NEET Biology Gene Expression Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Co-repressor is a:
- Protein
- Metabolite
- Hormone
- Enzyme.
Answer: 2. Metabolite
Question 2. Reverse transcription was discovered by :
- Watson and Crick
- Porter
- Wilkins
- Temin.
Answer: 4. Temin.
Question 3. In the operon concept, the regulator gene regulates chemical reactions in the cell by :
- Inhibiting transcription of mRNA
- Inactivating enzymes in the reaction
- Inhibiting the substrate in the reactions
- Inhibiting the migration of tn-RNA in cytoplasm.
Answer: 1. Inhibiting transcription of mRNA
Gene Expression MCQs For NEET
Question 4. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
- Genetic code is ambiguous.
- Genetic code is degenerate.
- Genetic code is universal.
- Genetic code is non-overlapping.
Answer: 2. Genetic code is degenerate.
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question and Answers
Question 5. In E. coli according to the operon concept, an operator gene combines with:
- Inducer gene to switch on
- Regulator protein to “switch on” structural gene transcription
- Regulator gene to “switch off’ structural gene transcription
- Regulator protein to switch off structural gene transcription.
Answer: 3. Regulator gene to “switch off’ structural gene transcription
Question 6. Exons and introns arc parts of :
- DNA
- RNA
- mRNA
- Circular DNA.
Answer: 1. DNA
Question 7. Eukaryotes have :
- One promoter in gene structure
- Two promoters in gene structure
- No promoter gene
- Many promoters in gene structure.
Answer: 3. No promoter gene
Question 8. In Rous sarcoma virus:
- DNA → RNA→ Protein
- RNA → DNA → Protein
- RNA →DNA → RNA→ Protein
- DNA → RNA → RNA → Proleins.
Answer: 4. DNA → RNA → RNA → Proleins
Gene Expression MCQs For NEET
Question 9. Presence of F factor in bacteria :
- Indicates it as male
- Female
- Fast factor
- Free factor
Answer: 1. Indicates it as male
Question 10. The viral genes are expressed by :
- Lytic processes
- Lysogenic
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
Question 11. Which of the following is not a carcinogen?
- X-rays
- Virus
- HNO2
- Starch.
Answer: 4. Starch
Question 12. According to the operon concept, the regulator gene forms.
- An inducer
- A repressor
- A small peptide
- A general inhibitor,
Answer: 2. A repressor
Gene Expression MCQs For NEET
Question 13. Which virus has a double-stranded RNA?
- Rheovirus
- Φ×174
- T2 phage
- TMV
Answer: 1. Rheovirus
Question 14. In the lysogenic cycle, the virus is:
- Virulent
- Temperate
- Harmless to the host cell
- Reproduces slowly.
Answer: 2. Temperate
Question 15. In bacteria, the exchange of genetic material between two different cells is brought by the process of:
- Transformation
- Transduction
- Conjugation
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Gene Expression MCQs For NEET
Question 16. Phage host represents :
- Virion protein coat
- Virion nucleic acid
- Virion protein and nucleic acid
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Virion protein coat
Question 17. The regulated unit of genetic material is called :
- Operator gene
- Regulator
- Operon
- Promoter gene.
Answer: 3. Operon
Question 18. A retrovirus is:
- TMV
- HIV
- Papillomavirus
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 2. HIV
NEET Biology Gene Regulation Questions
Question 19. Bacteriophages are :
- Modified bacteria
- Primitive bacteria
- Viruses infecting bacteria
- Viruses infecting cyanobacteria.
Answer: 3. Viruses infecting bacteria
Question 20. Provirus differs from prophage about:
- Integration of RNA with host DNA
- Integration of genetic DNA with host DNA
- Integration of copy DNA of retrovirus with host DNA
- None of above
Answer: 3. Integration of copy DNA of retrovirus with host DNA
Question 21. Which virus has a rod-shaped structure 7
- Rlieo viruses
- Φ×174
- T phage
- TMV.
Answer: 4. TMV
Question 22. Tryptophan Operon is:
- Repressible system
- Inducible
- Controlled by regulator gene
- Made of 3 structural genes.
Answer: 1. Repressible system
Question 23. The presence of F-Factor in bacteria helps as :
- Fertility factor
- Female
- Fast factor
- Free factor.
Answer: 1. Fertility factor
Question 24. Exons and Introns are parts of;
- DNA
- mRNA
- RNA
- None of the above
Answer: 1. DNA
NEET Biology Gene Regulation Questions
Question 25. Eukaryotes have:
- One glue per cell
- Ten genes per cell
- Hundred genes per cell
- Thousand genes per cell.
Answer: 4. Thousand genes per cell.
