NEET Biology Origin Of Life
Life– The inherent capacity of organisms to utilise outside materials for energy, growth and reproduction through chemical reactions. Life is regarded as a power that an organism possesses to maintain and produce itself.
Big Bang Theory – A single huge explosion
- The universe expanded → Temperature came down – Hydrogen and Helium formed later on.
- Gases condensed under gravitation and formed galaxies of the present-day universe.
- Earth formed almost 4.5 billion years ago.
- No atmosphere on early Earth.
- Water vapours, methane, CO2, NH3 released from molten mass covered the surface.
UV rays of the sun broke up.
Read and Learn More NEET Biology Notes
Oxygen is combined with ammonia, and methane to form water CO2 and other simple molecules. An ozone layer was formed.

Biopoiesis – the process by which life originated.
According to the Cosmozoic theory developed by Richter and supported by Thomson, Helmholtz and Arrhenius states that life (protoplasm) reached the earth in the form of spores or germs from outer space.
NEET Biology Origin Of Life
Theory of special creation—By Father Suarez.According, to it life was created by super supernatural power in 6 days.
- 1st day — he made heaven and earth
- 2nd day—separated sky from water
- 3rd day—dry land of plants
- 4th day—Sun, moon and stars
- 5th day—Birds and fishes
- 6th day—Land animals and human beings.
Theory of eternity of Life—By Richter (1865), Preyer (1880), Helmholtz (1884), Arrhenius (1908), Moyle (1950), Bonds (1952).
According to it, “Life is immortal”. Living matter has occurred in association with non-living matter from the beginning. Thus according to this theory, Life changes its form and it was never created.
- According to spontaneous generation theory, life originated from non-living things. It is estimated that life originated approximately 3,600 million years ago.
- Scientists supporting this theory— Aristotle, Van Helmont, William Harvey, Haeckel, Plato, Xanophanes, Thales, Anaximander, Empedocles
- Experimental support was provided by the Van Helmont experiment (1642).
- Abiogenesis was challenged on the basis of experiments by—Francisco Redi and Spallanzani. Finally disapproved by – Louis Pasteur.
Biogenesis. The fact that new life (nowadays) comes from any pre-existing life (Omne vivutn exvivo).
Theory Of Catastrophism. It states that there have been several creations each preceded by a catastrophe due to some geological disturbance. Each catastrophe completely destroyed life and each creation consisted of life quite different from that of the previous one. (George Cuvier and Orbigney)
NEET Biology Origin Of Life
Oparin-Haldane Theory (Naturalistic, Chemical or Heterotroph Theory)
A.I. Oparin and J.B.S. Haldane’s (1936)
The theory of the “Origin of Life” is widely acknowledged.
- Life emerged by chemical evolution, as the primordial Earth’s atmosphere was decreasing, characterized by elevated temperatures and the presence of gases like as nitrogen, hydrogen, methane, ammonia, and water vapor.
- As the temperature decreased, certain gasses condensed into liquids, while some liquids solidified. Free oxygen was nonexistent.
- Extensive polymers, including proteins, nucleic acids, and other molecules, were methodically synthesized by the influence of high-energy solar radiation, energy from alternative sources (likely isotopes on primordial Earth), and energy from electrical discharges.
The main steps of the theory are as follows:

- The first organisms were heterotrophs and anaerobic containing nucleoproteins which gave rise to autotrophs.
- Universe – 15-20 bya (Billion years ago.)
- Earth – 4.5/4.6 bya
- Life 4.0 bya (life appeared 500 mya after the formation of the earth)
- Non-cellular form of life may have originated 3 by (RNA + Protein + Polysaccharides)
- Cellular form of life 2000 mya(million years ago)
- Life was present on earth about 3.9 bya.
- Microfossils of cyanobacteria appeared 3.3 to 3.5 bya.
- Origin of Eukaryotic cell – 1.5 bya.
NEET Biology Origin Of Life Some Early Contributors To The Knowledge Of Evolution And Related Topics
Thales (624-548 B.C.): A Greek who proposed a theory that water (ocean) was the mother of all life.
Anaximander (611—547 B.C.): A Greek who thought that life arose from a mixture of water and earth and that landforms arose from aquatic types, particularly under the influence of the sun’s heat.
