF sperm to a healthy donor into the vagina