Question 26. Oncogenic viruses are harmful in :
- Provirus stage
- Lytic phase
- Prophage stage
- Hybrid stage,
Answer: 1. Provirus stage
Question 27. Which of the following viruses have been extensively used to fuse cells in tissue culture :
- Sendai virus
- T2 viruses
- Phage lambda
- TMV,
Answer: 1. Sendai virus
Operon Model MCQs For NEET
Question 28. Jumping genes in maize were discovered by :
- H.G. Khorana
- Beadle
- Barbara McClintock
- Jacob.
Answer: 3. Barbara McClintock
Gene Regulation Recommended MCQs Question 29. Thalassemia is an example of:
- Mutation
- Silent mutation
- Frameshift mutation
- Genetic disorders.
Answer: 3. Frameshift mutation
Question 30. Who found the occurrence of sexuality in bacteria ‘!
- Lederberg and Tatum
- Beadle and Tatum
- Sutton and Boveri
- Briggs and Kings.
Answer: 1. Lederberg and Tatum
Question 31. Operon consists of the following :
- Regulator and repressor
- Regulator, structural, and operator
- Regulator, structural, operator, and promoter
- Regulator and operator.
Answer: 3. Regulator, structural, operator, and promoter
Operon Model MCQs For NEET
Question 32. Restriction enzymes are used in genetic engineering because :
- They can cut DNA at specific base sequences.
- They are proteolytic enzymes which can degrade harmful proteins.
- They are nucleases that cut DNA at various sites
- They can join different DNA fragments.
Answer: 1. They can cut DNA at specific base sequence
Question 33. Wild-type E.cali cells are growing in a normal medium with glucose. They are transferred to a medium containing only lactose as the sugar. Which one of the following changes takes place?
- The lac operon is repressed
- All operons are induced
- E.coli cells stop dividing
- The lac operon is induced.
Answer: 4. The lac operon is induced
Question 34. An environmental agent that triggers transcription from an operon is a :
- Derepressor
- Inducer.
- Regulator
- Controlling element.
Answer: 2. Inducer
Question 35. The lac operon is an example of:
- Arabinose operon
- Inducible operon
- Repressive operon
- Overlapping genes,
Answer: 2. Inducible operon
NEET Previous Year Questions On Gene Regulation
Question 36. In split genes, the coding sequences are called :
- Cistrons
- Operons
- Exons
- Introns.
Answer: 3. Exons
Question 37. In the case of cyanobacteria :
- DNA → RNA → Protein
- RNA → DNA → Protein
- RNA → DNA → RNA → Protcin
- DNA → RNAH → RNA → Proteins.
Answer: 1. DNA → RNA → Protein
Question 38. A retrovirus is :
- TMV
- HIV
- Rheo virus
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 4. Both 2 and 3
NEET Previous Year Questions On Gene Regulation
Question 39. The sequence of structural genes of Lac operon is :
- Lac Z, Lac Y, Lac A
- Lac Y, Lac Z, Lac A
- Lac A, Lac Z, Lac Y
- Lac A, Lac Y, Lac Z.
Answer: 1. Lac Z, Lac Y, Lac A
Question 40. Which virus has a single-stranded DNA :
- Rhevirus
- Φ×174 virus
- T2 phage
- TMV.
Answer: 2. Φ×174 virus
Question 41. In the lytic cycle, the virus is :
- Virulent
- Temperate
- Harmless to the host cell
- Reproduces slowly.
Answer: 1. Virulent
Lac Operon MCQs For NEET
Question 42. Resistance to antibiotics is a genetic trait that spreads naturally from one type of bacterium to :
- Another bacterium of the same strain
- Enkaryolic cells of all types
- Almost any other type of bacterium
- Any other cell containing copy DNA.
Answer: 3. Almost any other type of bacterium
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes NEET Questions Question 43. Reverse transcriptase is :
- RNA-dependent DNA polymerase
- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
- DNA-dependent DNA polymerase
Answer: 2. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
Question 44. Transduction in bacteria is mediated by :
- Cosmids
- Phage vectors
- Plasmid vectors
- F-factors.
Answer: 2. Phage vectors
Question 45. The nuclease enzyme which begins its attack from a free end of a polynucleotide :
- Endonuclease
- Kinase
- Exonuclease
- Polymerase.
Answer: 3. Exonuclease
Question 46. Normally, the DNA molecule has A-T, and G-C pairing. However, these bases can exist in alternative, valency consistent status, owing to rearrangement called :
- Tautomerization
- Base analogue
- Frameshift mutation
- Point mutation
Answer: 3. Frameshift mutation
Lac Operon MCQs For NEET
Question 47. The fertility factor or F+ factor that plays a key role in conjugation is a:
- Retrovirus
- Plasmid
- Viroid
- Lysogenic phage
Answer: 2. Plasmid
Question 48. When DNA is exchanged between two bacteria via cytoplasmic bridges, the process is called :
- Transformation
- General transduction
- Restricted transduction
- Conjugation.
