NEET Biology Classification Of Taxonomy Of Angiosperms
Features of Flowering Plants (Angiosperms. (Gk. cmgion-vessel. sperma-sned).
Angiospermae is a large category of flowering plants characterized by seed formation within fruits and the arrangement of sporophylls into flowers.
They exhibit the following traits:
Sporophylls amalgamate to form flowers.
- A microsporophyll, or stamen, consists of a filament and an anther. A megasporophyll (carpel) is intricately folded and partially sterilized to produce a stigma, style, and ovary containing ovules.
- Double fertilization consistently takes place. Endosperm is produced via triple fusion and is generally triploid.
- The fertilized ovule matures into seeds that are enclosed within fruits. A fruit is, by definition, a mature ovary that facilitates the protection and dispersal of seeds.
- Xylem consists of vessels, whereas phloem is composed of sieve tubes and partner cells.
- Secondary growth occurs in the stems and roots of dicotyledons.
- Angiosperms exhibit the distinctive plant alternation of generations. The dominating phase is the sporophyte, whereas the gametophyte is markedly reduced in size and wholly dependent on the sporophyte for nourishment.
- This condition is not limited to angiosperms but is found in all seed plants.
Taxonomy Of Angiosperms NEET Notes
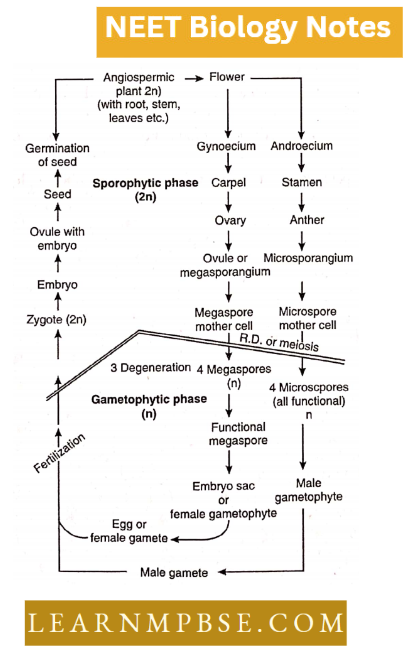
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
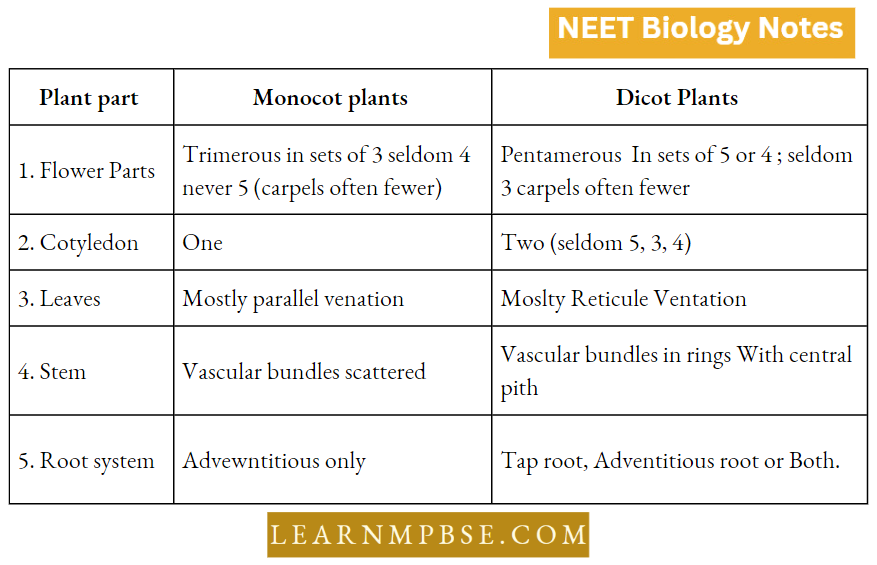
NEET Biology Taxonomy Of Angiosperms Important Characters Of Selected Families
Characteristics of Solanaceae
- Aerial parts are hairy.
- Stem usually with collateral vascular bundles.
- Leaves alternate becoming opposite in the floral region.
- Flower actinomorphic, hypogynous.
- Sepals 5, gamosepalous.
- Petals 5, gamopetalous.
- Stamens 5, polyandrous antipetalous and epipetalous.