Heraclitus (510—450 B.C.): A Greek natural philosopher who stated that “struggle is life” and “all is flux”— thoughts that are basic to modem ideas in evolution.
Empedocles (495-435 B.C.): A Greek who theorized that living organisms were generated spontaneously from scattered materials, being attracted by love and hate.
“Founder of the concept of organic evolution”
Aristotle (384-322 B.C.): A Greek who theorized that in the living world, there was a gradual change from the simple and imperfect to the more complex and perfect, thus suggesting the idea of evolution.
Saint Augustine (353-439 A.D.): Saint Augustine interpreted the first chapter of Genesis, stating that in the beginning matter was created with the properties and potentialities to evolve into living and non-living worlds as we know them today.
Origin Of Life NEET Notes
Leonard de Vinci (1412-1529) “Father of Palaeontology”
Francisco Redi (1621-1697): An Italian who overthrew the theory of spontaneous generation, which stated that life arose from non-living materials spontaneously, by discovering that eggs and larvae of insects originated from previous living insects, rather than from non-living substances.
Carl Linnaeus: Father of taxonomy
Giovanni Avadeuna (1760) proposed Geological time scale
Thomas’ Robert Malthus (1766-1834): An English economist whose “Essay on Population,” published in 1798, inspired both Darwin and Wallace in their theories of evolution.
Charles Lyell (1797-1875): A Scottish geologist who laid the foundations for the science of earth structure in his Principles of Geology (1830-1832). He is considered an important contributor to the theory of organic evolution because of his influence on Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace.
Georges Cuvier (1769-1832): A Frenchman who supported the “Cataclysmic Theory,” in which he stated that there had been numerous creations, each of which was followed by a cataclysm (catastrophe) that destroyed it, and its place was taken by new forms. He is regarded as the founder/father of modern palaeontology
Georges de Buffon (1707-1788): A French naturalist who excluded the possibility that species have the ability to evolve (change). He probably was influenced by the ancient ideas revived during the Renaissance that discredited such a possibility.
Charles Bonnet (1720-1793): A Swiss naturalist and philosopher who first used the term “evolution” but not quite as we do today, and conceived that organisms could be arranged in a ladder-like, linear series.
Erasmus Darwin (1731-1802): An English evolutionist who was the grandfather of Charles Darwin. He believed that acquired traits could be transmitted to future generations and he may have influenced Lamarck, who had similar views.
Jean Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829): A French biologist who was a student of organic evolution. He believed that environmental influences, and the effects of the use and disuse of body parts, were causes of evolutionary changes—a theory that laid the foundation for the “Theory of the Inheritance of Acquired Traits.”
Charles Darwin (1809-1882): Darwin, on a voyage around the world in the sailing ship HMS Beagle, indicated the descent of species by the development of varieties from common stocks. This process entailed a “struggle for existence,” which resulted in a “natural selection of species” and a “survival of the fittest.” He wrote The Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection (1859).
Evolution And Origin Of Life NEET
Thomas Henry Huxley (1825-1895): An English surgeon who actively supported the views of Charles Darwin and assisted in promoting them extensively.
Alfred Russel Wallace (1823-1913): An Englishman who studied animal geography in the East Indies and concluded that the life of wild animals is a struggle for existence. He worked on the problem of the origin of species and arrived at conclusions concerning evolution that resembled those of Charles Darwin.
Louis Pasteur (1822-1895): A French microbiologist and chemist who proved that only living organisms such as bacteria and yeasts could cause fermentation. He proposed a method of preventing this process by heating to a temperature high enough to kill the germs. This method is known as pasteurization. Pasteur’s work ended the controversy regarding the possibility of the spontaneous generation of living organisms from non-living materials.
August Weismann (1834-1914): A German who distinguished between body cells and germ cells and proposed the “Theory of the Continuity of Germplasm from Generation to Generation” (1885). He opposed the idea that acquired traits might be transmitted.
Mendel’s work published (1866)—(Unknown to Darwin)
Henry Walter Bates (1825—1913). Proposed the concept of Batesian mimicry in 1862.