Answer: 4. Conjugation
Question 49. When a bacteriophage, in its lytic phage, carries some of the bacterium’s partially digested chromosome with it to another host cell, the process is called :
- Transformation
- General transduction
- Restricted transduction
- Conjugation
Answer: 2. General transduction
Question 50. In general, bacterial genes are regulated at the time of:
- Transcription
- Translation
- Post translation
- Post transcription.
Answer: 1. Transcription
Lac Operon MCQs For NEET
Question 51. The activity of a repressor depends on whether :
- The repressor is positioned next to the operon
- The repressor is positioned next to the promoter
- A key substance in the metabolic pathway is present
- There is enough RNA polymerase present.
Answer: 2. The repressor is positioned next to the promoter
Question 52. In gene therapy, DNA is inserted in a cell to compensate for :
- The absence of plasmid
- Mutant alleles
- Holes in the DNA made by viruses
- The lack of copy DNA.
Answer: 2. Mutant alleles
Question 53. In the lac operon structural gene ‘Z’ is responsible for the synthesis of the enzyme :
- β-galactosidase
- Galactosidase permease
- Galactosidase transacetylase.
Answer: 1. β-galactosidase
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes NEET Questions Question 54. In the genetic code dictionary, how many codons are used to code for all the 20 amino acids?
- 64
- 61
- 60
- 20.
Answer: 2. 61
Question 55. Replication of DNA occurs during the S-phase of interphase Okazaki fragments are joined in a correct sequence by:
- DNA polymerase I
- DNA ligase
- Primase and helicase
- RNA polymerase.
Answer: 2. DNA ligase
Question 56. Which of the following makes use of RNA as a template to synthesize DNA?
- DNA polymerase
- RNA polymerase
- Reverse transcriptase
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase.
Answer: 3. Reverse transcriptase
Lac Operon MCQs For NEET
Question 57. Which one of the following triplet codes is correctly matched with its specificity for an amino acid in protein synthesis or as a start or stop signal?
- UUU – Stop
- UGU Lencino
- UAC – Tyrosine
- UCG – Start.
Answer: 2. UGU Lencino
Question 58. How many genes are present on chromosomes Y and A respectively :
- 2869,231
- 232, 2968
- 231,2968
- 2968,231.
Answer: 3. 231,2968
Question 59. UTR is present on :
- MRNA at one end
- 3′ end of tRNA
- 5′ and 3′ end of mRNP
- 3′ end 5′ end of tRNA.
Answer: 3. 5′ and 3′ end of mRNP
Question 60. Which of the following is a ‘dual function’?
- AUG
- UUU
- GUA
- CCC.
Answer: 1. AUG
Question 61. The base sequence for a nucleic acid segment is given as GAG AGG GGA CCA. From this it can be concluded that it is a segment of:
- DNA strand
- mRNA
- t-RNA strand
- Data is not sufficient.
Answer: 4. Data not sufficient
Question 62. Which of the following does not follow the central dogma of molecular biology?
- mUcor
- Chlamydomonas
- HIV
- Mycobacterium.
Answer: 3. HIV
Question 63. The largest gene in humans is
- Oncogene
- Tumor suppress gene
- Dystrophin
- Insulin.
Answer: 3. Dystrophin
Question 64. In a DNA molecule, adenine is 15% what would be % the age of Guanine?
- 15%
- 30%
- 35%
- 85%.
Answer: 3. 35%
Question 65. The length of DNA with 23 base pairs is :
- 78.4 A°
- 78.2
- 78 A°
- 74.8A°
Answer: 2. 78.2
Transcription And Translation NEET MCQs
Question 66. Which of the following have ds RNA?
- TMV
- Ribozyme
- SnRNA
- Rheovirus.
Answer: 4. Rheovirus
Question 67. Regulation of lac operon by repressor is referred to as :
- +ve regulation
- – ve regular
- Repressible
- Anabolic.
Answer: 2. – ve regular
Question 68. The accessibility of the promoter region of prokaryotic DNA is many cases regulated by the interaction of proteins with a sequence termed operator. The operator region is adjacent to :
- Structural gene
- Regulator gene
- Promoter element
- Gene ‘a’.
Answer: 3. Promoter element
Question 69. At the time of organogenesis, genes regulate the process at different levels and a different times due to the:
- Promoter
- Regulator
- Intron
- Exon.
Answer: 4. Exon
Question 70. In Negative operon :
- Co-repressor binds with repressor
- Co-repressor does not bind with the repressor
- Corepressor binds with inducer.
- cAMP hurts lac operon
Answer: 1. Co-repressor binds with repressor
Question 71. Restriction enzymes:
- Are endonucleases that cleave DNA at specific sites
- Make DNA complementary to an existing DNA or RNA
- Cut or join DNA fragments
- Are required in vectorless direct gene transfer.