- Gynaecium, bicarpellary, syncarpous, superior, ovary obliquely placed.
- Axile placentation with swollen placenta
- Fruit Berry or Capsule.
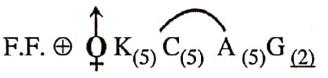
- Important Genera. Solatium tuberosum (Potato), Capsicum annum (Chillies) Nicotiana tobacum (tobacco), Cestrum noctumum (night queen), Datura.
Taxonomy Of Angiosperms NEET Notes
The old names of some families have been changed new names are given below
- Old Name – New Name
- Cruciferae – Brasicaceae
- Papilionoideae- Fabaceae
- Umbelliferae- Apiacae
- Compositae- Asteraceae
- Labiatae- Lamiaceae
- Gramineae- Poaceae
- Palmae- Arecaceae
- Caesalphiniaceae- Cassiaceae
- Mimosoidae- Mimosaceae
The old family Leguminosae now includes three sub-families:
- Mimosoideae,
- Caesalpinioideae and
- Papilionoideae.
These subfamilies have now been raised to the level of families are called:
- Mimosaceae
- Caesalpiniaceae and
- Fabaceae.
Characteristics of Family Cruciferae
- Mostly sulphur-smelling herbs.
- Absence of flowers.
- Hexacyclic flowers.
- Calyx 4, free sepals arranged in two whorls of two each 2 + 2u’
- Corolla 4, clawed petals, Cruciform, 4 x.
- Androecium typically (6), tetradynamous lateral stamens arranged in two whorls, 2, shorter + 4 longer median.
- Pollen grains with a reticulate exine.
- Presence of green, dot-like nectaries at the bases of stamens.
- Gynaecium is typically bicarpellary, syncarpous, superior.
- The ovary is bilocular owing to the formation of a false septum stretching between the two parietal placentae. The two carpels are placed transversely.
- Fruit is typically a siliqua or silicula.
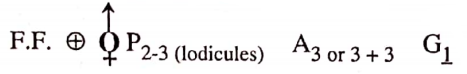
- Important plants. Brassica campestris (Mustard), Raphanus sativus (Radish), Iberis amara (Candytuft) Brassica juncea (halon).
Characteristics of Family Leguminosae
- Alternate, stipulate, pulvinate, and generally pinnately compound leaves.
- Gamosepalous, persistent calyx with odd sepal or lobe anterior.
- Polypetalous corolla generally with ascending or descending imbricate aestivation, sometimes valvate.
- Monocarpellary gynaecium.
- Ovary unilocular with marginal placenta along the ventral suture which is always posterior.
- Fruit is a legume, sometimes a lomentum.
- Sub-family Papilionatae. It is characterized by zygomorphic flowers, gamosepalous calyx, papilionaceous corolla, stamens usually 10, diadelphous, sometimes monadelphous, pollen grains simple, seeds without arterioles, leaves pinnate, digitate, trifoliate, sometimes simple.
Characteristics of Family Leguminosae
- Alternate, stipulate, pulvinate, and generally pinnately compound leaves.
- Gamosepalous, persistent calyx with odd sepal or lobe anterior.
- Polypetalous corolla generally with ascending or descending imbricate aestivation, sometimes valvate.
- Monocarpellary gynaecium.
- Ovary unilocular with marginal placenta along the ventral suture which is always posterior.
- Fruit is a legume, sometimes a lomentum.
- Sub-family Papilionatae. It is characterized by zygomorphic flowers, gamosepalous calyx, papilionaceous corolla, stamens usually 10, diadelphous, sometimes monadelphous, pollen grains simple, seeds without arterioles, leaves pinnate, digitate, trifoliate, sometimes simple.
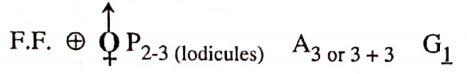
- Important plants. Pisum sativum, Cicer arienum, Lupinus, Dalbergia sisoo, Arachis hypogea.
- Sub-family Caesalpinoideae. Flowers irregular, calyx free or united, imbricate, corolla polypetalous, ascending imbricate in bud condition, stamens 10 or less, free rarely many, pollen grains simple, leaves usually pinnate, sometimes bipinnate, rarely simple.
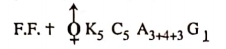
- Important plants. Cassiafistula, Buhinia and Tamarindus indica.