J Fritz Muller (1821—1897). Described in 1879 the Mullarian mimicry.
Scaler (1858) divided the earth into six realms for the distribution of birds,
Richard Leaky (1930). Modem Palaeontologist
Lewis and Leaky (1955) excavated fossil forms of Ramapithecus and Kenyapithecus
Evolution And Origin Of Life NEET
Lucy, C. Johanson (1981) American anthropologist discovered the complete skeleton of a 30-35 lakhs years female fossil hominid resembling Australopithecus
Eugene Dubois (1891) excavated a fossil of Homo erectus erectus
Laplace (1749—1827) proposed a nebular hypothesis to explain the origin of the solar system
Horowitz suggested that the earliest form of life was in the form of naked gene
Solar System. Sun along with orbiting planets and their satellites, the comets and asteroids constitute the solar system.
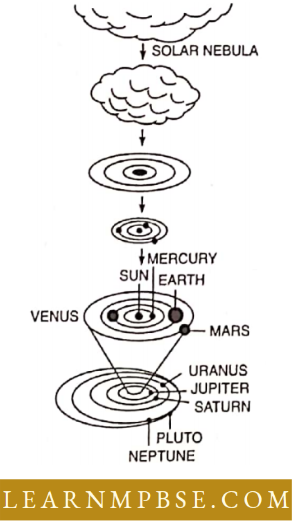
Origin Of The Solar System. The solar system originated from the gravitational contraction (condensation) of a solid cosmic cloud and dust called a nebula.
- During condensation, this cloud began to rotate due to the initial velocities of particles brought together. The condensation and spin continued. Thus most of the mass is concentrated near the centre. The flattened discs broke into a number of whirling masses of smaller clouds. The sun was formed from the central dense part.
- The sun started radiating energy. The other planets including the Earth were formed from the cooler, less dense outer regions almost in the same plane.
Cosmology. The study of heavenly bodies and the cosmos is called cosmology. The major theories of the origin of the universe are chemical origin and the Big Bang is the most accepted theory about the origin of the universe.
According to the Big Bang theory universe came into existence some 19 billion years ago by a thermonuclear explosion, called the Big Bang, or a dense entity will eventually contract again. Sun and its planets including Earth came into existence at the same time from a common source.
Theories Of Origin of Life NEET
Two Major Events Of The History Of Life Are:
- Origin of life (biopoiesis).
- Evolution of life.
The Major Theories Of the Origin Of Life Are:
- Special Creation (Proposed by Father Saurez). This theory of special creation attributes the origin of life to a supernatural or vitalistic event at a particular time in the past. In other words, this theory believes in the creation of life by God.
- Spontaneous Generation. (Concept held by Thales, Anaximander, Empedocles, plants). This theory discards abiogenesis and believes in the biogenetic origin of life i.e. life originates from pre-existing life-biogenesis.
- Extraterrestrial or Cosmic Origin (Richter). This theory believes that life on Earth came from some other planet.
- Terrestrial Origin or Abiogenic Origin (Oparin and Haldane). This theory states that life originates on Earth from collections of organic molecules that were produced early in the history of Earth.
This theory of terrestrial origin has a scientific base.
Role Of Catalytic Rna In Origin Of Life
- The precursor of RNA of ciliate protozoan, Tetralymena was found to contain a self-splicing intron-containing 413 nucleotides which act as enzymes,
- The very first living molecule might have been an RNA replicase that catalysed its own replication without the help of a protein.
- Catalytic RNA are now considered to be molecular fossils.
- Biogeny. Origin of first life.
- Chemogeny. Origin and evolution of organic chemicals.
- Cognogeny Is The Evolution of different forms of living species.
- Biopoiesis. Origin of life.
- Biogenesis. Origin of life from life.
- Continental Drift Theory. Proposed by Wagener (1912) that about 250-200 million years there was a single land mass or continent which subsequently got split into continents as are known today.
Plate Tectonics:
John Tujo Wilson (1965) posited that the Earth’s outer surface comprises a mosaic of thick plates, both large and small, with a thickness of 70-100 km, which move in relation to one another, perhaps due to convection currents in the semi-molten mantle underneath.