Answer: 1. Are endonucleases which cleave DNA at specific sites
Question 72. The process of introduction of foreign genes for improving genotype is called :
- Tissue culture
- Vernalization
- Genetic engineering
- Eugenics.
Answer: 4. Eugenics
Transcription And Translation NEET MCQs
Question 73. The diagram shows an important concept in the genetic implication of DNA. Fill in the blanks A to C.
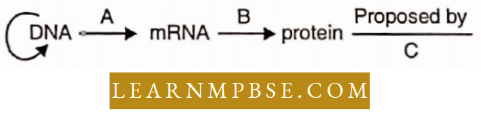
- A – translation B – transcription C – Erevin Chargaff
- A – transcription B – translation C – Francis Crick
- A – translation B – extension C – Rosalind Franklin
- A – transcription B – replication C – James Watson
Answer: 2. A – transcription B – translation C – Francis Crick
Question 74. Which one of the following conditions though harmful in itself, is also a potential saviour from all mosquito-borne infectious diseases?
- Pernicious anemia
- Leukaemia
- Thalassaemia
- Sickle cell anemia.
Answer: 4. Sickle cell anemia
Question 75. In E. coli, during lactose metabolism repressor binds to :
- Regulator gene
- Promoter gene
- Operator gene
- Structural gene.
Answer: 2. Promoter gene
MCQs on Regulation Of Gene Expression In Eukaryotes Question 76. The genes are responsible for the growth and differentiation of living organisms through the regulation of :
- Translation
- Transcription
- Transduction
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 3. Transduction
Question 77. Which of the following is specifically used in genetic engineering?
- Ligase
- Gyrase
- Restriction endonuclease
- DNA polymerase.
Answer: 3. Restriction endonuclease
Question 78. Restriction endonucleases :
- Are present in mammalian cells for degradation of DNA when the cell dies
- Are used in genetic engineering for ligating two DNA molecules
- Are used for in vitro DNA synthesis
- Are synthesized by bacteria as part of their defense
Answer: 4. Are synthesized by bacteria as part of their defense
Transcription And Translation NEET MCQs
Question 79. Cancer cells are more easily damaged by radiation than normal cells because they are :
- Starved of mutation
- Undergoing rapid division
- Different in structure
- Non-dividing.
Answer: 2. Undergoing rapid division
Question 80. DNA fingerprinting refers to :
- Molecular analysis of profiles of DNA samples
- Analysis of DNA sample using imprinting device
- Techniques used for molecular analysis of different specimens of DNA
- Techniques used for identification of fingerprints of
Answer: 4. Techniques used for the identification of fingerprints of
Question 81. What kind of evidence suggested that man is more closely related to chimpanzees than to other hominoid apes?
- Evidence from DNA from sex chromosomes only
- Comparison of chromosomal morphology only
- Evidence from fossil remains and the fossil mitochondrial DNA alone
- Evidence from DNA extracted from sex chromosomes, autosomes, and mitochondria.
Answer: 4. Evidence from DNA extracted from sex chromosomes, autosomes, and mitochondria
Question 82. In transgenics, expression of transgene in target tissue is determined by :
- Enhancer
- Promoter
- Transgene
- Reporter.
Answer: 4. Reporter
MCQs on Regulation Of Gene Expression In Eukaryotes Question 83. The Ti plasmid is often used for making transgenic plants. This plasmid is found in :
- Azotobacter
- Rhizobium of the roots of leguminous plants
- Agrobacterium
- yeast as a 2μm plasmid.
Answer: 3. Agrobacterium
Gene Expression MCQs For NEET
Question 84. Which enzyme/s will be produced in a cell in which there is a nonsense mutation in the lac Y gene?
- Lactose permease
- Transacetylase
- Lactose permease and transacetylase
- β-galactosidase.
Answer: 4. β-galactosidase.
Question 85. Supercoiled DNA can be traced in :
- Prokaryotes and eukaryotes
- Eukaryotes only
- Prokaryotes only
- None of these
Answer: 1. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Question 86. Phosphorus is present in :
- Protein
- DNA
- RNA
- Both DNA and RNA.
Answer: 4. Both DNA and RNA
Question 87. In a given DNA segment ATG, ACC, AGG, ACC, CCA, ACA, the first base gets mutated. The effect of this on coding by this DNA segment will result in :
- A complete change in the type as well as a sequence of amino acids
- Change in the first amino acid only
- One amino acid less in the protein
- No change in the sequence
- No coding.
Answer: 2. One amino acid less in the protein
Question 88. Okazaki fragments are joined in a correct sequence by :
- DNA polymerase I
- DNA ligase
- RNA polymerase
- Primase
- Heliease.
Answer: 2. DNA ligase
Gene Expression MCQs For NEET
Question 89. In the lac operon, the structural genes are switched off when :
- The repressor binds to the operator
- Repressor binds to the promoter
- The repressor binds to the regulator
- Repressor binds to the inducer
- The repressor binds to the allolactose.