- Sub-family Mimosoideae. Flowers regular, calyx gamosepalous, corolla gamopetalous, stamens 4—many, free or monadelphous, pollen grains compound, seeds marked with arterioles, leaves usually bipinnate.
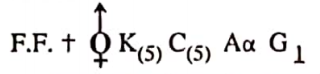
Important plants. Acacia arabica, Acacia catechu, Mimosa pudica.
Taxonomy Of Angiosperms NEET Question Bank
Characteristics of Family Malvaceae
- Younger parts are covered with stellate hairs and contain a lot of mucilage.
- Leaves alternate, stipulate, palmately veined.
- Presence of epicalyx.
- Sepals and petals typically 5, stamens numerous, monadelphous, forming a staminal tube, epipetalous.
- Twisted aestivation of the corolla.
- Monothecous anthers and spiny (echinulate) pollen grains.
- Schizocarpic, carcerulus fruit or a loculicidal capsule.
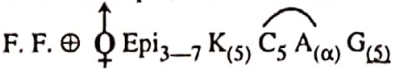
Important plants. Gossypium, Hibiscus rosa sinensis, Malva sylvestris, Althea rosea.
Distinguishing Characters of Family Compositac (Astcraccae)
- Plants are generally herbs.
- Inflorescence a capitulum-homogamous or heterogamous.
- Calyx-sepals pappus or 2-3 scales.
- Corolla —Ray florets—ligulate Disc, florets—tubular.
- Androecium-stamens 5, epipetalous syngenesious.
- Gynaecium-carpellary, syncarpous ovary inferior, unilocular with a single basal ovule, stigma bifid.
- Fruit a cypsella.
- F.F. Ray Florets Br or neuter,

Examples Ornamental. Chrysanthemum, Helianthus, Dahlia, Zinnia, Aster, Cosmos. Oil yielding. Carthamus tinctorius, Helianthus annus. Medicinal. Artemisia maritima, Saussurea lappa.
Characteristics of Family Liliaccae
- Generally actinomorphic, trimerous, and hypogynous flowers.
- Perianth petaloid, biseriate.
- Stamens are 6, biseriate, epiphyllous anisophyllous.
- Tricarpellary syncarpous superior ovary with axile placentation.
- Fruit a berry or loculicidal capsule.
- Seed monocot endospermic.
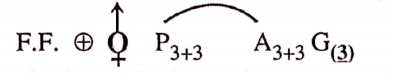
Important Genera. Allium cepa, (Onion) Asparagus, Smilax, Yucca, Gloriosa, and Aloe
Characteristics of Family Cucurbitaccae
- Plants herbs, generally climbing.
- Flowers, unisexual, epigynous.
- Androceium-stamens synandrous.
- Gynaecium-tricarpellary, ovary inferior, trilocular with parietal placentation.
- Fruit —a pepo.
- Vascular bundle in stem collateral.
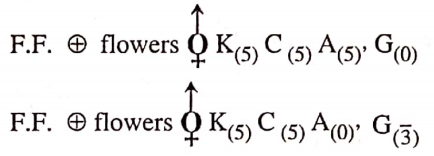
Examples. Vegetables, Cucurbita, Coccinia, Cucumis sativus, Trichosanthes anguinFruit. Cucumis melo.
Classification Of Angiosperms NEET
Characteristics of family Gramirieae
- Flowers are arranged in spikelets which in turn are grouped in spikes.
- Each spikelet is enclosed with two scales called glumes.
- Each flower is covered with two scales called lemma and palea.
- Anthers generally divaricate and versatile.
- Ovary unilocular and two feathery stigmas.
- Fruit is commonly a caryopsis or grain.
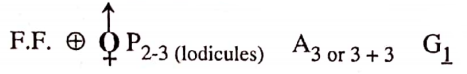
Important plants
Triticum aestivum (wheat), Oryza sativa (rice), Zea mays (maize), Hordeum vulgare (barley), Avena sativa (oats), Andropogon odoratus, and Saccharum munja.
- The floral formula delineates the arrangement of various whorls of the flower, their quantity, cohesiveness, adhesion, and any interrelationships.
- The Brassicaceae family, previously referred to as Cruciferae, comprises 375 genera and around 3,200 species, including 150 endemic to India.