- This movement is thought to have commenced approximately 2000 million years ago at a velocity of 6 centimeters per year. As a result, the continents are gradually rotating around the Earth. They have previously accomplished this four times.
- Francisco Redi denied the spontaneous creation of flies from decaying flesh in 1668.
- The energy radiated by the sun originates from nuclear fusion events.
- The initial kind consists of seas created from atmospheric water.
- Clay is optimal for the concentration of monomers. cs Cells with extended metabolic pathways were favored as primitive cells depleted the directly usable organic compounds.
- The most ancient fossilized cells resemble heterotrophic bacteria.
- The primordial autotrophs were likely anaerobic chemoautotrophs.
- The initial creatures to emit oxygen were likely cyanobacteria.
NEET Biology Origin Of Life Synopsis
The study of the universe or cosmos is called cosmology.
- Exobiology. Investigation of life on heavenly bodies other than the earth.
- The first organisms were — Heterotrophs. (Chemo- heterotrophs).
- Age of the earth – 4600 million yrs.
- Earliest prokaryotes – 3600 million yrs.
- The first formed compounds were probably – proteins and nucleic acids.
- Aristotle – The first proponent of the theory of abiogenesis.
- Origin of life – somewhere between 4.5 x 108 to 3.6 x 108 years ago.
- Origin of life – in water (probably sea).
- Gas is absent in the primitive atmosphere – free oxygen.
Gases present in the primitive atmosphere – N2, CH4, H2, NH3, H2O(g)
- Spontaneous generation (Abiogenesis) theory was proposed by Van Helmont (1577—1644) and the concept was supported by – Thales, Xanophanes, Empedocles, Plato, and Anaximander.
- Empedocles is regarded as the father of evolutionary concepts.
- Spontaneous generation theory challenged by – Fran-cisco Redi, Spallanzani and Pasteur Tyndall
- No life on the moon as there is no atmosphere on the moon because of the low escape velocity on the moon in which gas molecules easily cross.
- A.I. Oparin wrote a book “Genesis and Evolutionary Development of Life” and “Origin of Life” on Earth.
- “Evolution from Space” was written by Fred Hoyle.
- F.H.C. Crick (1982) published a book with the title ‘Life itself’.
- Cosmozoic theory of the origin of life was proposed by Richter and supported by Arrhenius.
Sydney W. Fox. discovered aqueous suspension of polymers’ spherical aggregates. He called the coacervates a microsphere.
- S.W Fox demonstrated that if a nearly dry mixture of amino acids is heated, polypeptide molecules are formed.
- Melwin Calvin (1951) strongly irradiated CO2 and H2 in a cyclotron to form formic acid, succinic acid and oxalic acid.
- J.B.C. Haldane bom on 5 Dec. 1897 in England. He shifted to India in July 1957 and settled in Bhubnashwer. He died on 1st Dec. 1964. He was a biologist, biochemist and geneticist.
- Louis Pasteur gave “Germ Theory of Disease and Immunology.”
- Progenote is regarded as early single-celled common ancestors of archaebacteria, eubacteria and eukaryotes. Thus, no present-day bacterial type can be regarded as an ancestor of eukaryotes.
NEET Biology Origin Of Life Of Earth
The genesis of life is associated with the inception of Earth, the Cosmos, and the Universe, which emerged 10 to 20 billion years ago due to the Big Bang (a thermonuclear explosion). A galaxy, such as the Milky Way, consists of billions of stars, including our Sun, together with its respective planets and satellites.
- The solar system comprises the sun, its planets, and their satellites.
- Earth is the third planet, characterized by its rocks, water, and atmosphere. It commenced as gaseous clouds of metallic and non-metallic atoms, subsequently condensing to create surface rocks, a boiling fluid core, and a gaseous atmosphere.
- Cosmology. Investigation of the cosmos.
- The oldest extant rock is 4.3 billion years old and contains no evidence of life.
- 3.9 billion-year-old rocks contained carbonates indicative of biological activities.
- The most ancient microfossils of Cyanobacteria date back 3.3 to 3.5 billion years.
- Francis Crick and Leslie Orgel suggested the notion of guided panspermia, which was substantiated by genetic code and the function of the metal molybdenum.