Answer: 1. The repressor binds to the operator
Question 90. In the lac operon structural gene V is responsible for the synthesis of the enzyme :
- β-galactosidase
- Galactosidase permease
- Galactosidase transacetylase
- None of these.
Answer: 1. β-galactosidase
Question 91. When lactose is added to the culture of E.coli, a few of its molecules get into the cells with the help of:
- Galactosidase
- Permease
- Lactase
- Transacetylase.
Answer: 2. Permease
Gene Regulation Recommended MCQs Question 92. During transcription, holoenzyme RNA polymerase binds to a DNA sequence and the DNA assumes a saddle Ike structure at that point. What is that sequence called?
- TATA box
- AAAT box
- GGTT box
- CAAT box
Answer: 1. TATA box
NEET Biology Gene Regulation Questions
Question 93. In the lac operon model, lactose molecules function a is :
- Inducers that bind with the operator gene
- Repressors that bind with the operator gene
- Inducers that bind with the repressor protein
- Compressors that bind with repressor protein.
Answer: 3. Inducers that bind with the repressor protein
Question 94. Protein synthesis in an animal cell occurs :
- Only on the ribosomes present in the cytosol
- Only on ribosomes attached to the nuclear envelope and endoplasmic reticulum
- On ribosomes present in the nucleolus as well as in the cytoplasm
- No ribosomes are present in the cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria.
Answer: 4. No ribosomes present in the cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria
Question 95. E.coli cells with a mutated z gene of the lac operon cannot grow in a medium containing only lactose as the source of energy because :
- In the presence of glucose, E.coli cells do not utilize lactose
- They cannot transport lactose from the medium into the cell
- The lac operon is constitutively active in these cells
- They cannot synthesize functional beta-galactosidase.
Answer: 4. They cannot synthesize functional beta-galactosidase
Question 96. Which one of the following makes use of RNA as a template to synthesize DNA?
- Reverse transcriptase
- DNA dependant RNA polymerase
- DNA polymerase
- RNA polymerase.
Answer: 1. Reverse transcriptase
Question 97. Differentiation of organs and tissues in a developing organism is associated with:
- Differential expression of genes
- Lethal mutations
- Deletion of genes
- Developmental mutations.
Answer: 1. Differential expression of genes
NEET Biology Gene Regulation Questions
Question 98. Intron transcripts in heterogenous nuclear RNA (hn- RNA) are removed and exon transcripts are joined together under the direction of protein complexes. These complexes are :
- Polysomes
- Cdk complex
- Spliceosomes
- Endopeptidases.
Answer: 3. Spliceosomes
Question 99. In regulation of gene expression in prokaryotes :
- Lactose acts as the suppressor for gene expression
- Tryptophan acts as the inducer of gene expression
- The regulator gene is the one that produces the repressor molecule
- 1 alone correct
- alone correct
- 3 alone correct
- 2 and 3 are correct.
Answer: 3. 3 alone correct
Question 100. The sequence of structural genes in the lac operon concept is :
- Lac A, lac Z, lac Y
- Lac A, lac Y, lac Z
- Lac Y, lac Z, lac A
- Lac Z, lac Y, lac A.
Answer: 4. Lac Z, lac Y, lac A.
NEET Biology Gene Regulation Questions
Question 101. All genes located on the same chromosome :
- Form different groups depending on their relative distance
- Form one linkage group
- Will not form any linkage groups.
- Form interactive groups that affect the phenotype
Answer: 2. Will not form any linkage groups.
Question 102. Conditions of a karyotype 2 n+1 and 2n ± 2 are called:
- Aneuploidy
- Polyploidy
- Allopolyploidy
- Monosomy.
Answer: 1. Aneuploidy
Question 103. Distance between the genes and advantage of recombination shows :
- A direct relationship
- An inverse relationship
- A parallel relationship
- No relationship.
Answer: 2. An inverse relationship
Question 104. If genetic disease is transferred from a phenotypically normal but carrier female to only some of the male progeny, the disease is :
- Autosomal dominant
- Autosomal recessive
- Sex-linked dominant
- Sex-linked recessive.
Answer: 4. Sex-linked recessive.
Operon Model MCQs For NEET
Question 105. In sickle cell anaemia glutamic acid is replaced by valine. Which one of the following triplets codes for valine?
- G G G
- A A G
- GAA
- GUG.
Answer: 4. GUG.
Question 106. A person having genotype IA IB would show the blood group as AB. This is because of:
- Pleiotropy
- Co-dominance
- Segregation
- Incomplete dominance.
Answer: 2. Co-dominance
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes NEET Questions Question 107. ZZ / ZW type of sex determination is seen in :
- Platypus
- Snails
- Cockroach
- Peacock.