- The Fabaceae family was previously referred to as Papilionideae. In the Poaceae family, the perianth is referred to as lodicule.
- The inflorescence in Poaceae or Gramineae is a spikelet.
- In the Gramineae family, the fruit is a caryopsis, wherein the pericarp is merged with the testa.
- Bamboo is utilized for the production of sticks, flutes, ladders, furniture, and other items.
- Khus oil is derived from the roots and rhizomes of Vetiveria zizanoides.
- In the Liliaceae family, the flowers are trimerous, pentacyclic, and hypogynous.
- In Liliaceae, the gynoecium is tricarpellary, syncarpous, and trilocular with axile placentation.
- The odd sepal is positioned anteriorly in Papilionaceae. Nodulated roots occur on the roots of Papilionaceae members.
- The corolla is papilionaceous in the family Papilionaceae.
- Oil is derived from the seeds of Arachis hypogea (groundnut) and Glycine max (soybean). Oil undergoes hydrogenation to produce vanaspati ghee.
- The fruit is referred to as siliqua or silicula in the Brassicaceae family.
- The stamens in Brassicaceae are six in number, polyandrous, and tetradynamous.
- The inflorescence of Brassica oleracea var. botrytis (cauliflower) is consumable.
- The roots of Lepidium sativum treat syphilis, hemorrhoids, and cough.
- The inflorescence is a capitulum in the family Compositae.
- The fruit of Compositae is a cypsella, which may or may not possess a pappus.
- The gynoecium of the sunflower is carpellary, syncarpous, inferior, unilocular, and contains a single basal ovule.
- In the Solanaceae family, the gynoecium is carpellary, syncarpous, superior, and features an obliquely positioned ovary with a large placenta. The placentation is axile.
- Tomatoes, potatoes, and chilies are members of the Solanaceae family.
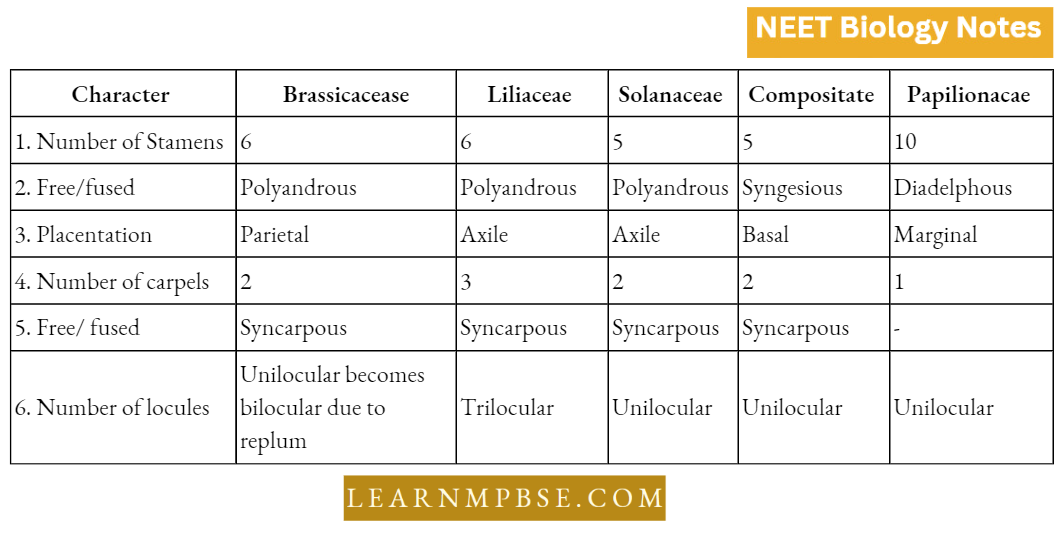
Floral Formulae

NEET Biology Taxonomy Of Angiosperms Quanta To Memory
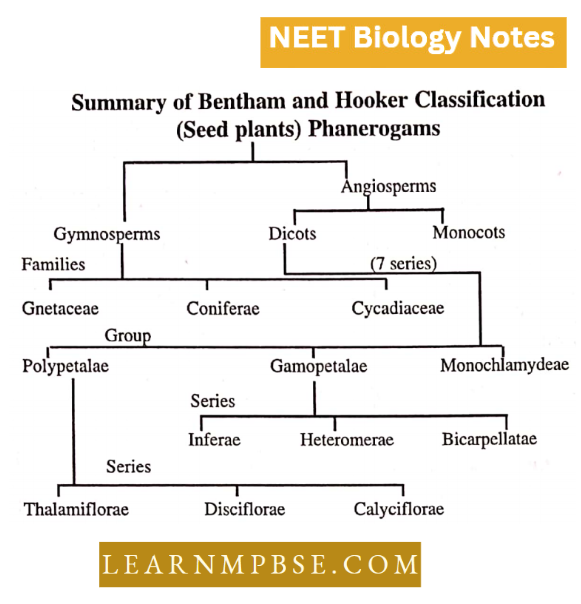
- Bentham and Hooker classified seed plants into three divisions: Dicots, Monocots, and Gymnosperms.
- Hooker characterized taxa based on direct examination of the specimens.
- These are the most prevalent vascular plants on the planet.
- The plant structure is the sporophyte, which is differentiated into authentic roots, stems, and leaves.
- In botany, phytospecies constitutes the fundamental unit of classification.
- In the phylogenetic categorization system, plants are categorized based on evolutionary tendencies.
- The biological definition of species mostly relies on the attributes of reproductive structures.
- A novel species is identified based on floral characteristics.
- Floral organs, such as stamens and carpels, exhibit less changes compared to vegetative traits.
- For instance, In Malvaceae, the stamens are typically monadelphous.
- Currently, woody plants are considered primitive, whereas herbaceous plants are viewed as advanced.
- Fruits are exclusive to angiosperms, vascular tissue is highly developed, and tap roots are prevalent in dicots.
- In angiosperms, bees serve as the predominant pollinators of agricultural species due to their attraction to floral nectar and fragrance.
- Insectivorous plants thrive on nitrogen-poor soil.
- They obtain partial nitrogen satisfaction from deceased insects.
Plant Taxonomy NEET
- Pollination by bats is called chiropterophily. Bats are attracted due to nectar and pollen grains.
- Stems have conjoint, collateral, or concentric vascular bundles which may be open as in dicots or closed as in monocots.
- Dependence on water is overcome by siphonogamy.
- Monocots do not grow in girth, though they grow in length and produce new leaves and flowers.
- Seeds are perennating structures and help in the dispersal of plants.
- Smallest parasitic plant is Arceothobium minastissimum. In cyathium inflorescence, a single male flower is represented by a single stamen.
- When an entire inflorescence is converted into a fruit, it is called a composite fruit.
- The flowers are unisexual and are on the same plant, this condition of a plant is referred to as monoecious.
- The entire family of Compositae is characterized by the presence of head or capitulum inflorescence.
- Agave and Bamboo are perennial but are monocarpic monocots, usually with no normal secondary growth due to the absence of cambium.
- Xylem has vessels, i.e., wood is porous. However, vessels are absent in some members of Ranales, for Example, Tetracentron, Trochodendron, Sarcandra, etc.
- Phloem has companion cells in association with sieve tubes.
- Double fertilization is a regular phenomenon.
- Endosperm is usually triploid and is formed as a result of triple fusion after fertilization.
- Seeds are enclosed within the pericarp i.e., fruits are formed due to the presence of the ovary.
- The leaves of bryophyllum have buds on the margins of leaves. These buds develop into new plants.
- In Arachis hypogea (groundnut), the flowers after pollination bury themselves inside the soil and develop into fruits and seeds. Such movements are called geocarpic movements.
- Royal Botanical Garden Herbarium at Kew (England) is the biggest famous herbarium in the world and has 65,000,000 plants.
- Indian Botanical Garden Herbarium at Sibpur (Kolkata) is the biggest in India and has 25,000,000 plants.
NEET Biology Taxonomy Of Angiosperms Questions from competitive examinations
Question 1. The flora! Formula condition +, <j> k5, c5, a7 + 3, g1 is found in the family
- Mimosoidcac
- Caesalpiniaceae
- Papilionaceac
- Cruciferae
Answer: 2. Caesalpiniaceae
Question 2. A plant has a butterfly-shaped flower with one standard wing-like and two keel petals. The plant belongs to the family:
- Papilionaceae
- Compositae
- Malvaceae
- Rubiaceae.
Answer: 1. Papilionaceae
Question 3. Gloriosa superba has parallel venation with leaf apex modified as tendril belongs to which of these families?