Answer: 4. Peacock.
Question 108. A cross between two tall plants resulted in offspring having few dwarf plants. What would be the genotypes of both the parents?
- TT and Tt
- Tt and Tt
- TT and TT
- Tt and tt.
Answer: 2. Tt and Tt
Question 109. In a dihybrid cross, if you get a 9:3:3:1 ratio it denotes that:
- The alleles of two genes interact with each other
- It is a multigenic inheritance
- It is a case of multiple alleles
- The alleles of two genes segregate independently.
Answer: 4. The alleles of two genes are segregating independently.
Operon Model MCQs For NEET
Question 110. Which of the following will not result in variations among siblings?
- Independent assessment of genes
- Crossing over
- Linkage
- Mutation.
Answer: 3. Linkage
Question 111. Mendel’s law of independent assortment holds good for genes situated on the :
- Non-homologous chromosomes
- Homologous chromosomes
- Extranuclear genetic element
- Same chromosome.
Answer: 1. Non-homologous chromosomes
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes NEET Questions Question 112. Occasionally, a single gene may express more than one effect. The phenomenon is called :
- Multiple allelism
- Mosaicism
- Pleiotropy
- Polygeny.
Answer: 3. Pleiotropy
Question 113. In a certain taxon of insects, some have 1 7 chromosomes and the others have 18 chromosomes. The 17 and 18 chromosome-bearing organisms are :
- Males and females, respectively
- Females and males, respectively
- All males
- All females.
Answer: 1. Males and females, respectively
Question 114. The inheritance pattern of a gene over generations among humans is studied by the pedigree analysis. The character studied in the pedigree analysis is equivalent to :
- Quantitative trait
- Mendelian trait
- Polygenic trait
- Maternal trait.
Answer: 2. Mendelian trait
Question 115. It is said that Mendel proposed that the factor controlling any character is discrete and independent. This proposition was based on the :
- Results of F3 generation of a cross.
- Observations that the offspring of a cross made between the plants having two contrasting characters show only one character without any blending.
- Self-pollination of F1 offspring
- Cross-pollination of parental generations.
Answer: 2. Observations that the offspring of a cross made between the plants having two contrasting characters show only one character without any blending.
Question 116. Two genes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are linked. In a dihybrid cross involving these two genes, the F1 heterozygote is crossed with the homozygous recessive parental type (aa bb). What would be the ratio of offspring in the next generation?
- 1 : 1: 1: 1
- 9 : 3 : 3: 1
- 3:1
- 1: 1.
Answer: 1. 1: 1 : 1: 1
Operon Model MCQs For NEET
Question 117. In the F2 generation of a Mendelian dihybrid cross the number of phenotypes and genotypes are :
- Phenotypes – 4; genotypes – 16
- Phenotypes – 9; genotypes – 4
- Phenotypes – 4; genotypes – 8
- Phenotypes – 4; genotypes – 9
Answer: 4. Phenotypes – 4; genotypes – 9
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes MCQ Question 118. The mother and father of a person with the ‘O’ blood group have ‘A’ and ‘B’ blood groups respectively. What would be the genotype of both mother and father?
- The mother is homozygous for the ‘A’ blood group and the father is heterozygous for ‘B’.
- Mother is heterozygous for ‘A’ blood group and father is homozygous for ‘B’
- Both mother and father are heterozygous for the ‘A’ and ‘B’ blood groups, respectively
- Both mother and father are homozygous for the ‘A’ and ‘B’ blood groups, respectively.
Answer: 3. Both mother and father are heterozygous for the ‘A’ and ‘B’ blood groups, respectively
Question 119. In a DNA strand, the nucleotides are linked together by:
- Glycosidic bonds
- Phosphodiester bonds
- Peptide bonds
- Hydrogen bonds.
Answer: 2. Phosphodiester bonds
Question 120. A nucleoside differs from a nucleotide. It lacks the
- Base
- Sugar
- Phosphate group
- Hydroxyl group.
Answer: 3. Phosphate group
Question 121. Both deoxyribose and ribose belong to a class of sugars called :
- Trioses
- Hexoses
- Pentoses
- Polysaccharides.
Answer: 3. Pentoses
Question 122. The fact that a purine base is always paired through hydrogen bonds with a pyrimidine base leads to, in the DNA double helix :
- The antiparallel nature
- The semi-conservative nature
- Uniform width throughout DNA
- Uniform length in all DNA.
Answer: 3. Uniform width throughout DNA
Question 123. The net electric charge on DNA and histones is :
- Both positive
- Both negative
- Negative and positive, respectively
- Zero
Answer: 3. Negative and positive, respectively
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes MCQ Question 124. The promoter site and the terminator site for transcription are located at :
- 3’ (downstream) end and 5’ (upstream) end, respectively of the transcription unit
- 5’ (upstream) end and 3’ (downstream) end, respectively of the transcription unit
- The 5’ (upstream) end
- The 3’ (downstream) end.