- Cucurbitaceae
- Malvaceae
- Labiatae
- Liliaceae.
Answer: 3. Labiatae
Angiosperm Families NEET
Question 4. The flower of Fabaceae is:
- Actinomorphic, complete, trimerous
- Actinomorphic, incomplete, pentamerous
- Zygomorphic, complete, trimerous
- Zygomorphic, complete, pentamerous
Answer: 4. Zygomorphic, complete, pentamerous
Question 5. Choose the correct description of the flower depicted in the floral diagram given below

- United, valvate sepals; free, imbricate petals; free stamens; unilocular ovary with marginal placenta
- United, valvate sepals: free, imbricate petals, epipetalous stamens; unilocular ovary with marginal placenta
- United, valvate sepals; free, imbricate petals; free stamens; unilocular ovary with axile placenta
- United, valvate sepals; free, twisted petals; free stamens; unilocular ovary with marginal placenta
Answer: 1. United, valvate sepals; free, imbricate petals; free stamens; unilocular ovary with marginal placenta
Question 6. Angiosperms have dominated the land flora primarily by their:
- Power of adaptability to diverse habitats
- Nature of pollination
- Domestication by humans
- A large number of seeds
Answer: 1. Power of adaptability to diverse habitats
Question 7. Lady’s finger belongs to the family:
- Liliaceae
- Cucurbitaceae
- Brassicaceae
- Malvaceae
Answer: 4. Malvaceae
Question 6. The botanical name of chana is:
- Dolichos
- Lablab purpeureuns
- Phaseolus assets
- Cicer arietinum
Answer: 1. Dolichos
Angiosperm Families NEET
Question 9. Plants of which one of the following groups of genera are pollinated by the same agency?
- Triticum, cocos, mangifera
- Ficus, kigelia, casuarina
- Salvia, morus, euphorbia
- Bombax, butea, bauhinia
Answer: 4. Bombax, butea, bauhinia
Question 10. Pentamerous actinomorphic flowers, bi-carpellary ovary with oblique septa, and fruit a capsule or barry are characteristic features of:
- Solanaceae
- Liliaceae
- Asteraceae
- Brassicaceae
Answer: 1. Solanaceae
Question 11. What type of placentation is seen in sweet peas?
- Free central
- Marginal
- Basal
- Axile
Answer: 4. Axile
Question 12. “Ordines anomaly” of Bentham and hooker includes
- Seed plants showing abnormal forms of growth and development
- Plants described only in a fossil state
- Plants described in the literature but which Bentham and hooker did not see in original
- A few orders which could not be placed satisfactorily
Answer: 1. Seed plants showing abnormal forms of growth and development
Question 13. Observe the given floral diagram and choose the suitable floral formula from the following:

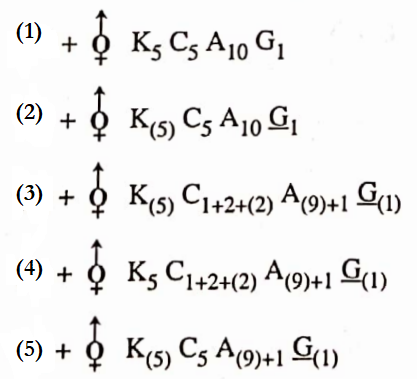
Answer: 3. 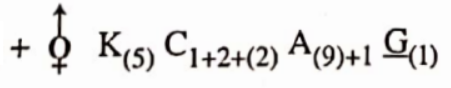
Question 14. In the members of the family Malvaceae, anthers are described as
- Diadelphous and distichous
- Diadelphous and monotonous
- Monadelphous and distichous
- Monadelphous and monotonous
Answer: 4. Monadelphous and monotonous
Question 15. Syngcncsious stamen is found in family
- Atasteraccac
- Solaanacceae
- Fabaceae
- Poaceae
Answer: 1. Atasteraccac
Characteristics Of Angiosperms NEET
Question 16. Which of the following is a merit in the Bentham and hooker’s system of classification?
- At the position of gymnospermae in between decals and mounts
- Closely related families are placed apart
- The placement of the family Asteraceae at the beginning of gamopetalous
- The placement of order rentals at the beginning
- The placement of orchidaccae in microspermae.
Answer: 4. The placement of Orchidaceae in microspermae.
Question 17. Which of the following represents the floral characters of Liliaccae?
- Six tepals. Zygomorphic, six stamens, bilocular ovary, axile placentation
- Tetramerous, actinomorphic, polyphyllous, unilocular ovary, axile placentation
- Trimerous, actinomorphic, polyandrous, superior ovary, axile placentation
- Bisexual, zygomorphic, gamophyllous, inferior ovary, marginal placentation
- Unisexual, actinomorphic, trilocular, inferior ovary, axile placentation.
Answer: 3. Trimerous, actinomorphic, polyandrous, superior ovary, axile placentation
Question 18. The botanical name of soybean is:
- Cajanus cajan
- Glycine max
- Glycyrrhiza glabra
- Abrus precatorius
- Dolichos lablab.
Answer: 2. Glycine max
Question 19. Which of the following is/are not characteristic features of Asteraceae?
- Cypsela type of fruit
- Syngenesious stamens
- Ovary bicarpellary and superior
- Placentation marginal
- Head type of inflorescence.
Answer: 3. Ovary bicarpellary and superior
Question 20. Family podostemaceae is placed under the series:
- Mulliovulatae aquatic
- Microembryeae
- Dephnales
- Uniscxuales
- Hetcromerae.
Answer: 1. Mulliovulatae aquatic
Question 21. In guava, cucurbits flowers are:
- Hypogynous flower
- Epigynous flower
- Pcrigynous (lower)
- Both hypogynous and perigynous
Answer: 2. Epigynous flower
Angiosperm Taxonomy NEET Exam Preparation
Question 22. In floral formula (k) denotes :
- Polysepnlous
- Gamoscpalous
- Polypetalous
- Gamopctalous.
Answer: 2. Gamoscpalous
Question 23. Consider the following statements for gymnosperms and angiosperms.
- Double fertilization is an event unique to gymnosperms.
- Angiosperms range in size from microscopic to tall trees of sequoia.
- In gymnosperms, the seeds are not covered.
- In gymnosperms, the male and female gametophytes have an independent free-living existence.
Of the above statements
- A and b alone are correct
- C alone is correct
- B and c alone are correct
- C and D alone are correct
- D alone is correct.
Answer: 1. A and b alone are correct
Question 24. Match die following and choose the correct combination from the options given.
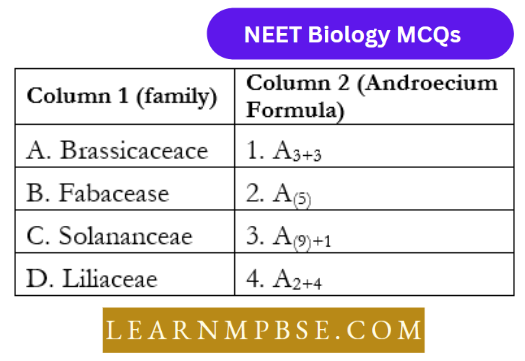
- A-4,B-3,C-2,D-1
- A-1,B-2,C-3,D-4
- A-2,B-3,C-4,D-1
- A-4,B-3,C-1,D-2
- A-4,B-3,C-1,D-2
Answer: 1. A-4,B-3,C-2,D-1
Question 25. The distinct features of Fabaceae are
- Zygomorphic, diadelphous, and monocarpellary
- Actinomorphic, monadelphous, and monocarpellary
- Zygomorphic, monadelphous and pentacarpellary
- Zygomorphic, polyadelphous and tricarpellary
- Zygomorphic, diadelphous, and bicarpellary.
Answer: 1. Zygomorphic, diadelphous, and monocarpellary
Question 26. Among bitter gourd, mustard, brinjal, pumpkin, china rose, lupin, cucumber, sunn hemp, gram, guava, bean, chili, plum, petunia, tomato, rose, Withania, potato, onion, aloe, and tulip how many plants have hypogynous floowers?
- Ten
- Fifteen
- Eighteen
- Six
Answer: 1. Ten
Question 27. In China rose flowers are:
- Actinomorphic, epigynous with valvate aestivation
- Zygomorphic, hypogynous with imbricate aestivation
- Zygomorphic, epigynous with twisted aestivation
- Actinomorphic, hypogynous with twisted aestivation
Answer: 4. Actinomorphic, hypogynous with twisted aestivation