Answer: 2. 5’ (upstream) end and 3’ (downstream) end, respectively of the transcription unit
Question 125. Which of the following statements is the most appropriate for sickle cell anemia?
- It cannot be treated with iron supplements
- It is a molecular disease
- It confers resistance to acquiring malaria
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 126. One of the following is true concerning AUG
- It codes for methionine only
- It is also an initiation codon
- It codes for methionine in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above
Question 127. The first genetic material could be :
- Protein
- Carbohydrates
- DNA
- RNA
Answer: 4. RNA
Question 128. About mature ntRNA in eukaryotes :
- Exons and introns do not appear in the mature RNA
- Exons appear but introns do not! appear in the mature RNA
- Introns appear but exons do not appear in the mature RNA
- Both exons and introns appear in the mature RNA.
Answer: 2. Exons appear but introns do not! appear in the mature RNA
Question 129. The human chromosomes with the highest and least number of genes in them are respectively :
- Chromosome 21 and Y
- Chromosome 1 and X
- Chromosome 1 and Y
- Chromosome X and Y.
Answer: 3. Chromosome 1 and Y
Question 130. Who amongst the following scientists had no contribution in the development of the double helix model for the structure of DNA?
- Rosalind Franklin
- Maurice Wilkins
- Erwin Chargaff
- Meselson and Stahl.
Answer: 4. Meselson and Stahl.
Question 131. DNA is a polymer of nucleotides that are linked to each other by a 3″-5’ phosphodiester bond. To prevent the polymerization of nucleotides, which of the following modifications would you choose?
- Replace purine with pyrimidines
- Remove/Replace 3″ OH group in deoxyribose
- Remove/Replacc 2’ OH group with some other group in deoxyribose
- Both ‘2’ and ‘3’.
Answer: 2. Remove/Replace 3″ OH group in deoxyribose
Question 132. Discontinuous synthesis of DNA occurs in one strand, because :
- DNA molecule being synthesized is very long
- DNA-dependent DNA polymerase catalyzes polymerization only in one direction (5’- 3’)
- It is a more efficient process
- DNA ligase has to have a role.
Answer: 2. DNA-dependent DNA polymerase catalyzes polymerization only in one direction (5’-3’)
Question 133. Which of the following steps in transcription is catalyzed by RNA polymerase?
- Initiation
- Elongation
- Termination
- All of the above.
Answer: 2. Elongation
Question 134. Control of gene expression takes place at the level of:
- DNA-replication
- Transcription
- Transition
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Transcription
NEET Previous Year Questions On Gene Regulation
Question 135. Regulatory proteins are the accessory proteins that interact with RNA polymerase and affect its role in transcription. Which of the following statements is correct about regulatory protein?
- They only increase expression
- They only decrease expression.
- They interact with RNA polymerase but do not affect the expression
- They can act both as activators and as repressors
Answer: 4. They can act both as activators and as repressors
Question 136. Which was the last human chromosome to be completely sequenced :
- Chromosome 1
- Chromosome 11
- Chromosome 21
- Chromosome X.
Answer: 1. Chromosome 1
Question 137. Which of the following are the functions of RNA?
- It is a carrier of genetic information from DNA to ribosomes synthesizing polypeptides
- It carries amino acids to ribosomes
- It is a constituent component of ribosomes
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 138. While analyzing tire DNA of an organism a total number of 5386 nucleotides were found out of which the proportion of different bases was: Adenine = 29%, Guanine = 17%, Cytosine = 32%. Thymine = 17%. Considering Chargaffs rule it can be concluded that:
- It is a double-stranded circular DNA
- It is a single-stranded DNA
- It is a double-stranded linear DNA
- No conclusion can be drawn.
Answer: 2. It is single-stranded DNA
Question 139. In some viruses, DNA is synthesized by using RNA as a template. Such a DNA is called :
- A-DNA
- B-DNA
- cDNA
- DNA.
Answer: 3. cDNA
Question 140. IfMeselson and Stahl’s experiment is continued for four generations in bacteria, the ratio of 15N-/15N: 15N/14N/: 1 4N/ 14N containing DNA in the fourth generation would be :
- 1:1:0
- 1:4:0
- 0:l:3
- 0:1:7.
Answer: 4. 0:1:7
Question 141. If the sequence of nitrogen bases of the coding strand of DNA in a transcription unit is: 5’ – ATG A ATG-3’, the sequence of bases in its RNA transcript would be :
- 5’ – AUG A AUG-3’
- 5’-UACUUAC-3’
- 5’ – CAUUCAU-3’
- 5’ – G U A A G U A – 3’.
Answer: 1. 5’ – AUG A AUG-3’
Question 142. The RNA polymerase holoenzyme transcribes :
- The promoter, structural gene, and the terminator region
- The promoter, and the terminator
- The structural gene and the terminator regions
- The structural gene only.
Answer: 3. the structural gene and the terminator regions
Question 143. If the base sequence of a codon mmRNA is 5’-AUC- 3’, the sequence of tRNA pairing with it must be :
- 5’ – UAC – 3’
- 5’ – CAU – 3’
- 5’ -AUG -3’
- 5’ – GUA – 3’
Answer: 2. 5’ – CAU – 3’
Question 144. The amino acid attaches to the tRNA at its :
- 5’-end
- 3’-end
- Anti codon site
- DHU loop
Answer: 2. 3’-end
Question 145. To initiate translation, the mRNA first binds to :
- The smaller ribosomal sub-unit,
- The larger ribosomal sub-unit
- The whole ribosome
- No such specificity exists.
Answer: 1. The smaller ribosomal sub-unit,
Question 146. In E.coli, the lac operon gets switched on when :
- lactose is present and it binds to the repressor
- The repressor binds to the operator
- RNA polymerase binds to the operator
- Lactose is present and it binds to RNA polymerase.
Answer: 1. lactose is present and it binds to the repressor
Question 147. Which of the following statements are correct?
- RNA polymerase 1 transcribes rRNAs
- RNA polymerase 2 transcribes snRNAs
- RNA polymerase 3 transcribes hnRNA
- RNA polymerase 2 transcribes hnRNA.
- 1 and 2 correct
- 1 and 3 are correct
- 1, 2, and 4 are correct
- 2 and 3 are correct
- 1 and 4 are correct.
Answer: 5. 1 and 4 are correct.
Question 148. In Hershey and Chase experiments, radioactive 32P was used to culture bacteriophages which resulted in radioactive :
- ViralDNA
- Bacterial capsule
- Viral proteins
- Plasma membrane of bacteria.
Answer: 1. ViralDNA
Question 149. The inducer for switching ‘on’ the lac operon in bacteria is:
- Presence of lactose
- Number of bacteria
- Presence of structural genes in the bacteria
- Presence of sucrose
- Presence of RNA polymerase
Answer: 1. Presence of lactose
Question 150. Select the incorrect statement (s):
1. Six codons do not code for any amino acid.
2. Codon is read in mRNA in a continuous fashion
3. Three condoms function as stop codons
4. The initiator codon AUG codes for methionine.
- 1,2 and 4 are incorect
- 1, 2 and 3 are incorect
- 2, 3 and 4 are incorect
- 2 alone is correct
- 1 alone is incorrect.
Answer: 5. 1 alone is incorrect.
Question 151. The collection of cloned DNA segments obtained from the complete genome is called :
- DNA library
- Genomic bank
- Gene bank
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 4. Both 2 and 3
NEET Previous Year Questions On Gene Regulation
Question 152. In the operon model, the regulator gene functions as :
- Regulator
- Inhibitor
- Repressor
- Stimulator.
Answer: 3. Repressor
Question 153. Genes involved in turning on and off of structural genes are:
- Operator genes
- Regulator genes
- Redundant genes
- Promoter genes.
Answer: 2. Regulator genes
Question 154. Lac operon is related to :
- Synthesis of enzymes for lactose catabolism
- Synthesis of enzymes for lactose anabolism
- Synthesis of lac by lac insects
- Degradation of lac by lac insects.
Answer: 1. Synthesis of enzymes for lactose catabolism
Question 155. According to the operon concept, the regulator gene regulates chemical reactions in the cell by :
- Inactivating enzyme in the reaction
- Inhibiting the substrate in the reaction
- Inhibiting transcription of m-RNA
- Inhibiting the migration of mRNA into the cytoplasm.
Answer: 3. Inhibiting transcription of m-RNA
Question 156. The modem concept of a gene is that it is :
- A segment of DNA
- A segment of chromosome
- A functional unit of DNA
- All of these
Answer: 3. A functional unit of DNA
Question 157. SV 40 has five genes but the type of proteins synthesized by it is more than twice the number of genes present in it. It shows the presence of:
- Contained genes
- Split genes
- Overlapping genes
- Degenerate genes.
Answer: 3. overlapping genes
Question 158. Provirus differs from prophage about:
- Integration of RNA with host DNA
- Integration of genetic DNA with host DNA
- Integration of copy DNA of retrovirus with host DNA
- None of the above.
Answer: 3. Integration of copy DNA of retrovirus with host DNA
Question 159. Which virus has a rod-shaped structure?
- Rheo viruses
- Φ× 174
- T phage
- TMV.
Answer: 4. TMV.
Question 160. Tryptophan Operon is :
- Repressible system
- Inducible
- Controlled by regulator gene
- Made of 3 structural genes.
Answer: 1. Repressible system
